Ámbito Comunicación - Inglés
Diunggah oleh
Raquel Marcos-alberca CalongeJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ámbito Comunicación - Inglés
Diunggah oleh
Raquel Marcos-alberca CalongeHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CEPA E.
Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Mdulo IV ESPAD
mbito de la Comunicacin.
INGLS.
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Bloque 10. Tema 1: Future plans
NDICE
1. Welcome Back!!! 2. Futuro 2.1. Futuro con WILL 2.2. Futuro con Going to, futuro de intencin 2.3. Presente Simple con idea de futuro 2.4. Presente Continuo con idea de futuro 3. Pronombres interrogativos 4. Autoevaluaciones 5. Tareas
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
1. Welcome Back!!!
Ahora vas a leer una conversacin entre Karen Smith y su amiga espaola Marta. Lee con atencin el texto e identifica las formas de futuro que vers en l y que encontrars explicadas a continuacin. Hay varias formas, aunque todas estn resaltadas en negrita. Karen: Marta: Karen: Hi Marta! Hi Karen! Whats up? Its very hot today and Im thirsty. Shall we have a beer? Marta: A beer? No, thanks. I dont like beer, but I will have a coke. Karen: Well, Marta, what are your plans for next year? Marta: Karen: Marta: Karen: Marta: Karen: Marta: Karen: I am going to study at university. Here in Toledo? I dont know. I will stay here in Toledo or I will go to Madrid. Oh, and what are you going to study? I am going to study Medicine. Is there a Medicine school in Toledo? There will be one soon. What about you, Karen? Me? Oh, I will I will be a mother next year. Marta: Really? Youre joking!! Karen: No, Im not. I am pregnant and I am going to have a baby in 6 months. Marta: Karen: Marta: Karen: Wow! Congratulations! Thats very good news. Thank you! Are you going to work? Of course! I am going to be a teacher back in the USA. I will teach Spanish or Spanish Literature, Im not sure. Marta: Karen: Thats very interesting! Well, and what are your plans for next weekend?
3
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Marta: Karen:
Im going to a concert on Friday. Look! I have the tickets here. Im visiting a friend in Salamanca and Im going by train. Marta: What time does it leave from Toledo?
Karen: Marta: Karen: Marta:
It leaves at 5 in the afternoon. Ok, I will go to the station with you, mommy! You are a very good friend, Marta (laughing) And you will be an excellent mother! (laughing too)
Vocabulario
Whats up? Congratulations Qu tal? Enhorabuena
What about you? Y t, qu? Very good news Youre joking! The train leaves I am pregnant Laughing Muy buenas noticias
Ests de broma! El tren sale Estoy embarazada Riendo
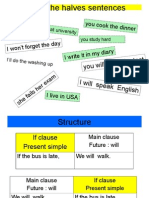
2. Futuro
1. Futuro simple o futuro con WILL
Afirmativa: Sujeto + will + verbo + resto de la oracin Will con todos los sujetos (I / you / he / she / it / we / they) + infinitivo sin to Will se puede contraer con el sujeto: ll I will -> Ill / You will -> Youll I will (I'll) clean the car this afternoon You will (you'll) go to the bank tomorrow They will (they'll) be here in a couple of minutes The boys will forget to do their homework. Please remind them! Negativa: Sujeto + will not (wont) + verbo + resto de la oracin Will not puede contraerse en wont
4
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
I will not (won't) watch that film on TV They will not (won't) give Sheila a present I wont be at home next week Sandra wont pass her exams Interrogativa: Yes / no questions: Will + sujeto + verbo + resto de la oracin? Will they work here next year? Yes, they will / No, they wont Will she go to London next summer? Yes, she will / No, she wont Will Bessie stay in a hotel? Yes, she will Will Peter go shopping ? Yes, he will Will they have something to drink? Short answers: Yes, pronombre will: Yes, I / you / he/ she / it / we / they will No, pronombre wont: No, I / he / she / it / we / they won't Preguntas con who o what como sujeto de la oracin Wh-word + will + verb + rest of sentence? Who will be the main actor? John will walk the dog -> Who will walk the dog? Lesley will buy the flowers -> Who will buy the flowers? The children will visit their grandparents -> Who will visit their grandparents? The alarm clock will wake us -> What will wake us? The bus will be late -> What will be late? That car will crash -> What will crash? Preguntas con el interrogativo en funcin de complemento de la oracin wh-word + will + subject + verb + rest of sentence? What will we have for dinner?
5
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Who will they meet at the party? They will ride round London on a double-decker bus-> Where will they ride on a double-decker bus? They will watch the changing of the guard outside Buckingham Palace-> What will they watch outside Buckingham Palace? They will go to the West End on Tuesday -> When will they go to the West End? Steve will see Pat at the cinema -> Who will Steve see at the cinema? USOS DEL FUTURO CON WILL Decisiones de futuro sin planificar, decididas que se toman en el momento de hablar The bell is ringing. I'll go and open the door What would you like to drink? Ill have a cup of coffee Did you phone Mary? No, I forgot. Ill phone her now Predicciones sobre el futuro sin evidencia en el presente: Mark will win the race Chris will pass the exam easily This time next year, Ill be in Japan Shell be twenty next Friday Promesas: I will bring you some chocolate Thanks for the money. Ill give it back to you on Monday Amenazas: You will be sorry! You'll be punished Ofrecimientos: That bag looks heavy. I'll help you to carry it.
6
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Dont worry. Ill do the washing up Peticiones: Will you lend me 100 ? No, I won't Will you help me with my homework? Acuerdo: Can I have my book back? Of course. Ill bring it back this afternoon Con determinadas expresiones: Ill probably be late this evening I havent seen Carol today. I expect shell phone this evening Dont worry about the exam. Im sure youll pass Do you think Sarah will like the present we bought her? I wonder what will happen EJERCICIOS Ex. 1.- Derek is 18 years old now. What will he be like in 10 years from now? How will his life be different then? Complete what Derek says using will/won't. Example: I hope I'll have a job in 10 years' time. 1 I hope / have a job in 10 years time. 2 Perhaps I / have a good job. 3 I probably | not | be very rich. 4 I / not | look the same as I do now. 5 I think I / be married. 6 I / probably | have children. Ex. 2.- Complete the sentences using I'll or I won't and the verbs: go answer not go put on not have lend wait Example: I'm tired, I think I'll go to bed early tonight. 1 'I haven't got any money.' 'Haven't you? Oh,________ you some if you like.'
7
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
2 'The telephone is ringing.'
'Oh,_______ it.'
3 I'm a bit cold. I think _______ a sweater. 4 'Would you like something to eat?' you. I'm not very hungry.' 5 'I'm going out for a walk.' _______until it's stopped.' Ex. 3.- Peter wants to see Sally. He is talking to her on the telephone. Complete the conversation using will/won't and one of these verbs: be (x5); end; meet; see; finish (x2); Peter: Will you be at home this evening, Sally? Sally: W ell, I'm working late. I don't expect I ________until after 9.00, so I _______home until quite late. Peter: Oh, I see. W hat about tomorrow? _______ (you) free for lunch? Sally: No, I'm afraid I__________ in a m eeting at lunchtime. Peter: W hat time do you think _________ (the meeting)? Sally: I'm not sure, but it probably__________ before 2.00. Listen, Peter. W hy don't we meet for a coffee after work tomorrow evening? Peter: W hat time___________________(you) fin ished tomorrow? Sally: I ________free by 6.00. Peter: All right. I ____________ you at your office at 6.00, then. Sally: Right. I ______________ you then. 'It's raining.' 'Oh, is it? Well, _______out now, then, 'I ___________anything at the moment, thank
2.- Futuro con Going to, futuro de intencin
Presente continuo de "go" seguido de TO + INFINITIVO Afirmativa I am going to examine him first The ambulance is going to be here soon You are going to open the door Dr Newton is going to get into his car Mr. Lester is going to answer the phone
8
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
We are going to have lunch They are going to change trains in Reading Interrogativa: Are you going to smoke a cigarette? Is it going to rain? Is Arthur going to bring anything to the scene of the accident?
Who is going to drive Mrs. Newton home? What is going to happen? He is going to fall into the hole
What are you going to do this evening? Who are you going to invite? Where are they going to live? What is she going to wear at the party? When is your father going to leave on holiday? How are you going to get in contact with Malcolm?
Short answers: las mismas del presente continuo Negativa: Dr Newton is not going to take Bruce out of the car I'm not going to work They are not going to phone the police USOS DEL FUTURO CON GOING TO Decidido de antemano I have bought some bricks and I'm going to build a garage. Tom has borrowed the axe. He's going to chop some wood Why are you taking down all the pictures? I'm going to repaper the room.
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Condiciones actuales nos llevan a pensar que algo va a ocurrir: prediccin I feel terrible. I think Im going to be sick Our team is in the lead. They are going to win The sky is very dark, it is going to rain. Those people are going to get wet Hurry up! Its getting late. You are going to miss the bus I AM DOING // I AM GOING TO DO Cuando hablamos de lo que tenemos intencin de hacer, podemos usar tanto presente continuo, como la forma going to What time are you meeting Ann this evening? = What time are you going to meet Ann this evening? Im leaving tomorrow// Im going to leave tomorrow Ive got the plane ticket Why are you sitting in the armchair? Im watching a film on TV // Im going to watch The windows are dirty. Yes, I know. Im going to clean them later // Im cleaning them later) I dont like this neighbourhood. Tomorrow Im going to look for a new flat. // Im looking for No podemos usar presente continuo para hacer predicciones sobre el futuro: Our team are going to win (NO our team are winning) It is going to rain. (It is raining) Those people are going to get wet (Those people are getting wet) You are going to miss the bus (youre missing the bus) EJERCICIOS Ex. 4.- What is going to happen in the pictures?
Example: She's going to answer the phone.
10
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Ex. 5.- Completa usando going to y los verbos entre parntesis. Example: 'I've made up my mind I'm going to change (change) my job.' 'What are you going to do (you | do)?' 'I'm not sure yet.' 1 'What_____________________ (you | wear) at the party on Saturday?' 'I haven't
decided yet. What about you? _________________(you | wear) your new black dress?' 2 'Why have you bought all that wallpaper? What ______________________(you do)?' 'I ___________________________ (decorate) the living room.'
3 He's decided that he ___________________________ (not | leave) school this summer. He _________________________ (stay) on for another year. 4 'I _____________________ (buy) a new motorbike.' (you | pay) for it? You haven't got enough money.' my bank to lend me the money.' Ex. 6.- Completa usando will o going to y los verbos entre parntesis. Example: 'What can I do this evening? I know! I'll go (go) and see Sue.' 1 Someone told me that you're moving from London.' 'That's right. I . (live) in Manchester.' 2 Would you like to come to my house this evening?' 'Yes, all right. I .. (come) at 9 o'clock.' 3 I don't feel very well. I think I ... (faint). 4 'It's Simon's birthday soon. I've decided to buy him the new Blues Brothers record.' 'Oh, he doesn't like the Blues Brothers any more.' (get) him something to wear.'
11
'How __________________
'I ___________________ (ask)
'Oh, really? Well, I
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
5 Oh, no! Look at those cars! They .... (crash)! 6 'I could lend you some money if you like.' back on Friday.' 7.- Completa usando present continuous o going to. A veces ambas estructuras son posibles. Ejemplos: I (see) Sarah this afternoon. I'm seeing Sarah this afternoon. / I'm going to see Sarah this afternoon. Hurry up! We (miss) our bus. 1 It (snow) later tonight. -> 2 She (meet) them tomorrow morning. 3 What (you | do) this afternoon? 4 Be careful! You (break) that glass. -> 5 He (not | come) next Saturday. 6 Look out! You (hurt) yourself with that knife. -> Hurry up! We're going to miss our bus. 'Could you? I . .. (pay) you
3. Presente Simple con idea de futuro
Eventos sometidos a un horario o un programa preestablecidos Theres a train to London every hour. The next one leaves at 15.40 We take a bus in Liverpool at 6.30, change at Oxford at 9.30 and arrive in London at 11 o'clock. I've got a new job. I start next Monday We have an exam in two hours I go into the army on the first of the next month We meet again at Christmas, as usual 8.- Completa usando el presente simple de los verbos entre parntesis. Example: Our boat leaves (leave) Dover at 2.00 on Friday and arrives (arrive) in Calais at 6.00. 1 The conference start) on June 3rd, and (finish) on June 10th. 2 We've got plenty of time. Our plane .. (not take off) until 9 o'clock 3 Tonight's concert (begin) at 8.00 and it (not | end) until 11.00 4 When (the next train leave) for Bristol
12
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
9.- Elige la mejor respuesta: a) 'Do you have any plans for your birthday?' 'Yes,.. 2.. a party.' 1) I'll have 2) I'm having b) 'I need some help with the shopping tomorrow.' 'Don't worry,' 1) I'll help. 2) I'm helping. c) What . when you grow up and leave school? 1) will you do 2) are you going to do
d) 'Do you want to come to a football match on Saturday?' 'Which teams..?' 1) are playing 2) are going to play e) Don't carry all those heavy books. Some of the children you. 1) will help 2) are going to help f) The doctor is on his way. He .. in fifteen minutes. 1) will be here 2) is being g) Good news. Ann . a baby. 1) will have 2) is going to have h) I'm sorry I can't come to the lesson tomorrow. my grandmother in hospital. 1) I'll visit 2) I'm visiting
10.- Completa con the continuous form de los verbos entre parntesis. a) Next summer Kate (spend) is spending a month in France. b) Hurry up, Mehmet. Everyone (wait) for you. c) (you do)..anything on Friday? Do you want to come to a party? d) Helen (read). in bed at the moment. e) We (go). to the cinema this evening. f) I can't answer the phone. I (have).. a bath. g) What (you do). later? Do you want to come for a walk? h) David (leave).tomorrow. Have you said goodbye to him? 11.- Corrige los errores en cada frase a) We'll go to the cinema this evening. Do you want to come?-> We are going to the cinema this evening. Do you want to come? c) Bye for now! I'm going to see you tomorrow. ->
13
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
d) Sorry I can't meet you. I will go to the doctor's.-> e) Have you heard the weather forecast? It's raining tomorrow.-> f) I've bought my ticket. I'll leave tomorrow.
3. Pronombres interrogativos
Los pronombres interrogativos nos sirven para hacer preguntas ms concretas. Cuando no nos vale que nos respondan con un s o un no, cuando queremos datos concretos, debemos utilizar los pronombres interrogativos para centrar nuestras preguntas y que nos respondan exactamente lo que queremos saber. Los pronombres interrogativos ocupan el primer puesto en las preguntas, incluso por delante del verbo auxiliar. Si tenemos en cuenta que en castellano utilizamos dos smbolos de interrogacin ? y en ingls slo uno, piensa que los pronombres interrogativos se ponen en el lugar de la primera interrogacin , como si fuera abriendo la oracin para que sepamos desde el principio que es una pregunta sin tener que llegar al ltimo smbolo de interrogacin ?. A) Pronombres ms utilizados
PRONOMBRE INTERROGATIVO
PARA PREGUNTAR EJEMPLOS POR:
Why? Por qu? Where? Dnde?
Razones / Causas
Lugares
Why are you happy? Because I am going to a concert tonight Where do you live? I live in Ciudad Real Where is your mobile phone? Its on the table When is Megans birthday? Its in September When were you born? I was born
th
When? Cundo?
Momentos
on March 12 What? Qu? Who? Quin? What is your name? My name is Steve Cosas Who is that woman? Oh, its Emily Personas Sister
14
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
How? Cmo?
Procesos Estados Cmo hacer las cosas Eleccin de una cosa entre varias
How is Susan after the accident? Shes much better How did you come here? I came here by bus
Which? Qu? Cul?
Which colour do you prefer? Red Which film do you want to see? I want to see Grease Whose coat is this? Its Susans Whose glasses are these? They are mine How long have you lived in York? Since 1993. How long have you studied English? For eight years How often do you go out at night? Every weekend How often do you travel to Argentina? Once a year How far is Toledo? Its about 85 km away from Madrid How much milk do you need? Half a litre, more or less How much are these shoes, please? 35. How many people are coming for dinner? 3 people How many books did you read last year? More than 20
Whose? (indica posesin) De quin? How long? Cunto tiempo? Desde hace cunto? How often? Cada cunto?
Cosas que pertenecen a personas Periodo de tiempo
Frecuencia
How far? A qu distancia? Distancia How much? Cunto / Cunta? Cosas incontables (lquidos, tiempo, dinero, etc.) Cosas contables
How many? Cuntos / Cuntas?
