Copy of PPclues-Combined
Diunggah oleh
Alexis Ramos0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
151 tayangan73 halamanWhat electrolytes does the low volume state have? inc total Na. Dec serum Na (dilutional effect) What pH does diarrhea have? What happens if pulse inc >10 on standing? hypovolemic shock What happened if pulse dec 5 on standing? What are the most common infections of the low energy state? restrictive - interstitial problem (non-bacterial) small stiff lungs (dec VC)
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Copy of Copy of PPclues-Combined
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniWhat electrolytes does the low volume state have? inc total Na. Dec serum Na (dilutional effect) What pH does diarrhea have? What happens if pulse inc >10 on standing? hypovolemic shock What happened if pulse dec 5 on standing? What are the most common infections of the low energy state? restrictive - interstitial problem (non-bacterial) small stiff lungs (dec VC)
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
151 tayangan73 halamanCopy of PPclues-Combined
Diunggah oleh
Alexis RamosWhat electrolytes does the low volume state have? inc total Na. Dec serum Na (dilutional effect) What pH does diarrhea have? What happens if pulse inc >10 on standing? hypovolemic shock What happened if pulse dec 5 on standing? What are the most common infections of the low energy state? restrictive - interstitial problem (non-bacterial) small stiff lungs (dec VC)
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 73
What electrolytes does the low volume state have?
inc total Na ...
dec serum Na (dilutional effect) ...
dec Cl ...
dec K
What pH does the low volume state have?
alkalotic because aldosterone dumps H ...
EXCEPT: diarrhea, RTA Type , DKA
What pH do vomiters have? alkalotic because you vomit out H
What pH does diarrhea have? acidosis because stool has bicarb
What happened if pulse inc >10 on standing? hypovolemic shock
What happened if pulse dec <5 on standing? autonomic dysfunction
What are the sx of a low energy state?
CNS: mental retardation, dementia ...
CV: heart failure, pericardial effusion ...
Muscle: weakness, SOB, vasodilation, impotence, urinary
retention, constipation ...
Rapidly Dividing Cells: ...
skin - dry ...
nails - brittle ...
hair - alopecia ...
bone marrow - suppressed ...
vascular endothelium - breaks down ...
lungs - infection, SOB ...
kidney - PCT will feel the effect first ...
G - N/V/D ...
bladder - oliguria ...
sperm - decreased ...
germ cells - predisposed to cancer ...
breasts - atrophic ...
endometrium - amenorrhea
What are the most common signs of the low energy
state?
tachypnea and dyspnea
What are the most common sx of the low energy state? weakness and SOB
What are the most common infections of the low energy
state?
UT and respiratory infections
Explain all restrictive lung diseases ...
restrictive - interstitial problem (non-bacterial) ...
small stiff lungs (dec VC) ...
trouble breathing in => FEV1/FVC > 0.8 ...
ABG: dec pO2 => inc RR ... dec pCO2 ... inc pH ...
CXR: reticulo-nodular pattern, ground glass appearance
...
die of cor pulmonale ...
tx: pressure support on ventilation, inc O2, inc RR, inc
inspiratory time
Explain all obstructive lung diseases ...
obstructive - airway problem (bacterial) ...
big mucus-filled lungs (inc RV ... inc Reid index => inc
airway thickness/lumen) ...
trouble breathing out => FEV1/FVC < 0.8 ...
ABG: inc pCO2 => inc RR ... dec pH ...
die of bronchiectasis ...
tx: manipulate rate on ventilator, inc RR, inc expiratory
time, inc O2 only if needed
What sx does a "more likely to depolarize" state have?
brain - psychosis, seizures, jitteriness ...
skeletal muscle - spasms, tetany ...
SM - diarrhea then constipation ...
cardiac - tachycardia, arrhythmias
What sx does a "less likely to depolarize" state have?
brain - lethargy, mental status changes, depression ...
skeletal muscle - weakness, SOB ...
SM - constipation then diarrhea ...
cardiac - hypotension, bradycardia
What is the humoral immune response? B cells and PMNs patrol the blood looking for bacteria
What is the cell-mediated immune response?
T cells and macrophages patrol the tissues looking for
non-bacteria
What are macrophages called in each area of the body?
blood = monocytes ...
brain = microglia ...
lung = T1 pneumocytes ...
liver = Kupffer cells ...
spleen = RES cells ...
lymph = dendritic cells ...
kidney = mesangial cells ...
Peyers patches = M cells ...
skin = Langerhans ...
bone = osteoclasts ...
CT = histioctyes, giant cells, epitheloid cells
What is the CBC for every vasculitis?
dec RBC ...
dec platelets ...
inc WBC ...
inc T cells ...
inc MP ...
schistocytes ...
inc ESR
What is the time course of the inflammatory response?
1 hr - swelling ...
1 day - PMNs show up ...
3 days - PMNs peak ...
4 days - MP/T cells show up ...
7 days - MP/T cells peak, fibroblasts arrive ...
30 days - fibroblasts peak ...
3-6 months - fibroblasts leave
What state does estrogen mimic?
the neuromuscular disease state (estrogen is a muscle
relaxant)
What do high GABA levels lead to?
bradycardia ...
lethargy ...
constipation ...
impotence ...
memory loss
What organs have resistance in series? liver and kidney
What organs have resistance in parallel? everything but the liver and kidney
What organ has the highest A-V O2 difference at rest? heart
What organ has the highest A-V O2 difference after
exercise?
muscle
What organ has the highest A-V O2 difference after a
meal?
gut
What organ has the highest A-V O2 difference during an
exam?
brain
What organ as the lowest A-V O2 difference? kidney
Where does a Type A thoracic aortic dissection occur?
ascending aorta ...
associated with cystic medial necrosis and syphilis
Where does a Type B thoracic aortic dissection occur?
descending aorta ...
associated with trauma and atherosclerosis
What layers does a true aortic aneurysm involve? intima, media, and adventitia
What layers does a pseudo aortic aneurysm involve? intima and media
What is pulse pressure? systolic - diastolic
What vessel has the thickest layer of smooth muscle? aorta
What vessels have the most smooth muscle? arterioles
What vessels have the largest cross-sectional area? capillaries
What vessel has the highest compliance? aorta
What vessels have the highest capacitance? veins and venules
What is your max heart rate? 220 - age
What is stable angina?
pain on exertion ...
associated with atherosclerosis
What is unstable angina?
pain at rest or first event ...
associated with transient clots
What is Prinzmetal angina?
intermittent pain ...
associated with coronary artery spasm
What stain is used to see amyloidosis? congo red (apple green birefringence)
What is hemochromatosis?
Fe deposition in organs ...
leads to hyperpigmentation, arthritis, and DM
What is cardiac tamponade?
pressure equalized in all 4 chambers ...
quiet precordium ...
no pulse or BP ...
Kussmaul's sign ...
pulsus paradoxus (dec systolic P > 10 mmHg on
inspiration)
What is a transudate?
effusion of mostly water ...
too much water (heart failure and renal failure) ...
not enough protein (cirrhosis and nephrotic syndrome)
What is a exudate?
effusion of mostly protein ...
purulent (bacteria) ...
hemorrhagic (trauma, cancer, PE) ...
fibrinous (collagen vascular disease, uremia, TB) ...
granulomatous (non-bacterial)
What is systole?
ventricles contract ...
dec blood flow to coronary arteries ...
inc O2 extraction
What is diastole?
ventricles relax and fill ...
in blood flow to coronary arteries ...
dec O2 extraction
What are the only arteries with deoxygenated blood? pulmonary and umbilical arteries
What murmur has a waterhammer pulse? aortic regurg
What murmur has pulsus tardus? aortic stenosis
What cardiomyopathy has pulsus alternans? dilated cardiomyopathy
What disease has pulsus bigeminus? HSS
What murmur has an irregularly irregular pulse? a-fib
What murmur has a regularly irregular pulse? PVC (para-ventricular contractions)
What murmur radiates to the carotids?
aortic stenosis ...
aortic regurg
What murmur radiates to the axilla? mitral regurg
What murmur radiates to the back? pulmonic stenosis
What disease has a boot-shaped x-ray? right ventricular hypertrophy
What disease has a banana-shaped x-ray? HSS
What disease has an egg-shaped x-ray? transposition of the great arteries
What disease has a snowman-shaped x-ray? total anomalous pulmonary venous return
What disease has a "3" shaped x-ray? aortic coarctation
What is Osler-Weber-Rendu?
AVM in lung, gut and CNS ...
sequester platelets leading to telangiectasias
What is Von Hippel-Lindau?
AVM in head and retina ...
inc risk of renal cell carcinoma
When do valves make noise? closure
What valves make noise at the start of systole? M and T (S1)
What murmurs occur during systole?
holosystolic/pansystolic - MR, TR, VSD ...
ejection - AS, PS, HCM
What valves make noise at the start of diastole? A and P (S2)
What are the diastolic murmurs?
blowing - AR and PR
rumbling - MS and TS
What murmurs are continuous? PDA and AVM
What has a friction rub while breathing? pleuritis
What has a friction rub while holding your breath? pericarditis
What does a mid-systolic click tell you? mitral valve prolapse
What does an ejection click tell you? AS or PS
What does an opening snap tell you? MS or TS
What does S2 splitting tell you? normal on inspiration (b/c pulmonic valve closes later)
What does wide S2 splitting tell you?
inc O2 ...
inc RV volume ...
delayed PV opening
What does fixed wide S2 splitting tell you? ASD
What does a paradoxical S2 split tell you? AS or LBBB
What is cor pulmonale? pulmonary HTN leading to RV failure
What is Eisenmenger's?
pulmonary HTN leading to a reversal of an L-R shunt to
and R-L shunt
What causes transposition of the great arteries? aorticopulmonary septum did not spiral
What is tetrology of Fallot?
overriding aorta ...
PS (prognostic) ...
RV hypertrophy ...
VSD (L-R shunt)
What is trucus arteriosus?
spiral membrane didn't develop (neural crest origin) ...
one A/P trunk (mixed blood)
What is Epstein's anomaly?
tricuspid sits very low (large right atria) ...
teratogenic effects of lithium
What is cinchonism?
hearing loss ...
tinnitus ...
thrombocytopenia
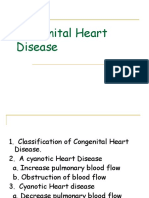
What are the cyanotic heart diseases?
transposition of the great arteries ...
tetralogy of fallot ...
truncus arteriosus ...
tricuspid atresia ... aortic atresia ... pulmonic atresia ...
total anomalous pulmonary venous return ...
hypoplastic left heart syndrome ...
Epstein's anomaly
What causes a machine-like murmur?
AVM's ...
heart: PDA ...
elbow: dialysis fistula ...
brain: Von Hippel-Lindau ...
lungs: Osler-Weber-Rendu
What are the heart block clues?
pain with a normal heart rate ...
fever with a normal heart rate (should increase by 10 bpm
for every degree inc in temp)
What ion is important for the P-wave? calcium
What ion is important for the QRS complex? sodium
What ion is important for the ST interval? calcium
What ion is important for the T-wave? potassium
What ion is important for the U-wave? potassium
What are the MC non-cyanotic congenital heart disease?
VSD ...
ASD ...
PDA ...
coarctation of the aorta
What are the M enzymes?
troponin ...
CKMB ...
LDH
When does troponin appear, peak, and disappear after
an M?
appears 2 hrs ...
peaks 2 days ...
gone 1 wk
When does CKMB appear, peak, and disappear after an
M?
appears 6 hrs ...
peaks 12 hrs ...
gone 2 days
When does LDH appear, peak, and disappear after an
M?
appears 1 day ...
peaks 2 days ...
gone 3 days
------------------------------
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
epinephrine adrenergic agonist
acute asthma
anaphylactic shock
activates d and but
is preferential for
norepinephrine
d1, d2 > 1 adrenergic
agonist
hypotention (potent
vasoconstrictor)
isoproterenol nonselective agonist
asthma (2
vasodilation)
tachycardia (1)
dopamine
D1=D2 > > d .
inotropic and
chronotropic
D2: shock, perfuse
kidney
1: contractility
d1: vasoconstrict,
afterload
dobutamine
1 > 2 adrenergic
agonist . inotropic
acute heart failure (
CO)
not chronotropic
phenylephrine d1 > d2 agonist nasal decongestion hypertension
------------------------------
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
amphetamine
stimulant - releases
NE, dopamine, and
5HT
narcolepsy
ADHD
weight reduction
dilated pupils
psychosis
hallucinations
contraindicated with
MAO
metabolized by liver
ephedrine
mixed adrenergic
agonist
nasal decongestion bld pressure
indirect general
agonist
releases stored
catecholamines (NE)
pseudoephedrine
d and adrenergic
agonist
nasal decongestion
tachycardia (1)
bld pressure (d1)
precursor for
methamphetamines
cocaine
stimulant - blocks
reuptake of NE,
dopamine, and 5HT
local anesthetic
vasoconstriction
hypertension
nasal mucus ischemia
------------------------------
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
clonidine
centrally acting d2
agonist
sympathetic outflow
hypertension
smoking, heroin,
cocaine withdrawal
dry mouth
rebound htn after
abrupt withdrawal
d-methyldopa
centrally acting d2
agonist
sympathetic outflow
hypertension (in
pregnant women)
hemolytic anemia positive coombs test
------------------------------
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
phenoxybenzamine d blocker pheochromocytoma
nasal congestion
miosis
orthostatic
hypertension
long acting
irreversible
phentolamine d blocker
diagnosis of
pheochromocytoma
hypertension
------------------------------
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
prazosin d1 blocker hypertension
first dose orthostatic
hypertension
terazosin d1 blocker
hypertension
BPH
postural hypertension
doxazosin d1 blocker
hypertension
BPH
------------------------------
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
mirtazapine
d2 blocker
release of NE and
5HT
major depression
hypertrichosis
pericardial effusion
serum cholesterol
------------------------------
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
albuterol 2 agonist
asthma, COPD,
bronchitis
(bronchodilation)
tremor
tachycardia
arrhythmia
salmeterol
2 agonist (long
acting)
asthma prophylaxis hand tremor
terbutaline 2 agonist
asthma
(bronchodilate)
inhibits preterm labor
(relaxes uterus)
ritodrine 2 agonist
inhibit preterm labor
(relaxes uterus)
------------------------------
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------
propranolol
timolol
pindolol
labetolol
carvedilol
------------------------------ ------------------------------
------------------------------
acebutolol
betaxolol
esmolol
atenolol
metoprolol
What are the 3 exceptions to the water-out, fat-in rule?
channels ...
pores ...
transmembrane proteins
What is the RDA for fat/carb/protein?
30% fats ...
30% proteins ...
40% carbohydrates
What are the 7 functions of a cell membrane?
provide structure ...
transport ...
active transport ...
heat/temp regulation ...
maintain gradient ...
depolarization ...
signal transduction
What is membrane transportation in a cell called? phagocytosis
What is it called to bring something into a cell? endocytosis
What is it called to put something outside the cell? exocytosis
What is it called to bring water into a cell? pinocytosis
What are the two things required for cellular transport? ATP and actin
What is the most important substance endocytosed? nutrition
What is the most important substance exocytosed? waste
What is the most important waste product produced by
cells?
lipofuscin (brown pigment)
What is the most important factor in the movement of
particles?
concentration gradient
How do you concentrate any substance in the body? with an ATPase
How does secondary active tranport work?
going with a concentration gradient using another
substance's gradient
What is the most common gradient used for secondary
active transport?
Na
What is true for all fat soluble and steroid hormone
receptors?
they never have cellular membrane receptors because
they readily cross the membrane
Where are fat soluble and steroid hormone receptors
located?
in the nucleus (except for cortisol with a cytoplasmic
receptor)
How do nuclear receptors work?
stimulate the nucleus to perform DNA replication,
transcription, and translation into proteins by which they
manifest their action
How do you differentiate between one fat soluble
hormone and another?
by the proteins they make
What factors affect transportation of water-soluble
compounds or hormones?
size ...
charge ...
pH ...
surface area ...
membrane thickness ...
flux ....
relfection coefficient ...
Fick's law
How does ions cross membranes? through channels
How do medium-size particles cross membranes? pores
How do larger molecules cross membranes? transport proteins
How does the body get rid of heat? vasodilate
How does the body keep heat? vasoconscrict
What is the most imporant substance that is transported
through pores?
sweat (NaCl and water)
Which hormones have cell membrane receptors? non-steroid hormones
What are the most common extracellular cations/anions? sodium and chloride
What are the most common intracellular cations/anions? potassium and proteins
What tissues are the best at depolarizing?
neuronal ...
purkinje fibers
What type of hormones have second messenger
systems?
water-soluble (protein)
Where are protein hormone receptors located? cell membrane
What is the reflection coefficient for protein hormones? close to 1
What are the 6 classes of second messengers?
cAMP ...
cGMP ...
P3/DAG ...
calcium ...
tyrosine kinase ...
nitric oxide
What is the action of cAMP? 2nd messenger for sympathetics
What is the action of cGMP? 2nd messenger for parasympathetics
What is the action of P3/DAG?
2nd messenger for: ...
all hypothalamic hormones except CRH ...
all smooth muscle contraction by hormone or
neurotransmitter
What is the action of calcium-calmodulin?
2nd messenger of all smooth muscle contraction by
distention
What is calcium a second messenger for? gastrin
What is the action of tyrosine kinase? 2nd messenger for insulin and all growth factors
What is the action of nitric oxide? 2nd messenger for nitrates
What is the MC 2nd messenger system? cAMP
What hormones are activated by phosphorylation? all catabolic
What hormones are deactivated by phosphorylation? all anabolic
What enzyme breaks down cAMP? phosphodiesterase breaks down cAMP
What substances inhibit phosphodiesterase? caffeine and theophylline
What bacteria ADP-ribosylate Gs subunit of the G-
protein?
ETEC and vibrio
What bacteria ADP-ribosylate Gi subunit of the G-
protein?
pertusses
What bacteria ADP-ribosylate EF-2? diphtheria and pseudomonas
How does nitric oxide work? increases cGMP
What 2nd messenger systems are enhanced by
increased calcium?
P3/DAG ...
calcium/calmodulin ...
calcium
What hypertensive medications both vaso and veno
dilate?
nitrates and ACE-inhibitors
What substances use nitric oxide as a second
messenger?
ANP ...
endotoxin ...
viagra (sildenafil) ...
all nitrates
What nitrate is used to treat cyanide poisoning? amyl nitrate
What nitrate is given V or sublingual for chest pain? nitroglycerine
What nitrate is used to treat a hypertensive crisis? sodium nitroprusside
What is the function of the smooth ER? detoxification and steroid synthesis
What is the function of the rough ER? makes proteins for packaging
What is the function of free ribosomes? makes proteins for cytoplasm
What is the function of the lysosome? degradation of waste
What is function of the golgi? post-translational modifications of proteins
What is the function of the mitochondria? makes energy
What is the function of the nucleus? contains all genetic information
What is the function of the nucleolus? produces ribosomal RNA
Damage to what organelles is irreversible?
nucleus ...
mitochondria ...
lysosomes
What organ uses the SER for detoxification? kidney
What organ uses the SER for steroid synthesis? liver
What is the form of proteins when they start off? pre-pro-protein
Which is the only protein modified in the rough ER? collagen
Where are all proteins except collagen modified? golgi
What are the tissues with the most SER? liver and kidney
What substances do lysosomes have a lot of? acid hydrolases
What do acid hydrolases do to the pH of lysosomes? cause the pH to be very acidic
What is the structure formed when a lysosome
phagocytoses something?
phagosome of phagolysosome
What component of tuberculosis prevents phagocytosis cord factor
What ion damages lysosomes by coating their surface? calcium
What does damage to lysosomes cause?
acid hyrdrolases leak out and damage the nuclease,
particularly DNAse and RNAse
What is the most important primary active transport
system?
sodium ATPase (3 Na out, 2 K in)
What is the most important secondary active transport
system?
sodium-calcium exchanger (3 Na out, 2 Ca in)
What transport system is used to make the cell more
negative?
Na/K ATPase
What transport system is used to make the cell more
positive?
Na/Ca exchanger
What does a lysosomal inclusion body indicate? missing enzyme => inability to digest the substance
Which parent transmits mitochondrial DNA? mother
What is the outcome of all chromosomal abnormalities? they all die
What is a monosomy that doesn't die? Turner's
What is the major concept behind all monosomies? if they do not die, things won't grow
What are the trisomies?
Trisomy 13 - Patau ...
Trisomy 18 - Edwards ...
Trisomy 21 - Downs
What are clues for Patau?
die shortly after birth ...
high arched palate ...
polydactyly
What are clues for Edwards?
die shortly after birth ...
95% rockerbottom feet
What are clues for Downs?
MR ...
congenital heart dz ...
hypothyroidism ...
cancer (ALL) ...
early onset Alzheimer's ...
simian crease ...
mongolian slant ...
wide space 1st and 2nd toe
What is the MC cyanotic heart dz in Downs? tetrology of fallot
What is the most common and most frequent cancer
seen in Down's?
most common - ALL ...
most frequent - AML
What are the 3 types of nuclear damage?
pyknosis (blobs) ...
karyorrhexis (chunks) ...
karyolysis (dissolves)
What is coagulative necrosis?
due to ischemia ...
architecture is preserved
What is liquefactive necrosis?
half solid, half liquid ...
no maintenance of architecture ...
e.g. brain abscess
What is hemorrhagic necrosis? organs with soft capsule or more than one blood supply
What is caseous necrosis?
cheesy ...
TB only
What is fat necrosis?
occurs in pancreas with chronic pancreatitis ...
blunt trauma to breast
What is purulent necrosis? pus due to bacteria (PMN)
What is granulomatous necrosis?
granulomas ...
T-cells and macrophages ...
non-bacterial
What is fibrinous necrosis?
collagen vascular dz ...
uremia ...
TB
What is the MCC of necrosis? ischemia leading to coagulative necrosis
What substances stop the Na/K pump?
digitalis ...
digoxin ...
ouabain
What is the normal resting potential for cells? -90
How does the body maintain stroke volume during
hypovolemic shock?
by constricting veins and venules
What type of epithelium makes up the aorta? stratified squamous
What is calcification of the aortic arch due to trauma and
age called?
Monckeberg calcification
What gives veins and venules the ability to have such
great compliance?
elastin
As you age, what happens to the aorta? it calcifies
What affect does calcification of the aorta have on blood
pressure and pulse pressure?
BP - increases (mainly systolic) ...
PP - increases (diastolic relatively unchanged)
How do you treat hypertension in the elderly? calcium channel blockers
What are the vasodilators for the brain?
inc pCO2 ...
dec pO2
What are the vasodilators for the cardiovascular system? adenosine
What are the vasodilators for the lung? inc pO2
What are the vasodilators for muscle?
inc pCO2 ...
dec pH
What are the vasodilators for the G system? food (esp fat)
What are the vasodilators for skin?
inc temp ...
inc pCO2
What are the vasodilators for the renal system?
D2 receptors ...
prostaglandins ...
