SID V9.0 Web
Diunggah oleh
inam_qauDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SID V9.0 Web
Diunggah oleh
inam_qauHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
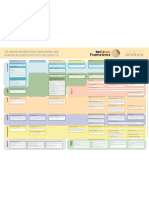
TM FORUM INFORMATION FRAMEWORK (SID) DOMAIN BUSINESS ENTITIES RELEASE 9.
0
STRATEGY & COMMIT INFRASTRUCTURE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT PRODUCT LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT OPERATIONS SUPPORT & READINESS FULFILLMENT ASSURANCE
AMDOCS > CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE SYSTEMS INNOVATION
For the Shared Information/Data model please refer to the TM Forum document suite GB922 v9.0 at www.tmforum.org. An electronic copy of this poster is available at http://www.amdocs.com/Posters | SID poster design Amdocs. SID content TM Forum 2011
BILLING
MARKET STRATEGY AND PLAN
Supports the business plans and strategies on how to address the market with appropriate products and channels.
MARKET/ SALES PRODUCT SERVICE RESOURCE SUPPLIER/PARTNER ENTERPRISE
SALES CHANNEL
Keeps track of distribution channels and sales activities, sales quotas, sales contests, commission/bonus plans, commissions/bonuses, and maintains groups of individuals that make up the sales force.
SALES STATISTICS
Maintains sales forecasts, new service requirements, customer needs, and customer education, as well as calculating key performance indicators about Sales & Marketing revenue and sales channel performance.
CONTACT/LEAD PROSPECT
Provides the ability to track sales leads through their life cycle up until the time the leads become customers, including lead and contact information, sales prospects, proposals made to potential customers, and the amount of potential revenue the leads represent in the form of a sales pipeline.
PRODUCT USAGE
Represents occurrences of employing a Product for its intended purpose. Product Usage is dened by a Product Usage Specication and its associated Product Usage Specication Characteristic entities. Product Usage is an enrichment of Service Usage records and can be static (les with pre dened usage records) or dynamic (as part of a synchronous protocol)
MARKET SEGMENT
Supports market segments, market statistics, and forecasts.
MARKET STATISTIC A categorization of performance measures by Market Segment. Performance is measured for the Service Provider and a Service Providers Competitors in the market place. PARTY DEMOGRAPHIC A feature or quality used to make recognizable or to dene a Party playing a Party Role, such as age, income, education, revenue, and so forth. PARTY PROFILE A match between a Party and a Party Prole Type. It is based on matching Party Demographics and other Party characteristics, such as use of a product, with the characteristics of a Party Prole Type. A Party Prole Type is Characteristics used to group Parties for the formulation and targeting of MarketingCampaigns. Prole Types can be based on Party Demographics, Geographic Areas, Product Offerings, and Market Segments.User-dened Data Points can also be specied.
MARKETING CAMPAIGN
MEDIA A mechanism by which Marketing Campaigns, Product Promotions, and Product Placements are be launched into the marketplace. It describes such mechanisms as the press, radio, trade shows, internet, and so forth. It is also used to advertise other provider Product Promotions and Product Placements.
CUSTOMER BILL COLLECTIONS
Handles credit violations, actions for overdue debts, and facility billing audits.
CUSTOMER BILL INQUIRY PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
Denes the functionality and characteristics of product offerings made available to the market.
PRODUCT PERFORMANCE
Handles product performance goals, the results of end-to-end product performance assessments, and the comparison of assessments against goals. The results may include the identication of potential capacity issues.
PRODUCT
PRODUCT PRICE An amount, usually of money, that represents the actual price paid by a Customer for a purchase, a rent or a lease of a Product. The price is valid for a dened period of time.
Represents invoice inquiries associated with invoices sent to customers and handles disputes and adjustments on individual charges, invoices, and accounts.
CUSTOMER BILL
Identies other providers who compete in the same market segments, accumulates intelligence about the competitors, including products (price, Key Performance Indicators and so forth).
COMPETITOR INTELLIGENCE Facts gathered about a Competitors plans and activities. These facts can be used to perform Competitor Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, Threat (SWOT) analysis in order to better understand a Competitor. COMPETITOR PRODUCT CORRELATION A comparison or relationship between an enterprises Product Offering with a Competitors' Product Offerings. Information about the correlation may include Market Segments, Product Offering life cycle stage, Jurisdiction, or denable Competitor Product Offering Correlation Characteristics.
