PD DEMO Abdomen
Diunggah oleh
Martin Allen BuenaventuraDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PD DEMO Abdomen
Diunggah oleh
Martin Allen BuenaventuraHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1
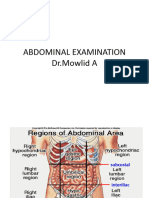
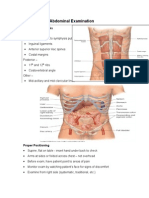
PD DEMO ABDOMEN BOUNDARIES -topography: expose from xiphoid process symphysis pubis -margins >Lower end of costal margin >ASIS >left and right midclavicular line (MCL) -px points with -entire hand: 4 equal quadrants -finger: 9 quadrants Region 2: above the stomach = epigastrium Organ: stomach - peptic ulcer disease, gastritis Regions 1&3: below costal margin/chondrium = R & L hypochondrium Organs (1): liver & gallbladder (3): spleen blood dyscrasias Region 5: umbilical region Regions 4&6: approximates the area of the lumbar vertebra = R & L lumbar Region 8: below the stomach = hypogastrium Above the pubis = suprapubic Organs: urinary bladdercystitis;uterus,fallopian tube Region 7&9: = R & L iliac At inguinal canal = R & L inguinal Organ (7): Appendix Examination of Abdomen Prepare the patient. Position = supine 2 pillows; 1 under the head and another (smaller) under the knees Expose: xiphoid symphysis pubis MD: R-handed = R side of the patient L-handed = L side of the patient if not indicated=right hand na agad Sit or stand = oblique view Palpation is the most difficult. INSPECTION SKIN Color: if same color arm & abdomen=produces too many melanocyte stimulating hormone; hyperpigmentation=Addisons or adrenal insufficiency Lesions: description & distribution Scar: from surgery or trauma; possibility of the scar to adhere to nearby bowel loop cause obstruction = post scarring adhesions SHAPE Flat Globular Scaphoid: anorexia nervosa, bulimia SYMMETRY Asymmetric=due to tumor/mass BULGING FLANKS & ABNORMAL BULGES ascites=fluid goes to the flanks, lulubog na yung flank pantay na sa pwet BLOOD VESSELS there should be none, if present: Dilated capillaries = spider angiomas Dilated veins = above umbilicus obstruction in superior mesenteric vein below umbilicus obstruction in inferior mesenteric vein UMBILICUS Flat Everted: 2 to umbilical hernia (congenital) Inverted inverted everted: below abdomen (+) mass=pushes the umbilicus outward
underneath epigastrium=abdominal aorta (+) pulsation anywhere else = abnormal PERISTALSIS contractions of the bowel loops to propel the contents from oral anal Bowel sound=gurgling sound to hear the BS, but not see the peristalsis MASS if (+) @ transverse colon: distal will be emptied; peristalsis stronger than usual=visible peristalsis= bad sign emergency! Operate! PULSATIONS AUSCULTATION -use diaphragm (stet) = BS are high frequency sound BOWEL SOUND anywhere, preferentially @ RLQ=gurgling sounds within 2-3 s Normoactive Hyperactive=high pitched, almost no interval Hypoactive=very soft, interval is very far/distant Absent=(-)BS for 5mins in at least 2 locations=abN obstruction: early=hyper; middle=hypo; late= absent = ileus = paralysis of the muscles that causes peristalsis BRUIT turbulent blood flow in the blood vessels flow = laminar Epigastrium area = abdominal aorta; if (+) = AAA R & L Paraumbilical area = renal arteries; if (+) congenital renal artery stenosis-very young HPN PERCUSSION -contents of abdomen are mostly gas = tympanitic -all 4 quadrants LIVER SPAN Normal value: 6-12cm Vertical landmark: RMCL 1. Start at the level slightly lower than the umbilicus, tympaniticdullness = lower border of liver rd th 2. Start at 3 or 4 ICS RMCL, from resonantdullness = upper border of liver SLEEN DULLNESS -at left hypochondrium -spleen=dull -base of the lungs=resonant -splenic flexure=tympanic Vertical landmark: LMAL Horizontal landmark: L 9, 10, 11 ICS Normal findings: no spleen dullness is percussed/ spleen dullness in any 1 ICS If 2 or 3 ICS =spleen is enlarged= abnormal PALPATION -ask if px feels any pain in the abdomen -area with pain examined LAST -if (-) pain: elicit tenderness= (+) pain if area is touched or pressed Ask patient to cough LIGHT (SUPERFICIAL)PALPATION -use tip of the fingers, palm on patients abdomen -dipping motion -1cm deep -dipglidedipglide (swift motion, dont lift palms)