ANP
What is the pathology of sick sinus syndrome in the
elderly?
carotid sinus is so calcified that it does not respond ...
sick sinus means pausing for more than one second
What is the mechanism responsible for immediate
regulation of BP?
carotid reflex
What is the mechanism responsible for intermediate
regulation of BP?
norepinephrine (alpha-1 receptors then beta-1 receptors)
What is the mechanism responsible for long term
regulation of blood pressure?
kidney
What substance is the most potent vasoconstrictor in the
body?
angiotensin
What are the two most important actions of angiotensin
?
vasoconstriction ...
stimulate aldosterone release
What is the treatment for hypertension in heart failure? ACE-inhibitors
What kind of heart block has a fixed lengthening of the
PR interval?
first degree ...
no tx
What kind of heart block has a normal PR interval and
erratic loss of QRS?
second degree (Mobitz 2) ...
tx with pacer
What type of heart block has AV dissociation?
third degree ...
tx with pacer
What kind of heart block has a gradual lengthening of the
PR interval and erratic loss of QRS?
second degree (Mobitz 1) ...
tx with pacer if sxs
What is a frameshift mutation? substitution for one or two bases
What is a silent mutation? makes the same protein
What is a missense mutation? makes a different protein
What is a nonsense mutation? makes a stop codon
What is a transition mutation? purine to purine
What is a transversion mutation? purine to pyrimidine or vice versa
What is necrosis?
non-programmed cell death = noisy ...
inflammation ...
nucleus destroyed first
What is apoptosis?
programmed cell death = quiet ...
no inflammation ...
nucleus guides it and is destroyed last
What is pyknosis? nucleus turns into blobs
What is karyohexis? nucleus fragments
What is karyolysis? nucleus dissolves
What is a somatotrope? GH
What is a gonadotrop? LH, FSH
What is a thyrotrope? TSH
What is a corticotrope? ACTH
What is a lactotrope? PRL
What receptors do protein hormones use? cell membrane receptors
What receptors to steroid hormones use? nuclear membrane receptors
What are the steroid hormones?
PET CAD ...
note: TH acts like a steroid hormone
P: progesterone ...
E: estrogen ...
T: testosterone ...
C: cortisol ...
A: aldosterone ...
D: vitamin D ...
What dose endocrine mean? secretion into blood
What does exocrine mean? secretion into non-blood
What is autocrine? works on itself
What is paracrine? works on its neighbor
What is merocrine? exocytosis (cell is maintained)
What is apocrine? apex of cell is secreted
What is holocrine? whole cell is secreted
What organs do not require insulin?
BRCKLE ...
B: brain ...
R: RBC ...
: intestine ...
C: cardiac/cornea ...
K: kidney ...
L: liver ...
E: exercising muscle
What does GnRH do? stimulates LH and FSH
What does GRH do? stimulates GH
What does CRH do? stimulates ACTH
What does TRH do? stimulates TSH
What does PRH do? stimulates PRL
What does DA do? inhibits PRL
What does SS do? inhibits GH
What does ADH do?
conserves water ...
vasoconstricts
What does oxytocin do?
milk letdown ...
baby letdown
What does GH do? GF-1 release from liver
What does TSH do? T3 and T4 release from thyroid
What does LH do?
testosterone release from testes ...
estrogen and progesterone release from ovary
What does FSH do? sperm or egg growth
What does ACTH do? cortisol release from adrenal gland
What does MSH do? skin pigmentation
What are the stress hormones?
immediate: epinephrine
20 min: glucagon
30 min: insulin
30 min: ADH
2-4 hrs: cortisol
24 hrs: GH
What does ADH do? concentrates urine
What is Diabetes nsipidus? too little ADH ... urinate a lot
What is Central D? brain not making ADH
What is Nephrogenic D?
blocked ADH receptor ...
can be caused by lithium and demecocycline
What does the water deprivation test tell you? if fail to concentrate urine => D
What does giving DDAVP tell you? if concentrate >25% => central D
What is SADH? too much ADH => expanded plasma volume => pee Na
What is the difference between D and SADH?
D has dilute urine ...
SADH has concentrated urine
What is psychogenic polydipsia?
pathologic water drinking ...
low plasma osmolarity
WHat does aldosterone do?
reabsorbs Na ...
secretes H/K
What is a neuroblastoma?
adrenal medulla tumor in kids ...
dancing eyes/feet ...
secretes catecholamines
What is a pheochromocytoma?
adrenal medulla tumor in adults ...
5 P's:
pressure ...
palpitations ...
pain (h/a) ...
perspiration ...
pallor
What does the Zona Glomerulosa make? aldosterone ... "salt"
What does the Zona Fasiculata make? cortisol ... "sugar"
What does the Zona Reticularis make? androgens ... "sex"
What is Conn's syndrome?
high aldosterone (due to tumor) ...
captopril test makes it worse
What does ANP do?
inhibits aldosterone ...
dilates renal artery (afferent arteriole)
What does calcitonin do? inhibits osteoclasts
What is MEN ?
"Wermer's" PPP ...
Pancreas ...
Pituitary ...
Parathyroid adenoma ...
(high gastrin)
What is MEN ?
"Sipple's" ...
Parathyroid ...
Pheochromocytoma ...
Medullary thyroid cancer ...
What is MEN ?
"MEN b" ...
Pheochromocytoma ...
Medullary thyroid cancer ...
Mucosal neuromas (oral/G) ...
Marfanoid
What does CCK do?
gallbladder contraction ...
bile release ...
inhibits gastric motility (closes sphincters)
What does cortisol do?
gluconeogenesis by proteolysis ...
leads to thin skin
What is Addison's disease?
autoimmune destruction of adrenal cortex ...
hyperpigmentation ...
increased ACTH
What is Waterhouse Friderichsen?
adrenal hemorrhage ...
MC bug implicated N. meningitidis
What is Cushing's syndrome?
high cortisol due to ...
pituitary tumor ...
small cell lung tumor ...
adrenal tumor
What is Cushing's Disease? high cortisol due to a pituitary tumor
What is Nelson's syndrome? hyperpigmentation after adrenalectomy
f the low-dose dexamethasone test suppresses, what
does that tell you?
normal, obese, or depressed
f the low-dose dexamethasone test does not suppress,
what does that tell you?
Cushing's ... do a high dose test
f the high-dose dexamethasone test suppresses, what
does that tell you?
Pituitary tumor
f the high-dose dexamethasone test does not suppress,
what does that tell you?
if ACTH high - small cell lung cancer ...
otherwise - adrenal adenoma
What are the survival hormones
cortisol: permissive under stress ...
TSH: permissive under normal
What does epinephrine do?
gluconeogenesis ...
glycogenolysis
What does erythropoietin do? makes RBCs
What does gastrin do? stimulates parietal cells to release F and H+
What does growth hormone do?
growth ...
sends somatomedin to growth plates ...
gluconeogenesis by proteolysis
What is a pygmie? no somatomedin receptors
What is achondroplasia (Laron Dwarf)? abnormal FGF receptors in extremities
What is a midget? low somatomedin receptor sensitivity
What is acromegaly?
adult bones stretch ... "my hat doesn't fit" ...
coarse facial features ...
large furrowed tonge ...
deep husky voice ...
jaw protrusion ...
increased GF-1 due to GH tumor
What is gigantism? childhood acromegaly
What does GP do?
enhances insulin action ...
leads to post-prandial hypoglycemia
What does glucagon do?
gluconeogenesis ...
glycogenolysis ...
lipolysis ...
ketogenesis
What does insulin do? pushes glucose into cells and K+ follows
What is Type DM?
anti-islet cell Ab ...
GAD Ab ...
coxsackie B virus ...
low insulin ...
DKA ...
polyuria ...
polydypsia ...
polyphagia
What is Type DM?
insulin receptor insensitivity ...
high insulin ...
HONK coma ...
acanthosis nigricans
How does DKA present?
Kussmaul respirations ...
fruity breath (acetone) ...
altered mental status
What is the Dawn Phenomenon? morning hyperglycemia secondary to GH
What is the Somogyi Effect?
morning hyperglycemia secondary to evening
hypoglycemia
What is factitious hypoglycemia? insulin injection (high insulin and low C-peptide)
What is an insulinoma? tumor (high insulin and high C-peptide)
What is erythrasma? rash in skin folds
What is Metabolic Syndrome X?
"Pre-DM" ...
hypertension ...
dyslipidemia ...
hyperinsulinemia ...
acanthosis nigricans
What are foot ulcer risk factors?
DM/glycemic control ...
male smoker ...
bony abnormalities ...
previous ulcers
What conditions cause weight gain?
obesity ...
hypothyroidism ...
depression ...
Cushing's ...
anasarca
What does motilin do?
stimulates segmentation (primary peristalsis - myometric
complexes)
What does oxytocin do? milk ejection, baby ejection
What does PRL do? milk production
What does PTH do? chews up bone
What does vitamin D do? builds bone
What do parathyroid chief cells secrete? PTH
What do stomach chief cells secrete? pepsin
What is the difference between norepinephrine and
epinephrine?
NE: neurotransmitter ...
epi: hormone
What is primary hyperparathyroidism? parathyroid adenoma
What is secondary hyperparathyroidism? renal failure
What is familial hypocaliuria hypercalcemia? decreased Ca excretion
What if both serum Ca and PO4 decrease? vitamin D deficiency
What if serum Ca and PO4 change in opposite
directions?
PTH problem ...
if high Ca: hyperparathyroid ...
otherwise: hypoparathyroid
What is the most common cause of primary
hypoparathyroidism?
thyroidectomy
What is pseudohypoparathyroidsim?
bad kidney PTH receptor ...
decreased urinary cAMP
What is pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism?
G-protein defect ...
no Ca problem
What is hungry bone syndrome? remove PTH and bone sucks in Ca
What does secretin do?
secretion of bicarb ...
inhibit gastrin ...
tighten pyloric sphincter
What does somatostatin do? inhibits secretin, motilin, and CCK
What do T3 and T4 do? growth and differentiation
What disease has exophthalmos? Grave's
What disease has enopthalmos? Horner's
What are the hyperthyroid diseases?
Grave's ...
DeQuervain's ...
Silent ...
Plummer's ...
Jod-Basedow
What is Grave's disease?
hyperthyroid ...
exophthalmos ...
pretibial myedema ...
TSH-receptor Ab
What is DeQuervain's?
hyperthyroid ...
viral ...
painful jaw
What is silent thyroiditis?
hyperthoid ...
post-partum
What is Plummer's?
hyperthyroid ...
benign adenoma ...
old person
What is Jod-Basedow? transient hyperthyroid due to increased iodine
What are the hypothyroid diseases?
Hashimoto's ...
Reidel's struma ...
cretinism ...
euthyroid sick syndrome ...
Wolf-Chaikoff
What is Hashimoto's
hypothyroid ...
antimicrosomial Ab = TPO Ab
What is Reidel's struma?
hypothyroid ...
woody neck
What is cretinism?
hypothyroid mom and baby ...
freak features
What is euthyroid sick syndrome? low T3 syndrome
What is Wolff-Chaikoff? transient hypothyroidism
What does testosterone do? makes external male genitalia
What does Mullerian nhibiting Factor do? makes internal male genitalia
What do TPO and thymosin do? help T cells mature
What does VP do? inhibits secretin, motilin, and CCK
How does a VPoma present? watery diarrhea
How does a SSoma present? constipation
What are the hormones with disulfide bonds?
"PG" ...
P: prolactin ...
: inhibin ...
G: growth hormone ...
: insulin
Which hormones have the same alpha-subunits?
LH, FSH ...
TSH ...
beta HCG
What hormones produce acidophils?
"GAP" ...
GH ...
PRL
What hormones produce basophils?
"B FLAT" ...
FSH ...
LH ...
ACTH ...
TSH
What hormones are released from the posterior pituitary?
ADH (supraoptic nucleus) ...
oxytocin (paraventricular nucleus)
What causes a corkscrew x-ray? esophageal spasm
What causes an apple core x-ray? cancer
What causes a stacked coin x-ray? intussusception
What causes an abrupt cutoff in an x-ray? volvulus
What causes a bird's beak on x-ray? achalasia
What causes a string sign on x-ray? pyloric stenosis
What are causes of solid dysphagia?
Schatzki's rings ...
strictures ...
cancer
What are Schatzki's rings? lower esophageal webs
What are causes of liquid dysphagia?
scleroderma ...
achalasia ...
esophageal spasm
What is Barrett's esophagus?
metaplasia ...
increased risk of adenocarcinoma
What are esophageal varices?
due to portal hypertension ...
vomit blood when they rupture
What is Mallory-Weiss?
chronic vomiters ..
tear at LES mucosa
What is Boerhaave's esophagus? transmural (all layers) rupture of the esophagus
What is alchalasia?
increased LES pressure ...
decreased peristalsis ...
lost LES Auerbach's plexus ...
bird's beak on x-ray
What is Hirschsprung's?
congenital lack of Auerbach's in the rectum ...
newborn won't pass meconium
What is a Zenker's diverticulum?
above UES ...
cough undigested food ...
halitosis
What is a traction diverticulum? below the UES
What is Plummer-Vinson syndrome?
esophageal webs (UES) ...
spoon nails ...
iron deficiency anemia
What is a TE fistula (H-type)? choke with each feeding
What is esophageal atresia with a TE fistula (C-type)?
vomit with first feeding ...
huge gastric bubble
What is duodenal atresia?
bilious vomiting with first feeding ...
double bubble ...
Down's syndrome
What is pyloric stenosis?
non-bilious projectile vomiting (3-4 wk old) ...
RUQ olive sign
What is choanal atresia?
turns blue with feeding ...
"smurf on a nipple"
What makes scleroderma unique? decreased LES pressure
What makes esophageal spasms unique? increased peristalsis
What makes achalasia unique? decreased peristalsis and increased LES pressure
What disease has a RUQ olive mass? pyloric stenosis
What disease has a RLQ sausage mass? intussusception
What is a bezoar?
mass of undigestable material ...
antrum obstruction
What is Type A gastritis?
autoimmune ...
anti-parietal cell Ab ...
atrophic / achlorhydria ...
adenocarcinoma risk increased
What is Type B gastritis?
H. pylori ...
spicy foods
What is a duodenal ulcer?
loss of barrier ...
pain after meal and during the night ...
relieved by eating (weight gain) ...
assoc with H. pylori and type O bld
What is a gastric ulcer?
loss of barrier ...
pain during meals ...
associated with NSADS and type A bld
What is a sliding hiatal hernia? fundus slides through esopheal hiatus into thorax
What is a rolling hiatal hernia?
bowel protrudes through a defect in the diaphragm ...
strangulates bowel
What is Menetrier's disease?
loose protein through rugal folds (generalized edema) ...
thick rugal folds
What defines constipation? < 3 BM per wk
What defines diarrhea? > 200g per day
What is osmotic diarrhea? watery
What can cause secretory diarrhea? laxative use
What is inflammatory diarrhea? blood and pus
What is celiac sprue?
jejunum ...
wheat allergy ...
villous atrophy ...
anti-gluten / gliadin Ab
Where is tropical sprue? distal ileum
What is mesenteric ischemia? pain out of proportion to exam
What are the bugs that cause bloody diarrhea?
CASES ...
C: campylobacter ...
A: amoeba (E. histolytica) ...
S: shigella ...
E: E. coli ...
S: salmonella
What is cholangitis? inflammation of the bile duct
What is Charcot's triad?
jaundice ...
fever ...
RUQ pain
What is Reynold's pentad?
jaundice ...
fever ...
RUQ pain ...
hypotension ...
change in mental status
What is ascending cholangitis? common bile duct infection due to stone
What is primary sclerosing cholangitis?
p-ANCA ...
bile duct inflammation ...
beading ...
associated with ulcerative colitis
What is primary biliary cirrhosis?
anti-mitochondrial Ab ...
bile ductules destroyed ...
xanthelasma
What is cholestasis?
obstruction of bile duct ...
pruritis ...
increased alk phos ...
jaundice
What is cholecystitis?
inflammatin of the gall bladder ...
Murphy's sign
What is cholelithiasis?
formation of gallstones ...
RUQ pain
What is choledocholithiasis? gallstone obstructs bile duct
What is the most common gall stone? cholesterol (invisible on x-ray)
What is conjugated bilirubin?
water soluble ...
direct
What is unconjugated bilirubin?
fat soluble ...
indirect
What are signs of alcoholic cirrhosis?
spider angioma ...
palmar erythema ...
gynecomastia
What is hepatorenal syndrome? build-up of liver toxins causing renal failure
What is a xanthoma? cholesterol buildup (elbow, Achilles)
What does high cholesterol cause? atherosclerosis
What is a xanthelasma? triglyceride bulidup under the eye
What do high triglycerides cause? pancreatitis
What is type 1 hyperlipidemia?
bad liver LPL ...
high chylomicrons
What is type 2a hyperlipidemia?
bad LDL or B-100 receptors ...
high LDL ...
most common in general population
What is type 2b hyperlipidemia?
fewer LDL/VLDL receptors ...
high LDL and VLDL
What is type 3 hyperlipidemia?
bad ApoE ...
high DL and VLDL
What is type 4 hyperlipidemia?
bad adipose LPL ...
high VLDL
What is type 5 hyperlipidemia?
bad C2 ...
high VLDL and chylomicrons ...
associated with diabetes mellitus
What do chylomicrons do? take triglycerides from G to liver and endothelium
What does VLDL do? takes triglycerides from liver to adipose
What does DL do? take triglycerides from adiopose to tissue
What does LDL do? only one to carry cholesterol
What are the breakdown products of VLDL? DL and LDL
What is Crigler-Najjar Type ? unconjuaged bilirubin buildup in infants
What is Gilber's syndrome?
stress leads to increased unconjugated bilirubin ...
increased load saturates glucuronyl transferase
(deficiency in UDP glucuronyl transferase)
What is Rotor's?
bad bilirubin storage leads to increased conjugated
bilirubin
What is Dubin Johnson?
bad bilirubin excretion leads to increased conjugated
bilirubin ...
black liver
What is Cullen's sign?
hemorrhagic pancreatitis ...
bleeding around umbilicus
What is Turner's sign?
hemorrhagic pancreatitis ...
bleeding into flank
What are the tests for pancreatitis?
amylase (sensitive) - breaks down carbohydrates ...
lipase (specific) - treaks down triglycerides
What does Ranson's Criteria tell you? prognosis of pancreatitis
What is carcinoid syndrome?
flushing ...
wheezing ...
diarrhea
How is carcinoid syndrome diagnosed? 5-HAA in the urine
What is the most common primary location for a carcinoid
tumor?
appendix
What is the most common metastatic origin for a
carcinoid tumor?
small bowel
What are the most common metastatic sites for a
carcinoid tumor?
lung and heart
What is the most common location for a benign carcinoid
tumor?
appendix
What does current jelly sputum tell you? Klebsiella
What does current jelly stool tell you? intussusception
What is familial polyposis?
100% risk of colon cancer ...
APC defect ...
begin annual colonoscopy at 5 yo
What is Gardener's syndrome? familial polyposis with bone tumors
What is Turbot's syndrome? familial polyposis with brain tumors
What is Peutz-Jegher syndrome? hyperpigmented mucosa
What is Chron's disease?
BD with ...
cobblestones ...
melena ...
creeping fat ...
fistulas
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
BD with ...
pseudopolyps ...
hematochezia ...
lead pipe colon ...
toxic megacolon
What is intussusception?
current jelly stool ...
stacked coin enema
How does diverticulosis present? bleeds
How does diverticulitis present? LLQ pain
How does spastic colon present? intermittent severe cramps
How does BS present? alternating diarrhea/constipation with a hx of stress
How doe external hemorrhoids present? pain on defecation
How do internal hemorrhoids present? no pain
What is pseudomembranous colitis?
overgrowth of C. difficile due to normal flora being killed
off ...
usually by clindamycin use
What is Whipple's disease?
T. whippleii destroys G tract and then spreads causing
malabsorption and arthralgias ...
PAS +
What color is an upper G bleed? black
What color is a lower G bleed? red
What adds color to stool? stercobilinogen being oxidized to stercobilin
What gives urine its yellow color? urobilinogen being oxidezed to urobilin
What is the default color of stool? clay-colored
What is the default color of urine? tea-colored
What are the risk factors for primary liver cancer?
Hep B and C ...
aflatoxin ...
vinyl chloride ...
alcohol ...
carbon tetrachloride ...
anyline dyes ...
smoking ...
hemochromatosis ...
benzene ...
schistosomiasis
What are the risk factors for esophageal and gastric
carcinoma?
smoking ...
alcohol ...
nitrates ...
japanese
What caues gastroenteritis within 8 hours of eating?
pre-formed toxin ...
S. aureus (potato salad) ...
C. perfringens (holiday turkey/ham) ...
B. cereus (fried rice)
What bacteria are associated with colon cancer?
C. malanogosepticus ...
S. bovis
What are the hepatitis B labs during the window period?
ABeAb + ...
HBcAb +
What are the hepatitis B labs for an acute recent
infection?
HBcAg + ...
HBsAg + ...
HBcAb +/-
What are the hepatitis B labs within 2 weeks of
immunization?
HBsAg +
What are the hepatitis B labs greater than 2 weeks after
immunization?
HBsAb +
What are the hepatitis B labs of somebody with a
previous infection who is now immune?
HBcAb + ...
HBsAb +
What are the hepatitis B labs of somebody who is
currently infectious?
HBeAg +
What are the hepatitis B labs of a chronic carrier?
HBsAg + for > 6 months ...
HBsAB +/-
What is the only renally excreted statin? preavastatin
What statins need liver enzymes check every 3 months?
atorvastatin ...
lovastatin ...
simvastatin
What is the MOA of statins?
inhibit HMG CoA reductase ...
most active around 8 pm ...
must take every night for max efficacy
What is the name of vitamin A? retinoic acid
What does vitamin A do?
night vision ...
CSF production ...
PTH cofactor
What does a deficiency in vitamin A cause?
poor night vision ...
hypoparathyroidism
What is the name of vitamin B1? thiamine
What does vitamin B1 do? cofactor for dehydrogenases and transketolase (PPP)
What does a deficiency in vitamin B1 cause?
beriberi ...
Wernicke's encephalopathy ...
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
What is the name of vitamin B2? riboflavin
What does vitamin B2 do? FAD cofactor
What does a deficiency in vitamin B2 cause? annular cheilosis
What is a source of vitamin B2? milk
What breaks down vitamin B2? sunlight
What is the name of vitamin B3? niacin
What does vitamin B3 do? NAD cofactor
What does a deficiency in vitamin B3 cause?
Pellagra (4 D's) ...
diarrhea ...
dermatitis ...
dementia ...
death
What disease looks like pellagra? Hartnup
What cannot be transported in Hartnup? tryptophan
What is the name of vitamin B4? lipoic acid
What does vitamin B4 do? glycolysis
What does a deficiency in vitamin B4 cause? no deficiency state
What is the name of vitamin B5? pantothenic acid
What does vitamin B5 do? part of acetylCoA
What does a deficiency in vitamin B5 cause? no deficiency state
What is the name of vitamin B6 pyridoxine
What does vitamin B6 do?
transaminase cofactor ...
myelin integrity
What does a deficiency in vitamin B6 cause? neuropathy
What is the name of vitamin B9? folate
What does vitamin B9 do? cofactor for HMT and MMM
What does a deficiency in vitamin B9 cause?
magloblastic anemia ...
hypersegmented neutrophils ...
neural tube defects
What is the name of vitamin B12? cyanocobalamin
What does a deficiency in vitamin B12 cause?
megaloblastic anemia ...
hypersegmented neutrophils ...
neuropathy
What does vitamin C do? collagen synthesis - proline and lysine hydroxylation
What does a deficiency in vitamin C cause? scurvy
What does vitamin D do? mineralization of bones and teeth
What does a deficiency in vitamin D cause?
rickets (children) ...
osteomalacia (adults)
What does a deficiency in vitamin E cause? increased free radical damage
What does vitamin K do? clotting
What does a deficiency in vitamin K cause?
loss of gamma-carboxylation ...
bleeding
What does biotin do? carboxylation
What does a deficiency in biotin cause? loss of carboxylase function
What does calcium do?
neuronal function ...
atrial depolarization ...
smooth muscle contractility
What does a deficiency in calcium cause? poor bone and teeth development
What does copper do? collagen synthesis
What does a deficiency in copper cause? Minky Kinky Hair Syndrome
What does iron do?