COMPETITOR
Represents tangible and intangible goods and services made available for a certain price to the market in the form of product catalogs. This ABE is also responsible for targeting market segments based on the appropriate market strategy.
PRODUCT CATALOG A list of Product Offerings made available for sale or procurement using some other method, with prices and illustration. A Product Catalog could take on the form of a book or on the web. Product Catalogs can be used by Customers during a self-care ordering process and may be used across one or more Distribution Channels. PRODUCT OFFERING PRICE An amount, usually of money, that is asked for or allowed when a Product Offering is bought, rented, or leased. The price is valid for a dened period of time and may not represent the actual price paid by a customer. PRODUCT OFFERING PRICE RULE Policy-based rules used that dene the method by which the price for a Product Offering is determined. These rules are in addition to more basic rules set forth in Product Offering Price and its components. PRODUCT PLACEMENT A description of how Product Offerings are marketed, such as via direct mail. A Product Placement contains qualitative statements, or assessments that describe such things as market penetration, product strategy, and so forth. PRODUCT PROMOTION The publication of a Product Offering used to encourage Parties to buy, rent, or in some other way procure the offering. PRICING LOGIC ALGORITHM Interface to an external (black box) rating function that rates recurring, one time or usage events.
PRODUCT OFFERING
CUSTOMER
Is the focus for the Customer domain. Customer data is the enterprises knowledge of the customer and accounts held by a customer.
CUSTOMER SLA
Is a special case of the Service Level Agreement ABE where an involved party in the agreement is a Customer. See the Agreement ABE in the Common Business Entity Domain for details.
Handles real-time and non-real-time Call Detail Records (CDRs) and other sources of data that result in invoice items. The Customer Bill ABE also represents the format of a bill, schedule the production of bills, customer invoicing proles, all the nancial calculations necessary to determine the total of the bill (except for rating and rating discounts), and credits and adjustments to bills.
CUSTOMER BILLING CREDIT The amount of a deduction that can be applied against an amount charged for a Product on a Customer Bill. Billing credits are typically governed by Product Price Rule(s) and Product Price Alteration(s). CUSTOMER BILLING STATISTIC Collected data derived from Customer Bills. It is dened by Customer Billing Statistic Specication.
CUSTOMER ORDER
Handles single customer orders and the various types thereof, such as regulated and non-regulated orders.
CUSTOMER PROBLEM
Focuses on technical assistance and problem handling for customers.
CUSTOMER INTERACTION
Represents communications with customers, and the translation of customer requests and inquiries into appropriate events such as the creation of an customer order, the creation of a customer bill inquiry, or the creation of a customer problem.
CUSTOMER
STRATEGIC PRODUCT PORTFOLIO PLAN
Is concerned with the plans of the product portfolio, which product offerings to make available to each market segment and the plans to development and deploy product offerings, as well as retirement of products.
CUSTOMER STATISTIC
Represents the analysis of customer usage patterns, customer protability statistics and churn and retention statistics.
APPLIED CUSTOMER BILLING RATES
Deals with the correlation of related usage for subsequent rating, rates applied to the usage (both regulated and non-regulated), discounts to usage, and any taxes due on the rated usage.
SERVICE STRATEGY & PLAN
Addresses the need for enhanced or new Services, as well as the retirement of existing Services, by the enterprise. These entities have a strong dependency to both entities in the Resource and Product domains. Resulting efforts, such as deciding what Resources to use to host a Service, or what Services are used to support new Product Specications, are also supported, as are service demand forecasts.
SERVICE SPECIFICATION
Denes the invariant characteristics and behavior of both types of Service entities. This enables multiple instances to be derived from a single specication entity. In this derivation, each instance will use the invariant characteristics and behavior dened in its associated template. Entities in this ABE focus on adherence to standards, distinguishing features of a Service, dependencies (both physical and logical, as well as on other services), quality, and cost. In general, entities in this ABE enable Services to be bound to Products and run using Resources.
SERVICE
Represents both customer-facing and resource-facing types of services. Entities in this ABE provide different views to examine, analyze, congure, monitor and repair Services of all types. Entities in this ABE are derived from Service Specication entities.