15
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
EJERCICIOS: PREGUNTAS 1.- Completa las preguntas con la forma correcta de BE o DO. Contesta YES o NO.Ejemplos: Are you sometimes shy? Yes, I am // Do you enjoy puzzles? No, I dont 1. you sometimes day-dream? 2. . she ambitious? 3. . your room usually tidy? 4. . he like getting up early in the morning? 5. . clothes important to you? 6. . he serious about sports? 7. . money important to you? 8. . you worry when you make mistakes? 9. . they often bored? 10.. she cry during sad films? 11.. you laugh a lot? 12.. they often get angry? 13.. some colours make you feel happy 2.- Escribe preguntas con las palabras entre parntesis Ejemplo: I watch television. (When) When do you watch it? 1 I read comics. (How often) 2 They play games. (What) 3 Mary goes out at the weekend. (Where) 4 John swims at the pool. (What time) 5 I collect things. (What) 6 We write to pen-friends. (How often) 7 He plays football. (Where) 8 I take my sister to school. (What time)
1 0 Liz goes to a sports club. (When)
16
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
1 1 My children watch cartoons on television. (When) 1 2 I take my dog for a walk. (When) 1 3 The boys go to a youth club. (How often) 1 4 My daughter goes to piano lessons. (What time) 1 5 I go shopping. (Where) 3.- Completa las preguntas con Where, When, What, How. Ejemplo: Where do you live?
1. __________ do you get up? 2. __________ do you have for breakfast? 3. __________ do you leave home? 4. __________ do you go to school? By bicycle or by bus? 5. __________ do lessons start? 6. __________ do you have lunch? At home or at school? 7. __________ do you like best at school? Games? 8. __________ do you go after school? 9. __________ do you do your homework? Before or after dinner? 10. __________ do you do on Saturday and Sunday? 11. __________ do you have holidays? 12. __________ do you wear to school? 13. __________ do you wear for games? 14. __________ do you carry your books to school? In a school bag? 15. __________ do you want for your birthday? 4.- Completa las preguntas usando: what who which whose where when why how how often how much how many how old how long 'Ejemplo: 'How old are you?' 'I'm 20.' 1 '__________do you do?' 'I'm a student.' 2 '__________do you live?' 'In London.' 3 '__________have you lived there?' 'For two years.' 4 '__________brothers and sisters have you got?' 'Two brothers and two sisters.' 5 '__________is your favourite pop singer?' 'Michael Jackson.' 6 '__________is your birthday?' 'November the 3rd.'
17
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
7 '__________do you play tennis?' 'About once a week.' 8 '__________does it cost to play tennis in Britain?' 'It's not very expensive.' 9 '__________bag is this?' 'I think it's Simon's.' 10 '__________do you usually get to work?' 'By car.' 11 '__________of those girls is your sister?' 'She's the one in the black skirt.' 12 '__________are you smiling?' 'Oh, I'm happy 5.- Utiliza estas expresiones con HOW para completar las preguntas How old ...? / How big ...? How far ...? How fast...? How long ...? How often ...? How tall...? How well ...?
Ejemplo: How old are you?' '37 next birthday' 1 '.your house from here?' 'About 5 km.' 2 '... John?' 'Very tall - nearly two metres.' 3 '.... she driving?' 'The police say she was doing 160 km/h.' 4 '. see your parents?' 'Every week.' 5 '.. Ann's flat?' 'Very small - just one room and a bathroom.' 6 '.. stay in China?' 'I was there for six months.' 7 '. speak English?' 'Not very well.' 6.- Alguien ha asesinado al actor Henry Farthing. Completa las preguntas de la polica con : WHO, WHAT, WHEN, WHERE, WHY, HOW, o HOW MUCH. Ejemplos WHO shot the actor? WHAT did the police find out? 1. ____________ was the motive? 2. ____________ is the main suspect? 3. ____________ information have the police got? 4. ____________ happened on the night of the murder? 5. ____________ did Farthing go when he left the house? 6. ____________ did he meet? 7. ____________ did he meet him at six o'clock? 8. ____________ saw Farthing last? 9. ____________ did the murderer get into Farthing's flat? 10. _ ____________ does Janet Jones, his girlfriend, know? 11. _ ____________ did Farthing phone her that evening? 12. _ __________ is the gun?
18
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
4. Autoevaluciones
Autoevaluacin 1
Ahora vamos a comprobar que has aprendido los contenidos del tema y los sabes poner en prctica. Para ello, tienes que contestar a 10 preguntas, eligiendo entre tres posibilidades. 1. Will you come to the party with me? Yes, a. I am 2. She will a. to visit 3. We a. am 4. My train a. leaves 5. a. Are you going 6. I a. going 7. a. Which 8. a. When b. visit b. you will us tomorrow. c. visits c.I will .
going to study English next year. b. is at 10:00 a.m. b. leaving c. will leaves go to the concert tonight? I dont know, Im not sure. b. Are you going to c. Will you c. are
visit London next summer. I have the tickets. b. will go c. am going to
film do you prefer? Benhur or Titanic? b. What c. Who
did you find those glasses? In the park. b. Why c. Where
9.- ________________ are you going to buy these trouser? a. Who 10. b. Whose c. why
girls do you know? a. How much b. How many c. How often
Autoevaluacin 2
1. Vamos a comprobar que has entendido el texto que aparece en el primer apartado del tema 1 que acabas de ver. Elige la respuesta correcta entre las tres opciones siguientes: 1. Karen will have a. a coke b. some water c. a beer
19
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
2. Marta is going to a. have a baby 3. Karen is going to a. Salamanca 4. Marta will b. Toledo
next year b. study at university next weekend c. Madrid c. work
with her c. go to the concert
a. go to the station b. work
2. Vuelve a leer con atencin el texto del primer apartado del tema 1 y di si las siguientes afirmaciones son verdaderas (TRUE) o falsas (FALSE) 1. Karen is thirsty 2. Marta likes beer 3. Marta is going to be a teacher 4. Karen is pregnant 5. Marta is happy with the news 6. Karen is going to be a doctor in the USA 7. Karen and Marta are going to a concert 8. Marta will go to the train station with Karen 3. Karen ha ido a visitar a una pitonisa para que le prediga su futuro. Escribe lo que la pitonisa le ha predicho a Karen sobre su futuro. Usa en tus respuestas la forma no contrada (You will). Ejemplo: You (live) for many years: You will live for many years 1. You (win) ___________ the lottery 2. You (not go) ___________ back to the USA 3. You (not be) ___________ a teacher 4. You (marry) ___________ a Spanish man 5. You (have) ___________ five children 6. You (work) ___________ in a hotel 7. You (be) ___________ very happy 8. You (not live) ___________ in Toledo 4. En este ejercicio tendrs que hacer una pregunta utilizando WILL y responder con una respuesta corta: Yes + pronombre + will / No + pronombre + wont
20
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Ejemplo: You / be / 25 next year-> Will you be 25 next year? Yes, I will / No, I wont. 1. Marta and Karen (be) friends forever. 2. Marta (be) a good doctor in the future. 3. You (go) on holiday next summer. 4. You (have) a baby in the next two years. 5. It (rain) a lot next year. 5. Escribe oraciones utilizando las palabras entre parntesis y futuro con GOING TO. - Ejemplo: (buy a car) -> I am going to buy a car / I am not going to buy a car 1. (get up before 7.00) [+] 2. (have a big breakfast) [+] 3. (listen to the radio in the morning) [-] 4. (have lunch at home) [-] 5. (drive a car) [-] 6. (be with your family) [+] Escribe tus repuestas afirmativamente si ves [+] o negativamente si ves [-]. 6. Mira el siguiente reparto de tareas en una casa. Utiliza Presente Continuo: Monday John Alison Cooking washing-up Tuesday cleaning Ironing Wednesday washing-up Cooking Thursday ironing Cleaning
Completa las frases: 1. On Monday, Alison 2. On Tuesday, Alison 3. On Wednesday, Alison 4. On Thursday, Alison and John and John and John and John . . . .
7. Completa las siguientes preguntas con WHAT / WHICH / WHO. 1. 2. 3. 4. is that girls name? sandwich do you want? Chicken and curry or tuna? is your favourite film? is your favourite actor?
21
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
5. 6. 7. 8.
is more expensive, fish or meat? is younger, you or your sister? is your mobile number? is your best friend?
8. Escribe preguntas con WHO y WHAT. En estas oraciones, actan de sujeto. 1. Somebody is going to phone you. 2. Something is going to happen. 3. Somebody is reading my books. 4. Something is making noise. 9. Ahora escribe preguntas con WHO y WHAT en las que no acten como objeto. 1. Im meeting somebody. 2. Im doing something tomorrow. 3. Im going to see somebody now. 4. Im going to cook something tonight. 10. Ahora vamos a poner en prctica todos tus conocimientos sobre los pronombres interrogativos. Completa las siguientes oraciones con los pronombres interrogativos que faltan segn sea necesario. How often / Where / When / How far / Why / How/ What / Whose / How long / Which / Who / How much / How many 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. is this girl in the photograph? My little sister. are you going on holiday next summer? Im going to Denia. will you be in Italy next summer? Ill be there for two weeks. is your favourite ice cream? Chocolate or vanilla? money do you need to buy a dress? I need 60 . do you think about me? I think you are very nice. children are you going to have? Im going to have three kids. are you crying? Because Im very sad. glasses are these? They are mine. do you go to the supermarket? Once a week. are you? Fine, thanks is Albacete from Alicante? About 170km. is Helens party? Its next Saturday.
22
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Tareas
Tarea 1
Vamos ahora a practicar el futuro. Comenzaremos con WILL. Para ayudarte con el vocabulario, te puedes apoyar en las siguientes fotografas, con su significado en ingls debajo. En primer lugar, hars una serie de predicciones para el futuro, ya sea prximo o lejano. Qu pasar? T decides.
Be sunny tomorrow
Fall in love
Snow next winter
A continuacin, te vamos a plantear una serie de actividades y t decidirs si te apetece hacerlas o no. No pienses mucho, tan slo practica esta forma de futuro.
Have a coffee tonight
Go shopping next weekend
Visit my best friend
Escribe las oraciones segn tus propias ideas, tanto en afirmativa (I WILL) como en negativa (I WILL NOT) y enva el documento a tu tutor/a para que lo corrija. nimo!
23
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Tarea 2
Cules son tus planes para el futuro? Puedes escribir sobre tus planes para dentro de unos aos, para el prximo verano o incluso para esta misma noche. Para ayudarte con el vocabulario, te puedes apoyar en las siguientes fotografas, con su significado en ingls debajo.
have a baby
Watch TV Travel around Europe
Go on holiday
Be with my family
Play football
Escribe las oraciones segn tus propios planes, tanto en afirmativa (I AM GOING TO) como en negativa (I AM NOT GOING TO) y enva el documento a tu tutor/a para que lo corrija. nimo!
24
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Bloq.10. Tema 2: Job opportunities
NDICE 1. Job offers (anuncios de trabajo) 2. Verbos modales Caractersticas generales de los verbos modales CAN (habilidad, permiso informal, posibilidad) MUST (obligacin) MUSTNT (prohibicin) MAY (probabilidad, permiso formal) SHOULD (consejos, recomendaciones) 3. Conectores de tiempo 4. Autoevaluaciones 5. Tareas
25
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
1. Job offers (anuncios de trabajo)
Necesitas encontrar un trabajo? Ests cansado del que tienes y quieres encontrar uno mejor? Manos a la obra: el primer sitio para buscar ofertas de trabajo es el peridico (real o digital). Santiago, que es quien nos va a guiar por toda esta Unidad, empieza su bsqueda. Lo primero es empezar a ver qu ofrecen. Vamos a realizar una bsqueda distinta: empezaremos por mirar las pginas de ofertas de trabajo de los peridicos ingleses. Y lo primero que Santiago encuentra es este anuncio: NEEDED: Full time secretary position available. Applicants must have at least 2 years experience and should be able to type 60 words a minute. No computer skills required. Applicants should have perfect written and spoken German. Must be over 20. Must have driving licence. Apply in person at United Business Ltd., 17 Browning Street, Leeds. Salary: 12000,00 per annum.
Visto as, seguro que entiendes poco. DONT WORRY!!! No lo entiendes primero porque est en ingls (evidentemente), pero sobre todo porque los anuncios de ofertas suelen utilizar una terminologa particular y un estilo propio en el que existe una evidente intencin de comunicar lo ms posible en el mnimo espacio (de hecho estos anuncios se contratan por el nmero de palabras). La caracterstica principal de estos anuncios es que emplean un tipo de lenguaje muy especial, casi telegrfico, en el que en lugar de las oraciones completas nos encontramos lo sustancial de ellas: Needed: Full time secretary = we need a secretary to work full time Must be over 20 = he/she should be older than 20 (years old) Antes de seguir, intenta comprender la idea general de este anuncio: En qu consiste el trabajo? Dnde se ofrece el trabajo? Pone lo que se va a ganar? Cmo se debe contactar con la empresa? Esta informacin es la que bsicamente vamos a encontrar en los anuncios de
26
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
trabajo, aunque no siempre encontramos ni todos estos elementos, ni el mismo orden (es el anunciante el que decide cules son los datos que quiere poner y cmo); por eso te ofrecemos ahora distintos modelos de anuncios para empezar a reconocer estos elementos en cada uno.
27
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Ya hemos dicho que el lenguaje y la forma de expresarse son especiales en estos anuncios: te vamos a ofrecer una gua de vocabulario de anuncios con la que podrs seguir recopilando la informacin, y que contiene una serie de trminos especficos que se van a repetir recurrentemente en toda esta Unidad: - to need /needed: necesitar / se necesita, se busca. - part-time / full time: trabajo a tiempo parcial / trabajo a tiempo total - appointment / in person / phone /e-mail: cita / en persona / llamada telefnica / correo electrnico. - to require / requirements: requerir / requisitos - to apply / applicant: solicitar / candidato - position /vacancy: puesto laboral / puesto vacante - skill: habilidad, competencia - to contact: ponerse en contacto Tras ver estos cuatro anuncios Santiago ha decidido llamar al nmero 1; mira con atencin la informacin del anuncio y deja el siguiente mensaje: Hello, my name is Santiago Gmez and I am interested in the job offer, Ive had some experience as a waiter, I can work full time or part time. My contact telephone number is 44-548- 761.
2.- VERBOS MODALES: CAN, MUST, SHOULD, MAY
Cmo enterarse de las condiciones de los trabajos que ha encontrado? Qu requisitos piden? sta es ahora la preocupacin de Santiago: ya que sabe interpretar los datos bsicos de una oferta o anuncio, tiene que enterarse bien de las condiciones y requisitos. Vamos a rescatar el primer anuncio que vio Santiago para buscar la manera en que se expresan las condiciones y requisitos: NEEDED: Full time secretary position available. Applicants must have at least 2 years experience and should be able to type 60 words a minute. No computer skills required. Applicants should have perfect written and spoken German. Must be over 20. Must have driving licence. Apply in person at United Business Ltd., 17 Browning Street, Leeds. Salary: 12000,00 per annum.
28
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Para hablar de los requisitos que se pide que cumplan los candidatos se han utilizado dos verbos modales que expresan obligacin y deber: should se suele interpretar y traducir como una recomendacin (deberas) must aporta un pequeo paso ms adelante en la obligacin,(debes)
Caractersticas comunes de los verbos modales:
Tienen slo algunos tiempos It may rain She might come later Can he swim? Could you open the window? Necesitan de otros verbos para el resto de tiempos: You must go I had to work late yesterday Ill have to go to Madrid tomorrow She hates having to get up early She has had to work hard all her life
They could come yesterday They can come today Will they be able to come tomorrow? Van seguidos de un infinitivo sin la partcula to: I can swim We can go home now You should study She mustnt smoke They may come
29
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
NOTA: Hay una excepcin a esta regla: ought to, que va seguido de infinitivo con la partcula to: Ej. we ought to go now (deberamos irnos ya). Pero este verbo no lo vamos a estudiar de momento. Todas las personas tienen la misma forma, no aadimos s a la tercera del singular: I must go now // she must go now They can speak English // she can speak French We may be late // She may be here soon You should be home early // He should shave more often Negativa: Modal + not / nt She can swim -> She cannot swim / She cant swim We should go -> we shouldnt go It may rain -> it may not rain Preguntas: Modal + sujeto? Can he swim? Should we go? No usamos auxiliar DO / DOES: does she can swim o she doesnt can swim
CAN: Poder / saber
FORMA: Can + infinitivo sin 'to' Afirmativa I can run very fast You can play the guitar Mary can sing well We can speak English They can swim
30
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Interrogativa Can you cook? Can they drive? Can she go out tonight? Short answers: Yes + pronoun + can // No + pronoun + can't Can you hear me? Yes, I can / No, I can't Can you speak Chinese? Yes, I can / No, I can't Negativa: cannot - > can't Arthur cannot (can't) get up in the morning Mrs. Harrison can't cook very well
USO: Usamos CAN para expresar: Capacidad, habilidad o conocimiento (poder / saber) He can lift two hundred kilos She can run very fast I can drive Mary can dance Mr. Steele can speak several languages My brother can swim very well I can't play any musical instruments She can sing and play the guitar We can speak seven languages Pedir algo o pedir permiso (informal) Can you lend me a pound? Can I use your telephone? Can I borrow your pen? Can I come in?