Hb function ...
electron transport
What does a deficiency in iron cause? anemia
What is bronze pigmentation? Fe deposit in skin
What is bronze cirrhosis? Fe deposit in liver
What is bronze diabetes? Fe deposit in pancreas
What is hemosiderosis? Fe overload in bone marrow
What does magnesium do? PTH and kinase cofactor
What does a deficiency in magnesium cause?
loss of kinase function ...
hypoparathyroidism
What does zinc do?
taste buds ...
hair ...
sperm function
What does a deficiency in zinc cause?
dysgeusia ...
anosmia ...
poor wound healing
What does cromium do? insulin function
What does a deficiency in cromium cause? diabetes
What does molybdenum do? purine breakdown (xanthine oxidase)
What does a deficiency in molybdenum cause? loss of xanthine oxidase function
What does manganese do? glycolysis
What does a deficiency in manganese cause? loss of xanthine oxidase function
What does selenium do? heart function ... dilated cardiomyopathy
What does a deficiency in selenium cause? dilated cardiomyopathy
What does tin do? hair
What is the difference between carotid body and carotid
sinus?
carotid body - chemoreceptor ...
carotid sinus - baroreceptor
What color is air on xray? black (radiolucent)
What color is fluid/solid on xray? white (radiopaque)
What disease has a steeple sign on neck film? croup
What disease has a thumb sign on neck film? epiglottitis
What is a "blue bloater"? bronchitis
What is a "pink puffer?" emphysema
What are the PE syndromes?
Pulmonary nfiltrates with Eosinophilia ...
Churg-Straus ...
Loeffler's ...
allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis ...
strongyloides
What drugs cause pulmonary eosinophilia?
nitrofurantoin ...
sulfonamides
What are the risk factors for lung cancer?
smoking ...
radon ...
second hand smoke ...
pneumonconiosis (except anthracosis)
What diseases have hemoptysis?
bronchiectasis ...
bronchitis ...
pneumonia ...
TB ...
lung cancer ...
Goodpasture's ...
Wegner's
Where is a Bochdalek hernia? dorsal diaphragm
Where is a Morgagni hernia? anterior/middle diaphragm
What diseases have respiratory alkalosis?
restrictive lung disease ...
anxiety ...
pregnancy ...
gram negative sepsis ...
PE
What diseases have respiratory acidosis? obstructive lung disease
What diseases have metabolic alkalosis?
low volume state ...
vomiting ...
diuretics ...
G blood loss
What diseases have metabolic acidosis?
diarrhea ...
RTA ...
acid production (MUDPLES) ...
M: methanol, metformin ...
U: uremia ...
D: DKA ...
P: paraldehyde, phenformin ...
: iron, NH ...
L: lactate ...
E: ethylene glycol ...
S: salicylates, shock, sepsis, starvation
What does a stridor tell you? extrathoracic narrowing (narrows when breathing in)
What does wheezing tell you? intrathoracic narrowing (narrows when breathing out)
What do rhonchi tell you?
mucus in the airway ...
obstructive lung disease
What does grunting tell you?
blowing open collapsed alveoli ...
restrictive lung disease
What does dull percussion tell you?
something (fluid or solid) between airspace and chest
wall absorbing sound
What does hyperresonance tell you? air in lungs or lung space
What does tracheal deviation tell you? away from pneumothorax or toward atelectasis
What does fremitus, egophony, and bronchophony tell
you?
consolidation ... pathognomonic for pneumonia
What is restrictive lung disease?
small stiff lungs ...
trouble breathing in
What are the blood gasses in restrictive lung disease?
low pCO2 ...
low pO2 ...
high pH
What is obstructive lung disease?
big mucus-filled lungs ...
trouble breathing out
What are the blood gasses in obstructive lung disease?
high or nml O2 early ...
high pCO2 ...
low pH
What are clues for epiglottitis?
thumb sign on x-ray ...
drooling
What are clues for croup?
steeple sign on x-ray ...
barking cough
What are clues for tracheitis?
look toxic ...
grey pseudomembrane ...
leukocytosis
What are clues for asthma?
wheeze on expiration ...
gE ...
eosinophils
What is an indication for intubation in an asthma? normalized CO2 (indicates pt is getting tired)
What is bronchiolitis? asthma in children < 2 yo
What are clues for sinusitis? teeth pain (worse with bending forward)
What are clues for bronchiectasis?
bad breath ...
purulent sputum ...
hemoptysis
What are clues for bronchitis?
lots of sputum ...
"blue bloater"
What are clues for emphysema?
restrictive to obstructive pattern ...
"pink puffer"
What is laryngomalacia? epiglottis rolling from side to side
What is pneumonia? consolidation of the airway
What are clues for pneumothorax? decreased breath sounds on one side
What are clues for a pulmonary embolus?
tachypnea ...
increased V/Q
What are clues for cardiac tamponade?
decreased breath sounds ...
decreased BP ...
increased JVD
What is tracheomalacia?
soft cartilage ...
stridor since birth
What are clues for cystic fibrosis?
meconium ileus ...
steatorrhea ...
bronchiectasis
What is aspergillosis?
allergy to mold (basement, dead plants, hay, compost
piles)
Who gets asbestosis?
shipyard workers ...
pipe fitters ...
brake mechanics ...
insulation installers
Who gets silicosis?
sandblasters ...
glassblowers
Who gets byssinosis?
cotton workers ...
chest tightness
Who gets berylliosis? radio/TV welders
Who gets anthracosis?
coal workers ...
massive fibrosis
What are clues for sarcoidosis?
non-caseating granulomas ...
eggshell calcifications of lymph nodes ...
bilateral hilar lymph nodes
What id carcinoid syndrome?
flushing ...
wheezing ...
diarrhea
What is small cell carcinoma?
at carina ...
malignant ...
SVC syndrome ...
Cushing's (ACTH, 90%), SADH (5%), PTH (3%), TSH
(2%)
What is large cell carcinoma? large stuff
What is squamous cell carcinoma?
smoker ...
high PTH (PTHrP) ...
increased calcium
What is bronchoalveolar carcinoma?
looks like pneumonia ...
due to pneumoconiosis ...
not associated with smoking
What is a Pancoast tumor?
apical lung tumor ...
Horner's syndrome ...
arm weakness/parasthesias ...
horseness
What are the 6 low complement nephritic syndromes?
SBE ...
SLE ...
serum sickness ...
cryoglobulinemia ...
PSGN ...
MPGN
What are the hormones with disulfide bonds?
"PG" ...
prolactin ...
inhibin ...
GH ...
insulin
What do you see psammoma bodies in?
meningioma ...
mesothelioma ...
papillary carcinoma of thyroid ...
serous cystadenoma of the ovary
What are the Jones criteria for Acute Rhematic Fever?
J: joints ....
O: carditis ...
N: subcutaneous nodules ...
E: erythema marginatum ...
S: sydenham chorea
What are the gA nephropathies?
HSP (Henoch Schlonein Purpura) ...
Berger's ...
Allport's
What causes renal induced acidosis?
plasma RTA ...
metabolic acidosis ...
glutaminase ...
ammonia production in CD (10% of urea cycle)
What hormones are produced by small cell lung
carcinoma?
ACTH ...
ADH ...
PTH ...
TSH ...
ANP
What are the 5 causes of SADH?
small cell carcinoma ...
increased intracranial pressure ...
drugs ...
hypoxia
What are the low volume states with acidosis? diarrhea and RTA
What are the types of kidney stones?
calcium oxalate (80%) ...
struvite ...
uric acid ...
cysteine
What are the clues for pseudogout?
positively birefringent rhomboid crystals ...
calcium pyrophosphate ...
elderly pts ...
men = women
What are the bladder cancer risk factors?
smoking ...
aniline dyes ...
aflotoxin ...
benzenes ...
cyclophosphamide ...
Von Hippel Lindau ...
Tuberous Sclerosis ...
Schistosoma haematobium
What are the causes of papillary necrosis? ADS and vasculitides
What are the 3 narrowings of the ureter?
pelvic brim ...
hilum ...
entrance to the bladder
What is nephritic syndrome?
hematuria ...
protein loss < 3.5 g/dL ...
hypertension ...
RBC casts ...
increased size of fenestrations leading to vasculitis
What is nephrotic syndrome?
protein loss > 3.5 g/dL ...
edema ...
hyperlipidemia (VLDL) ...
hypercoagulable (2,7,9,10,C,S) ...
decreased serum albumin ...
increased urine albumin ...
loss of basement membrane charge due to deposition on
heparin sulfate leading to massive proteinuria and
lipiduria
What are the most common causes of UTs?
#1 E. coli ...
#2 Proteus ...
#3 Klebsiella
What is the most frequent cause of UT in females 5-10
yrs and 18-24 yrs?
Staph saprophyticus
What is pre-renal failure?
(emulates low volume state) ...
BUN:Cr > 20:1 ...
low flow to kidneys ...
high Na in urine ...
high FeNa ...
concentrated urine
What is intra-renal failure?
BUN:Cr 10-15 ...
damaged glomerulus ...
low Na in urine ...
low FeNa ...
dilute urine
What is the vasculitic pattern for renal artery stenosis? clot in front of renal artery
What is glomerulonephritis? inflamed glomeruli
What is the vasculitic pattern for interstitial nephritis? clot off the medulla
What is the vasculitic pattern for focal segmental
glomerulonephritis?
clot off part of the nephron
What do you see in rapidly progressive
glomerulonephritis?
crescents
What is the MC nephritic disease in adults? membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN)
What is the MC renal disease in blacks/hispanics? FSGN
What is the MC renal disease in HV/V drug users? FSGN
What is the MC renal mass? cyst
What is the MC malignant renal tumor in adults? adrenocarcinoma
What is the MC malignant renal tumor in kids? Wilm's tumor
What is the MCC of RPGN? Goodpastures
What is the MC nephrotic syndrome in kids? minimal change disease
What is associated with oxalate stones in a 3 yo white
female?
cystic fibrosis
What is associated with oxalate stones in a 5 yo black
female?
celiac spru
What is associated with oxalate stones in an adult
females?
Whipple's disease
What is associated with oxalate stones in adults? Chron's disease
What is seen in Type Renal Tubular Acidosis?
metabolic acidosis ...
distal collecting duct H/K exchange defective ...
hypokalemia ...
high urine pH ...
frequent UTs ...
stones
What is seen in Type Renal Tubular Acidosis?
no carbonic anhydrase in PCT ...
hypokalemia ...
high urine pH early but low late (b/c use up bicarb) ...
multiple myeloma
What is seen in Type Renal Tubular Acidosis?
hyporenin-hypoaldosteronism ...
infacted JG apparatus so no aldosterone ...
hyperkalemia ...
diabetics ...
NSADs, ACE-, Heparin
Which part of of the nephron concentrates urine? medulla
What is Goldblatt's kidney? contralateral flea-bitten kidney
What is uremia? azotemia + symptoms
What is azotemia? renal failure (increased BUN/Cr)
What is seen in post-strep glomerulonephritis?
subepithelial humps ...
gG/C3/C4 deposition ...
ASO Ab
What is seen in interstitial nephritis? urine eosinophils (drugs), toxins
What is seen in lupus nephritis?
glomerular destruction ...
subepithlial immune complex deposition ...
anti-ds-DNA
What is seen in mebranoglomerulonephritis? deposition
What is membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis? tram tracking (type has low C3)
What is seen in minimal change disease?
kids ...
fused foot processes ...
no renal failure ...
loss of charge barrier
What is the most common cause of kidney stones? dehydration
What type of kidney stones have coffin-lid crystals? triple phosphate
What type of kidney stones have rosette crystals? uric acid
What type of kidney stones have hexagonal crystals? cysteine
What type of kidney stones envelope or dumbbell-shaped
crystals?
calcium oxalate
What disease has aniridia? Wilm's tumor
What is phimosis? foreskin scarred to head of penis
What is paraphimosis?
foreskin retracted and scarred to base of penis ...
risk of strangulation
What is urge incontinence?
overactive detrusor muscle ...
small bladder volume
What is stress incontinence?
weak UG diaphragm muscles ...
estrogen connection
What is overflow incontinence? cannot fully empty
What structures have one way valves? urethra and ejaculatory duct
What has WBC casts? nephritis
What has WBC casts only? pylonephritis
What has WBC casts + eosinophils? interstitial nephritis (allergies)
What has WBC casts + RBC casts? glomerulonephritis
What has fat casts? nephrotic syndrome
What has waxy casts? chronic renal disease
What has tubular casts? RTA
What has muddy brown casts? RTA
What has hyaline casts? normal
What has epithelial cells? normal
What has crescents? RPGN
How do you measure afferent renal function? creatinine or inulin
How do you measure efferent renal function? BUN or PAH
What is the afferent arteriole's job? filter
What is the efferent arteriole's job? secrete
How do you test afferent renal function? GFR or inulin
How do you test efferent renal function? RPF or PAH
What is post-renal failure? obstruction
What is the job of the proximal convoluted tubule? reabsorb 60-80% of everything filtered
What is the job of the thick descending limb? reabsorb water
What is the job of the thick ascending limb?
make concentration gradient by reabsorbing solutes (Na,
K, Cl, Mg, Ca) without water
What is the job of the early distal tubule? concentrate urine by reabsorbing NaCl (hypotonic)
What is the job of the late distal tubule and collecting
duct?
concentrate urine by reabsorbing water ...
excretion of uric acid ...
make new bicarb
What does the macula densa do? measures osmolarity
What does the JG apparatus do? measures volume
What is Fanconi's syndrome?
old tetracycline use destroys PCT ...
phosphates, glucose, and amino acids in the urine
What is Bartter's syndrome?
baby with defective triple transporter ...
decreased Na, Cl, and K ...
normal BP
What is psychogenic polydipsia? dilute urine due to excess water intake
What is central pontine myelinosis? due to correcting Na faster than 0.5 mEq/hr
What is the central nervous system?
brain and spinal cord ...
oligodendrocytes
What is the peripheral nervous system?
everything but the brain and spinal cord ...
Schwann cells
What is the autonomic nervous system? automatic stuff
What is the somatic nervous system? moving your muscles
What is the parasympathetic system?
rest and digest ...
slows stuff down
How does the parasympathetic system behave?
DUMBBELS ...
D: diarrhea ...
U: urination ...
M: myosis ...
B: bradycardia ...
B: bronchoconstriction ...
E: erection ("point") ...
L: lacrimation ...
S: salivation
What is the sympathetic system?
fight or flight ...
speeds stuff up
How does the sympathetic system behave?
opposite of parasympathetic (opposite of DUMBBELS) ...
D: constipation ...
U: urinary retention ...
M: mydriasis ...
B: tachycardia ...
B: bronchodilation ...
E: ejaculation ("shoot") ...
L: xerophthalmia (dry eyes) ...
S: xerophstomia (dry mouth)
What is Cushing's triad?
hypertension ...
bradycardia ...
irregular breathing
What is Budd-Chiari? hepatic vein obstruction
What is Arnold-Chiari? foramen magnum obstruction
What is anencephaly?
notochord didn't make contact with the brain ...
only have medulla
What is an encephalocele? brain tissue herniation
What is a Dandy Walker malformation?
no cerebellum ...
distended 4th and lateral ventricles
What is an Arnold-Chiari malformation?
herniation of cerebellum through foramen magnum ...
Type : cerebellar tonsils (asx) ...
Type : cerebellar vermis/medulla => hydrocephalus and
syringomyelia (loss of pain/temp)
What is spina bifida occulta? covered by skin with tuft of hair
What is spina bifida aperta? has opening (high AFP)
What is a meningocele? sacral pocket with meninges in it
What is a meningomyelocele? sacral pocket with meninges and nerves in it
What is open-angle glaucoma?
overproduction of fluid ...
painless ipsilateral dilated pupil ...
gradual tunnel vision ...
optic disc cupping
What is closed-angle glaucoma?
obstruction of the canal of Schlemm ...
sudden onset ...
pain ...
emergency
What are the watershed areas? hippocampus and splenic flexure
What bug loves the frontal lobe? rubella
What bug loves the temporal lobe? HSV
What bug loves the parietal lobe? toxoplasma
What bug loves the hippocampus? rabies
What bug loves the posterior fossa? TB
What but loves the DCML tract? treponema
How do migraines present?
aura ...
photophobia ...
numbness and tingling ...
throbbing headache ...
nasea
How do tension headaches present?
"band-like" pain starts in posterior neck ...
worse as day progresses ...
sleep disturbances
How do cluster headaches present?
rhinorrhea ...
unilateral orbital pain ...
suicidal ...
facial flushing ...
worse when lying down
How does temporal arteritis present?
pain with chewing ...
blind in one eye (emergency)
How does trigeminal neuralgia present? sharp, shooting face pain
What are the 2 kinds of partial seizures?
simple (aware) ...
complex (unaware)
What are the 3 kinds of generalized seizures?
tonic-clonic ...
absence ...
status epilepticus
How does an epidural hematoma present?
intermittent consciousness ...
"lucid intervals"
How does a subdural hematoma present?
headache 4 wks after trauma ..
elderly
How does a subarachnoid hemorrhage present?
"worse headache of my life" ...
hx of berry aneurysm
What is an astrocytoma?
rosenthal fibers ...
#1 in kids with occipital headaches
What is an ependymoma?
rosettes ...
in 4th ventricle ...
hydrocephalus
What is a craniopharyngioma?
"motor oil biopsy" ...
tooth enamel ...
Rathke's pouch ...
ADH problem ...
bitemporal hemianopsia
What is glioblastoma multiforme?
pseudopalisading ...
necrosis ...
worst prognosis ...
intralesional hemorrhage
What is a hemangioblastoma?
cerebellum ...
Von-Hippel-Lindau
What is a medullablastoma?
pseudorosettes ...
compresses brain ...
early morning vomiting
What is a meningioma?
parasagittal ...
psammoma bodies ...
whorling pattern ...
best prognosis
What are the most common places to metastasize to the
brain?
see at gray-white junction ...
lung ...
breast ...
skin
What is an oligodendroglioma?
fried-egg appearance ...
nodular calcification
What is a pinealoma?
loss of upward gaze ...
loss of circadian rhythms ...
percocious puberty
What is a Schwannoma?
CN8 tumor ...
unilateral deafness
What is neurofibromatosis?
cafe au lait spots ...
peripheral nerve tumors ...
axillary freckles ...
Type : Von Recklinghausen's - peripheral - chr 17 - optic
glioma - Lisch nodules - scoliosis ...
Type : acoustic neuroma - central - chr 22 - cataracts -
bilateral deafness
What is Sturg-Weber?
port wine stain on forehead ...
angioma of retina
What is Tuberous Sclerosis?
ashen leaf spots ...
primary brain tumors ...
rhabdomyolysis of heart ...
renal cell carcinoma ...
shagreen spots (leathery)
What is Lewy body dementia?
stiff ...
visual hallucinations
What is normal pressure hydrocephalus?
incontinence ...
ataxia - "magnetic gait" ...
dementia
What is Korsakoff psychosis? alcoholic thiamine deficiency
What is vascular "multi-infarct" dementia?
sudden onset ...
uneven progression of deficits ...
"stair-step" decline
What is Huntington's?
in caudate/putamen ...
triplet repeat disorder ....
choreiform movements ...
change in personality
What is Creutzfeldt-Jacob?
prion induced ...
die within 1 year ...
post-cornea transplant
What is Pick's disease?
frontal lobe atrophy ...
disinhibition
What is Alzheimer's?
dec Ach in nucleus basalis of Meynert ...
bad ApoE ...
amyloid plaques ...
tangles of tau
What is Parkinson's?
in substantia nigra ...
bradykinesia ...
pill-rolling tremor ...
shuffling gait ...
Lewy bodies
How is depression diagnosed?
need 5 SGECAPS >2 wks ...
S: sleep disturbances (wake in AM) ...
: interest/libido loss ...
G: guilt ...
E: energy loss ...
C: concentration loss ...
A: appetite loss ...
P: psychomotor agitation ...
S: suicidal (hopelessness)
What is autism?
repetitive movements ...
lack of verbal skills and bonding ...
sx since birth
What is Asperger's?
good communication ...
impaired relationships ...
no mental retardation
What is Rett's?
only in girls ...
dec head growth ...
lose motor skills ...
hang-wringing ...
normal until 5 mo
What is childhood disintegrative disorder? kid stops walking and talking
What is selective mutism? kid talks sometimes
What is separation anxiety disorder? kid screams when mom leaves
What is conduct disorder?
<15 yo ...
aggressive ...
disregard for rules ...
no sense of guilt ...
harm animals ...
illegal activity
What is oppositional defiant disorder?
defiant ...
noncompliant ...
directed at authority
What is attention deficit hyperactivity disorder?
overactivity ...
difficulty in school
What is dysthymia? low lever sadness >2 yrs
What is cyclothymia? dysthymia with hypomania
What is double depression? depression followed by dysthymia
What is bipolar ? depression and mania (psychosis)
What is bipolar ? depression and hypomania (no psychosis)
What are loose associations?
ideas switch subjects ...
incoherent
What is tangentiality? wanders off the point
What is circumstantiality? digresses, but finally gets back to the point
What is clanging? words that sound alike
What is word salad? unrelated combinations of words
What is perseveration? keeps repeating the same words
What is neologisms? new words
What is delusion? false belief
What is illusion? misinterprets stimulus
What is hallucination?
false sensory perception ...
EtOH withdrawal ...
cocain intoxication => formication
What is nihilism? thinks the world has stopped
What is loss of ego boundaries? not knowing where end and you begin
What are ideas of reference? believes the media is monitoring you
What is thought blocking? stops mid-sentence
What is thought broadcasting? believes everyone can read his thoughts
What is thought insertion? believes others are putting thoughts into his head
What is thought withdrawal? believes that others are taking thoughts out of his head
What is concrete thinking? can't interpret abstract proverbs, just sees the facts
What is synesthesia? smells colors
What is cataplexy? loss of muscle tone due to strong emotions
What is paranoid personality disorder?
suspicious about everything ...
use projection
What is schizotypal personality disorder?
"magical thinking" ...
bizarre behavior
What is antisocial personality disorder?
lie ...
steal ...
cheat ...
destroy property ...
impulsive without remorse ...
illegal activity
What is histrionic personality disorder?
theatrical ...
sexually provocative ...
use repression
What is borderline personality disorder?
"perpetual teenager" ...
splitting (love/hate) ...
projection ...
acting out ...
self-mutilation
What is narcissistic personality disorder?
pompous ...
no empathy
What is dependent personality disorder?
clingy ...
submissive ...
low self-confidence ...
regression
What is obsessive compulsive personality disorder?
perfectionist ...
doesn't show feelings ...
detail-oriented ...
uses isolation
What is avoidant personality disorder?
socially withdrawn ...
afraid of rejection but wants to fit in
What is kleptomania? steals for the fun of it
What is pyromania? starts fires
What is intermittent explosive disorder? loses self-control without adequate reason
What is pathological gambling?
can't stop gambling ...
affects others
What is trichotillomania? pull out their hair
What is Lewy body dementia?
stiff ...
visual hallucinations
What is normal pressure hydrocephalus?
incontinence ...
ataxia - "magnetic gait" ...
dementia
What is Korsakoff psychosis? alcoholic thiamine deficiency
What is vascular "multi-infarct" dementia?
sudden onset ...
uneven progression of deficits ...