SERVICE PERFORMANCE
Collects, correlates, consolidates, and validates various performance statistics and other operational characteristics of customer and resource facing service entities. It provides a set of entities that can monitor and report on performance. Each of these entities also conducts network performance assessment against planned goals, performs various aspects of trend analysis, including error rate and cause analysis and Service degradation. Entities in this ABE also manage the trafc generated by a Service, as well as trafc trend analysis. This is important for newer technologies that separate data, control and management functions for a given Service.
SERVICE CONFIGURATION
Represents and manages congurations of CustomerFacingService and ResourceFacingService entities. It provides details on how the conguration can be changed. The entities depend on entities in the Resource Domain, which provide the physical and logical infrastructure for implementing a Service. It denes dependencies between sub-Services used by the higher-level Service.
SERVICE TEST
Tests customer and resource facing service entities. These entities are usually invoked during installation, as a part of trouble diagnosis, or after trouble repair has been completed.
SERVICE TROUBLE
Manages faults, alarms, and outages from a Service point-of-view. This is then correlated to trouble tickets, regardless of whether the cause is physical or logical. Other entities in this ABE are used to direct the recovery from each of these three types of problems. They provide the ability to associate Resource faults and alarms to degradation and outages of Services that run on those Resources. These functions are independent of the Resources and technologies used to build the Service. A third set of entities in this ABE is used to differentiate between customer-reported problems and network-induced problems.
SERVICE USAGE
Collects Service consumption data, and generates Service usage records, for use by other business entities. The entities in this ABE provide physical, logical, and network usage information. Service Usage can be static (les with pre dened usage records) or dynamic (as part of a synchronous protocol)
RESOURCE
RESOURCE STRATEGY & PLAN
Used to plan networks and resource elements both initially and for growth. It will coordinate both logical and physical resource growth. Inputs are budgets from business sources, service forecasts, current and projected network utilization, new technologies, and retiring technologies. It handles the lifecycle (installation, modication, removal, and retirement) for both logical and physical resources.
RESOURCE TOPOLOGY
Denes physical, logical, and network topological information. This information is critical for assessing the current state of the network, as well as providing information on how to x problems, tune performance, and in general work with the network (both as a whole and with its components). Each of these topological views provides its own physical, logical, or network related information that can be used to manage one or more layers in a layered network.
RESOURCE SPECIFICATION
Denes the invariant characteristics and behavior of each type of Resource entities. This enables multiple instances to be derived from a single specication entity. In this derivation, each instance will use the invariant characteristics and behavior dened in its associated template.
Represent the various aspects of a Resource. This includes four sets of entities that represent: the physical and logical aspects of a Resource; show how to aggregate such resources into aggregate entities that have physical and logical characteristics and behavior; and show how to represent networks, subnetworks, network components, and other related aspects of a network.
RESOURCE TROUBLE
Manages problems found in allocated resource instances, regardless of whether the problem is physical or logical. Entities in this ABE detect these problems, act to determine their root cause, resolve these problems and maintain a history of the activities involved in diagnosing and solving the problem. Detecting problems can be done via software (e.g. responding to an alarm) and/or by hardware (e.g. a measurement or probe) and/or manually (e.g. visual inspection). This includes tracking, reporting, assigning people to x the problem, testing and verication, and overall administration of repair activities.
RESOURCE USAGE
Collects Resource consumption data, and generates Resource usage records, for use by other business entities. The entities in this ABE provide physical, logical, and network usage information. Resource usage collection is typically done within the network elements and is exposed to other business entities only as service usage. Synchronous protocols can retrieve resource usage data from the network elements for use of other applications.
RESOURCE CONFIGURATION
Represents and manages congurations of PhysicalResource, LogicalResource, and CompoundResource entities. It also provides details how the conguration is changed to meet product, service, and resource requirements, including activation, deactivation, and testing. Areas covered include verifying resource availability, reservation and allocation of resource instances, conguring and activating physical and logical resource instances, and testing.
RESOURCE PERFORMANCE
Collects, correlates, consolidates, and validates various performance statistics and other operational characteristics of Resource entities. It provides a set of entities that can monitor and report on performance. Each of these entities also conducts network performance assessment against planned goals, performs various aspects of trend analysis, including error rate and cause analysis and Resource degradation. Entities in this ABE also dene Resource loading, and traf c trend analysis.