kgdvibarra
-MUSCLE TONE/MASS/TENDERNESS Soft Firm Rigid=pag pinapalpate ndi bumibigay -voluntary: px is anxious, distract the px by asking him to breathe deeply or talk to him, normally abdomen softens. -involuntary: generalized peritonitis = bowel loop had ruptured tone of muscle (reflex) DEEP PALPATION Single handed (SH) assess if theres: MASS Double handed (DH) TENDERNESS (R) hand palpates, (L) hand pushes normally, the liver & spleen are not palpable BIMANUAL PALPATION -RUQ -palpate for LIVER & (R) KIDNEY 1. (R)hand parallel to rectus abdominis (pointing upwards, near costal margin), (L)hand at the back (last few ribs/thorax) 2. ask the patient to breathe through the abdomen, on expiration, (R)hand glides in then lift (L)hand diaphragm goes down, liver goes down, if something bumped (R) finger = abnormal; (-) palpation = ; if something hit the palm = kidney on bimanual palpation the liver & (R) kidney are NOT palpated HOOKING TECHNIQUE = liver -examiner faces towards the feet of the patient -both hands hooked at costal margin BIMANUAL PALPATION -LUQ -palpate for SPLEEN & (L) KIDNEY -(R)hand direct towards the spleen, other hand at (L)thorax/back of the patient (+): spleen is enlarged Mass at palm: (L) kidney MIDDLETON TECHNIQUE = spleen -(R)handed examiner moves to the LEFT side of the patient, hook fingers of both hands on costal margin, then feel for the spleen KIDNEY PUNCH Landmark: costovertebral angle-junction between ribs and spine -(R)handed: left palm @ CVA then punch -capsule is inflamed (+) pain receptors= painful patient complains of back pain, difficulty in urinating, blood-colored urine (-) kidney punch or CVA tenderness SPECIAL MANEUVERS Patients abdomen is globular, (+) ascites; to rule out, use: SHIFTING DULLNESS @ supine: tympanitic all throughout = fat Tympanitic then dull on dependent areas = ascites
Px on (R) Latl decubitus for 5 mins percuss: dull on dep. Side Then (L) Latl decubitus for 5mins percuss: dull on dep. Side the dullness have shifted from the R side to the L side FLUID WAVE -ask patient to place hands on the middle, ulnar aspect touching the abdomen (-): upon percussion, did not feel anything ATTRIBUTES MASS Size: small=pinch Large=ipitin between 2 hands then measure Location: ask px to lift head (muscle becomes rigid) Intraabdominal = less prominent Intramural = more prominent BALLOTEMENT -if with ascites: the mass will float -common with ovarian mass TENDERNESS = local peritonitis (+) during palpation: direct tenderness (+) upon removal of the palpating hand: rebound BLUMBERG = pain on the same site palpated ROVSING = pain away from the site of palpation referred pain: pathology is still@site of palpation JARRING TENDERNESS/ MARKLES px stands on tiptoes, then rest the toesshake abdomenpx touches tender area = (+) Markles sign PSOAS SIGN px lying down, press on the knee, ask px to elevate pressed knee psoas muscle contracts pulls the peritoneum = (+) if pain OBTURATOR SIGN px lying down, flex hip at right angle flex the knee at right angle internally rotate the leg obturator contract = pain MURPHYS SIGN -R hypochondrium pain = acute cholecystitis (+) rxn of px: inspiratory arrest
NOTES from Dr. Siocs lecture. also read PD MANUAL and BATES GOD BLESS!