"stair-step" decline
What is Huntington's?
in caudate/putamen ...
triplet repeat disorder ....
choreiform movements ...
change in personality
What is Creutzfeldt-Jacob?
prion induced ...
die within 1 year ...
post-cornea transplant
What is Pick's disease?
frontal lobe atrophy ...
disinhibition
What is Alzheimer's?
dec Ach in nucleus basalis of Meynert ...
bad ApoE ...
amyloid plaques ...
tangles of tau
What is Parkinson's?
in substantia nigra ...
bradykinesia ...
pill-rolling tremor ...
shuffling gait ...
Lewy bodies
What is somatization?
think they have different illness all the time (at least 4
organ systems)
What is hypochondriasis? think they have the same illness all the time
What is body dysmorphic disorder? imagined physical defect
What is pain disorder? prolonged pain not explained by physical causes
What is conversion?
neuro manifestation of internal conflict ...
indifferent to disability
What is malingering?
fake illness for monetary gain ...
avoids medical treatment
What is factitious?
fake illness to get attention ....
seeks medical treatment
What is Munchausen?
need to be the caregiver ...
mom fakes child's illness to get attention
What is Munchausen by proxy?
mom makes child ill for gain ...
move a lot
What is amnesia? can't recall important facts
What is dissociative fugue?
no past ...
travel to new place ...
usually due to trauma
What is multiple personality disorder?
have 5-10 alters ...
usually associated with incest
what is depersonalization disorder?
"out of body" experiences ...
deja vu
What is sublimation? substitute acceptable for unacceptable (boxer vs fighting)
What is imitation? dress like someone else
What is identification? act like someone else
What is displacement? take anger out on someone else
What is idealization? wait for "ideal spouse" while they are beating you up
What is transference? patient views doctor as parent
What is countertransference? doctor views patient as child
What is acting out?
expression of impulse ...
"tantrums"
What is regression? immature behavior
What is intellectualization? makes excuses for all situations
What is isolation of affect? isolate feeling to keep on functioning
What is supression? consciously block memory
What is repression? subconsciously block memory
What is reaction formation?
unconsciously act opposite to how you feel (tears of a
clown)
What is undoing?
doing exact opposite of what you used to do to fix a
wrong
What is compensation? doing something different from what you used to do
What is sadism? gives pain
What is masochism? receives pain
What is exhibitionism? exposure to others
What is voyerism? watching other people without their permission
What is telephone scatalogia? phone sex
What is frotteurism? rub penis against fully clothed woman
What is transvestite?
dress up as opposite sex ...
no identity crisis
What is transsexual?
gender identity crisis ...
"man trapped in a woman's body"
What is a fetish? objects (vibrators, dildos, shoes)
What is a pedophile? children (watching child pornography)
What is a necrophile? corpses
What is a beastophile? animals
Can you die during EtOH withdrawal? yes
Can you die during opoid withdrawal? no, just very painful
What is a neutrophil?
phagocyte ...
has anti-microbials ...
most abundant
What is an eosinophil?
parasite destroyer ...
allergy inducer
What is a basophil?
allergy helper ...
gE receptor => histamine release
What is a monocyte?
destroyer => macrophages ...
hydrolytic enzymes ...
coffee-bean nucleus
What is a lymphocyte? warrior => T, B, NK cells
What is a platelet?
clotter ...
no nuclei ...
smallest cell
What is a blast? baby hematopoietic cell
What is a band? baby neutrophil
What do high WBC and high PMNs tell you? stress demargination
What do high WBC and < 5% blasts tell you?
leukamoid reaction ...
seen in burn pts ...
extreme demargination, looks like leukemia
What do high WBC and > 5% blasts tell you? leukemia
What do high WBC and bands tell you? left shift => infection
What do high WBC and B cells tell you? bacterial infection
What diseases have high eosinophils?
"NAACP" ...
N: Neoplasm (lymphoma) ...
A: Allergy/Asthma ...
A: Addison's Disease (no cortisol => relative eosinophilia)
...
C: Collagen Vascular Disease ...
P: Parasites
What diseases have high monocytes (>15%)?
"STELS" ...
S: Syphilis (chancre, rash, warts) ...
T: TB (hemoptysis, night sweats) ...
E: EBV (teenager sick for a month) ...
L: Listeria (sick baby) ...
S: Salmonella (food poisoning)
What do high retics (>1%) tell you? RBC being destroyed peripherally
What do low retics tell you?
bone marrow not working right ...
low production
What is a poikilocytosis? different shapes
What is anisocytosis? different sizes
What is the RBC lifespan? 120
What does --penia tell you?
low levels ...
usually due to virus or drugs
What does --cytosis tell you? high levels
What does --cythemia tell you? high levels
What is the difference between plasma and serum?
Plasma: no RBC ...
Serum: no RBC or fibrinogen
What is Chronic Granulomatous Disease?
NADPH Oxidase deficiency ...
recurrent Staph/Aspergillus infections ...
Nitroblue Tetrazolium stain negative
What does MPO deficiency cause? catalase + infections
What is Chediak Higashi?
lazy lysosome syndrome ...
lysosomes are slow to fuse around bacteria
What organ can make RBCs if the long bones are
damaged?
spleen
What causes a shift to the right in the Hb curve?
"all CADETs face right" ...
C: increased CO2 ...
A: Acid/Altitude ...
D: 2,3-DPG ...
E: Exercise ...
T: Temp
How does CO poison Hb?
competitive inhibitor of O2 on Hb ...
cherry-red lips ...
pinkish skin hue
How does cyanide poison Hb?
non-competitive inhibitor of O2 on Hb ...
almond breath
What is MetHb? Hb with Fe3+
What is Acute ntermittent Porphyria?
increased porphyrin ...
urine delta-ALA ...
porphobilinogen ...
abdominal pain ...
neuropathy ...
red urine
What is Porphyria Cutanea Tarda?
sunlight causes skin blisters with porphyrin deposits ...
woods lamp = orange-pink
What is Erythrocytic Protoporphyria? porphyria cutanea tarda in a baby
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
homozygous HbS ...
beta chain Glu6 => Val substitution...
vaso-occlusion ...
necrosis ...
dactylitis (painful fingers/toes) at 6 mo ...
protects against malaria ...
crew haircut x-ray ...
avascular necrosis of femur ...
short fingers
What is HbC Disease?
beta chain Glu6 => Lys substitution ...
still charged so no sickling
What is alpha-thalassemia?
1 deletion: normal ...
2 deletions: "trait" - microcytic anemia ...
3 deletions: hemolytic anemia, HbH = 4-betas ...
4 deletions: hydrops fetalis, HbBart = 4-gammas ...
African Americans and Asians ...
Chromosome 16 deletion
What is beta-thalassema?
1 deletion: "beta minor" - increased HbA2 and HbF
2 deletions: "trait/intermedia/major" - only HbA2 and HbF
=> hypoxia at 6 mo ...
Mediterraneans ...
Chromosome 11 point mutation
What is Cooley's anemia?
seen with beta thalassemia major ...
no HbA => excess RBC production ...
baby making blood from everywhere ...
frontal bossing ...
hepatosplenomegaly ...
long extremities
What is Virchow's Triad?
thrombosis risk factors ...
1. turbulent blood flow - "slow" ...
2. hypercoagulable - "sticky" ...
3. vessel wall damage - "escapes"
What does acute hypoxia cause? shortness of breath
What does chronic hypoxia cause? clubbing of fingers and toes
What is intravascular hemolysis?
RBC destroyed in blood vessel ...
low haptoglobin (bind free floating Hb)
What is extravascular hemolysis?
RBC destroyed in spleen ...
problem with RBC membrane ...
splenomegaly
What enzymes need lead (Pb)? delta-ALA dehydrase and Ferrochelatase
What does EDTA bind? X2+ (divalent cations)
What disease has a smooth philthrum? fetal alcohol syndrome
What disease has a long philthrum? William's syndrome
What disease has sausage digits?
pseudo-hypoparathyrodism ...
psoriatic arthritis
What disease has 6 fingers? Trisomy 13 (Pateau's)
What disease has double-jointed thumbs? Diamond-Blackfan
What disease has painful fingers? sickle cell disease
What are the Microcytic Hypochromic anemias?
"FAST Lead" ...
F: Fe deficiency ...
A: Anemia of chronic disease ...
S: Sideroblastic anemia ...
T: Thalassemia (alpha and beta) ...
Lead: Pb poisoning
What are clues for Fe deficiency anemia?
increased TBC ...
menses ...
G bleed ...
koilonychia
What are clues for anemia of chronic disease? decreased TBC
What are clues for sideroblastic anemia?
decreased delta-ALA synthase ...
blood transfusions
What are clues for lead poisoning?
decreased delta-ALA synthase ...
decreased ferrochelatase ...
x-ray blue line ...
eating old paint chips
What are the Megaloblastic anemias?
vitamin B12 deficiency ...
folate deficiency ...
alcohol
What are clues for vitamin B12 deficiency?
tapeworms ...
vegans ...
type A gastritis ...
pernicious anemia
What are clues for folate deficiency?
old food ...
glossitis
What are clues for alcoholic megaloblastic anemia?
fetal alcohol syndrome ...
smooth philthrum ...
stuff doesn't grow
What are the ntravascular Hemolytic anemias?
gM ...
G6PD deficiency ...
cold autoimmune
What are clues for G6PD deficiency?
sulfa drugs ...
moth balls ...
fava beans ...
sudden drop in Hb
What are clues for cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia?
mononucleosis ...
mycoplasma infections ...
RBC agglutination
What are the Extravascular Hemolytic anemias?
gG ...
spherocytosis ...
warm autoimmune ...
paroxysmal cold autoimmune ...
sickle cell anemia
What are clues for spherocytosis?
defective shperin or ankyrin ...
positive osmotic fragility test
What are clues for warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia?
anti-Rh Ab ...
dapsone ...
PTU ...
anti-malarials ...
sulfa drugs
What are clues for paroxysmal cold autoimmune
hemolytic anemia?
bleeds after cold exposure ...
Donath-Landsteiner Ab
What are the Production anemias?
Diamond-Blackfan ...
aplastic anemia
What are clues for Diamond-Blackfan?
No RBCs ...
double-jointed thumbs
What are clues for aplastic anemia?
pancytopenia ...
autoimmune ...
benzene ...
AZT ...
CAM ...
radiation
What is basophilic stippling?
lots of immature cells ...
increased mRNA ...
lead poisoning
What is a bite cell (basket cell)?
unstable Hb inclusions ...
GDPD deficiency
What is a burr cell (echinocyte)?
pyruvate kinase deficiency ...
liver disease ...
post-splenectomy
What is Cabot's ring body?
vitamin B12 deficiency ...
lead poisoning
What is a Doehle body?
PMN leukocytosis ...
infection ...
steroids ...
tumor
What is a drepanocyte? sickle cell anemia
What is a helmet cell?
fragmented RBC ...
hemolysis (DC, HUS, TTP)
What is a Heinz body?
Hb precipitates and sticks to cell membranes ...
G6PD deficiency
What is a Howell-Jolly body?
spleen or bone marrow should have removed nuclei
fragments ...
hemolytic anemia ...
spleen trauma ...
cancer
What is a Pappenheimer body?
Fe precipitate inside cell ...
sideroblastic anemia
What is a pencil cell (cigar cell)? Fe deficiency anemia
What is a Rouleaux formation? multiple myeloma
What is a schistocyte?
broken RBC ...
DC ...
artificial heart valves
What is a sideroblast?
macrophages pregnant with Fe ...
genetic or multiple transfusions
What is a spherocyte? old RBC
What is a spur cell (acanthocyte)? lipid bilayer disease
What is a stomatocyte? liver disease
What is a target cell (codocyte)?
less Hb ...
thalassemias ...
Fe deficiency
What is a tear drop cell (dacrocyte)
RBCs squeezed out of marrow ...
hemolytic anemia ...
bone marrow cancer
What is the clotting cascade? how you stop bleeding
What do platelet problems cause? bleeding from skin and mucosa
What do clotting problems cause? bleeding into cavities
What causes increased PTT and bleeding time?
Von Willebrand disease ...
SLE
What is Bernard-Soulier?
baby with bleeding from skin and mucosa ...
big platelets ...
low GP1b
What is Glanzmann's?
baby with bleeding from skin and mucosa ...
low GP2b3a
How does Factor 13 deficiency present? umbilical stump bleeding
What is Factor V Leiden? protein C can't break down Factor 5 => more clots
How does von Willebrand disease present? heavy menstrual bleeding
What are the types of VWD?
Type 1 (AD): decreased VWF production ...
Type 2 (AD): decreased VWF activity (+ Ristocetin
aggregation test)
Type 3 (AR): no VWF
What is hemophilia A?
defective Factor 8 (< 40% activity) ...
bleed into cavities (head, abdomen, etc.)
What is hemophilia B?
Factor 9 deficiency ...
bleed into joints (knee, etc.)
What diseases have low LAP? CML and PNH
What diseases have high LAP? leukamoid reaction
What is the difference between acute and chronic
leukemias?
Acute: started in bone marrow, squeezes RBCs out of
marrow ...
Chronic: started in periphery, not constrained and will
expand
What is the difference between myeloid and lymphoid
leukemias?
Myeloid: increased RBC, WBC, platelets, macrophages
(decreased lymphoid cells) => do a bone marrow biopsy
...
Lymphoid: increased NK, T, B cells (decreased myeloid
cells) => do a lymph node biopsy
What defines ALL?
< 15 yo male ...
bone pain ...
positive PAS stain ...
positive TdT
What defines AML?
15-30 yo males ...
Sudan stain ...
Auer rods
What defines CML?
30-50 yo females ...
t(9,22) - "Philadelphia chromosome" ...
bcr-abl ...
decreased LAP
What defines CLL?
> 50 yo males with lymphadenopathy ...
"soccer ball" nuclei ...
smudge cells
What defines Hodgkin's lymphoma?
EBV ...
may have Reed-Sternberg cells
What are the B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas?
Follicular: t(14,18), bcl-2 ...
Burkitt: t(8,14), c-myc, starry sky macrophages (American
kids present with abdominal mass and African kids
present with jaw mass)
What are the T cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas?
Mycosis Fungoides: total body rash ...
Sezary Syndrome: cerebreform cells
What is polycythemia rubra vera?
Hct > 60% ...
decreased Epo ...
Budd-Chiari ...
"pruritis after bathing"
What is essential thrombocythemia?
very high platelets ...
stainable Fe ...
decreased c-mpl
What is myelofibrosis?
megakaryoctyes ...
fibrotic marrow ...
teardrop cells ...
extramedular hematopoiesis
What are plasma neoplasms? produce lots of Ab
What is Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia?
gM ...
hyperviscous
What is Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined
Significance?
old person with gamma spike
What is Multiple Myeloma?
serum M protein (gG) ...
urine Bence-Jones protein ...
rouleaux ...
punched out lesions
What is heavy chain disease? increased gA
What is Histocytosis X?
kid with ...
eczema ...
skull lesions ...
diabetes insipidus ...
exophthalmos
What does the Coombs test tell you? Ab involved
What does the direct Coombs test tell you? on surface (hemolytic anemias)
What does the indirect Coombs test tell you? in serum
What is type and cross?
you know you can use that blood ... save it for specific
patient
What id type and match? type it and wait
What is forward typing? uses Ab to detect Ag ("Fabulous")
What is backward typing? uses Ag to detect Ab
What does blood type A tell you? have the A antigen
What does blood type O tell you?
have no antigens ...
universal donor
What does blood type AB tell you?
has both antigens ...
universal recipient
What does Rh + tell you? has D antigen
What does Rh - tell you? does not have D antigen
What is hemolytic disease of the newborn?
Rh - mom's placenta tears, 100 cc baby's blood sees
Mom and Mom produces Ab and attacks fetus
What is RHOGAM? anti-D gG
When do you give RHOGAM?
1st dose: 28 wk gestation (2nd child) ...
2nd dose: 72 hrs post-delivery (Rh + baby)
What is the most common transplant? blood
What is a syngenic transplant? twin to twin
What is an autograft? self to self transplant
What is an allograft? human to human transplant
What is a xenograft? 1 species to another species
What is hyperacute rejection? within 12 hrs (preformed Ab)
What is acute rejection? 4 days to years later (T-cells, macrophages)
What is chronic rejection? > 7 days (fibroblasts)
What are immunoprivileged sites?
brain ...
cornea ...
thymus ...
testes ...
(no lymphatic flow => no Ab => easy to transplant)
What is NR? measured PT ... used to control PT
What organs have the most common occurrence of
metastasis?
brain (grey-white junction) ...
bone (marrow) ...
lung ...
liver (portal vein, hepatic artery) ...
adrenal gland (renal arteries) ...
pericardium (coronary arteries)
What is Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia?
gM ...
hyperviscous
What is the most common posterior mediastinum tumor? neuro tumors
What is the most common middle mediastinum tumor? pericardial
What is the most common anterior mediastinum tumor? thymoma
What is the difference between myeloid and lymphoid
leukemias?
Myeloid: increased RBC, WBC, platelets, macrophages
(decreased lymphoid cells) => do a bone marrow biopsy
...
Lymphoid: increased NK, T, B cells (decreased myeloid
cells) => do a lymph node biopsy
What is the difference between acute and chronic
leukemias?
Acute: started in bone marrow, squeezes RBCs out of
marrow ...
Chronic: started in periphery, not constrained and will
expand
What is polycythemia rubra vera?
Hct > 60% ...
decreased Epo ...
Budd-Chiari ...
"pruritis after bathing"
What is neoplasm? new growth
What is myelofibrosis?
megakaryoctyes ...
fibrotic marrow ...
teardrop cells ...
extramedular hematopoiesis
What is Multiple Myeloma?
serum M protein (gG) ...
urine Bence-Jones protein ...
rouleaux ...
punched out lesions
What is Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined
Significance?
old person with gamma spike
What is metaplasia? change from one adult cell type to another
What is malignant?
not well circumscribed ...
fixed ...
no capsule ...
doesn't obey physiology ...
hurts by metastasis ...
rapidly growing ...
(outgrows blood supply => huts for blood => secretes
angiogenin and endostatin to inhibit blood supply of other
tumors)
What is hypertrophy? increased cell size
What is hyperplasia? increased cell number
What is Histocytosis X?
kid with ...
eczema ...
skull lesions ...
diabetes insipidus ...
exophthalmos
What is heavy chain disease? increased gA
What is essential thrombocythemia?
very high platelets ...
stainable Fe ...
decreased c-mpl
What is dysplasia ("carcinoma in situ")? lose contact inhibition (cells crawl on each other)
What is desmoplasia? cell wraps itself with dense fibrous tissue
What is benign?
well circumscribed ...
freely movable ...
maintains capsule ...
obeys physiology ...
hurts by compression ...
slow growing
What is atrophy? decreased organ or tissue size
What is anaplasia? regress to infantile state
What is a hamartoma? abnormal growth of tissue
What is a choristoma? normal tissue in the wrong place
What does rhabdomyo-- tell you? skeletal muscle
What does osteo-- tell you? bone
What does lipo-- tell you? fat
What does leiomyo-- tell you? smooth muscle
What does hemangio-- tell you? blood vessel
What does fibro-- tell you? fibrous tissue
What does cancer staging tell you? degree of dissemination of the tumor
What does cancer grading tell you? severity of microscopic changes
What does adeno-- tell you? glandular
What does --sarcoma tell you? connective tissue cancer
What does --oma tell you? tumor
What does --carcinoma tell you? cancer
What defines Hodgkin's lymphoma?
EBV ...
may have Reed-Sternberg cells
What defines CML?
30-50 yo females ...
t(9,22) - "Philadelphia chromosome" ...
bcr-abl ...
decreased LAP
What defines CLL?
> 50 yo males with lymphadenopathy ...
"soccer ball" nuclei ...
smudge cells
What defines AML?
15-30 yo males ...
Sudan stain ...
Auer rods
What defines ALL?
< 15 yo male ...
bone pain ...
positive PAS stain ...
positive TdT
What cancers have psammoma bodies?
"PSAMMoma" ...
P: Papillary (thyroid) ...
S: Serous (ovary) ...
A: Adenocarcinoma (ovary) ...
M: Meningioma ...
M: Mesothelioma
What cancer is uricaria (hives) associated with? any ... especially lymphoma
What cancer is seborrheic keratosis associated with? colon cancer
What cancer is related to HPV? cervical cancer
What cancer is related to HV? Kaposi's sarcoma
What cancer is related to HCV? liver carcinoma
What cancer is related to HBV? liver carcinoma
What cancer is related to EBV? lymphoma
What cancer is Paget's disease associated with? intraductal carciinoma
What cancer is erythema nodosum associated with? granulomatous (nonbacterial)
What cancer is dermatomyositis (heliotropic, malar)
associated with?
colon cancer
What cancer is actinic keratosis associated with? squamous cell carcinoma of skin
What cancer is acanthosis nigricans associated with?
visceral cancer ...
end organ damage
What are the T cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas?
Mycosis Fungoides: total body rash ...
Sezary Syndrome: cerebreform cells
What are the risk factors for primary liver cancer?
Hep B and C ...
aflatoxin ...
vinyl chloride ...
alcohol ...
carbon tetrachloride ...
anyline dyes ...
smoking ...
hemochromatosis ...
benzene ...
schistosomiasis
What are the fastest killing cancers?
pancreatic ...
esophageal
What are the esophageal/gastric cancer risk factors?
smoking ...
alcohol ...
nitrates ...
Japanese
What are the bladder cancer risk factors?
smoking ...
aniline dyes ...
benzene ...
aflatoxin ...
cyclophosphamide ...
Schistosoma haematobium ...
Von Hippel-Lindau ...
Tubular Sclerosis
What are the B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas?
Follicular: t(14,18), bcl-2 ...
Burkitt: t(8,14), c-myc, starry sky macrophages (American
kids present with abdominal mass and African kids
present with jaw mass)
What are plasma neoplasms? produce lots of Ab
tumor marker/oncogenes for breast cancer HER-, neu, Erb, BRCA- & , p53, CSF-1
t(9,22) CML (Philadelphia chromosome)
t(8,14) Burkitt's lymphoma
t(17,22) neurofibromatosis
t(15,17) Promyeloblastic Leukemia (AML M3 = PML)
t(14,18) follicular lymphoma
t(11:22) Ewing's Sarcoma
t(11,14) Mantle Cell Lymphoma
S-100 melanoma
ret medullary thyroid cancer ... MEN A & B/
Rb
retinoblastoma ...
Ewing's sarcoma
Ras colon
PSA prostate
p53 breast
neu breast
n-myc neuroblastoma => pseudorosettes
l-myc small cell carcinoma of the lung
k-ras
lung ...
colon
HLA DR5 pernicious anemia
HLA DR4 pemphigus vulgaris
HLA DR3 celiac sprue
HLA DR2
Goodpasture's ...
MS
HLA B5 Behcet's
HLA B27
psoriasis ...
ankylosing spondylitis ...
Reiter's
HLA B13 psoriasis without arthritis
HLA A3, A6 hemochromatosis
HER- breast
Erb breast
CSF-1 breast
CEA
colon ...
pancreas
CA-19 pancreatic
CA-125 ovarian
c-sis
osteosarcoma ...
glioma ...
fibrosarcoma
c-myc Burkitt's lymphoma
c-myb
colon ...