RESOURCE TEST
Tests PhysicalResources, LogicalResources, CompoundResources, and Networks. These entities are usually invoked during installation, as a part of trouble diagnosis, or after trouble repair has been completed.
SUPPLIERPARTNER PLAN
Handles the strategies and the planning of the business relation with the SupplierPartner with input from other ABEs, such as MarketSales, S/P Performance and Competitor Analysis.
SUPPLIERPARTNER
Is the focus for the SupplierPartner Domain. SupplierPartner represents the enterprises knowledge of the SupplierPartner, their accounts and the relations the Enterprise has with the SupplierPartner. It also contains all Supplier Partner agreements and negotiations.
SUPPLIERPARTNER SLA
Manages SLA Specication that contain standard components used to negotiate and dene SLAs with SupplierPartners. The SupplierPartner SLA ABE also supports the negotiation and establishment of SLA instances. It also measures performance against the SLAs, and handles inquiries (both internal & external) about SLAs. It also handles SLA violations and the notication of the appropriate parties regarding violations. The ABE also identies discount reasons for SLA violations and noties S/P Payment of the discount reasons.
SUPPLIERPARTNER INTERACTION
Represents communication with SupplierPartners, and translating SupplierPartner requests and inquiries into appropriate events. Initiated by the Service Provider as a Customer such as the requisition for the Wholesale Service, the quotation order for the End-Customer instance, the quotation update Conrmation, requisition for Service Instance Problem reporting or Initiated by the Supplier_Partner such as the proposal for a Wholesale Service Purchase, the quotation proposal, the quotation update proposal, the requisition conrmation the order executed and the problem report answer.
SUPPLIERPARTNER ORDER
Handles single SupplierPartner orders and supervises various types thereof. This includes the quotation and order for the SupplierPartner Wholesale Service as well as the quotation and order for the EndCustomer instances within the Wholesale service.
SUPPLIERPARTNER PROBLEM
SUPPLIERPARTNER PRODUCT
Represents the Service Providers knowledge of the Products that the Service Provider may order from the SupplierPartner
Deals with problem associated with the Supplier Partner such as a request for technical assistance, Bill disputes etc.
SUPPLIERPARTNER BILL
Monitors the collection process and initiates different actions for overdue bills. It also handles credit violations. The ABE also provides the functionality to register disputes and adjustments on individual charges, invoices, and accounts.
SUPPLIERPARTNER PERFORMANCE
Contains data for which performance parameters are established by the Supplier/Partner SLA ABE. Only data that lies above the agreed tresholds and that may jeopardise the Service Providers service to the End Customer is sent by the SupplierPartner. The performance data from the SupplierPartner is analysed and redirected to the correct Service Mgmt process/actor to decide on appropriate actions.
SUPPLIERPARTNER BILL INQUIRY
Monitors the bill Disputes towards the Supplier Partner.
SUPPLIERPARTNER STATISTIC
Represents the usage analysis of services purchased from the SupplierPartner, SupplierPartner protability statistics and the overall performance of the Supplier/partner.
SUPPLIERPARTNER PARTNER PAYMENT
Monitors the payment process versus the Supplier/Partner.
COMMON BUSINESS
REVENUE ASSURANCE
REVENUE ASSURANCE CONTROL Denes policy-based rules that represent the logical denition of comparisons performed on entities, such as bills and call detail records (CDRs), to identify Revenue Assurance Violations REVENUE ASSURANCE KPI Models KPIs and Revenue Assurance Objectives whose violation trigger Revenue Assurance Trouble Tickets. KPIs are dened on Revenue Assurance Violations and on other revenue assurance related entities, such as bills and CDRs. REVENUE ASSURANCE TROUBLE TICKET Represents trouble tickets opened to resolve one or several causes (for example, Revenue Assurance Violations) that resulted in a Revenue Assurance KPI not meeting a Revenue Assurance Objective. REVENUE ASSURANCE ACTION/RESPONSE Represents the result of reconciling Revenue Assurance Trouble Tickets by initiating and performing a series of one or more activities. Revenue Assurance Action/Response ABE entities also model the root cause for Revenue Assurance Trouble Tickets based on rules that trigger root cause analysis. REVENUE ASSURANCE ASSESSMENT Measures the effectiveness of Revenue Assurance Controls, Revenue Assurance Objectives, and Revenue Assurance KPIs. Revenue Assurance Assessment ABE entities include recommendations of rening controls, objectives, and KPIs. REVENUE ASSURANCE VIOLATION Models discrepancies identied based on applying the rules dened by Revenue Assurance Control entities.