kgdvibarra
PD PRACS GUIDE: ABDOMEN PREP PT 1. POSITION 2. EXPOSURE INSPECTION 1. SKIN color, lesion, scar 2. SYMMETRY 3. SHAPE flat/ globular/ scaphoid 4. BULGING FLANKS/ABN. BULGES 5. DILATED BV spider angiomas, veins 6. UMBILICUS flat/ inverted/ everted 7. PULSATION 8. PERISTALSIS 9. MASS AUSCULTATION 1. BS 2. BRUIT
normo/ hypo/ hyper/ absent epigastrium R/L paraumbilical
PERCUSSION 1. LIVER SPAN DULLNESS 2. SPLEEN DULLNESS ASCITES 1. SHIFTING DULLNESS 2. FLUID WAVE ASK PAIN TENDERNESS LIGHT PALPATION 1. CONSISTENCY 2. MASS 3. TENDERNESS
soft/ firm/ rigid
DEEP PALPATION 1. SH NO MASS 2. DH TENDERNESS BIMANUAL RUQ 1. LIVER HOOKING 2. (R) KIDNEY LUQ 1. SPLEEN MIDDLETON 2. (L) KIDNEY SPECIAL MANUEVER TENDERNESS SUPINE DIRECT REBOUND BLUMBERG ROVSING-PSOAS-OBT BALLOTMENT MURPHYS
STANDING MARKEL
kgdvibarra
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- OMM Review SheetDokumen9 halamanOMM Review SheetSolomon Seth Sallfors100% (2)
- Free Nclex RN Study GuideDokumen25 halamanFree Nclex RN Study GuideKatie Shortt100% (11)
- Os 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Dokumen4 halamanOs 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Ronneil BilbaoBelum ada peringkat
- AbdomenDokumen7 halamanAbdomenShayne Lyrrie Pajela100% (1)
- LWW BATES 13 Abdomen Transcript FINALDokumen6 halamanLWW BATES 13 Abdomen Transcript FINALmuhammad Babar50% (2)
- Lessons Learned From The Dog GenomeDokumen11 halamanLessons Learned From The Dog GenomebellonicoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology Mcqs (4th Year)Dokumen9 halamanPathology Mcqs (4th Year)usmandumassar100% (7)
- Examination of Gastrointestinal System: I.InspectionDokumen7 halamanExamination of Gastrointestinal System: I.Inspectionvonon35132Belum ada peringkat
- Pemeriksaan AbdomenDokumen46 halamanPemeriksaan AbdomenPrystia_RBelum ada peringkat
- Pemeriksaan AbdomenDokumen91 halamanPemeriksaan AbdomenEndah Cahaya SufianyBelum ada peringkat
- Preparation: Palpation INSPECTION Inspect Abdomen ForDokumen2 halamanPreparation: Palpation INSPECTION Inspect Abdomen FornicoscribdBelum ada peringkat
- Abdomen ExaminationDokumen3 halamanAbdomen ExaminationLouie FigueroaBelum ada peringkat
- LI - Physical Examination - AbdomenDokumen6 halamanLI - Physical Examination - AbdomenTravis DonohoBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Abdominal ExaminationDokumen3 halamanBasic Abdominal Examinationcpradheep100% (1)
- PACES 3 - AbdomenDokumen14 halamanPACES 3 - AbdomenDrShamshad KhanBelum ada peringkat
- No. Description of Actions To Be Done Score 0 1 2Dokumen3 halamanNo. Description of Actions To Be Done Score 0 1 2Adiprayogo LiemenaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing the Abdomen: 4 Quadrants and 9 RegionsDokumen54 halamanAssessing the Abdomen: 4 Quadrants and 9 RegionsWilma Acorin OrillinedaBelum ada peringkat
- GI History and Abdominal ExamDokumen113 halamanGI History and Abdominal ExamTokichaw AwokeBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Pediatrics MsMMaMDokumen40 halamanClinical Pediatrics MsMMaMGoha Basha100% (3)
- Abdominal ExaminationDokumen107 halamanAbdominal Examinationaxmedfare138Belum ada peringkat
- Physical Assessment of Abdomen and RectumDokumen41 halamanPhysical Assessment of Abdomen and RectumLeonilyn Dagoplo RN100% (1)
- Digestion and Absorption in the StomachDokumen82 halamanDigestion and Absorption in the Stomachkristine_silangBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Exam GuideDokumen9 halamanAbdominal Exam GuideDarawan MirzaBelum ada peringkat
- Examination of Gastrointestinal SystemDokumen37 halamanExamination of Gastrointestinal SystemayushiBelum ada peringkat
- 5.abdominal ExamDokumen16 halaman5.abdominal ExamMaria AlwanBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Session 3 - AbdominalExamDokumen15 halaman3 Session 3 - AbdominalExamjhk0428Belum ada peringkat