AML
c-abl
CML ...
ALL
BRCA- & breast
bombesin neuroblastoma
beta-HCG choriocarcinoma
bcl-2
follicular lymphoma ...
(can show in burkitt's, but pick follicular first)
AFP hepatocellular carcinoma
AFP
liver ...
yolk sac
5-HT carcinoid syndrome
What are 1st degree burns? red (epidermis)
What are 2nd degree burns? blisters (hypodermis)
What are 3rd degree burns? painless neuropathy (dermis)
What diseases have palm and sole rashes?
toxic shock syndrome ...
rocky mountain spotted fever ...
coxsacki A (hand-foot-mouth disease) ...
kawasaki ...
scarlet fever ...
staph scalded skin ...
syphilis
What is erythema multiforme? target lesions (viral, drugs)
What is Stevens Johnson syndrome? erythema multiforme major (mouth, eye, vagina)
What is toxic epidermal necrolysis? Stevens Johnson with skin sloughing
What is pemphigus vulgaris?
Ab against desmosomes ...
circular immunoflueorescence ...
in epidermis ...
oral lesions ...
Nikolsky sign
What is bullous pemphigoid?
Ab against hemidesmosomes ...
liner immunofluorescence ...
subepidermal ...
"floating" keratinocytes ...
eosinophils
What is eczema? dry flaky dermatitis in flexor creases
What is nummular dermatitis? circular eczema
What is spongiotic eczema? weeping eczema - scratching causes oozing
What is lichenification? scratching => thick leathery skin
What is pityriasis rosea?
herald patch that follows skin lines ...
"Christmas tree pattern" ...
Tx: sunlight
What is lichen planus? polygonal pruritic purple papules
What is scabies?
linear excoriation "burrows" in webs of fingers, toes, belt
line (sarcoptes feces)
What does UV-A causes? Aging
What does UV-B cause? Burns and cancer
What are the ABCD's that indicate worse prognosis of
skin cancer?
A: asymmetric ...
B: irregular border ...
C: color differences ...
D: >4 mm diameter
What does the Clark level tell you? invasion of melanoma
What does Breslow's classification tell you? depth of melanoma
Where are malignant melanomas usually found?
males: back ...
females: leg
What is the precursor of a malignant melanoma? Hutchison's freckle
What are the types of malignant melanoma?
superficial spreading (most common, flat brown) ...
nodular (worst prognosis, black, dome-shape) ...
lentigo maligna melanoma (elderly pts, fair-skin) ...
acral lentigous (ADS pts, dark skin)
Where are squamous cell carcinomas usually found?
flat flaky sutff on lower face ...
keratin pearls
What is the precursor of squamous cell carcinoma? actinic keratosis (red scaly plaque)
What are the types of squamous cell carcinoma?
Bowen's disease (SCC in situ on uncircumcised penis
dorsum) ...
Verrucous carcinoma (wart on foot)
Where are basal cell carcinomas usually found?
pearly papules on upper face ...
palisading nuclei ...
good prognosis
What are the types of basal cell carcinomas?
nodular (waxy nodule with central necrosis) ...
superficial (red scaly plaques, like eczema) ...
pigmented (looks like melanoma) ...
sclerosing (yellow waxy plaques)
What is acne rosacea?
blush all the time ...
worse with stress and alcohol
What is a brown recluse spider bite? painful black necrotic lesion
What is cellulitis? warm red leg
What is cutaneous anthrax? panless black necrotic lesion
What is a decubitus ulcer? bedsore
What is a DVT?
blood clot in veins ...
associated with hypercoagulable state
What is erysipelas?
shiny red ...
raised ...
doesn't blanch ...
usually on face ...
associate with Strep pyogenes
What is ichthyosis? gradual lizard skin
What is miliaria? "heat rash" - burning, itching papules on trunk
What is molluscum contagiosum?
fleshy papules with central dimple ...
pox virus (STD)
What is psoriasis?
silver scales on extensors ...
nail pitting ...
differentiated too fast ...
worse with stress ...
Auspitz sign (remove scale => pinpoint bleeding) ...
Koebner's phenomenon (lesions at sites of skin trauma)
What is pyogenic granuloma? vascular nodules at site of previous injury
What is seborrheic dermatitis? dandruff in eyebrowns, nose, behind ears
What is seborrheic keratosis?
rubbery warts with aging ...
greasy
What is throbophlebitis? vein inflammation with thrombus
What is vitiligo?
white patches ...
anti-melanocyte Ab
What is xeroderma pigmentosa? bad DNA repair
What is erythema chronicum migrans? lyme disease (solitary lesion that spreads)
What is erythemaa infectiosum?
fifth disease ...
"slapped cheeks" ...
due to Parvovirus B19
What is erythema marginatum? rheumatic fever (red margins)
What is erythema multiforme? target lesions due to HSV, phenytoin, barbituates, sulfas
What is erythema multiforme major? Stevens Johnson syndrome (>1 mucosal surface)
What is erythema nodosum?
fat inflammation (painful red nodules on legs) ...
sarcoidosis
What is erythema toxicum?
newborn benign rash (looks like flea bites with
eosinophils)
Where is CK-MB found? heart
Where is CK-MM found? muscle
Where is CK-BB found? brain
Why should you wait 30 min after a meal before
swimming?
all blood in G so muscle has low ATP
How does a neurogenic muscle disease present?
distal weakness ...
fasciculations
How does a myopathic muscle disease present?
proximal weakness ...
pain
What is a light chain composed of? actin
What is a heavy chain composed of? myosin
What band of the sarcomere does not change length? A band
Where are the T-tubules located?
skeletal muscle: A- junction ...
cardiac muscle: Z line
What is Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy?
dystrophin frameshift mutation ...
Gower sign ...
pseudohypertrophy of the calf
What is Becker's Muscular Dystrophy?
dystrophin missense mutation ...
sx onset > 5 yo
What is Myotonic Dystrophy?
bird's beak face ...
can't let go when they shake hands
What is Myasthenic syndrome (Lambert Eaton)?
gets stronger as day goes by ...
stronger with EMG ...
associated with small cell carcinoma
What is Myasthenia Gravis?
gets weaker as day goes by ...
stronger with edrophonium ...
weaker with EMG ...
r/o thymoma
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
anti-myelin Ab ...
young woman with vision problems ...
sx wax and wane
What is Metachromatic Leukodystorphy?
arylsulfatase deficiency ...
kid with MS presentation
What is Ataxia Telangiectasia?
spider veins ...
gA deficiency
What is Friedreich's Ataxia?
retinitis pigmentosum ...
scoliosis
What is Adrenal Leukodystrophy?
carnitine shuttle problem ...
adrenal failure
What is Guillain Barre?
ascending paralysis ...
2 wks after UR
What is ALS?
descending paralysis ...
middle aged male with fasciculations ...
no sensory problems
What is Werdnig-Hoffman?
fasciculations in a newborn ...
no anterior horns
What is Polio?
asymmetric fasciculations in a child ...
2 wks after gastroenteritis
What is Choreoathetosis?
dance-like movements ...
wringing hands ...
quivering voice
What is atonic cerebral palsy? no muscle tone (floppy)
What is slipped capital femoral epiphysis? obese boys with dull achy pain
What is Osteonecrosis (Legg-Calves-Perthes)?
wedge shaped necrosis of femoral head ...
limp
What is Osgood-Schlatter? knee pain (tibial tubercle)
What is Septic Arthritis? joint pain (S. aureus)
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
ligament ossification (vertebral body fusion) ...
decreased lumbar curvature ...
stiffer in morning ...
kyphosis ...
uveitis ...
HLA B-27
What is Cauda Equina Syndrome?
"saddle anesthesia" ...
can't feel thighs, butt, perineum
Where do bone cancer metastases come from?
breast ...
prostate ...
lung ...
kidney
What is costochondritis?
painful swelling of chest joint-bone attachments ...
worse with deep breath
What is disk herniation? straight leg raise leads to shooting pain
What is lumbar stenosis?
MR "hourglass" ...
low back pain
What is ochronosis (alkaptonuria)?
kids with OA ...
homogentisic acid oxidase deficiency ...
black urine
What is Osteitis Fibrosis Cystic? inflammation of bone with holes
What is Osteogenesis mperfecta?
blue sclera ...
multiple broken bones
What is Osteomalacia?
Rickets ...
soft bones (waddling gait) ...
craniotabes (soft skull) ...
rachitic rosary (costochondral thickening) ...
Harrison's groove ...
pigeon breast (sternum protrusion)
What is Osteomyelitis? infected bones
What is Osteopenia? lost bone mass
What is Osteopetrosis?
decreased osteoclast activity ...
marble bones ...
obliterate own bone marrow
What is Osteoporosis?
loss of bone matrix ...
compression fractures
What is Osteosclerosis? thick bones
What is Paget's Disease?
"my hat doesn't fit" ...
increased osteoclasts and osteoblasts ...
increased alkaline phosphatase alone ...
paramyxovirus ...
fluffy bone ...
osteosarcoma ...
increased CO heart failure ...
deafness
How do osteocytes communicate? via gap junctions
How does parvovirus B19 present in adults? arthritis (self limited)
What is the most abundant amino acid in collagen? glycine
What is rheumatoid factor? an gM against gG Fc
What are tophi? gout crystals + giant cells
What is podagra? big toe inflammation
What is CREST syndrome?
C: calcinosis ...
R: raynaud's ...
E: esophageal dysmotility ...
S: sclerodactyly ...
T: telangiectasia
What Ab is associated with CREST? anti-centromere Ab
What diseases have Raynaud's syndrome?
scleroderma ...
Takayasu's ...
RA ...
SLE
What platelet count do most types of vasculitides have? low platelets
Which vasculitis has a high platelet count? Kawasaki disease
Which vasculitis has a normal platelet count? Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
What is osteoarthritis?
pain worse with activity ...
PP/DP joints
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
pain worse in morning ...
MCP/PP joints
What is Still's Disease? juvenile RA
What is Pseudogout? pyrophosphate crystals in knees and wrists
What is gout?
urate crystals in big toe ...
neg birefringence
What is myositis? 1 muscle hurts
What is polymyositis? >1 muscle weak
What is dermatomyositis? myositis + rash
What is fibromyalgia?
hurt all the time ...
11 trigger points
What is polymyalgia rheumatica?
weak shoulders ...
temporal arteritis
What is SLE (Lupus)?
discoid rash ...
oral ulcers ...
photosensitivity ...
arthritis ...
malar rash ...
immunologic disorder (anti-dsDNA, anti-Sm, anti-
cardiolipin Ab) ...
neurologic disorder (seizure or psychosis) ...
renal failure (die of this) ...
ANA ...
serositis (pleuritis/pericarditis - Libman-Sacks
endocarditis) ...
hemolytic anemia
What is scleroderma?
tight skin ...
fibrosis
What is Takayasu Arteritis?
pulseless Asian women ...
aorta inflammation
What is Polyarteritis Nodosa?
p-ANCA Ab ...
attacks gut/kidney ...
Hep B
What is Wegner's Granulomatosis?
c-ANCA Ab ...
attacks ENT, lungs, kidney
What is Goodpasture's?
Anti-GBM Ab ...
attacks lung/kidney ...
RPGN
What is Reiter's syndrome? males that can't see, can't pee, can't climb a tree
What is Sjogren's syndrome?
females that have dry eyes/mouth ...
RA
What is Behcet's syndrome?
oral and genital ulcers ...
uveitis
What is Churg-Strauss?
asthma ...
eosinophils ...
multi-organ involvement
What is Felty's syndrome?
RA ...
leukopenia ...
splenomegaly
What is Kawasaki's disease?
"CRASH" ...
C: conjunctivitis ...
R: rash (palms/soles) ...
A: aneurysm (coronary artery => M in kids) ...
S: strawberry tongue ...
H: hot (fever > 102 for at least 3 days + cervical
lymphadenopathy)
What is the complication of temporal arteritis? blindness
What is another name for temporal arteritis? giant cell arteritis
How do you diagnose temporal arteritis? temporal artery biopsy
What is the rule of 60's for temporal arteritis?
age > 60 ...
ESR > 60 ...
60mg prednisone to tx
What condition is associated with one muscle hurting? myositis
What condition is associated with several muscles
hurting?
polymyositis
What condition is associated with muscle pain plus a
rash?
dermatomyositis
What condition is associated with inflamed muscle
insertions?
fibrositis
What condition causes pain of muscle and muscle
insertion?
fibromyalgia
What condition is associated with the shoulder girlde
hurting most?
polymyalgia rheumatica
What condition is associated with visceral cancer? dermatomyositis (colon cancer)
What condition is associated with rifampin, NH, statins,
prednisone, and hypothyroidism?
myositis
What condition is treated with amitriptyline? fibromyalgia
What condition is increased in temporal arteritis? polymyalgia rheumatica
What condition is associated with multiple trigger points? fibromyalgia
What condition is associated with muscle pain when
moving?
fibrositis
What condition is associated with a heliotropic rash? dermatomyositis
What condition is associated with a throbbing temporal
headache?
temporal arteritis
What drugs cause myositis?
rifampin ...
NH ...
statins ...
prednisone
What disease causes myositis? hypothyroidism
What is the treatment for multiple sclerosis?
#1 steroids ...
#2 blocking immunoglobulins (TNF-beta) ...
#3 plasmaphoresis
What structure does MS like to attack?
medial longitudinal fasciculus => internuclear
opththalmoplegia
What is the diagnosis for a middle aged woman with optic
neuritis (eye problem)?
multiple sclerosis
What is the equivalent disease to MS in children < 10 yo? metachromatic leukodystrophy
What vasculitis occurs 2 wks after a common cold? Berger's
What disease presents as a smoking Jew with necrotizing
vasculitis?
Buerger's
What disease has a family history of deafness and
cataracts?
Alport's
What vasculitis has a strawberry tonge? Kawasaki's
What vasculitis has fibrin split products? DC
What vasculitis presents 2 wks after E. coli
gastroenteritis?
hemolytic uremic syndrome
What vasculitis presents with fever, thrombocytopenia,
and neuro problems?
TP
What vasculitis attacks midsize arteries (particuarly in G
and kidney)?
polyarteritis nodosa
What vasculitis affects the sinuses, lung, and kidney? Wegner's Granulomatosis
What vasculitis has linear immunofluorescence on GBM
with lung involvement?
Goodpastures
What vasculitis has pulmonary infiltrates with
eosinophilia?
Churg-Strauss
What glomerulonephritis occurs two weeks after a sore
throat?
Post-Strep Glomerulonephritis
What vasculitis presents two wks after vaccination? serum sickness
What disease leads to septic emboli? subacute bacterial endocarditis
What is the only vasculitis with a normal platelet count? HSP
What is the only vasculitis with a high platelet count? Kawasaki's
What is the MCC of death in SLE? renal failure
What protein is decreased in all vasculitides? haptoglobin
What cellular response is seen in all vasculitides? T cells and macrophages
What is gastroschisis?
aka paromphalocele ...
abdominal viscera develop outside the abdomen ...
abdominal wall defect ...
off center, no peritoneum cover
What is a nephroblastoma?
kidney (Wilms) tumor ...
hemihypertrophy ...
aniridia
What is a neuroblastoma?
adrenal medulla tumor ...
hypsarrhythmia ...
obsoclonus ...
increased VMA
What is polyhydramnios?
too much amniotic fluid (AF > 20) ...
baby can't swallow
What are the most common causes of polyhydramnios?
obstruction ...
G problem (duodenal atresia) ...
NM problem (Werdnig-Hoffman)
What is oligohydramnios?
too little amniotic fluid (AF < 5) ...
baby can't pee
What are the most common causes of oligohydramnios?
abdominal muscle problem (prune belly) ...
renal agenesis (Potter's syndrome)
What is Fifth disease?
parvovirus B19 ...
erythema infectiosum (slapped cheeks) ...
arthritis in mom ...
aplastic anemia
What is Sixth disease?
roseola ...
exanthema subitum (fever disappears, then rash
appears)
What is hand-foot-mouth disease?
mouth ulcers (won't eat or drink) ...
rash on palms and soles ...
coxsackie A virus
What is measles?
rubeola ...
1 - cough, coryza, conjunctivitis ...
2 - Koplik spots ...
3 - morbilliform blotchy rash
What is molluscum contagiiosum? flesh colored papules with central dimple
What is mumps? parotiditis
What is otitis media? fluid in middle ear
What is Pityriasis Rosea?
Herald patch migrates along skin lines ...
"Christmas tree" appearance
What is Rubella?
German 3-day measles ...
trunk rash ...
lymphadenopathy behind ears ...
don't look sick
How is smallpox different from chickenpox?
smallpox is on the face ...
same stage of development ...
fever
What is vericella?
chickenpox ...
1 - red macule ...
2 - clear vesicle on red dot ...
3 - pus ...
4 - scab
What is Zellweger's? neonatal seizures
What is the MCC of delayed speech development? hearing loss
What are the signs of child abuse?
multple ecchymoses ...
retinal hemorrhage ...
epidural/subdural hemorrhage ...
spiral fractures (twisted) ...
multiple fractures in different healing stages
What should you rule out when child abuse is suspected?
osteogenesis imperfecta ...
bleeding disorders ...
Fifth's disease ...
mongolian spots
What are the newborn screening tests?
PKU ...
congenital adrenal hyperplasia ...
biotnidase ...
beta-thalassemia ...
galactosemia ...
hypothyroidism ...
homocysteinuria
What is VATER syndrome?
Vertebral abnormality ...
Anal defect ...
TE fistula ...
Renal
What is VACTERL?
(VATER + cardiac and limb defects) ...
Vertebral abnormality ...
Anal defect ...
TE fistula ...
Renal ...
cardiac and limb defects
What is average Q? 85-100
What are the MCC of mental retardation in the US?
EtOH (fetal alcohol syndrome) ...
fragile X ...
Down's syndrome
What is rubeola also known as? measles
What is rubella also known as? german measles
What is the APGAR test?
test at 1 and 5 min (normal > 7) ...
Appearance (color) ...
Pulse ...
Grimace ...
Activity ...
Respiration
What is the MC eye infection the first day of life? clear discharge due to silver nitrate
What is the MC eye infection the first week of life? gonorrhea (purulent discharge)
What is the MC eye infection the second week of life? chlamydia
What is the MC eye infection the third week of life? herpes
What are the causes of hyperbilirubinemia?
sepsis ...
ABO incompatibility ...
hypothyroidism ...
breastfeeding
What is the cause of symmetrically small babies?
chromosomal abnormality ...
TORCHS
What is the cause of asymetrically small babies?
poor blood supply spares brain => small body and normal
head
What is the cause of large babies?
diabetes ...
twin-twin transfusion
What is milia?
neonatal whiteheads on malar area ...
aka milk spots
What is nevus flammeus?
"stork bites" on back of neck ...
looks like flames
What is seborrheic dermatitis? red rash with oily skin and dry flaky hairline
What are hemangiomas? flat blood vessels
What are mongolian spots? melanocytes on lower back
What is erythema toxicum?
white wheal on red area ...
has eosinophils
What is subgaleal hemorrhage? prolonged jaundice in newborns due to birthing trauma
What is caput seccedaneum? under scalp (edema crosses suture lines)
What is cephalohematoma? under bone (blood doesn't cross suture lines)
What is an Epstien's pearl? white perals on hard palates
What is "persistent eye drainage since birth" usually due
to?
blocked duct
What are wide sutures due to?
hypothyroidsim ...
Down's syndrome
What causes a cleft lip? medial nasal prominence did not fuse (maxillary sinus)
What causes a cleft palate? maxillary shelves did not fuse
What is the MCC of no red reflex? cataracts
What is the MCC of a white reflex? retinoblastoma
What is the sign of a clavicle fracture? asymmetric Moro reflex
What is an omphalocele?
intestines protrude out umbilicus ...
covered by peritoneum
What does the seminal vesicle give to sperm? food (fructose) and clothes (semen)
What do the bulbourethral (Cowper's) glands secrete? bicarb (neutralize lactobacilli)
What does the prostate secrete?
haluronidase ...
acid phosphatase ...
zinc
What is the capacitation reaction? An used to peel semen off
What is the acrosomal reaction? sperm release enzymes to eat corona radiata
What is the crystalization reaction? wall formed after 1 sperm enters (to prevent polyspermy)
Where does testosterone come from? adrenal gland and testicles
Where does DHT come from? testicles (at puberty)
What is a pseudohermaphrodite? external genitalia problem
What is a true hermaphrodite? internal genitalia problem => has both sexes
What is a female hermaphrodite? impossible because the default is female
What is a female pseudohermaphrodite? XX with low 21 hydroxylase => high testosterone
What is male hermaphrodite? XY with no MF
What is a male pseudohermaphrodite? XY that has low 17 hydroxylase => low testosterone
What is hirsutism? hairy
What is virilization? man-like
What is testicular feminization (androgen insensitivity)
syndrome?
bad DHT receptor => XY with blind pouch vagina
What is McCune Albright?
precocious sexual development ...
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia ...
"whorls of CT" ... "Coast of Maine" ...
pigmented skin macules
What is cryptochordism?
testes never descended => sterility after 15 mo ...
seminomas
Which stage of the menstrual cycle has the highest
estrogen levels?
follicular stage (has proliferative endothelium)
What stage of the menstrual cycle has the highest
temperature?
ovulatory stage
What stage of the menstrual cycle has the highest
progesterone levels?
luteal stage (has secretory endothelium)
What form of estrogen is highest at menopause? E1 - estrone (made by fat)
What form of is highest in middle-ages females? E2 - estradiol (made by ovaries)
What form of estrogen is highest at pregnancy? E3 - estriol (made by placenta)
What states have increased estrogen?
pregnancy ...
liver failure ...
p450 inhibition ...
obestity
What is adenomyosis?
growth of endometrium => myometrium ...
enlarged "boggy" uterus with cystic areas
What does DES taken by mom cause in her daughter?
adenomyosis => menorrhagia ...
clear cell carcinoma of vagina ...
recurrent abortions
What is Kallman's syndrome?
no GnRH ...
anosmia (can't smell)
What is polycystic ovarian syndrome?
inc cysts - no ovulation => no progesterone ...
(inc endometrial CA) => can't inhibit LH ...
obese ...
hairy ...
acne
What is Savage's syndrome? ovarian resistance to FSH/LH
What is Turner's syndrome (XO)?
high FSH ...
low E2 ...
ovarian dysgenesis
What does the progesterone challenge test tell you?
bleeds => she has estrogen ...
not bleed => she has no E2 or ovaries ...
... inc FSH => ovary problem ...
... dec FSH => pituitary problem ...
What is Sheehan syndrome?
post-partum hemorrhage => pituitary ...
hyperplasia infarcts => no laceration
What is Asherman's syndrome? previous D&C => uterine scars
What is oligomenorrhea? too few periods
What is polymenorrhea? too many periods
What is the most common cause of post-coital vaginal
bleeding?
cervical cancer
What is the most common cause of post-coital vaginal
bleeding in pregnant women?
placenta previa
What is the most common cause of vaginal bleeding in
post-menopause women?
endometrial cancer
What is chronic pelvic pain? endometriosis until proven otherwise
What is dysfunctional uterine bleeding?
diagnosis of exclusion ...
usually due to anovulation
What is dysmenorrhea?