ROOT A set of common business entities that collectively serve as the foundation of the SID business view. This set of entities enables the entities in different domains of the SID Framework to be associated with each other, providing greater overall coherence to the information framework. BASE TYPES A small simple object, like money or a date range, whose equality isn't based on identity BUSINESS INTERACTION Represents an arrangement, contract, or communication between an enterprise and one or more other entities such as individuals and organizations (or parts of organizations). Interactions take on the form of requests, responses, and notications.
PARTY Represents the abstract concept of organization or individual that can play varying roles during interactions with an enterprise. Roles include customer, supplier/partner, employee, and so forth. TIME Represents Entities used to provide time related functions. This includes scheduling, time conicts and time based presentation support. Currently the Calendar model is the only part of the Time ABE. USAGE An occurrence of employing a Product, Service, or Resource for its intended purpose, which is of interest to the business and can have charges applied to it. It is comprised of characteristics, which represent attributes of usage.
AGREEMENT Represents a contract or arrangement, either written or verbal and sometimes enforceable by law, such as a service level agreement or a customer price agreement. An agreement involves a number of other business entities, such as products, services, and resources and/or their specications. LOCATION Represents the site or position of something, such as a customers address, the site of equipment where there is a fault and where is the nearest person who could repair the equipment, and so forth. Locations can take the form of coordinates and/or addresses and/or physical representations.
POLICY A set of layered ABEs that dene specications (for example, templates) and denitions of Policy entities that can be used in managing the behavior and denition of entities in other Domains. Policy takes three primary forms. The rst is the denition of how policy is used to manage the denition, change, and conguration of other entities. The second is the denition of how policy itself is managed. The third is how applications use policies to manage entities. PROJECT Represents the tools used by project managers to ensure that enterprise objectives of quality, cost, and time are achieved by planning and scheduling work. It uses common industry denitions of Project, Work Breakdown Structure and Activity to provide support to project managers.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Poster InformationFramework v15Dokumen1 halamanPoster InformationFramework v15Prash Prak TestAcct100% (1)
- Etom IntroDokumen11 halamanEtom IntroNamita Razdan0% (1)
- Introduction To SID - Telecommunications OSS and BSSDokumen3 halamanIntroduction To SID - Telecommunications OSS and BSSKowshik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- ETOM (BusinessProcessFramework) Program PosterDokumen2 halamanETOM (BusinessProcessFramework) Program PosterAyoDeji AyeniBelum ada peringkat
- (PD) Documentos - ETOM - Real World Use Case R7-5 v1-2Dokumen34 halaman(PD) Documentos - ETOM - Real World Use Case R7-5 v1-2Luis Daniel Chumpitaz PucllasBelum ada peringkat
- GB922 E Information Framework SID Model in Excel R14 0 PDFDokumen49 halamanGB922 E Information Framework SID Model in Excel R14 0 PDFCarl Loiuse D. IsipBelum ada peringkat
- Shared Information/Data (SID) Model: Release 6.0Dokumen122 halamanShared Information/Data (SID) Model: Release 6.0MAGISTERSCBelum ada peringkat