31
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Dar o negar permiso Can you come to the party? You can't leave until the end of the class Peter can borrow the car tonight The children can go out if they have finished their homework Posibilidad o imposibilidad de hacer algo o de que algo ocurra My seat is too far from the stage. I cant see the actors clearly The door is not locked. You can open it Its dark in the house. I cant see anything
MUST: Tener que.
FORMA: must + infinitivo sin 'to' Afirmativa: Obligacion: tener que, estar obligado a I must phone home Arthur must wear a tie in the library Mary must be early for work You must be home by 10.00 You must drive carefully Ive got a terrible pain in my back. I must go and see the doctor I must stop smoking Interrogativa Must you go now? Must I answer the phone? Must Bruce pay the bill? Negativa: (must not -> mustn't ) obligacin de no hacer / prohibicin You must not (mustn't) open the door Waiters mustn't smoke at work She mustn't stay there You mustn't wear pyjamas in class
32
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
You mustn't drive a car without a licence
MAY: Poder, puede que
May May not May I? Yes, you may No, you may not USO: PERMISO a) Pedir permiso (formal) May I come in? May I borrow your car? May I use your telephone? b) dar permiso / denegar permiso, prohibir You may go now She may come late tonight They may watch television for a while He may not go swimming until he does his homework En este sentido equivale a mustnt You may not drive on the right in England You mustnt drive on the right in England Young people under eighteen may not drink in pubs Young people under eighteen mustnt drink in pubs POSIBILIDAD (puede que) He may come today, he may come tomorrow Put on your raincoat. It may rain He may not come today
33
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
SHOULD. Deber (recomendacin)
Forma: Should Should not -> shouldnt Should he? Yes, he should No, he shouldnt Recomendacin, consejo. You should cross the street carefully We should visit him tomorrow You should study a little harder You should not go out the night before an exam I should visit my grandmother You shouldnt eat so quickly. Pedir parecer o consejo Its hot in here. Should I open the window? The oven isnt working. Should I call a technician?
MODALS.- EXERCISES
1.- Wrong or right? Give the correct answers Elephants can fly. Wrong. Elephants cant fly Dogs can swim. Right 1. Penguins can swim. 2. Penguins can fly. 3. Horses can swim. 4. Dogs can climb trees. 5. Parrots can fly. 6. Cats can fly. 7. Camels can run.
34
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
8. Bears can catch fish. 9. Lions can climb trees. 10. Elephants can catch fish. 11. Spiders can swim. 12. Sheep can jump. 2.- Ask permission with Can I...? Then give the probable answer. You want to >>> go to see a horror film. Ask your father. Can I go to see a horror film ? No, you can't! 1. invite ten friends to lunch. Ask your mother. 2. go camping in the woods. Ask your mother. 3. have some extra English homework. Ask your teacher. 4. eat sweets in bed. Ask your dentist. 5. cook lunch on Sunday. Ask your mother. 6. go swimming with a bad cold. Ask your doctor. 7. wash the car. Ask your father. 8. have more pocket money. Ask your mother. 9. watch television until midnight. Ask your father. 10. do this exercise again. Ask your teacher 3.- Classroom rules. Put in WE MUST or WE MUSTN'T. Make true sentences. Example: >> sit still. You must sit still 1. ___________________ jump on the desks. 2. ___________________ fight. 3. ___________________ do what the teacher says 4. ___________________ go to sleep. 5. ___________________ be quiet. 6. ___________________ play football. 7. ___________________ look at the blackboard. 8. ___________________ eat crisps. 9. ___________________ draw on the desks. 10. ___________________ listen to the teacher. 11. ___________________ give answers.
35
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
12. ___________________ read comics. 13. ___________________ make a lot of noise. 14. ___________________ look at the teacher. 15. ___________________ jump out of the windows. 16. ___________________ listen to music. 17. ___________________ write letters to friends. 4.- Put in MUST or MUSTN'T. 1. It's a secret. You.. tell anybody 2. Shhh. Dad's asleep. We..be quiet. 3. Nick, you ..spend all your pocket money at once. 4. We ..write to Grandmother. It's her birthday tomorrow. 5. I ..forget my homework again. The teacher gets angry. 6. You..eat so much. You are too fat. 7. You really..tidy your room, Nick. I can't open the door! 8. Chip (the dog), you ..tear the postman's trousers. 9. It's very late. I ..go home now. 10. Nick, you ..say 'Shut up' to adults. 11. Trig, you ..learn some new English words every day. 12. You're dirty. You ..have a shower! 5.- Say what Trig should or shouldn't do. > He gets up late. He shouldn't get up late. >He doesn't study English every day. He should study English every day. 1. He goes to bed late. 2. He doesn't practice writing every day. 3. He wastes time. 4. He eats all day. 5. He behaves badly. 6. He doesn't study grammar every day. 7. He squirts people with his water pistol. 8. He swings on the lamp. 9. He never uses his dictionary. 10. He pulls up the flowers.
36
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
11. He doesnt wash. 6.- What may happen in the future? What may life be like? Rewrite the sentences with may or may not. Perhaps people will live on the Moon. People may live on the moon Perhaps there won't be enough food -> there may not be enough food 1. Perhaps children will learn from computers at home. 2. Perhaps there won't be any schools. 3. Perhaps there will be cities on the Moon. 4. Perhaps there won't be enough room for everybody on Earth. 5. Perhaps people will live in space stations. 6. Perhaps there will be cities under the sea. 7. Perhaps people won't go to work anymore. 8. Perhaps robots will do all the work. 9. Perhaps there will be fast underground trains across the world.
3. Conectores de tiempo
Los conectores de tiempo son expresiones de tiempo que utilizamos para unir oraciones cuando contamos lo que hicimos ayer o durante unas vacaciones o incluso cuando narramos una divertida ancdota. Time connectors son las palabras encargadas de establecer el orden cronolgico en el que ocurren las cosas. Conectores de Tiempo / Time connectors FIRST OF ALL: En primer lugar FIRST: Primero, SECOND:segundo, THIRD: tercero BEFORE: Antes de Seguidos de Ejemplos
Oracin (S+V+C) Oracin (S+V+C)
First of all, my name is Ian
First, I phoned Lisa Second, I invited her Third, I said I love you Before dinner Before I get the job After the film After you read the book
37
Sustantivo Oracin (S+V+C) Sustantivo Oracin (S+V+C)
AFTER: Despus de
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
LATER: Ms tarde NEXT: Seguidamente THEN: Luego, despus WHILE: Mientras
Oracin (S+V+C) Oracin (S+V+C) Oracin (S+V+C) Pres. continuo Pasado continuo Presente simple Pasado simple Oracin (S+V+C)
Later, I had breakfast Next, I invited her Then, I said I love you While youre having lunch While you were sleeping When you find the answer When you phoned me Finally, I said goodbye
WHEN: Cuando FINALLY: Finalmente
J!!! Ten mucho cuidado con la expresin espaola DESPUS, porque en ingls se puede decir de dos formas distintas. Mira estos ejemplos: Yesterday I went to work and THEN I went home. Ayer fui a trabajar y despus me fui a casa. Como has visto, si slo quieres decir despus, tienes que utilizar THEN seguido de una oracin (es decir S+V+C: sujeto, verbo y complementos) Yesterday we watched a film on TV AFTER dinner. Ayer vimos una pelcula en la tele despus de la cena. Por el contrario, si quieres decir despus de tienes que utilizar AFTER + el sustantivo directamente, sin ms preposiciones. AFTER significa despus de, igual que BEFORE significa Antes de. Despus de y antes de se utilizan muchas veces seguidos de un gerundio: Before having lunch, you must wash your hands. Antes de comer, debes lavarte las manos. After having lunch, you must wash your teeth. Despus de comer, debes lavarte los dientes.
38
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
4. Autoevaluaciones Autoevaluacin 1
Ahora vamos a comprobar que has aprendido los contenidos del tema y los sabes poner en prctica. Para ello, tienes que contestar a 10 preguntas, eligiendo entre tres posibilidades. 1. Can I watch TV? Yes, a. you cant 2. She a. will 3. We a. must 4. I am very hungry. I a. should 5. You a. must 6. She a. must b. can b. you do . c. you can
go to the cinema tomorrow. Shes not sure. b. must c. may c. mustnt eat something. c. may c. mustnt c. mustnt
study a lot this year or we will fail. b. can
smoke at home. The baby is sleeping. b. should b. shouldnt
go to work today. Shes very ill.
7. ____________, I am going to tell you my name. Then, my phone number. a. First of all b. Second c. Finally she will go on holiday. c. First dinner? c. next
8. She is getting married in August. __ a. Then b. After
9. What are you going to do a. after b. then
10. After a long day, I ____________ got home. a. then b. finally c. before
39
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Autoevaluacin 2
Di si es verdadera o falsa la siguiente informacin sobre los tres anuncios que has visto al principio del tema 2. 1. En el anuncio n 1 la forma de contacto es por telfono. V / F 2. En el anuncio n 2 estn buscando trabajadores para una oficina. V / F 3. En el n 3 s pone lo que se va a ganar. V / F 4. En el n 1 no pone el lugar del trabajo. V / F 2. Completa las frases con MUST y uno de los verbos de la tabla. Meet 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. read buy phone go help
We to the bank today. We havent got any money. Shes a very interesting candidate. You her. I didnt phone Tim yesterday. I him today This is an excellent book. You it I have a very big problem. You me We some food. We havent got anything for dinner.
3. Completa las frases con MUSTNT y uno de los verbos de la tabla. Be tell smoke use anyone. here late.
1. This secret is very important. You 2. This is a public building. You 3. This interview is very important. You 4. You my car.
4. Completa las frases con SHOULD y uno de los verbos de la tabla. Be 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. go Read visit look at him. to bed. on time for the meeting. it. a seat-belt. it. Wear
When you speak to the manager, you She looks tired. She Everybody The cafeteria is very nice. We When you are driving, you Its a very good book. He
40
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
5. Usa los modales must y should en la forma apropiada segn los dibujos.
1. You stay outside. a. should
b. must
2. You .not light a fire. a. should b. must
3. You not use your camera. a. should b. must
4. This is a danger sign. You be careful. a. should b. must
6. Completa las siguientes oraciones con CAN o CANT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Simon come today. Hes very ill. I think Helena is great. She type, speak English and German. Tom is a guitarist. He play de guitar. You drive! You dont have a driving licence! Sheila go to the party. She doesnt have permission you help me? I open the window. Its broken.
7. Escribe las siguientes oraciones utilizando MAY. Recuerda que perhaps significa quiz, tal vez y por tanto tambin indica probabilidad. Te damos un ejemplo para que veas cmo funciona. Ejemplo: Perhaps I will go to the cinema I may go to the cinema 1. Perhaps I will see Tom tomorrow. 2. Perhaps I will get the job. 3. Perhaps Monica will have a baby. 4. Perhaps Andrew will buy a car. Ahora haz las siguientes oraciones en negativa utilizando MAY NOT: 1. Perhaps they will not come -> 2. Perhaps she will not get the job-> 3. Perhaps we will not go out tonight ->
41
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
8. Vamos a utilizar los conectores de tiempo en una narracin sencilla. A continuacin tienes una serie de pequeos textos formados por varias oraciones. Para cada uno de ellos tienes que elegir el conector correcto de una pequea lista que te damos al principio del texto y colocarlo en su lugar correspondiente. THIRD FINALLY SECOND Im going to tell you your obligations in this job. every day. you have to answer the phone. to be polite. you have to wear a uniform. Then First While FIRST OF ALL you must be on time you have
After
Yesterday I had a very important job interview. I got up very early in the morning. _______I had a big breakfast. breakfast, I had a shower. I was having the shower, the telephone rang. Next Before When First
I will tell you a secret. I tell you my secret, you must promise you wont tell anyone. Yesterday, I had a job interview. , I went to the office. I met the manager, I was very nervous. I was calm and I may get the job! 9. Si Promosouth (que es la empresa que ofrece el trabajo) quisiese poner un anuncio en prensa cul sera el anuncio en prensa de esta oferta de trabajo?: a) Commercial Administrator needed; experience required. English nationality. b) Commercial department needs Spanish young professional, for office in Mlaga; no foreign language skills required. c) Young professionals needed. For office in Spain. Spoken and written Spanish and English required. No experience necessary.
42
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
6. Tareas
Tarea 1
Te acuerdas de Santiago, el chico con el que empezamos esta unidad? Ha conseguido una entrevista para el trabajo que est buscando y mira algunas de las cosas que tiene previstas en su agenda para maana. En este texto faltan los verbos modales, que tendrs que aadir segn el sentido que tenga la oracin. No te preocupes, te damos a elegir entre tres alternativas. 1. Santiago (must / can / may) 2. He (must / should / mustnt) 3. He (must / can / may) for breakfast. 4. At 8.30, he (must / mustnt / should) because he (mustnt / shouldnt / cant) 5. He (may / can / must) 6. He (can / should / mustnt) 7. He (shouldnt / may / must) leave home and take the bus drive a car. be at the company at 9:00. be late. go to university. get up at 7.30 in the morning. have a shower. have a cup of coffee and toasts
8. He will meet his friends for lunch at 14.00. They (should / may / must) ___ go to a caf or buy a sandwich at the supermarket. go to English lessons from 16.00 to speak a little English, but he needs to
9. He (may / can / must) 19.30. He (may / can / must) speak English very well to get the job.
10. At 20.00 he (can / mustnt / should) supermarket.
buy food at the
11. At 20.30 he will get home and have dinner. Then, he (must / should / may) watch TV. 12. He (may / must / should) go to bed early.
43
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Tarea 2
Mira lo que Santiago tiene previsto en su agenda para maana. Completa la narracin eligiendo el conector de tiempo correcto. Santiago must get up at 7.30 in the morning. WHEN / THEN he should have a shower and get dressed.
He may have a cup of coffee and some toasts for breakfast. WHILE / AFTER AFTER / BEFORE bus to the city centre. he is having breakfast, he will listen to the radio. breakfast, he must leave home and take the
He must be at the company at 9:00. FIRST / AFTER WHILE / WHEN university. NEXT / BEFORE , he will have some tests. THEN / THIRD , he will have an interview he finishes his interview, he must go to , he will meet his friends for lunch.
They may go to a caf or buy a sandwich at the supermarket. THEN / AFTER they have lunch, Santiago must go to his English lessons. He needs to speak English to get the job. BEFORE / NEXT the supermarket near his apartment. AFTER / FINALLY to bed. he goes home, he should buy some food at
, he will have dinner, watch a film on TV and go
Revisa tus apuntes de conectores y completa el texto. Si necesitas volver a repasar los contenidos, tmate el tiempo que necesites. Cuando lo tengas preparado, enva lo a tu tutor para que lo corrija
44
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Bloque 11. Tema 1: The media
NDICE
1. La prensa britnica 2. Tiempos verbales usados en las noticias: Pasado Simple, Pasado Continuo y Pretrito Pluscuamperfecto 3. Estructura de una narracin de hechos 4. Radio y Podcasts para aprender ingls 5. Internet 6. Autoevaluaciones 7.Tareas
45
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
1. La prensa britnica
En esta unidad vamos a conocer los distintos medios de comunicacin as como sus funciones primordiales (informacin, entretenimiento y aprendizaje). Los britnicos leen mucha prensa, ms que los espaoles. Por eso, lo primero que vamos a ver es la diferencia entre los dos tipos principales de prensa escrita que existen en el Reino Unido. Cuando se trata de peridicos (newspapers, papers), podemos diferenciar entre dos tipos de prensa (Press) en el Reino Unido. Por una parte existe la llamada, Prensa Seria llamada generalmente Broadsheets, que se ocupa de cuestiones generales de carcter nacional, local o internacional que intenta presentar las noticias desde el punto de vista mas independiente posible y huyendo de enfoques escandalosos.
Por otro lado est la Prensa Sensacionalista, llamada Tabloids, la que explota temas de actualidad, enfocndolos desde un punto de vista muy popular y llamando la atencin del lector con grandes titulares sobre escndalos, crmenes, personajes clebres, etc. En realidad, estas palabras tienen que ver con el tamao del peridico. Un Broadsheet, es un peridico de pginas muy grandes y un Tabloid, uno de un formato ms pequeo en el que la informacin va comprimida. Por tanto, un peridico como The Times o The Guardian, que siempre ha sido considerado como prensa seria, se publicara en hojas muy grandes, dobladas por la mitad y otro como
46
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
The Sun o Daily Mirror, considerado como sensacionalista, en el ms pequeo.