PG-F causes painful menstrual cramps (teenagers miss
school/work)
What is endometriosis?
painful cyclical heavy menstrual bleeding => "powder
burns, chocolate cysts" due to ectopic endometrial tissue
What is Kleine regnung? scant bleeding at ovultation
What is menorrhagia? heavy menstrual bleeding
What is fibroids (leiomyoma)?
benign uterus smooth muscle tumor ...
submucosal type => bleeding ...
subserosal type => pain
What is metorrhagia? bleeding or spotting in between periods
What is Mittleschmerz? pain at ovulation
What causes syphilis? treponema pallidum (spirochete)
What is herpes? dsDNA virus
What is HPV? dsDNA virus
What is chlamydia? obligate intracellular bacteria
What causes gonorrhea? gram neg diplococcus
What causes chancroid? H. ducreyi
What causes lymphogranuloma venereum? Chlamydia trachomatis
What causes granuloma inginale? C. granulomatosis
What causes epididymitis? Chlamydia
What is condyloma lata?
fat fleshy warts ...
ulcerate ...
secondary syphilis
What is condyloma accuminata?
verrucous "cauliflower" warts ...
koilocytes ...
HPV 6, 11
How does herpes present?
primary: painful grouped vesicles on red base ...
secondary: painful solitary lesion
How does syphilis present?
primary: painless chancre (1-6 wks) ...
secondary: rash, condyloma lata (6 wks) ...
tertiary: neuro, cardio, bone (6 yrs)
How does chancroid present?
painful with necrotic center ...
gram neg rod ...
"school of fish" pattern
How does lymphogranuloma venereum present?
painless ulcers => abscessed nodes => genital
elephantiasis
How does granuloma inguinale present?
spreading ulcer ...
Donovan bodies ...
granulation test
How does chlamydia present?
cervicitis (yellow pus) ...
conjunctivities ...
PD
How does gonorrhea present?
palmar pustules ...
arthritis ...
urethral discomfort
What is epididymitis? unilateral scrotal pain decreased by support
What causes congenital blindness? CMV
What causes neonatal blindness? chlamydia
What is lichen simplex chronicus?
raised white lesions ....
chronic scratching
What is lichen sclerosis? sweat gland cysts
What cases non-bacteral fetal infections?
TORCHS ...
T: toxoplasma ...
O: others ...
R: rubella ...
C: CMV ...
H: HSV-2 ...
S: syphilis
What is toxoplasmosis?
multiple ring-enhancing lesions ...
cat urine ...
parietal lobe
What is rubella?
cataracts ...
hearing loss ...
PDA ...
meningoencephalitis ...
pneumonia ...
"blueberry muffin" rash
What is CMV?
spastic diplegia of legs ...
hepatosplenomegaly ...
blindness ...
central calcifications
What is HSV-2?
temporal lobe hemorrhagic encephalitis ...
need C/S prophylaxis
What is syphilis?
Rhagade's (lip fissure) ...
saber shin legs ...
Hutchison's razor teeth ...
mulberry molars
What is Paget's disease of the breast?
rash and ulcer around nipple ...
breast cancer
What is lobular carcinoma?
cells line up single file ...
contralateral primary
What is comedocarcinoma?
multiple focal areas of necrosis ...
"blackheads"
What is inflammatory carcinoma?
infiltrates lymphatics ...
pulls on Cooper's ligaments ...
"peau d'orange"
What is cystosarcoma phylloides?
exploding mushroom" ....
firm ...
rubbery ...
movable ...
good prognosis
What is intraductal papilloma?
nipple bleeding ...
most common breast cancer
What is ductal carcinoma? worst prognosis breast cancer
What is sarcoma boyroides?
vagina cancer ...
ball of grapes
What is a Sister Mary Joseph Nodule? ovarian cancer spread to umbilicus
What is Meig's syndrome?
pleural effusion ...
ovarian fibroma ...
ascites
What are the side effects of estrogen?
weight gain ...
breast tenderness ...
nausea ...
headache
What are the side effects of progesterone?
acne ...
depression ...
HTN
Why do pregnant women get anemia?
dilutional effect ...
RBC rises 30% but volume rises 50%
What are the degrees of vaginal lacerations?
1st degree: skin ...
2nd degree: muscle ...
3rd degree: anus ...
4th degree: rectum
What is vernix? cheesy baby skin
What is meconium? green baby poop
What is lochia? endometrial slough
What is normal blood loss during a vaginal delivery? 500 mL
What is normal blood loss during a C-section? 1 L
How do you treat A1 Gestational DM? diet
How do you treat A2 Gestational DM? insulin
What are identical twins?
egg split into perfect halves ...
"monochorionic"
What are fraternal twins? multiple eggs fertilized by different sperm
What is Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome? weight gain and enlarged ovaries after clomiphene use
Who makes the trophoblast? baby
Who makes the cytotrophoblast? mom = GnRH, CRH, TRH, inhibin
Who makes the syncitotrophoblast? mom and baby => HCG, HPL
When does implantation occur? 1 wk after fertilization?
When is beta-HCG found in urine? 2 wks after fertilization
What is the function of estrogen?
muscle relaxant ...
constipation ...
inc protein production ...
irritability ...
varicose veins
What is the function of progesterone?
inc appetite ...
inc acne ...
dilutional anemia ...
quiescent uterus ...
pica ...
hypotension ...
melasma
What makes progesterone < 10 wk old? corpus luteum
What makes progesterone > 10 wk old? placenta
What is the function of beta-HCG?
maintains corpus luteum ...
sensitizes TSHr => act hyperthyroid (to inc BMR)
What makes beta-HCG? placenta
How fast should beta-HCG rise?
doubles every 2 days until 10 wks (when placenta is fully
formed)
What is the function of AFP? regulates fetal intravascular volume
What is the function of HPL?
blocks insulin receptors => sugar stays high ...
(baby's stocking up on stuff needed for the journey)
What is the function of inhibin? inhibits FSH => no menstruation
What is the function of oxytocin?
milk ejection ...
baby ejection
What is the function of cortisol in pregnancy?
decreases immune rejection of baby ...
lung maturation
What are the thyroid hormone levels during pregnancy?
inc TBG => inc bound T4 ...
nml free T4 levels
When can you first detect fetal heartones? wk 20
When can you tell the sex of a fetus by US? wk 16
What does an AF < 5 indicate? oligohydramnios (cord compression)
What does an AF > 20 indicate? polyhydramnios (DM)
How fast should fundal height change? uterus grows 1 cm/wk
What is the Pool Test? fluid in vagina
What is Ferning? estrogen crystallizes on slide
What is Nitrazine? shows presence of amniotic fluid
What is the risk of chorionic villus sampling? fetal limb defects
What is a normal biophysical profile?
"Test the Baby, MAN!" ...
T: tones of the heart ...
B: breathing ...
M: movement (BPD, HC, AC, FL) ...
A: AF ...
N: non-stress test (normal = "reactive")
What pelvis types are better for vaginal delivery?
gynecoid ...
anthropoid
What pelvis types will need C/S?
platypelloid ...
android
How do you predict a due date with Nagele's Rule? 9 months from last menses ... add 1 wk
Why is Nagele's Rule inaccurate? b/c it does not start from ovulation date
How do you correct Nagele's Rule for cycles >28 days? add x days if cycle x longer
How much weight should a pregnant woman gain? 1 lb/wk
When should intercourse be avoided during pregnancy?
3rd trimester b/c PG-F in semen may cause uterine
contractions
What are the Leopold maneuvers?
1. feel fundus ...
2. feel baby's back ...
3. feel pelvic inlet ...
4. feel baby's head
What is Stage of labor?
up to full dilation ...
1. Latent Phase (<20 h): contractions => 4 cm cervical
dilation ...
2. Active Phase (<12 h): 4-10 cm cervical dilation (1
cm/hr)
What is Stage of labor?
full dilation => delivery ...
Station 0: baby above pelvic rim (most uteri are
anteverted) ...
1. engage ...
2. descend ...
3. flex head ...
4. internal rotation ...
5. extend head ...
6. externally rotate ...
7. expulsion (LDA most common presentation)
What is Stage of labor?
delivery of placenta (due to PG-F) ...
blood gush => cord lengthens => fundus firms
How do you monitor baby's HR?
doppler ...
scalp electrode
What Bishop's score predicts delivery will be soon? >8
What are Braxton-Hicks contractions? irregular contraction with closed cervix
What is a Vertex presentation?
posterior fontanel (triangle shape) presents first ...
normal
What is a Sinciput presentation? anterior fontanel (diamond shape) presents first
What is a Face presentation? mentum anterior => forceps delivery
What is a Complete breech?
butt down ...
thighs and legs flexed
What is a Frank breech?
butt down ...
thigh flexed ...
legs extended ...
(pancake)
What is Footling breech?
butt down ...
thigh flexed ...
one toe is sticking out of cervical os
What is a Double Footling breech? two feet sticking out of cervical os
What is a Transverse Lie?
head is one one side ...
butt on the other
What is Shoulder Dystocia?
head out ...
shoulder stuck
Can you try vaginal delivery on woman who has had a
Classic Horizontal C/S previously?
no, must have C/S for all future pregnancies
Can you try vaginal delivery on a woman who has had
Low Transverse C/S previously?
yes
What is early deceleration?
normal ...
due to head compression
What is late deceleration?
uteroplacental insufficiency b/c placenta can't provide
O2/nutrients
What is variable deceleration? cord compression
What is increased beat-to-beat variability? fetal hypoxemia
What is decreased beat-to-beat variability? acidemia
What is pre-eclampsia? ischemia to placenta => HTN (>140/90)
What is the treatment for pre-eclampsia? delivery
What is HELLP syndrome?
hepatic injury causing - ...
H: hemolysis ...
EL: elevated liver enzymes ...
LP: low platelets
What is eclampsia? HTN + seizures
What are the symptoms of eclampsia?
headache ...
changes in vision ...
epigastric pain
What is the treatment for eclampsia? 4 mg Mg sulfate as seizure prophylaxis
What is chorioamnionitis?
fever ...
uterine tenderness ...
dec fetal HR
What are the sx of amniotic fluid emboli?
mom just delivered baby and has SOB => PE, death ...
(amniotic fluid => lungs)
What is endometritis? post-partum uterine tenderness
What is an incomplete molar pregnancy?
2 sperm + 1 egg (69, XXY) ...
has embryo parts
What is a complete molar pregnancy?
2 sperm + no egg (46, XX - both paternal) ...
no embryo
What is pseudocyesis? fake pregnancy with all the signs and symptoms
What is the most common cause of 1st trimester maternal
death?
ectopic pregnancy
What is the most common cause of 1st trimester
spontaneous abortions?
chromosomal abnormalities
What are the most common causes of 3rd trimester
spontaneous abortions?
anti-cardiolipin Ab ...
placenta problems ...
infection ...
incompetent cervix
What is a threatened abortion?
cervix closed ...
baby intact ...
tx: bed rest
What is an inevitable abortion?
cervix open ...
baby intact ...
tx: cerclage (sew cervix shut until term)
What is an incomplete abortion?
cervix open ...
fetal remnants ...
tx: D&C to prevent placenta infection
What is a complete abortion?
cervix open ...
no fetal remnants ...
test: beta-HCG
What is a missed abortion?
cervix closed ...
fetal remnants ...
tx: D&C
What is a septic abortion?
fever > 100 F ...
malodorous dishcharge
What is Placenta Previa?
post-coital bleeding ...
placenta covers cervical os ...
ruptures placental arteries
What is Vasa Previa? placenta aa hang out of cervix
What is Placenta Accreta? placenta attached to superficial lining
What is Placenta ncreta? placenta invades myometrium
What is Placenta Percreta? placenta perforates through myometrium
What is Placenta Abruptio?
severe pain ...
premature separation of placenta
What is Velamentous Cord nsertion? fetal vessels insert between chorion and amnion
What is Uterus Rupture?
tearing sensation ...
halt of delivery
What is an Apt test? detects HbF in vagina
What is Wright's stain? detects nucleated fetal RBC in mom's vagina
What is a Kleihauer-Betke test?
detects percental of fetal blood in maternal circulation
(dilution test)
What is maternity blues?
post-partum crying ...
irritability
What is post-partum depression? depression > 2wks
What is post-partum psychosis?
hallucinations ...
suicidal ...
infanticidal
What is the most common intracellular buffer? protein
What is the most common extracellular buffer? bicarbonate
What is the best amino acid buffer in the body? histidine
What is the RLE in glycolysis? PFK-1
What is the RLE in gluconeogenesis? pyruvate carboxylase
What is the RLE in the HMP shunt? G6PD
What is the RLE in glycogenesis? glycogen synthase
What is the RLE in glycogenolysis? glycogen phosphorylase
What is the RLE in FA synthesis? acetyl-CoA carboxylase
What is the RLE in beta-oxidation? CAT-1
What is the RLE in cholesterol synthesis? HMG CoA reductase
What is the RLE in ketogenesis? HMG CoA synthase
What is the RLE in purine synthesis? PRPP synthase
What is the RLE in pyrimidine synthesis? ASP transcarbamoylase
What is the RLE in the TCA cycle? isocitrate dehydrogenase
What is the RLE in the urea cycle? CPS-1
What is the RLE in heme synthesis? delta-ALA synthase
What does an isomerase do? creates an isomer
What does an epimerase do? creates an epimer, which differs around 1 chiral carbon
What does a mutase do?
moves a sidechain from one carbon to another
(intrachain)
What does a transferase do?
moves a sidechain from one substrate to another
(interchain)
What does a kinase do? phosphorylates using ATP
What does a phosphorylase do? phosphorylates using inorganic phosphate
What does a carboxylase do? forms C-C bonds (with ATP and biotin)
What does a synthase do? consumes 2 substrates
What does a synthetase do? consumes 2 substrates, uses ATP
What does a phosphatase do? breaks phosphate bond
What does a lyase do? cuts C-C bonds with ATP
What does a dehydrogenase do? removes H with a cofactor
What does a thio do? breaks S bonds
What is diffusion? from high to low concentration
What is active transport? goes against concentration gradient
What is zero-order kinetics? metabolism independent of concentration
What is first-order kinetics?
constant drug percentage metabolism over time, depends
on drug concentration
What is efficacy?
max effect regardless of dose (lower with non-competitive
antagonist)
What affects efficacy? Vmax
What is potency?
amount of drug needed to produce effect (lower with
competitive antagonist)
What affects potency? Km
What is Kd? concentration of drug that binds 50% of receptors
What is EC_50?
concentration of drug that produces 50% of maximal
response
What is competitive inhibition? fights for active sit, no change in Km, potency decreases
What is non-competitive inhibition?
binds a regulatory site, no change in Km, efficacy
decreases, Vmax decreases
What is an endothermic reaction? consumes heat
What is an exothermic reaction? gives off heat
What is the peak level? 4 hrs after dose (if too high, decrease dose)
What is the trough level? 2 hrs before dose (if too high, give less often)
What is t_1/2?
half-life, the time it takes for the body to use half of the
drug ingested
What is von Gierke?
glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency ...
hypoglycemia ...
hepatosplnomegaly
What is Pompe's? cardiac alpha-1,4-glucosidase deficiency ... DE early
What is Cori's?
debranching enzyme deficiency ... short branches of
glycogen
What is Anderson's? branching enzyme deficiency ... long chains of glycogen
What is McArdle's?
muscle phophorylase deficiency ...
muscle cramps with exercise
What is Essential Fructosuria?
fructokinase deficiency ...
excrete fructose (still have hexokinase)
What is Fructosemia?
"fructose intolerance" (aldolase B deficiency) ...
liver damage
What does a galactokinase deficiency cause? cataracts
What does galactosemia cause?
galactose-1-uridyl-transferase deficiency ...
cataracts ...
mental retardation ...
liver damage
What does the citrate shuttle do? FA transport out of mitochondria
What does the carnitine shuttle do? FA transport into mitochondria
What lysosomal diseases have a cherry-red spot? Tay-Sachs and Niemann-Pick
What lysosomal diseases have a gargoyle-face? Gaucher's and Hurler's
What is Tay Sachs?
hexosaminidase A deficiency ...
blindness ...
incoordination ...
dementia
What is Sandhoff's? hoxosaminidase A/B deficiency
What is Gaucher's?
glucocerebrosidase deficiency ...
wrinkled tissue ...
bone pain
What is Niemann-Pick?
sphingomyelinase deficiency ...
zebra bodies
What is Fabry's?
alpha-galactosidase deficiency ...
corneal clouding ...
attacks baby's kidneys ...
X-linked
What is Krabbe's?
beta-galactosidase deficiency ...
globoid bodies
What is Metachromatic Leukodystrophy?
arylsulfatase deficiency ...
childhood MS
What is Hunter's? iduronidase dficiency, milder form
What is Hurler's? iduronidase deficiency, worse form
What is Lesch-Nyhan?
HGPRT deficiency ...
gout ...
neuropathy ...
self-mutilation
What do white diaper crystals suggest? excess orotic acid
What does biotin donate methyl groups for? carboxylation
What does THF donate methyl groups for? nucleotides
What does SAM donate methyl groups for? all other reactions (not for carboxylation or nucleotides)
What is the difference between heterochromatin and
euchromatin?
heterochromatin is tightly coiled ...
euchromatin is loose (10 nm fibers)
What are the purines? A and G
What are the pyrimidines? C, U, T
What is a silent mutation? changes leave the same amino acid
What is a point mutation? changes one base
What is a transition? changes one purine to another purine
What is a traversion? changes one purine to a pyrimidine
What is a frameshift mutation? insert or delete 1-2 bases
What is a missense mutation? mistaken amino acid substitution
What is a nonsense mutation? early stop codon
What does a southern blot detect? DNA
What does a northern blot detect? RNA
What does a western blot detect? protein
What are the essential amino acids?
PVT TM HALL ...
P: phenylalanine ...
V: valine ...
T: tryptophan ...
T: threonine ...
: isoleucine ...
M: methionine ...
H: histidine ...
A: arginine ...
L: lysine ...
L: leucine
What are the essential fatty acids? linolenic and linoleic
What are the acidic amino acids? aspartate and glutamate
What are the basic amino acids? lysine and arginine (cut by trypsin)
What are the sulfur containing amino acids? cysteine and methionine (cut by beta-ME)
What are the O-bond amino acids? serine, threonine, tyrosine
What are the N-bond amino acids? asparagine and glutamine (denatured by acid hydrolysis)
What are the branched amino acids? leucine, isoleucine, valine
What are the aromatic amino acids? phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan (cut by chymotrypsin)
What is the smallest amino acid? glycine
What amino acids make disulfide bonds? cysteine and methionine
What amino acid is excitatory for the CNS? asparagine
What amino acide makes catecholamines? tyrosine
What amino acids causes kinks? proline
What amino acid is used to make cysteine? methionine
What does ketogenic mean? made from and broken into Acetyl-CoA
What does glucogenic mean? made from and broken into anything but Acetyl-CoA
What are the ketogenic amino acids? lysine and leucine
What are the glucogenic + ketogenic amino acids?
PTT ...
P: phenylalanine ...
: isoleucine ...
T: threonine ...
T: tryptophan
What are the hydrophobic amino acids? valine, alanine, isoleucine
What amino acids does trypsin cut? lysine and arginine (the basic amino acids)
What amino acids does beta-ME cut?
cysteine and methionine (the sulfur-containing amino
acids)
What amino acids does acid hydrolysis denature? asparagine and glutamine (the N-bond amino acids)
What amino acids does chymotrypsin cut?
phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan (the aromatic amino
acids)
What amino acid turns yellow on Nurhydrin reaction? proline
What does carboxypeptidase cut? left of any amino acid on the carboxy terminal
What does aminopeptidase cut? right of methionine
What does mercaptoethanol cut?
right of cysteine and methionine (the sulfur-containing
amino acids)
What does elastase cut? right of glycine, alanine, and serine
What does alpha_1-AT do? inhibit trypsin frm getting loose
What is PKU?
no phenylalanine to tyrosine (via phenylalanine
hydroxylase) ...
deficient in tyrosine ...
build-up of phenyl-pyruvate and phenyl-acetate ...
nutrasweet sensitivity ...
mental retardation ...
pale, blond hair, blue eyes ...
musty odor
What is albinism? no tyrosine to melanin (via tyrosinase)
What is Maple Syrup Urine disease?
defective metabolism of branched chain amino acids ...
defect in a nephron transport protein
What is Homocystinuria?
no homocysteine to cysteine ...
results in "COLA" stones ...
C: cysteine ...
O: ornithine ...
L: lysine ...
A: arginine
What is Pellagra?
niacin deficiency (vit B3) ...
diarrhea ...
dermatitis ...
dementia ...
death
What is Hartnup's?
no tryptophan to niacin + serotonin ...
presents like pellegra ...
can mimic a corn-rich diet
What causes anterior leg bowing? neonatal syphilis
What causes lateral leg bowing? rickets
What is Kwashiorkor?
malabsorption ...
big bell (ascites) ...
protein deficiency
What is Marasmus?
starvation ...
skinny ...
calorie deficiency
Where does the Pre label send stuff to? ER
Where does the Pro label send stuff to? Golgi
Where does the Mannose-6-P send stuff to? Lysosome
Where does the N-terminal sequence send stuff to? mitochondria
What are the 4 types of collagen?
SCAB ...
Type : Skin, bone ...
Type : Connective tissue, aqueous humor ...
Type : Arteries ...
Type V: Basement membrane
How does Scleroderma present? tight skin
How does Ehlers Danlos present? hyperstretchable skin
How does Marfan's present?
hyperextensble joints ...
arachnodactyly ...
wing span longer than height ...
aortic root dilation, aortic aneurysm ...
mitral valve prolapse ...
dislocated lens from bottom of eye (look up)
How does Homocystinuria present? dislocated lens from top of eye (look down)
How does Minky Kinky hair disease present?
hair looks like copper wire (Cu deficiency) ...
hair cuts face
How does Scurvy present?
bleeding gums ...
bleeding hair follicles
How does Takayasu arteritis present?
Asian female with very weak pulses ...
granulomatous arteritis
How does Osteogenesis mperfecta present?
shattered bones ...
blue sclera
What is the typical incidence of rare things? 1-3%
What is the typical incidence with 1 risk factor? 10%
What is the typical incidence with 2 risk factors? 50%
What is the typical incidence with 3 risk factors? 90%
What does autosomal dominant usually indicate?
structural problem ...
50% chance of passing it on
What does autosomal recessive usually indicate?
enzyme deficiency ...
1/4 get it ...
2/3 carry it
What are the X-linked recessive deficiencies?
Lesch Nyhan (HGPRT def, self mutilation, gout,
neuropathy) ...
Hunter's (iduronidase def) ...
Fabry's (alpha-galactosidase def, corneal clouding,
attacks baby's kidneys) ...
PDH deficiency ...
G6PD deficiency (infections, hemolytic anemia) ...
Chronic Granulomatous Disease (NADPH oxidase
deficiency)
Where did X-linked recessive diseases come from? maternal uncle or grandpa
What are the X-linked dominant diseases?
Na-Resistant Rickets (kidney leaks phosphorus, waddling
gait) ...
Pseudohypoparathyroidism (sausage digits,
osteodystrophy)
Where did X-linked dominant diseases come from? dad => daughter
What are the mitochondrial diseases?
Leber's (atrophy of optic nerve) ...
Leigh's (subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy)
Where did mitochondrial diseases come from? mom => all kids
Why do we stop CPR after 20-30 min? the brain has irreversible cell injury
What do we only have 6 hrs to use tPA? the body has irreversible cell injury
What is Turner's?
(X,0) ...
web neck ...
cystic hygroma ...
shield chest ...
coarctation of aorta, rib notching
What is Klinefelter's?
(47,XXY) ...
tall ...
gynecomastia ...
infertility ...
dec testosterone
What is XXX syndrome?