- TMF053 Main - V5 7Dokumen96 halamanTMF053 Main - V5 7MAGISTERSCBelum ada peringkat
- RA Maturity ListDokumen30 halamanRA Maturity Listsmasalmeh2872Belum ada peringkat
- Shared Information ModelDokumen16 halamanShared Information Modelrohitchawandke100% (1)
- GB992 Open API Map R18.0.1Dokumen80 halamanGB992 Open API Map R18.0.1Angel CuevasBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To eTOM: White PaperDokumen13 halamanIntroduction To eTOM: White PaperRobBelum ada peringkat
- TMF Frameworx 12.5 OverviewDokumen2 halamanTMF Frameworx 12.5 OverviewlostinsandBelum ada peringkat
- TM Forum Frameworx 12.0 PDFDokumen1 halamanTM Forum Frameworx 12.0 PDFYovanny SantistebanBelum ada peringkat
- GB929 Application Framework R4-5 v4-5Dokumen302 halamanGB929 Application Framework R4-5 v4-5YdaelVargasSalazarBelum ada peringkat
- TM Forum Input To ONAP Modeling Workshop 2017-12-14Dokumen20 halamanTM Forum Input To ONAP Modeling Workshop 2017-12-14Rajiv100% (1)
- Taking a Customer-Centric ApproachDokumen2 halamanTaking a Customer-Centric Approachmr6356Belum ada peringkat
- List DokumenDokumen2 halamanList DokumenApdev OptionBelum ada peringkat
- RN332 Business Process Framework Release Notes R18.5Dokumen11 halamanRN332 Business Process Framework Release Notes R18.5Preeda TeerakulvanichBelum ada peringkat
- eTOMS BUSINESS PROCESS FRAMEWORKDokumen59 halamaneTOMS BUSINESS PROCESS FRAMEWORKMAGISTERSCBelum ada peringkat
- TAM Poster v16 5Dokumen1 halamanTAM Poster v16 5fcBelum ada peringkat
- ETom Ebook PDFDokumen1.460 halamanETom Ebook PDFLalit Pandey100% (1)
- TMF API ListDokumen8 halamanTMF API ListMahesh ShriBelum ada peringkat
- Wed-04 MWA11 Customer Experience Analytics v0.6 PDFDokumen19 halamanWed-04 MWA11 Customer Experience Analytics v0.6 PDFОлег ДрошневBelum ada peringkat
- IRR: Customer Experience - Hitting A Moving TargetDokumen52 halamanIRR: Customer Experience - Hitting A Moving TargetFido FidoBelum ada peringkat
- SID9Dokumen1 halamanSID9vermvivBelum ada peringkat
- GB917-2 - Ver2!0!040422 - Concepts and PrinciplesDokumen172 halamanGB917-2 - Ver2!0!040422 - Concepts and PrinciplesArtur KiełbowiczBelum ada peringkat
- Implementing The SID V1dot0b Chapters 1 Through 3Dokumen71 halamanImplementing The SID V1dot0b Chapters 1 Through 3Luis Daniel Chumpitaz PucllasBelum ada peringkat
- eTOM ModelDokumen19 halamaneTOM ModelzhadnanBelum ada peringkat
- GB922 Addendum 5LR Logical Resource R9 0 V9-3Dokumen351 halamanGB922 Addendum 5LR Logical Resource R9 0 V9-3youssef MCHBelum ada peringkat
- R003etom Flows rb150705 Slides Only 150706134901 Lva1 App6892Dokumen38 halamanR003etom Flows rb150705 Slides Only 150706134901 Lva1 App6892Marco Tulio Holguín Tapia100% (2)
- ODA Architecture Vision: TM Forum Exploratory ReportDokumen51 halamanODA Architecture Vision: TM Forum Exploratory ReportbubblesBelum ada peringkat
- Sap Pm-Cr-Day 13 (Ip5 For PM) v1.0Dokumen38 halamanSap Pm-Cr-Day 13 (Ip5 For PM) v1.0gvlaxmipathiBelum ada peringkat
- GB921D - R5 0 - V0 6 1Dokumen261 halamanGB921D - R5 0 - V0 6 1Andrew Seit100% (1)
- Business Process Framework (eTOM) : For The Information and Communications Services IndustryDokumen16 halamanBusiness Process Framework (eTOM) : For The Information and Communications Services Industryroxanamau2002Belum ada peringkat
- GB921-D Process Decompositions Descriptions R8-0Dokumen4 halamanGB921-D Process Decompositions Descriptions R8-0Ahmed MallouhBelum ada peringkat
- Group Assignment 1 - DW DesignDokumen3 halamanGroup Assignment 1 - DW DesignipeeterBelum ada peringkat