Con el paso del tiempo y dado que las hojas grandes son ms difciles de manejar que las pequeas, las publicaciones empezaron a adoptar todas el formato pequeo Tabloid, por ser mucho mas cmodo. Desde entonces se prefiere usar el trmino Compact compacto, para el pequeo (usado ya casi por todos) y a los peridicos sensacionalistas se les conoce como red-top, porque es rojo el color que, por lo general, usan para sus titulares (Headlines). Ahora vamos a ver un ejemplo de esta diferencia entre la prensa sensacionalista y la prensa seria; son dos artculos que tratan la misma cuestin y queremos que te fijes en los titulares.
47
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
2. PASADO SIMPLE (RESUMEN) ESTRUCTURA DE LA ORACIN Afirmativa: sujeto + verbo en pasado + complementos I/He/She was here last summer We/You/They were in the same class at school I watched TV last night Pete played football last weekend They went to London two years ago Negativa: BE: sujeto + wasnt / werent + complementos I/he/she was not here last summer o wasnt We/You/They were not at school yesterday o werent RESTO DE VERBOS: sujeto + did + not + verbo en forma base + complementos I did not watch TV last night o I didnt Pete didnt play football last weekend o Tom didnt
48
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
They did not go to London two years ago o They didnt
Interrogativa: BE: Was / were + sujeto + complementos Was I/he/she here last summer? Were we/you/they here last summer? RESTO DE VERBOS: did + sujeto + verbo en forma base + complementos Did you watch TV last night? Did Pete play football last weekend? Did they go to London two years ago? USOS: Acciones que ocurrieron en pasado. Acciones cortas: The bomb exploded at 8:00am Acciones largas: I lived in Manchester for 5 years EXPRESIONES DE TIEMPO: Las expresiones de tiempo se colocan al final de la oracin, en el lugar de los complementos. Ejemplos: yesterday, last night, last weekend, last Monday, last month, last year; one day ago, two weeks ago, five minutes ago, half an hour ago; In 1997, in the 19th century, in the past; from 9 to 12, from Monday to Friday, from April to October; for two years, for three weeks, for ten minutes PASADO CONTINUO (RESUMEN) Estructura: Verbo to be en pasado (was / were) + verbo principal en ing Afirmativa: sujeto + was/were + verbo-ing + complementos I was reading a book at 10:30PM He was driving his car at 8:00am They were playing football yesterday morning Negativa: sujeto + was/were + not + verbo-ing + complementos She was not reading a book at 10:30PM o She wasnt He was driving his car at 8:00am o He wasnt They were not playing football yesterday o They werent
49
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Interrogativa: was/were + sujeto + verbo-ing + complementos Was she reading a book at 10:30PM? Was he driving his car at 8:00am? Were they playing football yesterday morning? USOS Acciones simultneas a un momento pasado concreto You were having dinner at 9:00PM last night It was raining this morning Acciones que son interrumpidas por otra Mary was reading when the phone rang Acciones que ocurren de forma simultnea I was reading while you were watching TV Expresiones de tiempo Las expresiones de tiempo se colocan al final de la oracin, en el lugar de los complementos. Siempre se dan momentos concretos. Ejemplos: I was having a shower at 10:30PM Albert was driving at 8:00am this morning They were playing basketball at 12:00 last Sunday morning
PAST PERFECT SIMPLE (PRETERITO PLUSCUAMPERFECTO) 1.- Forma: subjeto + had + past participle Had para todas las personas Had not para todas las personas en negativa had puede contraerse en -> d had not puede contaerse en -> hadnt I had worked -> Id worked She had come -> Shed come They had gone -> Theyd gone The play had not started-> The play hadnt started He had not got up-> He hadnt got up We had not washed up-> We hadnt washed up
50
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Had your friends arrived? Yes, they had / No, they hadnt Had you met Mary? Yes, I had / No, I hadnt Had they seen the film before? Yes, they had / No, they hadnt Had the match started when you arrived? Yes, it had / No, it hadnt Who had phoned the police? Bob (had) What had happened? There had been an accident Who had told you? Nobody Who had you seen? Mary Where had you seen her? At the cinema What had she told you? My brother was coming When had you had breakfast? Before we went out USOS: Pasado anterior a pasado: Cuando hablamos de una accin en pasado y nos referimos a un pasado anterior When I telephoned Sue, (pasado) she had gone out (pasado anterior) We arrived at the cinema at 8.00, (pasado) but the film had started at 7.30 (pasado anterior) When I spoke to the woman (pasado) I realized I had met her somewhere before (pasado anterior) When the police arrived, the thieves had left When I opened the safe, the money had disappeared EJERCICIOS pasado continuo o simple 1.- Pon los verbos entre parntesis en el tiempo que corresponda: pasado simple o continuo JENNY I . (dream) I.. (see) a tornado last night. I remember everything. You. (play) with the dog, Mum. (cook), Dad. (work) in the garden, and I. (look) for the cat, when the wind . (begin) to blow. NICK . and you . (see) the tornado.
51
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
JENNY Yes. It . (come) straight towards me when I . (run) into the house. I . (close) the window just when the tornado . (hit). NICK And? JENNY Well, I remember that the wind . (blow) and the house . (spin) when I. (hear) a terrible noise. NICK What . (be) it? JENNY It . (be) me. I . (fell) out of bed and . (wake) up. 2.- I saw (see) Sue in town yesterday hut she (not/see) me. She. . (look) the other way.
.
3.- I .. They..
meet) Tom and Ann at the airport a few weeks ago. (go) to Berlin and I . . a chat while we . . (go) to Madrid. (wait) for our
We.. (have) flights.
4.- I.. (cycle) home yesterday, when suddenly a man . . (step) out into the road in front of me. I . . (go) quite fast but luckily I . . (manage) to stop in time and . . (not / hit) him 5.- Pon los verbos en la forma correcta, pasado continuo o simple. 1. Jane ...was waiting... (wait) for me when I arrived (arrive).
52
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
2. 'What . . (you/do) this time yesterday?' 'I was asleep.' 3. '.. (you/go) out last night?' 'No, I was too tired.' 4. 'Was Carol at the party last night?' 'Yes, she. . (wear) a really nice dress.' 5. How fast. . (you/drive) when the accident(happen)? 6. John. . (take) a photograph of me while I . . (not/look). 7. We were in a very difficult position. We. . (not/know) what to do. 8. I haven't seen Alan for ages. When I last. . (see) him, he .. (try) to find a job in London. 9. I . . (walk) along the street when suddenly I . . (hear) footsteps behind me. Somebody.. (follow) me. I was frightened and I.. (start) to run. 10. When I was young, I.. (want) to be a bus driver. EJERCICIOS PAST PERFECT / PRETRITO PLUSCUAMPERFECTO 1.- Pon los verbos en pasado perfecto. > I couldn't get in because I had forgotten my keys. (forget) + > Ann wasn't at home. Where had she gone (go) ? > The telephone wasn't working because we hadnt paid the bill (pay) 1 The woman told me that she .... in China a few years before. (work) + 2 Everything in the garden was brown because it ...(rain) 3 The bathroom was full of water. What ....? (happen) ? 4 I knew I .. .. that man somewhere before. (see) + 5 We were surprised to see Mark, because we.. .. his letter. (get) 6 After three days the dogs came back home. Where ....? (be) 7 They gave me some money back because I . .. too much. (pay) + 8 There was nothing in the fridge. Peter . .. the shopping. (do)
53
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
2.- Rodea la respuesta adecuada I didnt recognize / l hadn't recognized Helen, because she cut / had cut her hair very short. 1 No one understood / had understood how the cat got / had got into the car. 2 Joe didn't play / hadn't played in the game on Saturday because he hurt / had hurt his arm. 3 When I looked / had looked in all my pockets for my keys, I started/ had started to get very worried. 4 Liz never travelled / had never travelled by train before she went / had gone to Europe. 5 I arrived / had arrived at the shop at 5.30, but it already closed / had already closed. 6 1 didn't have / hadn't had much money after I paid / had paid all my bills last week. 3.- Pon los verbos en past simple or past perfect. Bill didnt tell anybody how he had got into the house. (not tell; get) Emma went to France last week. Before that, she had never been outside Ireland. (go; be) 1 When their mother.. home, the children.. .. all the sweets. (get; eat) 2 Yesterday I ............ a man who.. .. at school with my grandmother. (meet; be) 3 It .. .. to rain, and I .. .. that I.. .. my window. (start; remember; not close) 4 I .. a letter on my desk that I .. Never .. (find; open) 5 I .. .. Bob I couldn't go to the theatre, but he.. already.. the tickets, (tell; buy)
54
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Cundo utilizar cada uno de ellos
A la hora de combinar los tres tiempos verbales en una narracin de hechos, conviene que sepamos para qu se utiliza cada uno de ellos. El Pasado Simple se utiliza para la accin o los hechos concretos, ya sea una accin aislada o una sucesin de ellas. El Pasado Continuo se utiliza para describir la situacin. El Pretrito Pluscuamperfecto (Past Perfect) nos remonta a acciones anteriores a otras del pasado. Mira los siguientes ejemplos. Como vers, en ambos describimos la situacin con el Pasado Continuo y la accin con el Pasado Simple: Ej.1: I was reading when I heard the shooting Ej. 2: She was driving when she had the accident En el ejemplo 1, yo estaba leyendo (descripcin de la situacin) cuando o el disparo (accin concreta) y me interrumpi. En el ejemplo 2, una persona que estaba conduciendo (descripcin de la situacin) tuvo un accidente (accin concreta). RECUERDA QUE Cuando tengas que combinar ambos tiempos verbales tienes que seguir este esquema: WHEN + PASADO SIMPLE WHILE + PASADO CONTINUO
55
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
3. Estructura de una narracin de hechos
Ahora vamos a aprender a escribir narraciones de hechos, para lo que utilizaremos los tres tiempos verbales que hemos visto en esta unidad. Este estilo se utiliza mucho a la hora de escribir noticias, que no son sino sucesiones de hechos. Lee con cuidado las instrucciones y despus estudia el ejemplo de la narracin de un rescate en una estacin de esqu.
Cuando narramos una sucesin de hechos, queremos ser fieles a lo que pas y hacer que la persona que lea nuestra redaccin lo entienda como si lo hubiera visto. Antes de empezar a escribir, haz un esquema de los hechos que quieres reflejar y ordnalos tal y como ocurrieron en el tiempo. Escribe un ttulo para tu redaccin. Es muy importante organizar estas ideas en prrafos de dos o tres lneas. Recuerda: o En la introduccin presenta la situacin: qu pas, por qu estabas all, etc. o Haz un prrafo para describir la situacin: usa el Pasado Continuo. o En otro prrafo describe las acciones que se sucedieron: stas irn en Pasado Simple y si hubiera alguna accin anterior a ellas, en Pretrito Pluscuamperfecto (recuerda: es el pasado del pasado). o Finalmente haz un pequeo prrafo para la conclusin y acabar la redaccin. Es muy importante utilizar conectores de tiempo para que el orden en el que ocurrieron los hechos quede bien claro. Finalmente, revisa que no haya errores de gramtica ni de ortografa.
56
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
EJEMPLO DE UNA NARRACIN DE HECHOS Esquema TTULO INTRODUCCIN Prrafo 1 Presenta la accin principal. Rescate en losPirineos PARTE CENTRAL Prrafo 2 Descripcin de la situacin Describe la situacin: .. esquiando en la nieve Tambin describe el mal tiempo. Una persona grita pidiendo ayuda. Prrafo 3 Sucesin de hechos tal como sucedieron para solucionar el problema. Modelo Rescue in the mountain Last winter I lived one of the most difficult situations in my life. I helped one person who had had an accident in the Pyrenees. It was 11:00am and I was skiing with my husband. It was snowing a lot but we were having a very good time. Suddenly, we heard a cry. At first, we thought it was the wind, but then, we knew someone was crying for help. We saw a man in the snow and he looked injured. First, we asked him if he was alright. Next, we tried to help him stand up, but he told us that he had fallen while he was skiing and he had broken his left leg.
My husband stayed with him and I went to the village. Finally, the ambulance arrived half an Utiliza Past Simple, Past Continuous y Past perfect hour later. I think we saved his life. [141 words] Para que te resulte ms fcil identificarlos, los verbos estn escritos en negrita y los conectores en cursiva. CONCLUSIN Prrafo 4
4.Conclusinpara aprender ingls Radio y Conclusin y
breve opinin personal opinin A) Radio personal sobre los hechos.
Te presentamos un recurso muy til para aprender ingls a travs de la radio. Se trata de Voice of America (VOA), una emisora que ofrece una programacin especial en ingls para estudiantes del idioma. En su pgina web, se explican los orgenes de lo que denominan Special English:
57
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
The roots of Special English On October 19, 1959, the Voice of America broadcast the first Special English program. It was an experiment. We wanted to communicate by radio in clear and simple English with people whose native language was not English. Special English programs quickly became some of the most popular on VOA. They still are. Special English continues to communicate with people who are not fluent in English. Over the years, its role expanded.
It helps people learn American English while they learn about American life and stay informed about world news and science. It provides listeners with information they cannot find elsewhere. 5.- INTERNET VOCABULARY Communicating Red de network comunicacin Wartime tiempo de guerra Stamp Sello de correos Exchange information Data Tool Intercambiar informacin Datos Herramienta
The Origin of the Internet The Internet started in the late 1960s as a project of the U.S. Department of Defense: the military wanted a communication network that would work even if parts of it broke down, things that usually happen during wartime! The military had many computers which were incompatible. This network had to work between different machines of different type. In October 1969, two computers talked to each other across a telephone line: the name of this network was ARPAnet. As time passed, ARPAnet grew and connected many computers between each other.
58
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
A good analogy to the Internet is the Postal Service: The IP (Internet Protocol) is equivalent to putting a stamp on a letter: you always need a stamp to send a letter anywhere in the world.
The internet is like the Postal Service: you send a letter and the service will redirect your letter using any available route to its destination. By the 1980s, the Internet gained popularity among research organisations and universities which started to use it in order to exchange information and data. The World Wide Web or WWW was created at CERN, a physics laboratory in Geneva, Switzerland. It was used as a tool to exchange and modify documents between scientists and other organizations.
6. Autoevaluaciones
Autoevaluacin 1
Ahora vamos a comprobar que has aprendido los contenidos del tema y los sabes poner en prctica. Para ello, tienes que contestar a 10 preguntas, eligiendo entre tres posibilidades. 1. La prensa britnica se divide en broadsheets y _________. a. newspapers b. tabloids c. compacts
2. Un ejemplo de broadsheet ingls es _________. a. The Times b. The New York Times c. The Sun
3. She ___________ a mobile phone in the street last Monday. a. buy b. bought c. buyed
4. We __________ to the theatre last Sunday because we were tired.
59
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
a. go
b. didnt go
c. didnt went
5. I ____________ yesterday at 3:00am. a. slept b. did sleeping c. was sleeping
6. We ______________ when the ambulance arrived. a. was waiting b. were waiting c. were waited
7. He had an accident ________ he was working. a. while b. when c. next
8. I ____________ the book before I saw the film. a. read b. had readed c. had read
9. _________ I saw the accident and then I phoned the police. a. first b. later c. next
10. After three years waiting, I ___________ had my operation. a. last b. while c. finally
Autoevaluacin 2
1. READING COMPREHENSION. Choose the best answer according to the information in the text. 1.- Qu peridico ataca ms directamente a Fernando Alonso? a.- The Times b.- The Sun
2.- Teniendo en cuenta lo dicho sobre los tipos de peridicos, cul de los dos crees que pertenece a la prensa sensacionalista. a.- The Times b.- The Sun 3.- Qu peridico habla del sueldo de Alonso? a.- The Times b.- The Sun
2. Escribe la forma de estos verbos regulares en pasado simple. 1. watch 2. cancel 3. live 4. want 5. lie 6. pass 7. clap 8. try 9. pray 10. shop 11. listen 12. pat
60
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
3. Escribe el Pasado Simple de los verbos siguientes: 1. go 2. meet 3. take 4. begin 7. drink 8. eat 9. drive 10. do 13. win 14. put 15. fight 16. spend
4. Completa las oraciones con el Pasado Simple de uno de los verbos siguientes: have finish meet stay Need Be not buy begin phone not be
1. Sue (________ ) those shoes because they (________ ) expensive. 2. Pam (________) in hospital because she (________) an operation. 3. The lesson (________) at 7:00PM and (________ ) at 8:00PM. 4. Did you (________) my sister at the party? No, she (________ ) there. 5. Chris (________) his mother because he ( ) some help. 5. Completa las siguientes oraciones con el Past Continuous de los verbos: 1. DO? What _________ you _______________at 5PM yesterday? 2. SLEEP Everything was silent and I thought they ____________ 3. SWIM Peter _________________ when you phoned him. 4. NOT SHOP I ___________________ on Monday morning. I was at home. 5. WRITE The boy __________________ an email to his friends. 6. Escribe los verbos de las siguientes oraciones en Past Perfect: 1. TRAVEL I ___________________ to Molina de Aragn before last summer. 2. NOT SEE The girl ________________ the present before we gave it to her. 3. LISTEN We went to a concert last weekend. We _______________ to the songs before. 4. NOT TRY She _____________________ the dress before she bought it. 5. BE I was in Ruidera last month. I _________________ there two years ago. 6. PLAN They __________________ the party before they sent the invitations. 7. NOT STUDY Richard _________________ and he failed the exam. 8. DRIVE You ______________________ a car before you bought one.