(47,XXX) ...
normal female with 2 barr bodies
What is XYY syndrome?
(47,XYY) ...
tall aggressive male
What is Trisomy 13?
Patau's ...
polydactyly ...
high arched palate ...
pee problem ...
holoprosencephaly
What is Trisomy 18?
Edward's ...
rocker bottom feet
What is Trisomy 21?
Down's ...
simian crease ...
wide 1st/2nd toes ...
macroglossia ...
mongolian slant of eyes ...
brushfield spots ...
retardation (MCC)
What disease has a dinucleotide repeat? HNPCC
What diseases have a trinucleotide repeat?
Huntington's ...
Fragile X ...
Myotonic Dystrophy ...
Friedreich's Ataxia
What is Angleman's?
"happy puppy syndrome" ...
ataxia
What is Prader-Willi?
hyperphagia ...
hypogonadism ...
almond-shaped eyes
What is Kallman's
anosmia ...
small testes
What is anaplasia? regress to infantile state
What is atrophy? decreased organ or tissue size
What is desmoplasia? cell wraps itself with dense fibrous tissue
What is dysplasia "carcinoma in situ?" lose contact inhibition (cells crawl on each other)
What is hyperplasia? increased cell number
What is hypertrophy increased cell size
What is metaplasia? change from one adult cell type to another
What is neoplasm? new growth
What is benign?
well circumscribed ...
freely movable ...
maintains capsule ...
obeys physiology ...
hurts by compression ...
slow growing
What is malignant?
not well circumscribed ...
fixed ...
no capsule ...
doesn't obey physiology ...
hurts by metastasis ...
rapidly growing ...
(outgrows blood supply => hunts for blood => secretes
angiogenin and endostatin to inhibit blood supply of other
tumors)
What are the fastest killing cancers? pancreatic and esophageal
What does Adeno- tell you? glandular
What does Leimyo- tell you? smooth muscle
What does Rhabdomyo- tell you? skeletal muscle
What does Hemangio- tell you? blood vessel
What does Lipo- tell you? fat
What does Osteo- tell you? bone
What does -oma tell you? tumor
What does -carcinoma tell you? cancer
What does -sarcoma tell you? connective tissue cancer
What is a hamartoma? abnormal growth of normal tissue
What is a choristoma? normal tissue in the wrong place
What is the most common anterior mediastinum tumor? thymoma
What is the most common middle mediastinum tumor? pericardial
What is the most common posterior mediastinum tumor? neuro tumors
What organs hve the most occurrence of metastasis?
brain (grey-whte jxn) ...
bone (marrow) ...
lung ...
liver (portal vein, hepatic artery) ...
adrenal gland (renal arteries) ...
pericardium (coronary arteries)
What cancers have psammoma bodies?
P: papillary (thyroid) ...
S: serous (ovary) ...
A: adenocarcinoma (ovary) ...
M: meningioma ...
M: mesothelioma
What cancer has CA-125? ovarian
What cancer has CA-19? pancreatic
What cancer has S-100? melanoma
What cancer has BRCA? breast
What cancer has PSA? prostate
What cancer has CEA?
colon ...
pancreatic
What cancer has AFP?
liver ...
yolk sac
What cancer has Rb?
Ewing's sarcoma ...
retinoblastoma
What cancer has Ret? medullary thyroid cancer
What cancer has Ras? colon
What cancer has bcl-2? follicular lymphoma
What cancer has c-myc? Burkitt's lymphoma
What cancer has l-myc? small cell lung carcinoma
What cancer has n-myc? neuroblastoma => pseudorosettes
What cancer has bombesin? neuroblastoma
What cancer has beta-HCG? choriocarcinoma
What cancer has 5HT? carcinoid syndrome
What has t(9,22)? CML (bcr-abl gene)
What has t(14,18)? follicular lymphoma (bcl-2 gene)
What has t(8,14)? Burkitt's lymphoma (c-myc gene)
What has t(15,17)? AML M3 (PML)
What has t(11,22)? Ewing's sarcoma
What has HLA A3, A6? hemochromatosis
What has HLA B5? Behcet's
What has HLA B13? psoriasis without arthritis
What has HLA B27?
psoriasis ...
ankylosing spondylitis ...
Reiter's
What has HLA DR2?
Goodpastures ...
MS
What has HLA DR3? celiac sprue
What has HLA DR4? pemphigus vulgaris
What has HLA DR5? pernicious anemia
Which cytokines to macrophages stimulate? L-1
Which cytokines to Th cells stimulate? everything but L-1
Which enlarged lymph nodes are most likely malignant?
supraclavicular ...
epitrochlear ...
inguinal
What is CD8?
Tk (killer) or Ts (suppressor) cell ...
responds to MHC- (self)
What cells express MHC-1? all except RBCs and platelets
What id CD4?
Th (helper) cell ...
responds to MHC- (non-self)
What type of immunity does Th1 provide? cell mediated
What type of immunity does Th2 provide? humoral
What do B cell deficient patients die from? bacterial infection
What is Common Variable Hypogammaglobulinemia
(CVD)?
kids with B cells that don't differentiate into plasma cells ...
low Ab ...
tyrosine kinase deficiency ...
late onset ...
frameshift/missense mutiation
What is Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia?
young adult with defective Tyr kinase ...
no Ab ...
X-linked
What is Job's Syndrome?
stuck in gE stage ...
red head females ...
tyrosine kinase deficiency
What is Multiple Myeloma?
multiple ostolytic lesions ...
gG ...
kappa light chains ...
rouleaux formation
What is Heavy Chain Disease? gA and Multiple Myeloma of the G tract
What is Selective gG2 deficiency? recurrent encapsulated infections
What is Selective gA deficiency?
tranfusion anaphylaxis ...
mucous membrane infections
What is Hairy Cell Leukemia?
fried egg ...
TRAP +
What is Ataxia Telangiectasia?
low gA ...
neuro problems
What is Hyper gM syndrome?
high gM ...
all other Ab low
What kind of problems do you see in patients with
defects in cell mediated immunity?
viral ...
fungal ...
mycobacteria ...
protazoa ...
parasite ...
neoplasm
What do T cell deficient patients die from? viral infection
What is DiGeorge Syndrome?
no thymus / inferior parathyroids ...
low Ca (only immunodeficiency with low Ca) ...
problem with 3rd and 4th pharyngeal pouches ...
deletion on Chr 22
What is Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis?
T cell defect against Candida albicans ...
chronic fatigue
What is SCD?
no thymus ...
frayed long bones ...
baby dies by 18 mo ...
adenosine deaminase deficiency ...
T cells more affected that B ...
frameshift/nonsense mutation ...
increase bacterial and fungal infections
What is Wiskott-Aldrich?
low gM ...
low platelets ...
high gA ...
increased L-4 ...
eczema ...
petechiae
What does the CD4 count tell you? status of HV (normal 800-1200; kids up to 1500)
What does the viral load tell you? progression of HV
What organs have CD4 receptors?
blood vessels ..
brain ...
testicles ...
cervix ...
rectum
What are the 3 tests used to screen for HV?
ELSA: detects gG Ab to p24 Ag ...
Western blot: see >2 proteins ...
PCR detects virus (use in babies)
What is the definition of ADS? CD4 < 200 or clinical sx
What is HV?
effects CD4 rich tissue ...
T cells more affected than B
What are the 9 live vaccines?
"MMR OR Very Yellow Sick Babies" ...
M: measles (rubeola) ...
M: mumps ...
R: rubella (German 3-day measles) ...
O: OPV (Sabin oral polio vaccine) ...
R: rotavirus ...
V: varicella ...
Y: yellow fever ...
S: smallpox ...
B: BCG (tuberculosis)
What is primary biliary cirrhosis?
anti-mitochondrial Ab ...
pruritis ...
females
What is primary sclerosing cholangitis?
p-ANCA ...
bile duct inflammation ...
onion skinning ...
BD
What is Type autoimmune hepatitis?
anti-SM Ab ...
young women
What is Type autoimmune hepatitis?
Anti-LKM Ab ...
kids
What is bullous pemphigoid?
anti-hemidesmosome Ab ...
skin bullae
What is celiac sprue?
anti-gliadin / anti-gluten Ab (wheat) ...
steatorrhea
What is CREST syndrome?
anti-centromere Ab ...
C: calcinosis ...
R: raynauds's ...
E: esophageal dysmotility ...
S: sclerodactyly ...
T: telangiectasia
What is dermatitis herpatiformis?
anti-BMZ ab ...
anti-endomysial Ab ...
vesicles on anterior thigh ...
assoc with celiac sprue
What is dermatomyositis?
anti-Jo-1 Ab ...
myositis + rash
What is DM type ?
anti-islet cell Ab ...
anti-GAD Ab ...
polyuria ...
polydipsia ...
weight loss
What causes drug-indued lupus?
anti-histone Ab (HPPPE) ...
H: hydralazine ...
: NH ...
P: procainamide ...
P: penicillamine ...
P: phenytoin ...
E: ethosuximide
What is Gastritis Type A?
anti-parietal cell Ab ...
atrophic gastritis ...
achlorhydria ...
adenocarcinoma (increased risk)
What is Goodpastures?
anti-GBM Ab ...
attacks lung and kidney ...
MCC RPGN
What is Grave's disease?
anti-TSHr Ab ...
hyperthyroid ...
exophthalmus ...
pretibial myxedema
What is Guillain-Barre?
anti-ganglioside Ab ...
ascending paralysis ...
2 wk after UR
What is Hashimoto's?
anti-microsomal Ab ...
anti-thyroid peroxidase Ab ...
hypothyroid
What is TP?
anti-platelet Ab ...
anti-GP2b3a Ab ...
thrombocytopenia
What is mixed connective tissue disease? anti-RNP Ab
What is mononucleosis?
hereophile Ab ...
teen with sore throat
What is MPGN Type ? anti-C3 convertase Ab (C3 nephritic factor)
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
anti-myelin Ab ...
middle aged female with vision problems
What is Myasthenia Gravis?
anti-AchR Ab ...
female with ptosis ...
weaker as day goes by
What is paroxysmal hemolysis?
Donath Landsteiner Ab ...
bleeds when cold
What is Pemphigus Vulgaris?
anti-desmosome Ab ...
skin sloughs off when touched
What is Pernicious Anemia?
anti-F Ab ...
vit B12 deficient ...
megaloblastic anemia
What is Polyarteritis Nodosa?
p-ANCA ...
attacks gut and kidney ...
megaloblastic anemia
What is Post-Strep Glomerulonephritis?
ASO Ab ...
nephritic with complement deposition
What is Rhematoid Arthritis?
rheumatoid factor ...
pain worse in the morning
What is scleroderma?
anti-Scl70 ...
anti-topo1 ...
fibrosis ...
tight skin
What is Sjogren's?
anti-SSA ...
dry "sand in" eyes ...
dry mouth ...
arthritis
What is SLE?
anti-dsDNA Ab ...
anti-smith Ab ...
anti-cardiolipin Ab ...
rash ...
photosensitivity ...
oral ulcers ...
RF
What is SLE cerebritis?
anti-neuronal Ab ...
anti-ribosomal Ab
What is Vitiligo?
anti-melanocyte Ab ...
white patches
What is warm hemolysis?
anti-Rh Ab ...
bleeds at body temp
What is Wegner's?
c-ANCA ...
attacks ENT, lungs, kidney ...
#2 cause RPGN
What drugs cause autoimmune hemolytic anemia?
PACSAP ...
P: PTU ...
A: alpha-methyldopa ...
C: cephalosporins ...
S: sulfa drugs ...
A: anti-malarials ...
P: penicillin
What drugs cause autoimmune thrombocytopenia?
aspirin ...
heparin ...
quinidine
What are T-cytotoxic cells?
CD8 + ...
recognize MHC- ...
also have CD-2 and CD-3 markers
What are T-helper cells?
CD4+ ...
recognize MHC- ...
also have CD-2 and CD-3 markers
What MHC do macrophages display? MHC-
What are the T and B cell deficiencies?
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome ...
SCD ...
CVD ...
HV (HTLV-1) ...
Job's Syndrome
What are the B cell deficiencies?
Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia ...
leukemias (98% B cells) ...
lymphomas (98% B cells)
What are the T cell deficiencies?
DiGeorge Syndrome ...
HV (T more affected than B)
What bugs cause acute bacterial endocarditis? Staph aureus (attacks healthy valves)
What bugs cause subacute bacterial endocarditis? Strep viridans (attacks damaged valves)
How do you diagnose acute rheumatic fever?
Polyarthritis ...
Carditis (MS > AS > TS) ...
Subcutaneous Nodules ...
Erythema Marginatum (red margins) ...
Sydenham's Chorea
What are the only gram negative diplococci? Neisseria
What is the only gram positive diplococci? Strep pneumo
What bugs cause heart block infections?
"LSD Loves Company" ...
Legionella ...
Salmonella typhi ...
Diphtheria ...
Lyme disease ...
Chagas disease
What are the gA protease bugs?
Strep pneumo ...
H. influenza ...
Neisseria
What do gA protease bugs cause?
sinusitis ...
otitis media ...
pneumonia ...
bronchitis
What are the simple gram negative bugs?
H. influenza ...
E. coli
What are the atypical (no cell wall) bacteria?
Chlamydia ...
Legionella ...
Ureaplasma ...
Mycoplasma
What is the only gram positive endotoxin? Listeria
What are the gram negative exotoxins?
H. influenza ...
Bordatella pertussis
What are the spore forming gram positive bacteria?
Bacillus anthracis ...
Clostridium botulinum ...
Clostridium tetani
What bugs cause walking pneumonia?
0-2 mo: Chlamydia pneumoniae ...
10-30 yo: Mycoplasma pneumoniae ...
>40 yo: Legionella pneumonia ...
ADS & premies: Pneumocystis jirovecii
What are the low complement bugs (cause
cryoglobulinemia)?
" AM HE" ...
nfluenza ...
Adenovirus ...
Mycoplasma ...
Hep B & C ...
EBV
What are the silver stainers?
H. pylori ...
Listeria ...
Vibrio ...
Campylobacter ...
Legionella ...
Pneumocystis ...
Bartonella henselae ...
Candida
What bacteria cause diarrhea <8 hrs after introduction?
"CBS" ...
Clostridium perfringens (holiday turkey/ham) ...
Bacillus cereus (fried rice) ...
Staph aureus (potato salad)
What are the gram negative capsules?
"Some Killers Have Pretty Nice Capsules" ...
Salmonella ...
Klebsiella ...
H. influenza B ...
Pseudomonas ...
Neisseria ...
Citrobacter
What is the gram positive capsule? Strep pneumoniae
What are the urease positive bugs?
"PPUNCHeS" ...
Proteus ...
Pseudomonas ...
Ureaplasma ...
Nocardia ...
Cryptococcus ...
H. pylori ...
Staph saprophyticus
What bugs cause monocytosis?
"STELS" ...
Syphilis ...
TB ...
EBV ...
Listeria ...
Salmonella
What are the Big Mama anaerobes?
Strep bovis ...
Bacteroides fragilis ...
C. melanogo-septicus ...
C. difficile
What bugs disrupt G proteins?
Pertussis: inhibits G_i
Cholera: stimulates G_s
E. coli: stimulates G_s
What bacteria cause UTs and prostatitis?
E. coli ...
Proteus ...
Klebsiella ...
Pseudomonas
What bug is associated with cat scratch? Bartonella henselae
What bug is associated with cat saliva? Pasturella multocida
What bug is associated with cat pee? Toxoplasmosis
What diseases are caused by the xodes Tick?
Lyme Disease: bull's eye lesion ...
Babesiosis: hemolytic anemia ...
Ehrlichiosis: puncture near eye
What bugs cause hospital abscesses?
Day 1-3: Staph aureus
Day 4-7: Strep viridans
Day >7: anaerobes
What kind of patients do Staph and Pseudomonas like to
attack?
DM ...
Cystic Fibrosis ...
Burn pts ...
Neutrophenic pts
What diseases have granulomas?
TB ...
sarcoidosis ...
syphilis ...
histiocytosis X
What diseases provide malaria protection?
Sickle Cell: AAs
G6PD: Mediterraneans
What bug causes multiple liver abscesses? Entamoeba histolytica
What bug causes multiple cerebral abscesses? Citrobacter
What disease has multiple lung aneurysms? Osler-Weber-Rendu
What bugs cause Loeffler syndrome?
"NASSA" ...
Necator americanus ...
Ancylostoma duodenale ...
Schistosomiasis ...
Strongyloides ...
Ascaris lumbricoides
What is the symptom of Loeffler syndrome? pulmonary eosinophilia
What is PE syndrome? Pulmonary nfiltrate with Eosinophilia
What diseases have PE syndrome?
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis ...
Loeffler's ...
Churg-Strauss
What disease does Coxsackie A cause? hand-foot-mouth disease
What diseases does Coxsackie B cause?
endocarditis ...
type DM
What bugs cause meningitis?
0-2 mo: GBS, E. coli, Listeria
>2 mo: Strep pneumo
10-21 yo: N. menigitidis
>21 yo: Strep pneumo
What are the CSF lab values for meningitis?
PMNs: bacteria
T cells and macrophages: non-bacterial
normal glucose: viral
What does the Hep B Core Ag tell you? gone before pt has symptoms (2 mo)
What does the Hep B Core Ab tell you? past infection
What does the Hep B Surface Ag tell you? current infection
What does the Hep B Surface Ab tell you? vaccination has occured
What does the Hep B e Ag tell you? tranmissibility/infectibility
What does the Hep B Ab tell you? low transmissibility
What antibody shows current Hep A? gM
What antibody shows past Hep A infection? gG
What types of people does Hep E like to infect?
pregnant women ...
Asians
What is associated with Staph aureus?
cellulitis ...
dairy products ...
gold pigment ...
endocarditis ...
styes (on eylid)
What is associated with Staph epidermidis?
central lines ...
VP shunts ...
white pigment
What is associated with Strep pyogenes?
ASO ...
hyaluronic acid capsule ...
rheumatic fever ...
PSGN ...
MCC: all throat infx, lymphangitis, impetigo, necrotizing
fasciitis, erysipelas, scarlet fever ...
2nd MCC: all other skin infx
What is associated with Propionibacterium acnes?
acne ...
progesterone => propionic acid
What is associated with Pasturella multicoda? cat/dog saliva => cellulitis with lymphadenitis
What is associated with Hemophilus aegyptus? swollen eyeball with pus
What is associated with Francisella tularenis?
ulcer at rabbit or deer tick bite site ...
Tx: streptomycin
What is associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
otitis externa ...
whirlpool folliculitis ...
ADP ribosylates EF-2
What is associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae?
otitis media ...
red buldging tympanic membrane
What is associated with Fusobacterium?
painful mouth ulcers ...
gum pus ...
Vincent's angina
What is associated with Strep mutans? dental cavities
What is associated with Strep viridans?
subacute bacterial endocarditis ...
green pigment
What is associated with Strep salivarius? cold agglutinin test
What is associated Corynebacterium diphtheriae?
chinese letters ...
gram positive ...
gray pseudomembrane ...
suffocation ...
acquires exotoxin from a virus via transduction ...
ADP ribosylates EF2 ...
stops cell synthesis ...
heart block ...
Elek test
What is associated with Strep pneumoniae?
gram positive diplococci ...
rusty sputum ...
gA protease ...
vaccine
What is associated with H. influenza?
gram negative pleomorphic rod ...
chocolate agar with factors V and X ...
Type A:
non-encapsulated ...
non-invasive ...
MCC sinusitis, otitis, bronchitis
Type B:
encapsulated (5C-ribose capsule) ...
invasive ...
gA protease ...
MCC meningitis, epiglottitis, sepsis ...
vaccine (capsule)
What is associated with N. catarrhalis? loves mucus - attacks respiratory tract
What is associated with Chlamydia psittaci? parakeets and parrots
What is associated with Chlamydia pneumonia?
staccato coughing ...
elementary and reticulate bodies
What is associated with Mycoplasma pneumonia?
bullous myringitis ...
ground glass CXR ...
P1 protein
erythema multiforme
What is associated with Legionella pneumonia?
air conditioning ducts ...
silver stains lung ...
Charcoal Yeast Extract Agar
What is associated with Pneumocystis jiroveciinia?
ADS/premies ...
rusty sputum ...
silver stains lung ...
inc LDH ...
Tx: steroids
What is associated with Clostridium botulinum?
canned food ...
honey ...
inhibits ACh release ...
respiratory failure ...
stool toxin ...
Tx: penicillin
What is associated with Clostridium tetani?
rusty nail wounds ...
inhibits Gly release ...
respiratory failure ...
risus sardonicus ...
tennis racquet shape
What is associated with Bordatella pertussis?
whooping cough ...
ADP ribosylates G_i
What is associated with Bacillus anthracis?
black eschar ...
woolsorter's lung disease ...
D-glucose ...
boxcar-like spore ...
Tx: ciprofloxacin
What is associated with H. pylori duodenal ulcers
What is associted with Salmonella?
raw chicken and eggs ...
turtles ...
rose typhoid spots ...
sickle cell osteomyelitis
What is associated with Campylobacter jejuni?
raw chicken and eggs ...
very bloody diarrhea ...
inactivated by gastric juice ...
Guillain-Barre ...
seagull-shape
What is associated with Clostridium perfringens?
holiday ham and turkey ...
DM gas gangrene ...
soil/feces
What is associated with Bacillus cereus?
fried rice ...
preformed toxin
What is associated with Listeria monocytogenes?
raw cabbage, hot dogs, spoiled milk ...
migrant workers ...
heart block ...
meningitis ...
abortions
What is associated with Vibrio parahaemolyticus? raw fish
What is associated with Actinomyces?
face fisulas ...
sulfur granules
What is associated with Vibrio vulnificus?
raw oysters ...
cellulitis in swimmer's cuts
What is associated with Shigella?
day care outbreaks ...
seizures ...
destroys 60S ribosome ...
infects M cells
What is associated with Vibrio cholera?
rice water diarrhea ...
ADP ribosylates Gs
What is associated with Clostridium difficile?
explosive diarrhea ...
pseudomembranous colitis
What is associated with Yersinia enterolitica?
presents like appendicitis + Reiter's ...
bloody diarrhea
What is associated with Strep bovis?
colon cancer ...
black pigment
What is associated with Clostridium septicum? colon cancer
What is associated with ETEC?
traverler's diarrhea ...
rice-water
What is associated with EHEC?
hemorrhagic diarrhea ...
renal failure
What is associated with EEC?
inflammatory diarrhea ...
loose stool
What is associated with EPEC?
pathogenic ...
newborn diarrhea
What is associated with E. coli?
raw hamburger ...
ADP ribosylates G_s ...
verotoxin ...
HUS
What is associated with Proteus mirabilis?
staghorn calculus ...
UT ...
Tx: norfloxacin
What is associated with Klebsiella pneumonia?
alcoholics ...
current jelly sputum ...
UT ...
lung fissures
What is associated with Staph saprophyticus? young and college girl's UTs
What is associated with Enterococcus?
UT ...
infective endocarditis post-G/GU procedure
What is associated with N. meningitides?
DC ...
pili ...
releases toxin in log phase
What is associated with Brucella?
farmers/vets ...
spiking fever 5x/day ...
animal placentas
What is associated with R. rickettsii?
ticks ...
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
What is associated with Coxiella burnetti?
dusty barn ...