- RN332 Release Notes Business Process Framework R17.0.1Dokumen16 halamanRN332 Release Notes Business Process Framework R17.0.1neuvBelum ada peringkat
- E TOMDokumen86 halamanE TOMFuad Khairul MuttaqinBelum ada peringkat
- TMF640 Service Activation and Configuration API REST Specification R18.5.0Dokumen36 halamanTMF640 Service Activation and Configuration API REST Specification R18.5.0DuyHung DangBelum ada peringkat
- ETOM - AssuranceDokumen32 halamanETOM - Assurancejaklaudiusz100% (1)
- GB935 Concepts & Principles V7.0Dokumen40 halamanGB935 Concepts & Principles V7.0RuwaniSandamali100% (1)
- (PD) Documentos - ETOM - Release 12-0 v12-3 1Dokumen1.460 halaman(PD) Documentos - ETOM - Release 12-0 v12-3 1Yesika RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- TAM EngDokumen1 halamanTAM EngruiquaresmaBelum ada peringkat
- ETOM SID FrameworkDokumen8 halamanETOM SID FrameworkPhạm Minh HoàngBelum ada peringkat
- GB922 InformationFramework Primer R9 5 V1-6-1Dokumen47 halamanGB922 InformationFramework Primer R9 5 V1-6-1karthikmkumarBelum ada peringkat
- GB962B Maturity Model R13.5Dokumen16 halamanGB962B Maturity Model R13.5leniadz2Belum ada peringkat
- IBM z13s ReportDokumen9 halamanIBM z13s ReportCherise MBelum ada peringkat
- Getting Started With The SID - R7-0 - V1-4Dokumen8 halamanGetting Started With The SID - R7-0 - V1-4zg2302viBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom Operations ETOM ThesisDokumen97 halamanTelecom Operations ETOM ThesisStill Waters0% (1)
- Etom Framework PDFDokumen2 halamanEtom Framework PDFGarlandBelum ada peringkat
- GB941 RA-Guide V1-0Dokumen70 halamanGB941 RA-Guide V1-0prog_man_0101100% (1)
- EtomDokumen89 halamanEtomTrevorP100% (1)
- 2.2 Data Modeling and Management Relationship TypesDokumen15 halaman2.2 Data Modeling and Management Relationship TypesTejesh VemulaBelum ada peringkat
- Smartrek eTOM-ITIL Full Case Study FINALDokumen10 halamanSmartrek eTOM-ITIL Full Case Study FINALGSorozBelum ada peringkat
- eTOM V9.0 WebDokumen1 halamaneTOM V9.0 WebvinitkhandkaBelum ada peringkat
- IT Organizational Design A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDari EverandIT Organizational Design A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- IT Infrastructure Deployment A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandIT Infrastructure Deployment A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Business Metrics Poster v5.5 April 2011 WebDokumen1 halamanBusiness Metrics Poster v5.5 April 2011 Webinam_qauBelum ada peringkat
- 2G KPI Anapysis Problem and SolutionsDokumen50 halaman2G KPI Anapysis Problem and Solutionselahe19100% (5)
- Pakistan Internet InfrastructureDokumen5 halamanPakistan Internet Infrastructureinam_qauBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco White Paper EPCDokumen7 halamanCisco White Paper EPCReid_ChangBelum ada peringkat
- Xi3-1 Deski SDK DG enDokumen74 halamanXi3-1 Deski SDK DG ena_shahjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Lte AttachDokumen3 halamanLte AttachsagarnewaseBelum ada peringkat
- Ossj OverviewDokumen26 halamanOssj Overviewinam_qauBelum ada peringkat
- ProductBro 01Dokumen3 halamanProductBro 01inam_qauBelum ada peringkat
- PR Elim Ina Ry: Tellabs 6300 Managed Transport SystemDokumen106 halamanPR Elim Ina Ry: Tellabs 6300 Managed Transport SystemVui Ha VanBelum ada peringkat
- Autonomic Network Engineering For The Self - Managing Future Internet (AFI)Dokumen167 halamanAutonomic Network Engineering For The Self - Managing Future Internet (AFI)Sodoma12Belum ada peringkat
- WCDMA Cell UpdateDokumen3 halamanWCDMA Cell Updateheom123Belum ada peringkat
- Tejas MuxDokumen2 halamanTejas MuxAnonymous BFND4MUaN8Belum ada peringkat
