Unemployance
Diunggah oleh
jawadhalhDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Unemployance
Diunggah oleh
jawadhalhHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
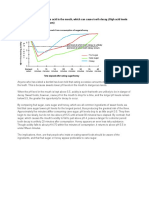
Unemployment has always been a problem in our society. The current unemployment rate in Ontario is approximately six percent.
This percentage does not usually f luctuate very much, unless there is some dramatic incident that affects the whol e economy, like inflation for example. There are numerous causes of unemployment that economists around the world have came up with. However, I will describe th e most important ones that are relevant to Canada. The biggest reason for unempl oyment, not just Canada, but also worldwide, is frictional unemployment. Many pe ople are always to be found in the process of moving from one job to another in order to improve their salary. And frictional unemployment is the delay in movem ent between jobs. It also applies to young people trying to find their first tim e job, language disabilities and lack of skills, including literacy. Frictional employment of this kind increases every year. The effects of this kind of unempl oyment is that there are more and more young job seekers out there, while the av erage level of formal education and job expectations of these new entrants to th e labour force is very high. But the most important effect of all is the reducti on in the rate of growth of new job opportunities. Frictional unemployment can o nly be reduced by better career counseling, guiding school leavers into areas wh ich have great number of jobs, by offering subsidies to employers, and by breaki ng down artificial barriers to certain trades and professions. The second cause of why there is unemployment is due to variations in climate. This type of unemp loyment is called season unemployment. Industries like farming, lumbering, fishi ng construction, and port operations are examples of the victims. Seasonal unemp loyment is popular in Canada because we encounter snow in most part of the count ry, therefore it has a great effect on the well-being of the economy. To reduce this, many municipalities undertake winter-works projects and industries that pr ovide winter employment have sometimes been given government financial assistanc e. Another cause of employment is that consumer demands different or better thin gs as time goes by. Therefore, some industries grow while other decline or even disappear. There are many negative effects upon this kind of structural unemploy ment. It means that new jobs are being created in some industries, while others are falling. And most workers cannot easily move from one industry to another. E ven though job retraining programs offered by the government are trying to help over come this, there is a natural reluctance in a person to uproot themselves a nd family to seek job elsewhere. Sometimes this type of structural unemployment affects industries that are vital to the economic well being of a whole region. The last, but not least, cause of unemployment is our advanced technology taking over labour work. Using machines instead of people is more profitable for a fir m because if there is an invention of some new machinery, employing it will have a more capital-intensive method of production. One example of this introduction is of microcomputer in small business, or the use of robots for automobile prod uction. This will likely reduce the rate of hiring. The obvious effect of this, like any other unemployment type, is aggravating local unemployment. These are s ome particular cause and effect situations that happen in a cyclical manner. The degree of which it affects the society plays a large part in whether or not our economy is stable
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Week 3 World of Work Lesson PlanDokumen7 halamanWeek 3 World of Work Lesson Planapi-300530206Belum ada peringkat
- 90,95,2000 Macro Multiple ChoiceDokumen37 halaman90,95,2000 Macro Multiple ChoiceAaron TagueBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Industries: One Mark QuestionsDokumen7 halamanManufacturing Industries: One Mark Questionskrishnareddy_chintalaBelum ada peringkat
- Education, Skills and The Emerging Labour Market in India: Ravi SrivastavaDokumen24 halamanEducation, Skills and The Emerging Labour Market in India: Ravi SrivastavaJBelum ada peringkat
- Wilson DecliningSignificanceRevisedDokumen16 halamanWilson DecliningSignificanceRevisedNatália AlvesBelum ada peringkat
- Career Guidance in Secondary SchoolsDokumen10 halamanCareer Guidance in Secondary SchoolsAfesoj BelirBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Labor: UnifctDokumen17 halamanDepartment of Labor: UnifctUSA_DepartmentOfLaborBelum ada peringkat
- Mayor Ras J. Baraka's 2023 State of The City AddressDokumen12 halamanMayor Ras J. Baraka's 2023 State of The City AddresserickieferBelum ada peringkat
- Study This Example and Find Out Unsuitable Language For Describing A GraphDokumen9 halamanStudy This Example and Find Out Unsuitable Language For Describing A GraphThị VyBelum ada peringkat
- Labor Standards Azucena NotesDokumen46 halamanLabor Standards Azucena NotesYen055100% (5)
- RRL 1Dokumen5 halamanRRL 1DEANNA DANIELLE REYESBelum ada peringkat
- Applying Indian FMCG Lessons in NigeriaDokumen8 halamanApplying Indian FMCG Lessons in NigeriaSunil Kumar SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Information System Management (Cousrework)Dokumen16 halamanInformation System Management (Cousrework)Mg ThuyeinBelum ada peringkat
- Bank of America Capital Market OutlookDokumen8 halamanBank of America Capital Market OutlookAceBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Business Studies A - Notes C1 Understanding Business ActivityDokumen38 halamanIGCSE Business Studies A - Notes C1 Understanding Business Activitymohamed100% (1)
- Education's Impact On Economic Growth and Productivity: Schooling Versus SkillsDokumen8 halamanEducation's Impact On Economic Growth and Productivity: Schooling Versus SkillsRodiahhalim84 hatijahBelum ada peringkat
- Malu Mohan 2019Dokumen9 halamanMalu Mohan 2019Chris MartinBelum ada peringkat
- Globalization: How It Has Affected Philippine Education and BeyondDokumen6 halamanGlobalization: How It Has Affected Philippine Education and BeyondTinBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Labor: 2002rulesDokumen61 halamanDepartment of Labor: 2002rulesUSA_DepartmentOfLaborBelum ada peringkat
- The USA, A Country in GlobalizationDokumen3 halamanThe USA, A Country in GlobalizationMelania RyuBelum ada peringkat
- Economics Syllabus Dot PointsDokumen11 halamanEconomics Syllabus Dot PointsDaniel MooneyBelum ada peringkat
- Kwantlen Polytechnic University Macroeconomics ECON1250 Questions AnswersDokumen34 halamanKwantlen Polytechnic University Macroeconomics ECON1250 Questions Answersmahbub100% (1)
- Hobsbawm Hartwell AbstractDokumen5 halamanHobsbawm Hartwell AbstractIqbal SanduBelum ada peringkat
- Delaying The Hunt For EmploymentDokumen3 halamanDelaying The Hunt For EmploymentNazeyra JamalBelum ada peringkat
- Macroeconomics Project: TopicDokumen30 halamanMacroeconomics Project: TopicSuryansh -Belum ada peringkat
- Eating Sweet Foods Produces Acid in The Mouth, Which Can Cause Tooth Decay. (High Acid Levels Are Measured by Low PH Values)Dokumen19 halamanEating Sweet Foods Produces Acid in The Mouth, Which Can Cause Tooth Decay. (High Acid Levels Are Measured by Low PH Values)Munawir Rahman IslamiBelum ada peringkat
- List at Least Three Prominent Characteristics of Developing Countries That Is Present in The Philippines. What Makes You Think So?Dokumen2 halamanList at Least Three Prominent Characteristics of Developing Countries That Is Present in The Philippines. What Makes You Think So?Monette DellosaBelum ada peringkat
- Marxist Theory of UnemploymentDokumen4 halamanMarxist Theory of UnemploymentSON OF WRATH HOLLOW POLBelum ada peringkat
- Unemployment Among Graduates Today Is Caused by Their Own AttitudeDokumen2 halamanUnemployment Among Graduates Today Is Caused by Their Own AttitudeSelvam YogamuhilanBelum ada peringkat