61
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
9. PHONE He ______________________ before he came home yesterday. 10. NOT TELL They __________________ us the truth before we knew. 7. Completa las oraciones utilizando el Pasado Simple o Pasado Continuo de los verbos: 1. FALL/RUN Ian __________ while he __________in the park. 2. BUY/LIVE She __________this dress when she __________in London. 3. PHONE/CLEAN Mary __________ while I __________the kitchen. 4. DRIVE/HAVE She __________when she __________the accident. 5. SIT/HEAR We __________outside when we __________a noise. 8. Elige la opcin correcta: 1. I didnt finish / hadnt finished my homework when Susan phoned me. 2. By the time we arrived / had arrived, the party had begun. 3. He left the museum after he saw / had seen everything. 4. I cleaned the kitchen after everyone left / had left. 5. I had run the marathon before I finally won / had won a medal. 6. Had she sent / Did she send the invitations before she saw the error? 7. By the time David arrived at school, the exam had started / started. 8. We hadnt bought / didnt buy anything because the shops had closed. 9. I left / had left the cinema early because I had already seen the film. 10. She waited / had waited until 6 oclock in the evening.
62
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
7. Tarea final
En esta tarea vamos a ver la gran diferencia que puede haber en una noticia dependiendo de qu peridico la publique. Mira las portadas de dos peridicos norteamericanos del 12 de septiembre de 2001. Seguramente recordars la catstrofe que ocurri el da anterior en Nueva York. Observa el aspecto general de las portadas y los titulares (las letras ms grandes) que resumen en un par de palabras la noticia.
1.- Which newspaper front page is more attractive? 2.- Which newspaper front page gives more information? 3.- Which newspaper is a broadsheet? 4.- Which newspaper is a tabloid? 5.- Which newspaper would you buy? Responde a las preguntas en un documento como ste y enva la respuesta a tu tutor/a.
63
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Bloque 11. Tema 2: Travelling
NDICE
1. A trip to 2. Introduccin a la condicin 3. Expresin de la opinin 4. Cmo contrastar ideas 5. Expresin de la hiptesis 6. Autoevaluaciones 7.- Tareas
64
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
1. A trip to
Busca las palabras TRIP y TRAVEL en un diccionario. Vers que la primera es el sustantivo (viaje) y la segunda el verbo (viajar). El ttulo de la unidad TRAVELLING tambin se traduce como viajar, puesto que estamos utilizando el verbo solo (sin ningn sujeto) y lo tenemos que poner en ING. Empecemos a planear nuestro viaje: ante todo, y dado el carcter de la asignatura, buscaremos un destino donde podamos practicar nuestro ingls. Eres capaz de reconocer los siguientes pases?
Picture A
Picture B
Picture C
Picture D
Picture E
Picture F
Which countries do these pictures represent? A.C.E.B.D.F.65
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
the Australian Outback
Mira esta fotografa de Australia. En ella un grupo de viajeros se para ante una seal que indica que en los siguientes 92 kilmetros lo nico que se van a encontrar son animales salvajes . Cmo ser la vida all? En esta primera parte de la unidad vamos a conocer el Australian Outback, que es la zona que ocupa todo el centro de Australia. Es un lugar muy inhspito y casi deshabitado que soporta condiciones de clima tan extremo que lo conv ierten en uno de los lugares habitados ms solitarios del mundo.
Life in the Outback: life is very difficult down in the Australian Outback, it is an area of 2,500,000 square kilometres in the centre of Australia; it is very hot (temperatures are usu ally over 30C in summer, it is almost a desert) and there are no facilities around; people live in stations (country houses or cattle farms) very far away from any small town. Life in a sheep station is very different from life in a town or in a city; the y look after the cattle and sometimes they travel some hundreds of kilometres a day looking for their food.
66
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
There is only one big town in the Outback, it is called Alice Springs. It is in the centre of the Australian Outback. Some children go to school by receiving their classes with a two -way radio because the nearest school is too far away to go and come back every day. The outback is not an empty place; lots of people and animals wander around the plains and hills. The Aborigines have always lived in the Outback and they think it is the most wonderful place in the world to live, but if you try and spend a week out there, you will realize the type of life you can have there.
2. Introduccin a la condicin
CONDICIONAL = CONDICIN + CONSECUENCI A Oraciones condicionales: s on oraciones compuestas de una oracin subordinada (If clause) y una oracin principal (main clause): Una de ellas, la subordinada, contiene la CONDICIN, mientras que la unidad principal es la CONSECUENCI A. Como puedes imaginarte, una depende de otra, por eso se llama condicional: con la condicin de que
67
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
En concreto, la CONDICIN es la que tiene la llave. As, si se da la condicin, se da la CONSECUENCIA que se considera la proposicin principal dentro de la oracin. Mira el siguiente esquema: Main clause (principal): I will buy a car If clause (subordinada) if I win the lottery I w ill buy a car if I w in the lottery Como puedes ver, son dos clauses. Tanto en la unidad de la izquierda como en la de la derecha hay un sujeto, un verbo y sus complementos. Se puede decir que son dos oraciones independientes, pero se unen para formar una sola, que acabara en el punto gramatical . como ya sabes. Si te fijas bien, el nexo de unin entre ambas es la partcula IF, que es la que indica la condicin. IF es el si condicional, se que en castellano no lleva nunca tilde. Tambin podras encontrarte que el orden de ambas proposiones (clauses) vaya invertido y la que empieza por IF se coloque delante, como puedes ver: If clause: If I get my pay on Saturday, Main clause: I will take my wife to a good restaurant If I get my pa y on Saturda y, I w ill take my w ife to a good restaurant En este caso, como IF no puede separar ambas clauses porque va al principio de la oracin, marcam os el lmite entre ambas con una coma , justo antes del sujeto de la segunda clause. Recuerda que clause se refiere a una unidad de SVC (sujeto+verbo+complementos). En ingls te puedes encontrar varios tipos de condicionales, aunque en este mdulo tan s lo te vamos a presentar la primera. Veamos ahora los tiempos verbales de cada una de las clauses en la condicional de tipo I .
68
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
TIPO 1.- CONDICIONES ABIERTAS : condiciones presentes que son bastante posibles o probables. Forma:: If (condicin): verbo en presente / O. principal: verbo en will future If you annoy the cat, it w ill scratch you If you are hungry, Ill make you something to eat If I pass my exams, Ill go to university If it rains, Ill go to the cinema Hell get there in time if he runs all the way W hat will you do if you see an accident? PREGUNTAS : oracin principal, al principio Yes / No questions: Will you come to the party if you don t have to work? Will you speak to him if he apologizes? Will you go to England this year if you have enough money? Wh-subject questions: Somebody will buy a car if he passes his driving test -> who will buy a car if he passes his driving test? Somebody will feed the cat if we go away for the weekend -> who will feed the cat if we go away for the w eekend? Something will happen if we are late -> What will happen if we are late? Wh-non subject questions: If the bus is late, we w ill do something-> What will we do if the bus is late? If I buy a new picture I will put it somew here -> Where will you put the new picture if you buy it? Mary will phone somebody if she doesnt know how to get to the cinema-> Who w ill Mary phone if she doesnt know how to get to the cinema?
69
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
EJERCICIOS ORACIONES CONDICIONALES 1.- Rellena los espacios en blanco con la forma adecuada del verbo entre parntesis 1. If you drink lemon tea, your sore throat will feel (feel) better. 2. If he. (not study) hard, he won't pass the exam. 3. If the baby (touch) the heater, she will burn herself. 4. The theatre will be full if we . (not get) there soon. 5. If we . ( not find) a baby -sitter, we'll have to stay at home. 6. If you eat too much, you .. (put) on weight. 7. If she .. (not want) to arrive late, she will have to hurry. 8. I won't go out if it .. (n ot stop) snowing. 9. If Robert . (not arrive) soon, I'll leave without him. 10.If you . (not obey) the boss's orders, you (lose) your job!
2.- Elige la respuesta adecuada 1.If Terry . stop laughing, he w ill be sent to the headmaster's office. a. doesn't b. don't c. won't 2. If you're thirsty I you something to drink. a. will make b. will made c. should made 3.If nobody helps Brian, he .. able to do his homew ork. a. will be b . won't be c. can't be 4. If Jill . to the opera, Andrea w ill go instead. a. goes b. will go c. doesn't go 5.If Jean too many sw eets, she w ill put on w eight. a. eat a. doesnt take care b. will eat b. takes care c. eats c. took care 6. If Mandy of that cut, her leg w ill get infected. 7. Many people out of w ork if the factory closes dow n.
70
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
a. will
b. will be
c. won't
8. I w on't go out . I dont find my ke ys. a. if b. unless c. when c. ll switch 9. If you're cold I the air -conditioner on. a. switches b. switch 10. If this skirt .. fit you, I w ill change it. a. doesn't 3.- Make sentences w ith if. 1. I'm afraid the bus will be late. 2. get to work late again -> If the bus is late Ill get to w ork late again 3. lose my job -> If I get to w ork late again, Ill lose my job 4. not find another job 5. lose my flat 6. move back to my parents' house 7. get very bored 8. go swimming every day 9. Look very good 10. meet interesting people 11. go to lots of parties 12. have a wonderful time 4.- Put in the correct verb forms. If it rains, we w ill have the party inside, (rain; have) 1 I happy if Imy exam, (be; pass) 2 If you now, you the train, (leave; catch) 3 John says he as a taxi -driver if he money, (work; need) 4 If Ifree tomorrow evening, I you on Friday, (not be; see) 5 MaryChinese next year if she time, (study; have)
71
b. don't
c. does
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
6 Iyou to the station my car keys, (drive; find) 7 If heher, he a happy life, (marry; not have) 8 .you smoking if the doctor you that you must? (stop; tell) 9 the boss to us If we to him very politely,? (listen / talk) EX. 5.- Rellena los espacios con la forma correcta del verbo entre parntesis 1. If the baby ...... (be) thirsty, she ... ..... (cry). 2. If you (not give) babies love, they ( be) unhappy. 3. John . (get) plenty of exercise if he ( go) to the mountain. 4. If the director (not be ) there in person, it ( be) difficult to film.. 5. If they . (pa y) less than 10 an hour, I ( not take ) the job. 6. If he . (run), he . (not feel ) well. 7.- If you ( boil) water, it ( turn) to steam. 8.- If he . ( have) to use a computer, he (use) mine.
3. Expresin de la opinin
El mdulo anterior vimos algunas expresiones para expr esar nuestras opiniones sobre un tema concreto. En esta unidad vamos a repasar las expresiones ms importantes y a ver otras nuevas. Estas expresiones presentan nuestras ideas y van al principio de la oracin. Observa la siguiente tabla: Expressing Opini on In m y opinion, + clause (en mi opinin) I think (that) + clause (pienso que) I believe (that) + clause (creo que) Example In my opinion, smoking is bad for us I think (that) Susan is very beautiful I believe (that) the Internet is great
72
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
From my point of view , + clause (Desde mi punto de vista )
From my point of view , smoking is very bad for our health
Evidentemente, cuando alguien da su opinin sobre algo, podemos coincidir y estar de acuerdo o discrepar y tener una opinin
distinta. Veamos ahora un breve esquema para expresar nuestro acuerdo o desacuerdo sobre un tema. ACUERDO O DESACUERDO: AGREE / DONT AGREE WITH (SOMEBODY) PRESENTE Afirmativa: I / you / w e / the y agree I agree with you You agree with Susan He / she / it agrees Nick always agrees with his girlfriend My son never agrees with me Negativa: I / you / we / they dont agree W e dont agree with our children about holidays I dont agree with my brother about music He / she / it doesnt agree Peter doesnt agree with his wife about cars. She doesnt agree with him about clothes Interrogativa: Do + sujeto + agree ? // does + sujeto + agree? Do you agree with each other? Yes, we do / No, we dont Does Liz agree with you? Yes, she does / No, s he doesnt P AS ADO: Afirmativa: agreed para todas las personas They agreed (with us) to meet at six
73
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
She agreed to share expenses Negativa: did not (didnt) agree W hen I was a teenager I didnt agree with my father I suggested going to the cinema but they didnt agree Interrogativa: Did + sujeto + agree? Did you agree with your teachers? Yes, I did / No, I didnt Did they agree to pay the bill? Yes, they did / No, they didnt SO DO / AM / CAN I /// NEITHER DO / AM / CAN I Para decir que A es igu al B: So + verbo auxiliar (be, have, can, etc) + el sujeto. Se produce inversin del orden de la frase: Im hungry So am I (no So I am) Cuando en la primera frase no hay verbo auxiliar utilizamos do, does, did detrs de so My brother works in the theatre. So does my cousin SO + AUXILI AR + SUJETO I am going out later. So am I He can play the guitar, and so can I W eve got a house. So have they / So has Peter I like tennis. So does she She works in the evenings. So do I I went to the concert last week. So did I I passed the exam and so did Tom I will go to London and so will my wife NEITHER + AUXILIAR + SUJETO En oraciones negativas usamos neither + auxiliar + subject. Im not working today. Neither am I Mary cant drive. Neither can Pat Im not feeling very well. Neither am I She cant drive and neither can I
74
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
You havent got any money and neither have I Sue hasnt got a car and neither has Martin I dont want anything to eat and neither does Susan W e didnt go to the concert, and neither did they
EJERCICIOS: SO / NEITHER 1.- Expresa acuerdo con estas observaciones. Utiliza so / neither 1. 'I don't like noisy people.' 2. 'I'm a very tidy person.' 3. 'I'm not very interested in football.' 4. 'I enjoy travelling. ' 5. 'I've never been to Australia.' 6. 'Ill go there one day.' 7. 'I haven't got a very good memory.' 8. 'I haven't been working very hard recently.' 9. 'I often forget things.' 10. 'I went to bed quite late last night.' 11. 'I should go to bed earlier.' 12. 'I always tell the tru th.' 13. 'I didn't tell lies even when I was a child.'
4. Cmo contrastar ideas
Tal y como hemos visto anteriormente en el caso de las
condicionales, podemos combinar dos proposiciones independientes mediante conectores o nexos. En este apartado vamos a com binar dos proposiciones o clauses (es decir, dos unidades SUJETO + VERBO + COMPLEMENTOS) con ideas opuestas mediante los CONECTORES DE CONTRASTE .
75
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
CONECTOR (SIGNIFICADO) And (Y): Implica suma. Puede ir entre nombres, adjetivos, verbos, oraciones, etc. OR (O): Implica eleccin. Puede ir entre nombres, adjetivos, verbos, oraciones, etc. BUT (PERO) + oracin. Implica contraste, contraposicin. Va seguido de una oracin nominal (sin verbo), una oracin completa o un adjetivo
EJEMPLOS W e ate salad and fish Shes beautiful and clever He stood up and went out I went to Mercadona and shopping.
did
the
Do you want tea or coffee? You can go by car or by train You may stay or (you may) go W ill they come today or tomorrow? She asked for my e -mail, but I didnt give it to her The book is short, but interesting The book is short, but it is interesting
NOT BUT: (NO SINO)
Hes not clever but stupid we are not friends but neighbours They didnt come yesterday but this morning It wasnt Sheila but Mary who told me Although I fancy you, Im going out with somebody else Although the pupils had not studied, they passed the exam Although the weather was cold, she didnt take a coat // Despite the cold weather, she Although it was raining we went fishing // Despite the rain, we went fishing Despite his interest, I didn t give him my mobile number Despite the late hour, they went on with the meeting He arrived on time despite getting up
76
ALTHOUGH (AUNQUE) + oracin. Contraposicin. Va seguido por una oracin completa (sujeto + verbo).