- Notes On Physical Examination of AbdomenDokumen6 halamanNotes On Physical Examination of AbdomenMarwa Al-AzzawiBelum ada peringkat
- Bates Physical Exam Video NotesDokumen3 halamanBates Physical Exam Video Notesdulcedeleche12359Belum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Examination For PSIII Edited-1Dokumen33 halamanAbdominal Examination For PSIII Edited-1myarjddbzBelum ada peringkat
- Physical ExaminationDokumen10 halamanPhysical ExaminationChristine NaBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory exam checklistDokumen8 halamanRespiratory exam checklistKelly ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Exam: Order of Exam Is Critical. Auscultate BEFORE Palpating!Dokumen14 halamanAbdominal Exam: Order of Exam Is Critical. Auscultate BEFORE Palpating!RomanBelum ada peringkat
- Specific Examination - AbdomenDokumen9 halamanSpecific Examination - Abdomenlinna chinBelum ada peringkat
- Care of Clients With Gastrointestinal Disorders: Michael D. Manglapus, BSN-RN, RM, Man, PHDDokumen61 halamanCare of Clients With Gastrointestinal Disorders: Michael D. Manglapus, BSN-RN, RM, Man, PHDMichael Baylon DueñasBelum ada peringkat
- DokumenDokumen6 halamanDokumenPita Ayu lestariBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Exam GuideDokumen5 halamanAbdominal Exam GuideNesma AdelBelum ada peringkat
- Percussion of The Abdomen: Prof. R. Sukumar MD Institute of Internal Medicine MMC & GGHDokumen25 halamanPercussion of The Abdomen: Prof. R. Sukumar MD Institute of Internal Medicine MMC & GGHVignesh Kumar ChandiraseharanBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Assessment VideoDokumen4 halamanAbdominal Assessment VideoAmber Nicole HubbardBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal ExaminationDokumen9 halamanAbdominal Examinationthunderlike30Belum ada peringkat
- AbdomenDokumen2 halamanAbdomenskeebs23Belum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Assessment SlidesDokumen31 halamanAbdominal Assessment SlidesFarisa Jane BanggoBelum ada peringkat
- Pemeriksaan Abdomen: Psik Fikes UmmDokumen12 halamanPemeriksaan Abdomen: Psik Fikes UmmAbd RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- The Abdominal Examination Frequently Appears in Osces and This Guide DemonstratesDokumen14 halamanThe Abdominal Examination Frequently Appears in Osces and This Guide DemonstratesAli UmarBelum ada peringkat
- Meridian LimpaDokumen23 halamanMeridian LimpaHilyatul ilmi Al mufidahBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Abdominal Pain History and Exam HPCDokumen5 halamanAcute Abdominal Pain History and Exam HPCnaafBelum ada peringkat
- Gastro ExamDokumen2 halamanGastro ExamJessica Brittain-GeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Exam Guide: Palpation, Inspection & Surface MarkingsDokumen4 halamanAbdominal Exam Guide: Palpation, Inspection & Surface MarkingsPhysician AssociateBelum ada peringkat
- Physical ExaminationDokumen55 halamanPhysical Examinationdakshpanchal26369Belum ada peringkat
- Abdomen PE ChecklistDokumen6 halamanAbdomen PE ChecklistJulienne Sanchez-SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Internal MedicineDokumen5 halamanInternal MedicineManickanadarajah VanoBelum ada peringkat
- Ortho PE NotesDokumen35 halamanOrtho PE NotesSudesna Roy ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Semester 1 Physical Examination Skills Lab Handout Abdominal Exam IDokumen4 halamanSemester 1 Physical Examination Skills Lab Handout Abdominal Exam IFlowerBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing The Abdomen 1Dokumen20 halamanAssessing The Abdomen 1srslytrdBelum ada peringkat
- Pemeriksaan Fisik Abdomen 1Dokumen18 halamanPemeriksaan Fisik Abdomen 1Andini RizkyBelum ada peringkat
- ThompsonDokumen95 halamanThompsonoooo100% (1)