- Operation: Gateway Software Ne-Unigate V3.0 Omn:Ne-UnigateDokumen46 halamanOperation: Gateway Software Ne-Unigate V3.0 Omn:Ne-UnigateCarlos Alberto Riaño AgudeloBelum ada peringkat
- Manualfsp 3000r7 emDokumen500 halamanManualfsp 3000r7 emKamsai Ikamsai100% (1)
- Alcatel 1353 DN FR2.1F, The Subscribers Management System For Litespan-1540 Multiservice Access Networks, Technical DescriptionDokumen39 halamanAlcatel 1353 DN FR2.1F, The Subscribers Management System For Litespan-1540 Multiservice Access Networks, Technical DescriptionSergei SavchenkoBelum ada peringkat
- Wibas-2x System Description Ed7Dokumen88 halamanWibas-2x System Description Ed7dansun100% (1)
- 8DG42094BAAA - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 1350 OMS EML 9.1.1 User Guide (Maint-2)Dokumen534 halaman8DG42094BAAA - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 1350 OMS EML 9.1.1 User Guide (Maint-2)balla aubinBelum ada peringkat
- P N M T: PNMT (Java Version) Operation ManualDokumen147 halamanP N M T: PNMT (Java Version) Operation ManualCao CaoBelum ada peringkat
- Optical Multiservice Edge 6130 TL1 ReferenceDokumen152 halamanOptical Multiservice Edge 6130 TL1 ReferencemaximfBelum ada peringkat
- HSS Counter DescriptionDokumen218 halamanHSS Counter DescriptionRazi Haider RizviBelum ada peringkat
- Operation: Ne-Unigate V5.0/V5.1 Omn:Ne-UnigateDokumen46 halamanOperation: Ne-Unigate V5.0/V5.1 Omn:Ne-UnigateThiago Andrade RangelBelum ada peringkat
- DSX1 Digital Signal Cross Connect 103253AEDokumen76 halamanDSX1 Digital Signal Cross Connect 103253AEGeoffrey AlleyneBelum ada peringkat
- 009-2003-078 Alarm and Trouble Clearing PDFDokumen106 halaman009-2003-078 Alarm and Trouble Clearing PDF10gigtexBelum ada peringkat
- 162xLM 20 OH ENG ED03Dokumen60 halaman162xLM 20 OH ENG ED03Twan Dekker KleijnBelum ada peringkat
- Client - TNMSDokumen306 halamanClient - TNMSMarcelo MonteiroBelum ada peringkat
- ariesoGEO Data Collection Setup - Huawei UMTS PDFDokumen10 halamanariesoGEO Data Collection Setup - Huawei UMTS PDFWidagdho WidyoBelum ada peringkat
- Leaflet US5Ge ProtectedDokumen3 halamanLeaflet US5Ge Protectedquochung0606Belum ada peringkat
- 7 ZXUN USPP (HLR) BC en Commissioning and Debugging (Basic Data Configuration) 2 PDF 201008 (Draft) 164Dokumen164 halaman7 ZXUN USPP (HLR) BC en Commissioning and Debugging (Basic Data Configuration) 2 PDF 201008 (Draft) 164arun_sakre100% (2)
- Fault Solution Administration Guide Helix 11.1Dokumen131 halamanFault Solution Administration Guide Helix 11.1Yasir KhanBelum ada peringkat
- NetAct License Manager OverviewDokumen47 halamanNetAct License Manager OverviewMaverick24100% (1)
- Oss-Rc New and Enhanced Features OSS-RC 7.1 - OSS-RC 12.3 DELTA PresentationDokumen75 halamanOss-Rc New and Enhanced Features OSS-RC 7.1 - OSS-RC 12.3 DELTA Presentationhung_6715100% (1)
- Training CatalogueDokumen74 halamanTraining CatalogueSumit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- OSS-RC Functionality OverviewDokumen52 halamanOSS-RC Functionality Overviewchayhofmes100% (1)
- TL1 ReferenceGuide R4.7.1 PRELIMINARYDokumen376 halamanTL1 ReferenceGuide R4.7.1 PRELIMINARYpetersis100% (1)
- Alcatel-Lucent 1646 SM Equipment ManagementDokumen6 halamanAlcatel-Lucent 1646 SM Equipment ManagementhunterzzzBelum ada peringkat
- 3G Node B Alarm Troubleshooting NSN PDFDokumen6 halaman3G Node B Alarm Troubleshooting NSN PDFyunandaBelum ada peringkat
- 901-00-0081 LI ConfigDokumen160 halaman901-00-0081 LI ConfigBluesinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Airscale alarms guideDokumen148 halamanAirscale alarms guideAzzu Kh0% (1)