DESPITE (A PES AR DE): contraposicin. Va seguido de un nombre, gerundio, o pronombre
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
late (although he got up late) It was cold, but they went on the trip despite it
As opposed to my sister, I dont smoke AS OPPOSED TO ( A As opposed to most animals, elephants DIFERENCI A DE) + noun / cant jump pronoun As opposed to you, she likes living alone
I want tea instead of coffee Instead of going by car, she went by INSTE AD OF (EN LUG AR plane DE) + NOUN / PRONOUN / He went to the match instead of me GERUND He didnt be early: instead, he was half INSTE AD, + CLAUSE O an hour late NADA Sarah couldnt feed the cat, I fed it instead
On the one hand... (por una parte) On the other hand...(por otra parte) Contraposicin / contraste entre algo positivo y algo negativo
On the one hand, shes very intelligent. On the other hand , shes very lazy On the one hand, the beach is fun. On the other hand, I dont like the sand.
Como puedes ver, los BUT y ALTHOUGH v an seguidos de una clause (SVC). Es decir, inmediatamente detrs de ellos va el sujeto de la siguiente unidad SVC (sujeto + verbo + complementos). Los tres conectores que van a continuacin DESPITE, AS
OPPOSED TO y INSTEAD OF van seguidos de un sustantivo que no es sujeto, porque no lleva verbo detrs. Los dos ltimos conectores van juntos y te dan las dos caras de la moneda. Imagina que tienes todas las ventajas de algo en una mano
77
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
y todas las desventajas en la otra, y te pones a hacer ba lanza. Por eso muestras primero lo que tienes en una mano: ON THE ONE HAND, y despus lo que tienes en la otra ON THE OTHER HAND. Estos conectores, al igual que los primeros, van seguidos de una clause, una unidad SVC.
5. Expresin de la hiptesis
Llamamos
hiptesis
las
suposiciones
situaciones
imaginarias que a veces pueden convertirse en realidad y a veces no. En castellano, se expresan con el subjuntivo: Si yo tuviera; Si l viniera; Si ellos quisieran, etc. En ingls no exist e el subjuntivo, por lo tanto tenemos que utilizar otros recursos para expresar estas situaciones imaginarias que la mayora de las veces son fruto de nuestros deseos de cambiar nuestra situacin presente. Por ello, el tiempo que vamos a utilizar es el Pas ado Simple aunque nos refiramos a situaciones presentes, precisamente para marcar esa distancia con respecto a la realidad. Mira la siguiente estructura, te resultar muy til a la hora de expresar tus deseos e hiptesis:
DESEOS
SOBRE
EL
PRESENTE
(QUEREMOS
CAMBIAR
LA
SITUACIN ACTUAL): SUJETO + WISH + CLAUSE (SUBJECT + VERB P AST SIMPLE + COMPLEMENTS) Situacin real I dont own a helicopter Deseo (w ish) I wish I ow ned a helicopter
78
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
I have to go to school
I wish I didnt have to go to school! I wish I had a new car She wishes she passed the exam He wishes he could pla y the guitar I wish she w asnt/ werent so horrible to me I wish we knew Marias address I wish I w as/were older
I have an old car She has an exam
She cant play the guitar
Shes horrible to me
W e dont know Marias address Im not old enough to go to the disco
Habrs observado
algo que a lo mejor te parece extrao: I wish I
was/were older; I wish she w asnt / werent so horrible to me. Como sabes, I / SHE WAS es la forma correct a de hacer el pasado simple del verbo TO BE. En este caso se trata de una excepcin. El subjuntivo en ingls no existe, pero s que se utiliza en los siguientes casos excepcionales: I w ish I w ere / she w ere / he w ere / it w ere Siempre que veas esta estru ctura, no pienses que hay un error (lo correcto sera utilizar W AS en todos los casos), sino que se trata de un subjuntivo. Es decir, ese pasado seala una situacin imaginaria e hipottica.
79
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
WISHES.- EJERCICIOS
EX. 1 Elige la respuesta correcta: 1. I wish I (were, would be) older than you. 2. Mandy is flying to Spain next week. I wish I (could go, can go) with her. 3. I would love to play basketball. I wish I (were, had been) taller. 4. The party is terrific. I wish you (were, had been) there. 5. You look great! I wish I (looked, had looked) like you. 6. He will have an accident. I wish he (didn't drive, hadn't driven) so fast. 7. Alan wishes you (would have come, had come). 8. I'm having a great time in Spain. I wish you (were, had been) here. EX. 2 Rellena los huecos co n la forma correcta del verbo entre parntesis 1. I wish you (be) quiet. 2. Alan wishes he play) tennis as well as Jerry. 3. Do you wish you (speak) six languages? 4. I wish I (not be) so tall. 5. I wish Barry (love) me. 6. I wish Barry (not love) my cousin. 7. Jack and Jill wish they (sell) their house. 8. I wish you (not have to) go tomorrow. 9. Tom wishes he (be) stronger. 10.Jane's father wishes she help) him wash the car.
6.-Autoevaluaciones
Autoevaluacin 1
Ahora vamos a comprobar que has aprendido los contenidos del tema y los sabes poner en prctica. Para ello, tienes que contestar a 10 preguntas, eligiendo entre tres posibilidades.
80
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
1. Outback is the name of a _________. a. desert b. town c. city
2. If she _________ to Sydney, she will send me a postcard. a. go b. will go c. goes
3. You will be angry ________ you know the truth. a. and b. but c. if
4. Pam ____________ around the world if she wins the lottery. a. travel b. will travel c. travels
5. In my ___________, you should go to the doctor. a. view b. mind c. opinion 6. I like that car, ________ I dont have the money to buy it. a. although b. but c. despite
7. We went for a walk ___________ the cold. a. although b. but c. despite
8. From her ________ of view, Pretty Woman is a very good film. a. opinion b. point c. believe
9. I wish I _________ more free time to be with my children. a. have a. doesnt work b. will have c. had c. didnt work
10. Andrew wishes he __________ at weekends. b. works
Autoevaluacin 2
1. Reading and Listening Comprehension. Choose the correct answer: 1. It is _________________ hot in the daytime a. not very b. extremely c. a bit
2. People live in _________________ a. beautiful villages b. stations c. big cities
3. Alice Springs is a ____________ a. town b. cattle farm c. hospital
4. Children receive their lessons ___________________ a. at school b. with a two-way radio c. at night
81
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
5. The doctors visit the patients ___________ a. by helicopter or plane b. by car or motorbike c. by train
6. Ayers Rock is a ______________________ a. town b. building c. holy mountain
2. Elige la opcin correcta en cada caso: 1. I invite/will invite you to have dinner if you visit me. 2. If Ann will buy/buys that dress, she will spend all her money. 3. If you study/will study hard, you will pass your exams. 4. If she goes/go on holiday, she wont be here for your wedding. 5. If Susan knows the answer, she wins/will win a lot of money. 6. He will have a good time if he see/sees that film. 7. You will see/see an interesting exhibition if you go to the museum. 8. You will speak /speak English if you travel to London. 9. If we go out tonight, we go/will go to a disco. 10. If they play tennis, they are/will be tired. 3. Completa las oraciones con la forma correcta del verbo entre parntesis: 1. If I (arrive) on time, I will call you. 2. My sister (MAKE) lunch if she is at home today. 3. If we (not buy) our tickets soon, we wont get seats. 4. My friends (be) angry if I dont invite them to my party. 5. If Bob (not get) a job soon, he will sell his house. 6. Your wife (be) worried if you dont phone her. 7. If I (find) the book, I will buy it for you. 8. You (go) on holiday if you have the money. 9. If she (know) the truth, she will tell you. 10. I will phone the police if you (not leave) me alone.
4. Elige la respuesta correcta en cada caso: 1. In my opinion/believe, Dr House is a very good TV series.
82
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
2. I think/believe that Susan is a devoted mother. 3. From my point of opinion/view, you shouldnt buy that car. 4. I believe /opine that bullfighting is cruel to animals. 5. Completa las siguientes oraciones con las expresiones del cuadro: I agree So am I Neither am I Neither do I I dont agree So do I 1. I think that Mark is very good-looking. 2. I dont believe her. 3. U2 are the best rock band in the world. 4. Terrorism should be legal. 5. I am very happy to be here. 6. She is not interested in politics. 6. Completa las siguientes oraciones. Usa and / or / but ms las frases del cuadro. he didnt see me they dont go there very often did you stay at home? shall we go to the cinema? she bought a lot of clothes I cant remember your name do you go to the gym? she watched television he didnt read it his wife went shopping
1. Lisa stayed at home ________________ 2. Peter bought a book ________________ 3. I saw your boyfriend ________________ 4. Did you go out last Saturday ____________ 5. Mark cleaned the house ________________ 6. They have a house at the beach __________ 7. Do you go swimming ________________ 8. I can remember your face _____________ 9. Shall we go for a walk ________________ 10. Maria went shopping ________________ 7. Elige la opcin correcta. 1. Im studying now although/despite theres a good film on TV.
83
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
2. I want to talk to you despite/although I know you are busy. 3. Despite/although her nerves, she passed the exam. 4. Although/Despite our many problems, we were feeling optimistic. 5. We went to Paris despite/instead of London. 8. Completa las oraciones con although, despite o instead of. 1. We played football ________________ it was raining. 2. We played football ________________ the rain. 3. We played football ________________ tennis. 4. They didnt divorce ________________ their problems. 5. We bought the house ________________ it was very expensive. 6. I want water ________________ milk in my tea, please. 7. I phoned Susan but she didnt come. Lucy came ________________ her. 8. She failed the exam __________ she studied a lot. 9. I went to the school trip ________________ my age. 10. I didnt buy that dress ________________ I liked it a lot. 9. Completa las oraciones con la forma correcta del verbo en cada caso: 1. HAVE I wish I ________________ babies. 2. SLEEP I am very tired. I wish I _________ well at night. 3. BE I want to play basketball. I wish ______ taller. 4. NOT BE I want to play basketball. I wish I ________________ so short. 5. NOT HAVE I have many problems. I wish I ____________ so many.
Tarea final
Partiendo de dos situaciones hipotticas, debes hacer una cadena de hiptesis con oraciones condicionales, de forma que la consecuencia de una oracin sea la condicin de la siguiente. Mira el ejemplo: IF it rains tonight, I will stay at home. IF I stay at home, I will watch a film. IF I watch a film, I will eat popcorn. IF I eat pop-corn, I will be thirsty Ves? Se trata de coger la consecuencia (la que va en futuro con WILL) y ponerla en la condicin, que empieza con IF y va en Presente Simple. Ahora te vamos a presentar las situaciones de salida: Situation 1: win the lottery Situation 2: go to the USA
Haz una cadena de entre 7 y 10 oraciones condicionales para cada situacin y enva la tarea al tutor/a para que la corrija.
84
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Bloque 12. Tema 1: Made in
NDICE
1. Made in 2. Pronombres personales objeto 3. Introduccin a la voz pasiva 4. Cartas estructura y redaccin 5. Autoevaluaciones 6. Tareas
85
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
1. Made in
En esta unidad vamos a ver la voz pasiva, opuesta a la voz activa. Conoces la diferencia entre ambas? En la voz activa nos centramos en la persona o cosa que realiza la accin del verbo. En la voz pasiva nos centramos en la persona o cosa que recibe la accin del verbo. Antes de empezar con la parte de gramtica, veremos cmo se puede aplicar el uso de la pasiva mediante ejemplos prcticos, cogidos de la cultura anglosajona. MADE IN
It is well known that wine, cheese, olive oil, honey and even knives are some of the most representative products of Castilla - La Mancha. What are the most important and typical products of the British Isles? Do you know any of them? Pay attention and you will be surprised by this information.
Knives are manufactured in Sheffield, because the materials that are needed for the industry are near this area
Sheep have always been bred in the area of Yorkshire. Still today, wool is produced there and it is used to make clothes.
86
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Whisky is the most famous product of Scotland. Whisky is manufactured all over the country by all kinds of distilleries and then it is taken to different countries in the world.
Scotland was also famous because a lot of ships were made in Glasgow. Nowadays, the production has been reduced because of foreign competition.
The area of South Wales was very busy during the 1970s and 1980s because coal was mined here.
However, coal mining was stopped in the 1990s.
Fancy a beer? If you like black beer, then go to Ireland. Black beer is produced in Dublin and then it is sold in the United Kingdom and Europe.
2. Pronombres personales objeto
Como vemos en el cuadro, los pronombres personales tienen una forma (sujeto) cuando actan como sujeto de la oracin, y otra (objeto) cuando desempean otras funciones diferentes. SUJETO OTROS USOS / OBJETO I YOU HE SHE IT WE THEY THEM
ME YOU HIM HER IT US
SUJETO : Va delante del verbo. Realiza la accin del verbo
87
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
I like Mary. He needs help. The y want your address OBJETO: Van detrs del verbo. Desempean diferentes funciones Complemento directo o indirecto . Mary doesn't like me. Detrs de preposicin : Look at me. W hy is Jane w ith him? Detrs de be: 'W ho's there?' 'It's me.' (not usually 'It is I. ') Is that Joe?' 'Yes, that 's him.' En respuestas informales : 'W ho said that?' 'Me.' 'I'm tired.' ' Me too.' Is that for us? Help him. Don't tell them anything.
EJERCICIOS PRONOMBRES 1.- Rodea la respuesta correcta : (I) / Me don't understand. 1. 'W ho said that?' 'It was she / her.' 2. Tell we / us your address. 3. This isn't for you, it's for he / him. 4. I don't think they / them are here today. 5. 'W here's your brother?' 'That's he / him over there.' 6. W here are the children? Can you see they? / them? 7. Ask she / her why she / her is crying. 2.- PON: he, him, she, her, they or them. 1 'Does your father speak English?'' understands a little.'
2 'I'm seeing Lucy and Pete on Tuesday.' 'Oh, give .. my love.' 3 'Mr. Carter's here.' 'Ask .. to wait downstairs.' 4 W here are your friends? ... 're very late. 5 'Have you spoken to Mrs. Lewis?' 'Not yet. I'm going to phone this evening.' 6 'W here's Ann?'' .'s in Germany all this week.'
88
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
3.- PON: it, they or them. 1 'W here are my keys? ''.'re on that chair.' 2 'W here did that cat come from? ' '. came in through the window.' 3 'W hat did you think of the film? ''.'s not very good.' 4 'W hat shall I do with these letters?' 'Just put on the table.' 5 'Can I have John's address?' 'I'll give .. to you this afternoon.' 6 'Did you enjoy your ho liday in Ireland?' 'Yes, ..'s a wonderful place.' 7 'W here are your glasses?' 'I've lost ..' 8 'W ould you like tickets for the concert?' 'How much do cost?' 4.- Haz frases sustituyendo los nombres subra yados por el pronombre correcto.
Jo hn and I saw Peter yesterday. He bought John and me a cup of
coffee -> We saw Peter yesterday. He bought us a cup of coffee 1.- David and Mike are arriving today. I'm meeting David and Mike at the station. 2.- I'm looking for Mary. Have you seen Mary? Mary isn't at home. 3.- John and I saw a film called The Tiger yesterday. Have you seen The Tiger? 4.- Come to the swimming pool with Joanna and me. Joanna and I are leaving now. 5.- George and Jane are meeting Paul today. Paul is having lunch with George and Jane. 5.- Completa las frases con: me/us/him/her/it/them. 1. W ho is that woman? W hy are you looking at ? 2. Do you know that man?' 'Yes, I work with . 3. I'm talking to you. Please listen to ................ 4. These photographs are nice. Do you want to look at..... ?
89
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
5. I like that camera. I'm going to buy ................
6. W here are the tickets? I can't f ind ....................... 7. W e're going out. You can come with ............ 8. I don't like dogs. I'm af raid of ........................ 9. W here is she? I want to talk to ....... ............... 10. Those apples are bad. Don't eat....................
En las transformaciones de pasiva en activa y viceversa tambin tenemos que utilizar de manera correcta los pronombres personales, pues al trasformar las frases los pronombres que usemos van a cambiar de funcin.
3. Introduccin a la voz pasiva
En ingls se utiliza mucho la voz pasiva, que se centra en el objeto de una accin (quin o qu recibe la accin que expresa el verbo). Oraciones tan sencillas y habituales como Me dijeron la verdad, Maana inauguran el nuevo centro de adultos o En Estados Unidos se habla ingls no utilizan la voz pasiva en castellano, pero para decirlas en ingls S que necesitaremos conocer este tipo de estructura. Como decamos al principio de esta unidad, stas son las caractersticas principales de voz activa y voz pasiva: ? En la voz activa nos centramos en la persona o cosa que realiza la accin del verbo. ? En la voz pasiva nos centramos en la persona o cosa que recibe la accin del verbo. Por tanto, ? En la voz activa, el sujeto de la oracin es la persona o cosa que realiza la accin del verbo. ? En la voz pasiva, el sujeto de la oracin es la persona o cosa que recibe la accin del verbo.