- Respiratory Examination: The Position of The PatientDokumen24 halamanRespiratory Examination: The Position of The PatientMuhammed Barznji100% (1)
- Abdominal ExaminationDokumen70 halamanAbdominal ExaminationNur Hamizah Md FuziBelum ada peringkat
- GI System Exam GuideDokumen8 halamanGI System Exam GuideJaspreet KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Physical ExaminationDokumen5 halamanPhysical ExaminationAmniAzmi100% (1)
- H.A Abd SPLEENDokumen36 halamanH.A Abd SPLEENromaaBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal PEPDokumen7 halamanAbdominal PEPRandy TurnerBelum ada peringkat
- CDC - Fasciola - BiologyDokumen2 halamanCDC - Fasciola - BiologypecopecochanBelum ada peringkat
- Semen AnalysisDokumen3 halamanSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- Iam MahavetnetDokumen13 halamanIam MahavetnetVet_ashishtklBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 MariebDokumen5 halamanChapter 8 MariebmjhenkeBelum ada peringkat
- CRI Annual Report 2006Dokumen10 halamanCRI Annual Report 2006aptureincBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Quarter Exam Grade 10 Animal ProductionDokumen4 halaman3rd Quarter Exam Grade 10 Animal Productionbella flor villanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 7.2 - ElectrocardiogramDokumen2 halamanExercise 7.2 - ElectrocardiogramKevin F. CortesBelum ada peringkat
- Socio-Economic Profile and Constraints Faced byDokumen5 halamanSocio-Economic Profile and Constraints Faced byAmandeep Singh GujralBelum ada peringkat
- Annotated Reading Dengue FeverDokumen1 halamanAnnotated Reading Dengue FeverGoRbz SarmientoBelum ada peringkat
- Vital Spots 10 - Taranaki ITF Taekwondo PDFDokumen54 halamanVital Spots 10 - Taranaki ITF Taekwondo PDFMaria Elisa MonclusBelum ada peringkat
- 5090 - w22 - QP - 12 Biology O-Level PypDokumen20 halaman5090 - w22 - QP - 12 Biology O-Level Pypmuiz phiBelum ada peringkat
- Dental Caries Booklet PDFDokumen10 halamanDental Caries Booklet PDFIon BondariBelum ada peringkat
- GET17Report FinalDokumen56 halamanGET17Report Finalmnn164Belum ada peringkat
- LAMPIRAN RET PELAYANAN KESEHATAN (Rev)Dokumen167 halamanLAMPIRAN RET PELAYANAN KESEHATAN (Rev)RafliBelum ada peringkat
- Animal Farm RebellionDokumen3 halamanAnimal Farm Rebellionbrandenburgdaan0% (1)
- Anaesthesia For Paediatric Dentistry: Lola Adewale MBCHB DCH FrcaDokumen8 halamanAnaesthesia For Paediatric Dentistry: Lola Adewale MBCHB DCH FrcaJavier Farias VeraBelum ada peringkat
- Spirulina Improves Growth - Egg Production and Meat Quality - 2012Dokumen15 halamanSpirulina Improves Growth - Egg Production and Meat Quality - 2012julesverneBelum ada peringkat
- Poultry Welfare Developing CountriesDokumen12 halamanPoultry Welfare Developing CountriesshamalaksBelum ada peringkat
- OBDokumen4 halamanOBCharlie Cotoner FalgueraBelum ada peringkat
- ICD 10 Codes for Tuberculosis (TB) DiseasesDokumen111 halamanICD 10 Codes for Tuberculosis (TB) DiseasesMarnitaBelum ada peringkat
- SCHAEFER (2007) Lurking Pathogens - Parte1 PDFDokumen11 halamanSCHAEFER (2007) Lurking Pathogens - Parte1 PDFmarcelomfnBelum ada peringkat
- Sheep FactsDokumen50 halamanSheep FactsMoises Calastravo100% (1)
- KS3 Summary Revision Worksheets-2jnbiuu PDFDokumen104 halamanKS3 Summary Revision Worksheets-2jnbiuu PDFTrúc HồBelum ada peringkat
- Cellulitis: Clinical Review: Be The First To CommentDokumen9 halamanCellulitis: Clinical Review: Be The First To CommentAnonymous 1nMTZWmzBelum ada peringkat
- H1N1 Swine FluDokumen17 halamanH1N1 Swine Flurhtsghmagkfsy100% (5)
- Activity 6 IntegumentaryDokumen5 halamanActivity 6 Integumentaryhanna castueraBelum ada peringkat
- Alexander Holschneider, Prem Puri - Hirschprung Disease and Allied DisordersDokumen510 halamanAlexander Holschneider, Prem Puri - Hirschprung Disease and Allied DisordersDiana Lora ParvuBelum ada peringkat
- The Hall of Fire 05Dokumen29 halamanThe Hall of Fire 05maldreidor100% (1)