Q fever
What is associated with Yersinia pestis?
rats, fleas ...
bubonic plague
What is associated with Bartonella henselae?
cat scratch ...
single painful lymph node ...
silver stains
What is associated with Bacteroides fragilis?
post-op bowel abscess ...
grows in blood clots
What is associated with Chlamydia trachomatic? neonatal inturned eylashes - corneal ulcers
What is associated with Neisseria gonorrhea?
pili ...
urethritis ...
tenovitis ...
septic arthritis
What bugs cause Reiter's syndrome?
"SYCC with sore joints" ...
Shigella ...
Yersinia ...
Chron's ...
BD ...
Chlamydia
What are the comma shaped bugs?
Vibrio ...
Campylobacter ...
Listeria (g+, curved) ...
H. pylori
What bug looks like chinese letters? Corynebacteria
What is the crescent shaped protozoa? Giardia lamblia
What causes painful genital lesions?
herpes ...
chancroid (H. ducreyi) ...
Lymphogranuloma venerum ...
Lymphogranuloma inguinale
What are the hookworms?
"NEAT ASS" ...
N: Necator americanus ...
E: Enterocius vermicularis ...
A: Ankylostoma duodenale ...
T: Trichuris triturium ...
A: Ascaris lumbricoides ...
S: Strongyloides ...
S: Schistosomyces
f blood cultures grow S. bovis or C. melanogo-septicus,
what must be ruled out?
colon cancer
What is the encapsulated yeast? Cryptococcus
What are the live vaccines?
measles ...
mumps ...
rubella ...
oral polio ...
rotavirus ...
small pox ...
BCG (TB) ...
yellow fever ...
varicella
What bugs cause rashes of the palms and soles?
TSS (toxic shock syndrome) ...
rocky mountain spotted fever ...
Coxsackie A (hand, foot, and mouth dz) ...
kawasaki ...
scarlet fever ...
syphilis ...
Staph scalded skin ...
Streptobacillus moniliformis
What cancer is HPV related to? cervical cancer
What cancer is EBV related to? lymphoma
What cancer is Hep B and Hep C related to? liver carcinoma
What cancer is HHV (HV) related to? Kaposi's sarcoma
What bug causes rust colored sputum? Strep pneumo (pneumococcus)
What is the most common infection of shunts and central
lines?
Staph epidermidis
How do you tell catalase positive staphylococci apart?
pigment ...
aureus = gold ...
epidermidis = white ...
saprophyticus = none
What are the oddities about Listeria?
only g+ with endotoxin ...
crosses placenta ...
Lipid A is toxic part ...
causes granulomas ...
causes sepsis in neonates
What are the actions of E. coli?
supplies vit K, biotin, folate, pantothenic acid ...
aids in B12 absorption
What are the most common causes of croup and
bronchiolitis?
parainfluenza ...
RSV (MCC in ER) ...
adenovirus ...
influenza
What are the acid fast organisms?
mycoplasma ...
nocardia (partially g+) ...
cryptosporidium (partially protazoa)
What are the bacteria with elastase?
Staph aureus ...
Pseudomonas
What are the bacteria with toxins that inhibit EF-2?
Pseudomonas ...
Diphtheria
What are the phage mediated toxins?
Salmonella ...
Botulinum ...
Erythrogenic toxin ...
Diphtheria
What are the three toxins of bacillus?
lethal factor ...
protective factor ...
edema factor
What are the Group D Streptococci?
viridans (green pigment, SBE) ...
mutans (cavities) ...
saguis ...
salivaris ...
bovis
What are the most common causes of airway infections?
#1 - Strep penumo ...
#2 - H. influenza ...
#3 - N. meningitidis
What causes multiple cerebral abscesses in newborns? Citrobacter
What is the most common cause of osteomyelitis? Staph aureus
What is the most common cause of infection in burn pts
in the first week?
Staph aureus
What are the gram negatives that are strict anaerobes?
H. flu ...
Neisseria
What are the herpes viruses?
- oral ...
- genital ...
- VZV ...
V - EBV ...
V - CMV ...
V - roseola ...
V - Pityriasis rosea ...
V - Kaposi's sarcoma
What diseases can get picked up during delivery?
Group B strep ...
Strep pneumo ...
Herpes ...
N. gonorrhea ...
Chlamydia
What are the MCC of pneumonia in kids 6 wks to 18 yo?
RSV (infants only) ...
Mycoplasma ...
Chlamydia ...
Strep pneumo
What are the MCC of pneumonia in people 18 to 40 yo?
Mycoplasma ...
Chlamydia ...
Strep pneumo
What are the MCC of pneumonia in people 40 to 65 yo?
Strep pneumo ...
H. influenza ...
Anaerobes ...
viruses ...
Mycoplasma
What are the MCC of pneumonia in the elderly?
Strep pneumo ...
viruses ...
anaerobes ...
H. influenza ...
g- rods
What are Roth Spots? septic emboli in the eye
What are Janeway Lesions?
septic emboli in the palms and soles ...
hemorrhagic ...
non-tender
What are Osler's Nodes?
septic emboli in the finger and toes ...
raised lumps ...
painful
What are Splinter Hemorrhages? septic emboli in the fingernails
What is a Mycotic Aneurysm? septic emboli in the brain
What is the MC infection in HV? CMV
What is the MC pulmonary infection (CD 4 ~ 200) PCP
n HV, what is P41? surface marker to assist attachment to CD4
n HV, what is GP120? attachment to CD4
n HV, what does reverse transcriptase do? transcription
n HV, what does pol do? integration
n HV, what are p17 and p24?
non-glycosylated peptide chain ...
Ag (Gag) for Ab therapy
n HV, what are CCR5 and CCR4?
co-receptor in HV transmission ...
defective CCR5 or CCR4 gives some resistance
What is a normal CD4 count?
800-1200 in adults ...
up to 1500 in kids
What do you give to an HV pt with a CD4 count <500
(750 in kids)?
2 nucleoside inhibitors ...
1 protease inhibitor
What do you give to an HV pt with a CD4 count <200
(ADS)?
add treatment for PCP (Bactrim)
What do to you give to an ADS pt with a CD4 count
<100?
add treatment for MAC (Azithromycin)
What drugs act as haptens on platelets?
aspirin ...
heparin ...
quinidine
What drugs act as haptens on RBCs?
PAD PACS ...
P: penicillamine ...
A: alpha-methyl dopa ...
D: dapsone ...
P: PTU ...
A: antimalarials ...
C: cephalosporins ...
S: sulfa drugs
What drugs wipe out the bone marrow?
ABCV ...
A: AZT ...
B: benzene ...
C: chloramphenicol ...
V: vinblastine
What drugs wipe out granulocytes?
carbamazapine ...
clozapine ...
ticlopidine
What drugs case pulmonary fibrosis?
BBAT ...
B: busulfan ...
B: bleomycin ...
A: amiodarone ...
T: tocainide
What drugs dilate veins and arteries? nitrates and ACE-
What are the anti-inflammatory actions of steroids?
stabilizes: mast cells and endothelium
inhibits: macrophage migration and platelets
kills: T cells and eosinophils
What do opioid mu receptors cause? mental side effects
What do opioid kappa receptors cause? pain relief
What drugs have sulfur in them?
ACE- ...
dapsone ...
celecoxib ...
loop diuretics ...
thiazide diuretics ...
sulfonylureas ...
sulfonamides
What are the short acting DM Type drugs?
lispro ...
aspart ...
regular
What are the intermediate acting DM Type drugs?
NPH ...
lente
What are the long acting DM Type 1 drugs?
glargine ...
ultralente
What drugs cause SLE?
HPPPE ...
H: hydralazine ...
: NH ...
P: procainamide ...
P: phenytoin ...
P: penicillamine ...
E: ethosuximide
What antibody is associated with drug induced lupus? anti-histone Ab
What drugs cause labor induction?
PGE2 - ripens cervix ...
oxytocin - increases contractions ...
pitocin - increases contractions
What drugs halt labor (tocolytics)
hydration - stop ADH (oxytocin) ...
MgSO4 - decreases contractions ...
terbutaline - decrease contractions ...
ritodrine - increase edema
What drugs can be nephrotoxic? water soluble drugs
What drugs can be hepatotoxic? fat soluble drugs
How do you treat acetaminophen overdose? N-acetylcysteine
How do you treat benzodiazepine overdose? flumazenil
How do you treat beta-blocker overdose? glucagon
How do you treat calcium channel blocker overdose? calcium chloride + glucagon
How do you treat CO poisoning? 100% O2
How do you treat Cu, Gold, CD, Mercury, Arsenic
poisoning?
penicillamine
How do you treat cyanide poisoning? amyl nitrite
How do you treat ethylene glycol, methanol overdose?
ethanol ...
fomepizole
How do you treat Fe overdose? deferoxamine
How do you treat fibrinolytic overdose? aminocaproic acid
How do you treat heparin overdose? protamine sulfate
How do you treat lithium overdose? sodium polystyrene sulfonate
How do you treat nitrite overdose? methylene blue
How do you treat organophosphate poisoning? atropine + pralidoxime
How do you treat opioid overdose? naloxone
How do you treat lead poisoning? succimer
How do you treat salicylate overdose? charcoal
How do you treat TCA overdose? bicarbonate (prevent arrhythmias)
How do you treat theophylline overdose? esmolol
How do you treat warfarin overdose? vitamin K
What drugs cause myositis?
RPS ...
R: rifampin ...
: NH ...
P: prednisone ...
S: statins
What drugs cause disulfiram reactions?
metronidazole ...
cephalosporins ...
procarbazine
What drugs cause dysgeusia?
metronidazole ...
clarithromycin ...
lithium
What antibiotics are in a triple antibiotic?
bacitracin ...
neomycine ...
polymyxin D
What is the first dose treatment for chlamydia? azithromycin
What are the first dose treatments for gonorrhea?
ceftriaxone ...
cefixeme ...
cefoxitin ...
ciprofloxacin ...
ofloxacin ...
gatifloxacin
What bugs are treated with vancomycin?
MRSA ...
Staph epidermidis ...
enterococcus
What is the treatment for malaria?
quinine (tinnitus) ...
mefloquine (good liver penetration) ...
primaquine (prevents relapse, high bug resistance) ...
chloraquine (kills RBCs)
What is the mean? average
What is the median? middle value
What is the mode? most frequent value
What does sensitivity tell you? people that have the disease with a positive test
What does specificity tell you? people that don't have the disease with a negative test
What does positive predictive value tell you? probability of having a disease with a positive test
What does negative predictive value tell you? probability of not have a disease with a negative test
What does incidence tell you? new cases (rate per unit time)
What does prevalence tell you? total cases (at one time)
What does the odds ratio tell you? diseased are x times more likly to see risk factor
What does a confidence interval = 95% tell you? 95% sure it lies within the interval
What does relative risk tell you? risk of getting a disease with known exposure
What is NNT? number needed to treat to change 1 life
What does a p value < 0.5 tell you? random chance that you will be wrong 1 time out of 20
What does a null hypothesis tell you? nothing happened
What does power tell you? probability of detecting a true intervention
What is a type error?
P value error ...
false negative ...
"too optimistic"
What is a type error?
power error ...
false positive ...
"too pessimistic"
What is accuracy?
validity ...
"truth"
What is precision?
reliability ...
"keep making the same mistake"
What are the phases of clinical trials?
Phase - toxicity ("hurt pt?") ...
Phase - efficacy ("help pt?") ...
Phase - comparison ("any better?") ...
Phase V - post-marketing surveillance ("can they screw it
up?")
What is a cohort study?
prospective study that provides incidence (new cases) ...
uses relative risk
What is a case control study?
retrospective study that provides prevalence (total cases)
...
uses odds ratio
What is a cross sectional study? provides a prevalence "snapshot"
What is a case report? describes an unusual pt
What is a case series report? describes several unusual pts
What are consensus panels? panel of experts provide a recommendation
What is clinical wisdom? " think ..." paper
What is a meta-analysis? tries to combine data from many trials
What does pain radiating to the jaw indicate? M
What does pain radiating to the left shoulder indicate? M or spleen rupture
What does pain radiating to the scapula indicate? gall bladder problems
What does pain radiating to the trapezius indicate? pericarditis
What does pain radiating to the groin indicate? ureter stones or osteoarthritis of the hip
What is Blumberg's sign? rebound tenderness => peritonitis
What is Brudzinski's sign? bend neck, see knee flexion => meningitis
What is Chadwick's sign? puple vagina => pregnancy
What is Chandelier sign? cervical motion tenderness => PD
What is Chovstek's sign? tap facial nerve => muscle spasm
What is Courvoisier's sign? palpable gall bladder => cancer (pancreatic)
What is Cozen's sign?
dorsiflex wrist causes pain => lateral epicondylitis ...
"tennis elbow"
What is Cullen's sign? bleeding around umbilicus => hemorrhagic pancreatitis
What is Gottran's sign? scaly patches on MCP, PP joints => dermatomyositis
What is Hamman's sign?
crunching sound on auscultation => subcutaneous
emphysema
What is Homan's sign? pain in calf with dorsiflexion => DVT
What is Kehr's sign? left shoulder pain => spleen rupture
What is Kernig's sign? flexing knee causes resistance or pain => meningitis
What is Kussmaul's sign? big neck veins with inspiration => pericardial tamponade
What is Levine sign? hold clenched fist over sternum => angina
What is Murphy's sign?
pressed gallbladder causes pt to stop breathing =>
cholecystitis
What is Obturator sign? inward rotation of hip causes pain => appendicitis
What is Phalen's test? flexing wrists for 60s causes paresthesia => carpal tunnel
What is Psoas sign? extending hip causes pain => appendicitis
What is Rovsign's sign? palpating LLQ causes RLQ pain => appendicitis
What is Tinel's test?
percussing median nerve causes 1st-3rd finger pain =>
carpal tunnel
What is Trousseau's sign?
BP check causes carpal spasm => migratory
thrombophlebitis
What is Turner's sign? bleeding into flank => hemorrhagic pancreatitis
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CardiacDokumen23 halamanCardiacLauren LaMonicaBelum ada peringkat
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtDari EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Examinarea Clinică in Afecţiuni Ale Aparatului CardiovascularDokumen49 halamanExaminarea Clinică in Afecţiuni Ale Aparatului CardiovascularFranceska LtkBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisDari EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Cardiovascular SystemDokumen51 halamanThe Cardiovascular SystemAdeMumungBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDokumen43 halamanCongenital Heart DiseaseSalman Majid100% (1)
- Types of Cardiovascular Disease in The HeartDokumen7 halamanTypes of Cardiovascular Disease in The Heartissey1652Belum ada peringkat
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideDari EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuidePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Cardiovascular SystemDokumen43 halamanMedical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Cardiovascular Systemsarah morleyBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiology Qs 7th SemesterDokumen65 halamanCardiology Qs 7th SemesterJoshua-Majid ShahbaziBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Terminology 2Dokumen12 halamanMedical Terminology 2azzazy040Belum ada peringkat
- STROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesDari EverandSTROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac SystemDokumen5 halamanCardiac SystemTanya TuckerBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to Vascular Diseases, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDari EverandA Simple Guide to Vascular Diseases, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- CardiologyDokumen52 halamanCardiologyusmani_nida1Belum ada peringkat
- Rheumatic FeverDokumen12 halamanRheumatic FeverkeikoVBelum ada peringkat
- WWW - Natures.Ir: More Free Usmle, Mccee, Mcqe and Amq FlashcardsDokumen0 halamanWWW - Natures.Ir: More Free Usmle, Mccee, Mcqe and Amq FlashcardsMohammed FaragBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture CardiologyDokumen65 halamanLecture CardiologyshinhyejjBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines For Examination of Cardiovascular System: Bendehiba Latroche, MD, DIS, DIUDokumen22 halamanGuidelines For Examination of Cardiovascular System: Bendehiba Latroche, MD, DIS, DIUkskamkalpanaBelum ada peringkat
- IschemicHeartDisease LectureDokumen64 halamanIschemicHeartDisease Lectureahmad usmanBelum ada peringkat
- Med SurgDokumen62 halamanMed SurgJean Soriano98% (65)
- Cardiac Function Tests Anatomy of The HeartDokumen8 halamanCardiac Function Tests Anatomy of The HeartJosiah BimabamBelum ada peringkat
- Jansenkoh MRCP PacesDokumen209 halamanJansenkoh MRCP PacesBob Yong83% (6)
- CK PediatricsDokumen101 halamanCK PediatricsMayoBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiology DR Osama MahmoudDokumen138 halamanCardiology DR Osama MahmoudIsmail Habib100% (4)
- Coronary Artery Diseases: Ms Flavi Almeida 1 Year MSC Zukekha Nursing College ManagaloreDokumen109 halamanCoronary Artery Diseases: Ms Flavi Almeida 1 Year MSC Zukekha Nursing College ManagalorePriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Heart and CirculationDokumen16 halamanHeart and CirculationPRINCESS HOPE TAHURABelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDokumen21 halamanCongenital Heart DiseasesfahmiBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular Physical TherapyDokumen204 halamanCardiovascular Physical Therapydivyam2008Belum ada peringkat
- CVS McqsDokumen5 halamanCVS McqsNishanthy PirabakarBelum ada peringkat
- Heart: Exam 2Dokumen46 halamanHeart: Exam 2ChristinePagsisihanBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDokumen43 halamanCongenital Heart DiseaseSanjanaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular and Heart DiseaseDokumen65 halamanCardiovascular and Heart DiseasesarazalnoonBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Review Block 1Dokumen32 halamanAnatomy Review Block 1ngBelum ada peringkat
- Tabel SindroameDokumen4 halamanTabel SindroameAndreea RaduBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiology A. Woo PDFDokumen52 halamanCardiology A. Woo PDFiuliBelum ada peringkat
- The Mysterious Connection Between Aortic Insufficiency and Head BobbingDokumen11 halamanThe Mysterious Connection Between Aortic Insufficiency and Head BobbingMai LoBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular Disease TumoursDokumen9 halamanCerebrovascular Disease TumoursCindy Van WykBelum ada peringkat
- Tiki Taka AHMDDokumen378 halamanTiki Taka AHMDMuhammad NajjarBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To Cardiovascular DiseaseDokumen23 halamanApproach To Cardiovascular DiseasesanjivdasBelum ada peringkat
- TiKa TaKa PediatricsDokumen86 halamanTiKa TaKa PediatricsEmad MerganBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio and Hema - DR PueyoDokumen161 halamanCardio and Hema - DR Pueyoapi-3735995100% (2)
- Cardiovascular SystemDokumen74 halamanCardiovascular Systemاسامة محمد السيد رمضانBelum ada peringkat
- StrokeDokumen66 halamanStrokeJoshua Smith100% (1)
- 19 Cardiac DisordersDokumen51 halaman19 Cardiac DisordersChessie Garcia100% (1)
- 4 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Cardiology - and - Cardiovascular - SurgeryDokumen60 halaman4 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Cardiology - and - Cardiovascular - Surgeryqobsar100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Shoutouts: When She Says You SayDokumen7 halamanCardiovascular Shoutouts: When She Says You SayGbotemi AlaladeBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular Physical TherapyDokumen206 halamanCardiovascular Physical TherapyJuanitoCabatañaLimIII100% (2)
- CVS Exam Routine & Script: KoilonychiaDokumen4 halamanCVS Exam Routine & Script: Koilonychiajoelh9Belum ada peringkat
- Lecturio Cardiovascular Physical ExaminationDokumen10 halamanLecturio Cardiovascular Physical ExaminationPranjali WeladiBelum ada peringkat
- 42 Kelainanpatologi Cardiovasc Dr. DianDokumen126 halaman42 Kelainanpatologi Cardiovasc Dr. DianSurya ArhBelum ada peringkat
- Cardaic DrugsDokumen57 halamanCardaic DrugsJyoti KathwalBelum ada peringkat
- Cornell Notes 1Dokumen3 halamanCornell Notes 1api-330057205Belum ada peringkat
- Membranes L4 MSDokumen19 halamanMembranes L4 MSzaynabaziz52Belum ada peringkat
- RedroveractivityDokumen3 halamanRedroveractivityapi-279296553Belum ada peringkat
- Fa AbsrptionDokumen57 halamanFa AbsrptionMuhammad FaheemBelum ada peringkat
- ORGANISASI SELULER - Struktur Dan Fungsi-2017 PDFDokumen58 halamanORGANISASI SELULER - Struktur Dan Fungsi-2017 PDFMantanindah 0206Belum ada peringkat
- Cambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDokumen16 halamanCambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International Educationsubaita arwaaBelum ada peringkat
- 3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFDokumen23 halaman3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFtess_15Belum ada peringkat
- Glucose Transporters-Structure Function and Consequences of DeficiencyDokumen10 halamanGlucose Transporters-Structure Function and Consequences of DeficiencyGerman GodiBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry 214 Multiple Choice Question PracticeDokumen14 halamanBiochemistry 214 Multiple Choice Question PracticeabasifrekeetefiaofficialBelum ada peringkat
- B1 RevisionDokumen17 halamanB1 RevisionPierre BrocasBelum ada peringkat
- Viva in Medical Physiology 2nd (Kenneth) PDFDokumen267 halamanViva in Medical Physiology 2nd (Kenneth) PDFThida100% (5)
- Biology 2A03: Introduction To Physiology & HomeostasisDokumen409 halamanBiology 2A03: Introduction To Physiology & Homeostasisampedm100% (8)
- 2 Biomembran 2020Dokumen28 halaman2 Biomembran 2020ezebelluciBelum ada peringkat
- Membrane Transport: February 2016Dokumen24 halamanMembrane Transport: February 2016Aisya KhoirunnisaBelum ada peringkat
- Physeo WorkbookDokumen268 halamanPhyseo WorkbookCoda Maje100% (1)
- Unit2 - Membrane Structure and FunctionDokumen54 halamanUnit2 - Membrane Structure and FunctionAlbert Chon100% (1)
- Unit 1 SBI4U Exam Review June 2011Dokumen3 halamanUnit 1 SBI4U Exam Review June 2011Shivi YogarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Organization of Human Body Tutorial 2Dokumen118 halamanStructural Organization of Human Body Tutorial 2Mukhtar Ahmad Rufa'eyBelum ada peringkat
- Year 9 Science Revision BookletDokumen25 halamanYear 9 Science Revision BookletLabeenaBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Biology. Chapter Tests With Answer Key General and AdvancedDokumen250 halamanModern Biology. Chapter Tests With Answer Key General and AdvancedWllatakam100% (7)
- 4 - Physiology Main Handout Oct 2023Dokumen99 halaman4 - Physiology Main Handout Oct 2023Trisha Anne WacasBelum ada peringkat
- 7.transport in Plants NotesDokumen18 halaman7.transport in Plants NotesAhmed Noor100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structure & Functions-1 PDFDokumen17 halamanChapter 3 - Cell Structure & Functions-1 PDFSTEM 8 PRODUCTIONSBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingDokumen64 halamanLecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingDiabyBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1.1 - Cell TheoryDokumen6 halamanTopic 1.1 - Cell Theoryjahajaha_svensson609Belum ada peringkat
- HSBDokumen10 halamanHSBwilmarub71% (17)
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Dokumen6 halamanAP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Omar LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Cells The Basic Unit of LifeDokumen20 halamanCells The Basic Unit of LifeJyra Bianca CabalquintoBelum ada peringkat
- (284704265) 1.2 Fluid Mosaic ModelDokumen16 halaman(284704265) 1.2 Fluid Mosaic ModelNurul Hana OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Properties and Functions of Water BSB 111Dokumen56 halamanProperties and Functions of Water BSB 111Manak ThakurBelum ada peringkat