90
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Activa : Sujeto + verbo + complemento directo: PETER CREATED A COMPANY Pasiva: Sujeto paciente + verbo en pasiva + by + complemento agente : A COMPANY WAS CREATED BY PETER El verbo en pasiva est formado por to be que marca el tiempo, y el participio de pasado del verbo que usbamos en la frase en activa PARTICIPIO PASADO 1.- Verbos regulares: es igual que el pasado simple (infinitivo + ed) Work worked Love loved Study - studied Play played Plan planned Talk talked smoke smoked try tried enjoy - enjoyed stop stopped
2.- Verbos irregulares: Tercera columna de la tabla Go gone Get got Eat - eaten Speak spoken Do done See seen
TIEMPOS PASIVOS: El tiempo equivalente del verbo to be + participio pasado PRESENTE SIMPLE: Presente de to be (am / is / are) + participio pasado
They never invite me to parties -> I am never invited to parties They make paper from wood -> paper is made from wood You buy stamps in a post office -> stamps are bought in a post office People play football in many countries.> football is played in many countries We dont use this machine very often -> this machine isn't used
91
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
PASADO SIMPLE: Pasado de to be (was / were) + past participle
When did they clean the room? -> when was the room cleaned? They cleaned them yesterday -> they were cleaned yesterday. A thief stole Anns bicycle last week -> Ann's bicycle was stolen last week They sent the letters to the wrong address? The letters were sent to the wrong address
INFINITIVO: be + past participle (infinitivo pasivo simple)
They will clean the room later.-> the room will be cleaned The music was very loud and you could hear it from a long way away-> it could be heard They are going to build a new supermarket next year-> a new supermarket is going to be built You cant understand the problem without help -> the problem can't be understood without help Students cant wear pyjamas in class -> pyjamas can't be worn in class You must keep the door locked -> the door must be kept locked They cant do the job -> the job can't be done They are going to interview him next week -> he's going to be interviewed next week PRESENTE CONTINUO: Presente continuo de to be (am / is / are + being) + past participle
Somebody is cleaning the room at the moment -> the room is being cleaned at the moment Is anyone reading the paper? -> is the paper being read? They are working on new inventions -> New inventions are being worked on Somebody is using the computer at the moment -> the computer is being used at the moment
92
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
PASADO CONTINUO: Pasado continuo de to be (was / were + being) + past participle Somebody was cleaning the rooms -> the rooms were being cleaned They were recording our conversation -> our conversation was being recorded The government was building a new road -> a new road was being built (by the government) They were cooking the vegetables for too long -> the vegetables were being cooked for too long Paul was painting the fence -> the fence was being painted (by Paul) PRESENTE PERFECTO: Presente perfecto de to be (have / has been) + past participle They havent invited us to the party -> we havent been invited to the party They have delivered the post -> the post has been delivered They havent washed the windows ->the windows havent been washed They have postponed the concert? ->the concert has been postponed
BY + COMPLEMENTO AGENTE: El complemento agente se introduce con la preposicin by (por) Si no es relevante o se desconoce, no se hace constar
The radio was invented by Marconi The bridge was built by the Romans A number of trees were blown down by the strong wind. The post was delivered this morning by the postman Ten goals were scored last Saturday by the players The door is closed at nine Students arent allowed to leave before 14:25 English is spoken here
93
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
PASIVA. EJERCICIOS
1.- Rodea la respuesta correcta 1 English speaks / spoken / is spoken in Australia. 2 I studied / was studied French for three years at school. 3 We spent / was spent too much money on holiday. 4 This window broke / was broken by your little boy. 5 Her clothes made / are made in Paris. 6 This book written / was written by my brother. 7 The new university will open /will be opened by the Prime Minister. 8 Ann was driving / was driven much too fast, and she stopped / was stopped by the police. 2.- Escribe el presente simple pasivo de los verbos entre parntesis Ejemplo: A lot of olive oil is used in Greek cooking, (use) 1 Arabic .....................................(write) from right to left, 2 Those programmes . (watch) by millions of people every week, 3 Stamps .................................. (sell)in most newsagents in Britain, 4 The police say that nothing.(know) about the child's family, 5 In English, 'ough' ................................. (pronounce)in a lot of different ways, 6 Spanish .................................... (speak) in Peru, 7 Cricket ................................... (play) by two teams of eleven players, 8 Our windows ................................ (clean) once a month, 3.- Escribe oraciones negativas e interrogativas en presente simple pasivo. 'Jaguar cars .are not made in America.' (not make) 'Where are they made?' 'In the UK.' 1 'My name with a Y.' (not spell).
'How' 'L, E, S, L, I, E.'
'That kind of birdaround here.' (not usually see) 'Where' 'In warmer countries.'
'Wherelike were.' (not pronounce) 'How' 'Like wear.'
94
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
'Diamonds in Scotland.' (not find) 'Where ' 'In South Africa, for example.' 'My sister very well.' (not pay) 'How much ' 'I don't remember.'
4.- Escribe oraciones en futuro pasivo con los verbos del recuadro: clean close finish open send speak
The motorway will be closed for three days. 1. The museum by the Queen. 2. One day Englisheverywhere. 3. This job in a few days. 4. Your roomwhile you're out. 5. Your ticketsto you next week.
5.- Escribe oraciones negativas e interrogativas en futuro pasivo . 'The football match wont be played on Saturday.' (play) 'When will it be played? ' 'On Sunday.' 1 The visitors to the hotel by bus.' (take) 'How . ' 'By taxi.' 2 The new libraryin the Central Square.' 'Where . ' 'Behind the Police Station.' 3 'English at the conference.' (speak) 'What language .................................... ' 'Chinese.'
(build)
6.- Escribe oraciones en pasado simple pasivo: Don Quixote was written by Miguel de Cervantes 1 Our passportsby a tall woman in a uniform, (take) 2 These booksin the classroom yesterday, (leave) 3 I don't think this roomyesterday, (clean) 4 We at the airport by a driver from the university, (meet) 5 Nobodywhat was happening, (tell)
95
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
6 He away to school when he was twelve, (send)
7.- Escribe oraciones negativas e interrogativas en pasado simple pasivo: 'We werent paid when we finished the work.' (not pay) 'When were you paid? 'Two months later.' 1 'My fatherin England.' (not educate) 'Where' 'In Germany.' 2 'The letterson Tuesday.' (not post) 'When' 'On Thursday.' 3 'Thisin butter.' (not cook) 'How' 'In margarine.' 4 'My suitin England.' (not make) 'Where' 'In Hong Kong.' 5 The billin cash.' (not pay) 'How' 'With a credit card.' 8.- Usa las palabras del recuadro para completar las respuestas a las preguntas. Usa presente continuo pasivo. grass / cut she / interview I / send it / clean my watch / repair my hair / cut
'Can we play on the football pitch?' 'No, the grass is being cut' 1 'Can't you wear your blue suit tonight?' 'No, 2 Did Alice get that new job?' 'Not yet - today.' 3 'What time is it?' 'Sorry, I don't know: ' 4 'Why the big smile?' ' to Hawaii for a week.' 5 I usually read a magazine while 9.- Completa cada oracin con by ... y la mejor expression del cuadro. a farmer a tree loud music my granddaughter a committee the government The name of the new school is being decided by a committee of parents and governors. 1 Most of the cost of university education is paid 2 All the neighbours were woken up coming from the flat.
96
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
3 I'm being taught how to use a computer 4 A box of Roman jewels has been found in a field in Kent. 5 The window was broken that fell over in the storm. 10.- Tacha el complemento agente si no ofrece informacin relevante. A 54-year-old accountant was arrested for drunk driving last night by the police 1 'Romeo and Juliet' was written by Shakespeare. 2 All of these birds have been seen in Britain by people who watch birds. 3 Everest was first climbed in 1953 by mountain climbers. 4 Everest was first climbed in 1953 by Edmund Hillary and Sherpa Tensing 5 This house was built by Frank Lloyd Wright. 6 My sister's books have been translated into thirty languages by translators. 7 Sugar is made from sugar cane and sugar beet by sugar companies. 8 This letter wasn't written by an English person.
4. Las cartas: estructura y redaccin
En esta unidad vamos a aprender a escribir cartas formales para utilizarlas en nuestra bsqueda de empleo. En concreto, cartas de
acompaamiento, que son las que adjuntamos a los CVs cuando los enviamos a una empresa para buscar trabajo. Lee con cuidado las
instrucciones y despus estudia el ejemplo.
Cuando escribimos una carta de acompaamiento, queremos causar una buena impresin a la persona que va a leer la carta, y posiblemente a hacernos una entrevista de trabajo.
97
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
En la parte superior derecha escribimos nuestros datos: Direccin (en ingls el nmero se pone delante del nombre de la calle) Telfono Correo electrnico Fecha (la fecha en ingls con ordinales: 1st, 2nd, 23rd, 14th, etc.) A continuacin, los datos del destinatario: Nombre Puesto que ocupa en la empresa Direccin Al igual que hemos visto en anteriores redacciones, es muy importante organizar las ideas en prrafos de dos o tres lneas, siendo claro y conciso. Recuerda: En el saludo utilizamos Dear Sir/Madam si no conocemos el nombre de la persona a la que nos dirigimos, o Dear Mr/Ms X si conocemos el apellido. Observa que Dear no tiene gnero, por tanto se puede utilizar con nombres de mujer o de hombre por igual. Adems, vale para saludos formales (cuando utilizamos el apellido o Sir/Madam) o para cartas informales (cuando escribimos el nombre de la persona Dear Marta) Haz un prrafo para explicar el motivo de la carta. En otro prrafo argumenta por qu eres el candidato idneo para el puesto. No te extiendas: dirige la atencin al CV que envas con la carta. Utiliza un prrafo aparte para indicar los documentos que adjuntas, as como la disponibilidad para ampliar informacin, por ejemplo en una entrevista. Antes de firmar, escribe Yours sincerely, que es una manera formal de despedir la carta. Si te parece demasiado formal, escribe slo Sincerely. Finalmente firma la carta y escribe tu nombre. Es muy importante utilizar las frmulas que te indicamos para que tu carta parezca natural. Por ltimo, revisa que no haya errores de gramtica ni de ortografa.
98
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
EJEMPLO DE CARTA FORMAL Esquema DATOS DEL REMITENTE Modelo Mary Olsen 39 Bristol Road Tel.: +34 666-777-888 Email: maryolsen@goldmail.com March 15th, 2009 Mr Peter Maxwell Editor of The Literary Review Dear Mr Maxwell I read your advertisement in the newspaper for the post of Editors Assistant and I am very interested in it. I have worked as a secretary for three years and I think the post you offer is a good opportunity for me to do something more important. As you will see in my CV, I have finished Secondary School and I can speak English. I am a hard working and well organised worker. I can use a word processor and my spelling is very good. In my present job I have to do many different things and I am willing to learn. In my opinion, I am the person you need for the job. My CV and references are attached to this letter. I am available for interview at anytime. I look forward to hearing from you. Yours sincerely Mary Olsen.
DATOS DEL DESTINATARIO Saludo Prrafo 1 Motivo de la carta: respuesta a un anuncio de oferta de empleo Prrafo 2 Defensa de nuestra candidatura: explica las cualidades que tienes y di por qu eres la persona idnea para el puesto. Prrafo 3 Documentos adjuntos: CV, disponible para entrevista. Despedida Firma
99
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Autoevaluaciones
Autoevaluacin 1
Ahora vamos a comprobar que has aprendido los contenidos del tema y los sabes poner en prctica. Para ello, tienes que contestar a 10 preguntas, eligiendo entre tres posibilidades. 1. La voz activa se centra en ___________ que realiza la accin del verbo. a. el sujeto b. el objeto c. los complementos 2. La voz pasiva se centra en ___________ que recibe la accin del verbo. a. el sujeto b. el objeto c. los complementos
3. Los pronombres objeto van situados _______________ del verbo. a. delante b. detrs c. indistintamente delante o detrs
4. Los pronombres personales ________________. a. sustituyen a los sustantivos b. acompaan a los sustantivos, van delante de ellos c. van siempre delante del verbo 5. En ingles, la voz pasiva se utiliza ________________ castellano. a. mucho ms que en b. mucho menos que en c. igual que en 6. El verbo en pasiva se compone de _________________. a. auxiliar BE + participio presente (-ING) b. auxiliar HAVE + participio pasado (-ED; 3 columna verbos irreg) c. auxiliar BE + participio pasado (-ED; 3 columna verbos irreg.) 7. Elige la pasiva de la siguiente oracin: Anne bought the beautiful dress. a. The beautiful dress was buying by Anne b. The beautiful dress was bought by Anne c. The beautiful dress is bought by Anne 8. Nobody invited Peter to the party. a. Peter wasnt invited to the party b. Peter didnt invited to the party c. Peter didnt be invited to the party
100
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
9. Elige la oracin pasiva que no tiene errores. a. Your house will be painted last week b. Your house will be painted next week c. Your house has painted last week 10. Marca la oracin pasiva que tiene errores a. We were told the news by the doctor b. We was told the news by the doctor c. We were informed by the doctor
Autoevaluacin 2
1. En primer lugar, lee las preguntas. Despus, vuelve a leer el texto del apartado 1 del tema (Made in) antes de contestar las preguntas. Reading Comprehension. Choose the correct answer: 1. Sheffield is famous because ___________ are made there. a. knives b. materials c. knifes
2. Sheep are needed to make _______________. a. bred b. wool c. clothes
3. Whisky is manufactured _______________________. a. only in Glasgow b. all over Scotland c. in Edinburgh
4. ___________________ ships are made in Glasgow nowadays. a. Many b. More c. Not so many
5. In South Wales, mining was stopped _______________. a. in the 1970s b. in the 1980s c. in the 1990s
6. Black beer is sold in __________________. a. Ireland b. Dublin c. Europe
2. Reescribe estas frases sustituyendo los nombres subrayados por los pronombres (de sujeto y de objeto) que correspondan: 1. Simon and Susan were cooking. __________were cooking.. 2. Jane phoned Megan at half past four . Jane phoned _________ at half past four. 3. Marian gave Peter the shopping list. _____ gave __________ the shopping list.
101
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
3. Reescribe estas frases en activa usando el pronombre personal en su forma correspondiente: 1. I was selected for the team by the trainer. ________ selected __________ for the team. 2. Thomas and his brother were attacked by some teenagers. Some teenagers attacked __________ 3. My husband and I were invited to Ellens wedding. __________ invited __________ to her wedding. 4. Completa las siguientes oraciones: 1. Television _____________ (invent) in 1926. a. was invented b. were invented c. is invented
2. The big prize in Who wants to be a millionaire ____________ yesterday. a. is won b. was won c. are won
3. My favourite TV programme _______________ (show) on Mondays. a. was shown b. is shown c. are shown
4. In Spain, children _______________________ (give) free education. a. is given b. are given c. were given
5. Green ____________________ (make) with blue and yellow. a. is made b. are made c. was made
6. MTV (Music Television) __________ (watch) in more than 40 countries in the 1990s. a. are watched 6. b. was watched c. is watched
Completa las siguientes oraciones en pasiva con los verbos del cuadro: build sell export operate invent need
1. Scotch whisky__________ all over the world. [PRESENT SIMPLE] 2. One day all music __________ in the Internet. [FUTURE WITH WILL] 3. A lot of money __________ to buy a house these days. [PRESENT SIMPLE] 4. The telephone __________ by A. Graham Bell. [PAST SIMPLE] 5. This school __________ last year. [PAST SIMPLE] 6. She __________ next month. [FUTURE WITH WILL]
102
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
6. Completa la siguiente carta con las expresiones de la tabla:
th
March 17 , 2009 As you can see in my CV My CV is attached to this letter Yours sincerely,
I am looking to hearing from you 34, Castelar St Dear Mr. Montero I am the ideal person for the job
Maria Lizcano ____________________ Tel: +34 600 111 222 mlizcano@goldmail.com ____________________ Mr. Patricio Montero Commercial Manager of SPORTSWORLD ____________________ I am writing to you because I read the advertisement in the newspaper for a secretary. I find this job very interesting and I would like to apply for it. ____________________, I finished my Secondary Education and I can speak English. I am organised and hard-working. I also know the world of sports, so I think ____________________ ____________________ . I am available for interview at any time. ____________________ ____________________, Maria
7. Une cada pregunta (1 7) con su respuesta correspondiente (a g): 1. Are there any other skills you want to tell me? 2. Right, Mr. Garca, what can you tell me about yourself?
103
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
3. Is there anyone who can give me some references about you? 4. Can you describe yourself, please? 5. Do you have any professional experience? 6. What about your interests? What are your hobbies? 7. Tell me about your education.
A. I went to evening secondary school at CEPA Los Llanos. B. Yes, of course! For further information about me, please phone Mr. Lopez. His mobile number is 555 666 777 C. Right, I am from Socullamos in Ciudad Real, bu t I am living in Albacete at the moment. I am 23 years old and I am not married yet. D. In my free time, I like meeting my friends, walking my dogs and watching TV E. Yes, I do. I have worked for a similar company for 6 months. F. I am good at computers , I can type and my spelling is very good. I can also speak English. G. W ell, I am very organised and hard working. I like working with other people and I am very responsible. 8. Copia las preguntas y respuestas del ejercicio anterior en el orden lgico para que formen una conversacin. Empieza as: Right, Mr. Garca, what can you tell me about yourself? 9. COME ON, PLACE YOUR BETS! (Vamos, hagan sus apuestas!) A. - Knives are made in C. - W ool is made in E. - W hisky is made in B. - Black beer is made in D. - Ships w ere made in F. - Coal w as produced in
104
CEPA E. Tierno Galvn
INGLS
Mdulo IV- ESPAD
Tareas
Tarea 1: En esta primera tarea vamos a transformar oraciones
activas en oraciones pasivas . Recuerda los pasos para formar la oracin en voz pasiva: a) Pregntale QU? Al verbo. La respuesta de esta pregunta ser el sujeto de la oracin pasiva. b) Pon en pasiva la accin verbal, ya sabes, verbo TO BE + la accin verbal en participio. c) Coloca a continu acin el resto de los elementos de la oracin. 1. The y make shoes in that factory. Shoes ____ in that factory. 2. The y built that skyscraper in 1934. That skyscraper in1934. Ahora, transforma las oraciones enteras. Recuerda ir movindote por bloques. 3. The students finished the course last w eek. 4. The y repaired the streets last month. 5. The y make these toys of plastic. 6. The y finished the new motorw ay last September. 7. In England people eat lunch at one oclock. 8. The y performed Beethoven s Fifth S ymphony yesterda y.
Tarea 2: Completa el siguiente texto sobre el origen del chicle
(chew ing gum), poniendo los verbos entre parntesis en pasiva. Did you know that chewing gum ___________ (invent) in the Mayan culture? The chewing gum be came popular throughout America in the 19th century. The gum from and a ___________ a special (call)chiclet type of and tree. it The
___________
(produce)
trees___________ (cut)
liquid ___________ (collect). Finally,
different flavours ___________ (add) to make the gum tastier. Chewing gum ___________ (bring) to Europe at the beginning of the
20th century and it soon became popular Today chewing gum___________ (produce) in factories. These Chewing
factories use the same method as in the Mayan culture. gum___________ (sell) everywhere.
105
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Advanced Class - 27.11.17Dokumen3 halamanAdvanced Class - 27.11.17paul john shieldsBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet and Coronavirus 10 AcDokumen5 halamanWorksheet and Coronavirus 10 AcjimenaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1. - The Future. ExercisesDokumen12 halamanUnit 1. - The Future. ExercisesAntonio Sanchez LozanoBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Bachillerato Extra Grammar Full With ExplanationDokumen13 halaman1 Bachillerato Extra Grammar Full With ExplanationAndreaTürmeBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar Review (Key)Dokumen9 halamanGrammar Review (Key)Hoàng Bùi TânBelum ada peringkat
- English PracticeDokumen8 halamanEnglish PracticeHero GarkaBelum ada peringkat
- Vocabulary: Mark /7Dokumen3 halamanVocabulary: Mark /7hoangphiBelum ada peringkat
- Školsko Takmičenje Iz Engleskog Jezika VIII Razred 2014Dokumen6 halamanŠkolsko Takmičenje Iz Engleskog Jezika VIII Razred 2014Marijana Misic100% (2)
- Improve your fitness with gym membershipDokumen2 halamanImprove your fitness with gym membershipAnonymous 9ThJkQrYBelum ada peringkat
- Modal Verbs: Shall We ? According To The ModelDokumen34 halamanModal Verbs: Shall We ? According To The ModelSimon MarianBelum ada peringkat
- English Activity FutureDokumen11 halamanEnglish Activity FutureAna C SimancaBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Modals InglésDokumen8 halamanEjercicios Modals InglésAlbaDevBelum ada peringkat
- WhatDokumen3 halamanWhatJosmar Angeles IsidroBelum ada peringkat
- FutureDokumen19 halamanFutureberofugoBelum ada peringkat
- New Headway Intermediate Additional Exercises - Prof. Galo Proano. 2014 BDokumen18 halamanNew Headway Intermediate Additional Exercises - Prof. Galo Proano. 2014 BDoraNickoleVGBelum ada peringkat
- Guia #4 de La Competencia de Ingles: Instructor: Christin BeltranDokumen6 halamanGuia #4 de La Competencia de Ingles: Instructor: Christin BeltranYan CastañedaBelum ada peringkat
- Present Simple and Continuous: Try - Go - Learn - See - Live - LikeDokumen6 halamanPresent Simple and Continuous: Try - Go - Learn - See - Live - LikeCamo BritesBelum ada peringkat
- Ámbito Comunicación. InglésDokumen106 halamanÁmbito Comunicación. InglésRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- You Will Pa Ss The Test: I Will Speak Eng LishDokumen7 halamanYou Will Pa Ss The Test: I Will Speak Eng LishKelly DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Completo FuturoDokumen28 halamanCompleto Futurocactus1983Belum ada peringkat
- MUST KNOW EXERCISESDokumen10 halamanMUST KNOW EXERCISESDeea Paris-PopaBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Exam - Básico 6 PDFDokumen5 halamanMidterm Exam - Básico 6 PDFDENIS LEYVA100% (1)
- Future Tenses Check: Maria Speaks EnglishDokumen10 halamanFuture Tenses Check: Maria Speaks EnglishikerccBelum ada peringkat
- Test 2 (Tenses of Verbs, Phrasal Verbs, Expressions C1 & C2, Reading Comprehension)Dokumen5 halamanTest 2 (Tenses of Verbs, Phrasal Verbs, Expressions C1 & C2, Reading Comprehension)mariellecatralBelum ada peringkat
- PRACTICE Semana 12 InglésDokumen7 halamanPRACTICE Semana 12 InglésAlex VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Future TenseDokumen16 halamanFuture TenseivanelchinoinoinoiBelum ada peringkat
- Mixed TensesDokumen45 halamanMixed TensesberofugoBelum ada peringkat
- Ingles - SamuelDokumen23 halamanIngles - SamuelRosa MaríaBelum ada peringkat
- Intermediate Test Units 8 and 9 LíviaDokumen4 halamanIntermediate Test Units 8 and 9 LíviaJade BahmadBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Phrasal Verbs: SentencesDokumen8 halaman1 Phrasal Verbs: SentencesDiana PatriciaBelum ada peringkat
- CV4 Handout 2 M1 2020Dokumen4 halamanCV4 Handout 2 M1 2020Siphy MandlateBelum ada peringkat
- Future Forms Grammar RulesDokumen4 halamanFuture Forms Grammar RulesSiphy MandlateBelum ada peringkat
- GRAMMAR REVIEW 1 FINAL EXAMstudentsDokumen2 halamanGRAMMAR REVIEW 1 FINAL EXAMstudentsJaqueline SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Will or Be Going ToDokumen4 halamanWill or Be Going Toapi-329021051Belum ada peringkat
- Future FormsDokumen5 halamanFuture FormsIulia OstafiBelum ada peringkat
- Future Tense ExercisesDokumen6 halamanFuture Tense ExercisesPedro BjBelum ada peringkat
- Vocab Review (Key)Dokumen7 halamanVocab Review (Key)Hoàng Bùi TânBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Exam 12Dokumen5 halamanMid Exam 12Quetzal Rojas PadillaBelum ada peringkat
- Future ExercisesDokumen4 halamanFuture ExercisesMonicaBelum ada peringkat
- PronounsDokumen13 halamanPronounsKristal Almodovar DandiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Exercises: 1 Is The Verb in Bold An Auxiliary Verb (A) or A Full Verb (F) ?Dokumen5 halamanUnit 1 Exercises: 1 Is The Verb in Bold An Auxiliary Verb (A) or A Full Verb (F) ?Ralica CvetanovaBelum ada peringkat
- Verball Tense ReviewDokumen5 halamanVerball Tense ReviewPaolita CipaconBelum ada peringkat
- keys-GENERAL REVISION-2021lDokumen7 halamankeys-GENERAL REVISION-2021lNicoSuarezzBelum ada peringkat
- Express The FutureDokumen6 halamanExpress The FuturefifibraindacyBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 11: Seeing Is Believing: VocabularyDokumen4 halamanUnit 11: Seeing Is Believing: VocabularyCristina Rodriguez PardoBelum ada peringkat
- Unit II - 1st Class - June 01-FUTUREDokumen6 halamanUnit II - 1st Class - June 01-FUTUREJesús Alexander MejíazBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Pre IiiDokumen2 halamanQuiz Pre IiiJuan Carlos Chuquilin ZamoraBelum ada peringkat
- The Simple Future Tense How To Form The Simple Future Tense?Dokumen7 halamanThe Simple Future Tense How To Form The Simple Future Tense?Q uBelum ada peringkat
- Sectio N 12: Determi Ners: Revise The Basics: This, That, These, ThoseDokumen28 halamanSectio N 12: Determi Ners: Revise The Basics: This, That, These, ThoseMy MyBelum ada peringkat
- Revision For Primary SchoolDokumen7 halamanRevision For Primary SchoolKatka KokrdováBelum ada peringkat
- 2BACH Ingles OralDokumen12 halaman2BACH Ingles OralGabriela GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Pasiva InglésDokumen10 halamanEjercicios Pasiva InglésAna Sánchez50% (2)
- Grammar and vocabulary quizDokumen4 halamanGrammar and vocabulary quizJose Manuel Alegre MerceBelum ada peringkat
- Complete The Sentences With A Form of Going To or WillDokumen1 halamanComplete The Sentences With A Form of Going To or WillCrissy85Belum ada peringkat
- Will or Going To 2013 - 1Dokumen5 halamanWill or Going To 2013 - 1jojinjoBelum ada peringkat
- Be Going To 91604Dokumen53 halamanBe Going To 91604DAO NANCYBelum ada peringkat
- Progress Test Files 1-5 Grammar/Vocabulary GrammarDokumen5 halamanProgress Test Files 1-5 Grammar/Vocabulary GrammarRJ SmithBelum ada peringkat
- TIEMPOSVERBALESDokumen1 halamanTIEMPOSVERBALESRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Asterix in BritainDokumen12 halamanAsterix in BritainRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Ámbito Comunicación. InglésDokumen106 halamanÁmbito Comunicación. InglésRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Pasado ContinuoDokumen3 halamanPasado ContinuoRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Winter Word SearchDokumen1 halamanWinter Word SearchRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Reported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto) : A) DefiniciónDokumen19 halamanReported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto) : A) DefiniciónRaquel Marcos-alberca Calonge100% (2)
- U3 Alrededor de El MundoDokumen9 halamanU3 Alrededor de El MundoRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Depresente Simple y Presente ContinuoDokumen2 halamanEjercicios Depresente Simple y Presente ContinuoRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Choose The Correct Answer of These Sentences Using Modal VerbsDokumen1 halamanChoose The Correct Answer of These Sentences Using Modal VerbsRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- English Pronouns: Personal Pronouns, Possessive Determiners, Possessive PronounsDokumen7 halamanEnglish Pronouns: Personal Pronouns, Possessive Determiners, Possessive PronounsRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Table of English TensesDokumen36 halamanTable of English TensesRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Potencias 6Dokumen4 halamanPotencias 6Raquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Question WordsDokumen6 halamanQuestion WordsRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- ComparisonDokumen5 halamanComparisonRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Furniture and Appliances 4Dokumen1 halamanFurniture and Appliances 4Raquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Clothing Crossword HardDokumen1 halamanClothing Crossword HardRaquel Marcos-alberca Calonge50% (2)
- Question WordsDokumen6 halamanQuestion WordsRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Winter clothing choices and laundry tasksDokumen1 halamanWinter clothing choices and laundry tasksAna Angeleska-SpiroskaBelum ada peringkat
- English Pronouns: Personal Pronouns, Possessive Determiners, Possessive PronounsDokumen7 halamanEnglish Pronouns: Personal Pronouns, Possessive Determiners, Possessive PronounsRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Reported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto) : A) DefiniciónDokumen19 halamanReported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto) : A) DefiniciónRaquel Marcos-alberca Calonge100% (2)
- Asterix in BritainDokumen12 halamanAsterix in BritainRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- ComparisonDokumen5 halamanComparisonRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Table of English TensesDokumen36 halamanTable of English TensesRaquel Marcos-alberca CalongeBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study - Help DocumentDokumen2 halamanCase Study - Help DocumentRahBelum ada peringkat
- Priming An Airplane EngineDokumen6 halamanPriming An Airplane Enginejmoore4678Belum ada peringkat
- O - 6 Series Mill Operation Manual-ENDokumen119 halamanO - 6 Series Mill Operation Manual-ENLeonardo OlivaresBelum ada peringkat
- Yardi Commercial SuiteDokumen52 halamanYardi Commercial SuiteSpicyBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study, g6Dokumen62 halamanCase Study, g6julie pearl peliyoBelum ada peringkat
- Raptor SQ2804 Users Manual English v2.12Dokumen68 halamanRaptor SQ2804 Users Manual English v2.12JaimeBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise C: Cocurrent and Countercurrent FlowDokumen6 halamanExercise C: Cocurrent and Countercurrent FlowJuniorBelum ada peringkat
- Mutaz Abdelrahim - Doa - MT-103Dokumen17 halamanMutaz Abdelrahim - Doa - MT-103Minh KentBelum ada peringkat
- UFO Midwest Magazine April2011Dokumen16 halamanUFO Midwest Magazine April2011Jimi HughesBelum ada peringkat
- A Development of The Test For Mathematical Creative Problem Solving AbilityDokumen27 halamanA Development of The Test For Mathematical Creative Problem Solving AbilityanwarBelum ada peringkat
- Löwenstein Medical: Intensive Care VentilationDokumen16 halamanLöwenstein Medical: Intensive Care VentilationAlina Pedraza100% (1)
- Marriage Gift PolicyDokumen4 halamanMarriage Gift PolicyGanesh Gaikwad100% (3)
- VISCOSITY CLASSIFICATION GUIDE FOR INDUSTRIAL LUBRICANTSDokumen8 halamanVISCOSITY CLASSIFICATION GUIDE FOR INDUSTRIAL LUBRICANTSFrancisco TipanBelum ada peringkat
- Roll Covering Letter LathiaDokumen6 halamanRoll Covering Letter LathiaPankaj PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Systems: TermsDokumen19 halamanCost Systems: TermsJames BarzoBelum ada peringkat
- Hercules SegersDokumen15 halamanHercules SegerssuneelaamjadBelum ada peringkat
- 01 WELD-2022 Ebrochure 3Dokumen5 halaman01 WELD-2022 Ebrochure 3Arpita patelBelum ada peringkat
- Citation GuideDokumen21 halamanCitation Guideapi-229102420Belum ada peringkat
- Relation of Jurisprudence With Other Social Sciences - LLB NotesDokumen4 halamanRelation of Jurisprudence With Other Social Sciences - LLB NotesPranjaliBawaneBelum ada peringkat
- Indra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043Dokumen28 halamanIndra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043AnhTuấnPhanBelum ada peringkat
- CGL Flame - Proof - MotorsDokumen15 halamanCGL Flame - Proof - MotorspriteshBelum ada peringkat
- APTARE IT Analytics: Presenter NameDokumen16 halamanAPTARE IT Analytics: Presenter NameCCIE DetectBelum ada peringkat
- WCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Dokumen211 halamanWCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Antonio VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Putri KartikaDokumen17 halamanPutri KartikaRamotSilabanBelum ada peringkat
- Complex Numbers GuideDokumen17 halamanComplex Numbers GuideGus EdiBelum ada peringkat
- Special Proceedings Case DigestDokumen14 halamanSpecial Proceedings Case DigestDyan Corpuz-Suresca100% (1)
- 2020 - Audcap1 - 2.3 RCCM - BunagDokumen1 halaman2020 - Audcap1 - 2.3 RCCM - BunagSherilyn BunagBelum ada peringkat
- TESTIS PHYSIOLOGY Spermatogenic Cell Syncytium Makela and Toppari 2018Dokumen10 halamanTESTIS PHYSIOLOGY Spermatogenic Cell Syncytium Makela and Toppari 2018LudimilaBelum ada peringkat
- DJDokumen907 halamanDJDeepak BhawsarBelum ada peringkat
- Data Sheet FC SIDokumen2 halamanData Sheet FC SIAndrea AtzeniBelum ada peringkat