2008 EXAM 2 For PRACTICE With Answers Highlighted
Diunggah oleh
Tricia Lee CairnsDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2008 EXAM 2 For PRACTICE With Answers Highlighted
Diunggah oleh
Tricia Lee CairnsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2 Name__________________________________
Part I 1. (20 points) Carbon dioxide (CO2 (g)) dissolves in water to produce carbonic acid H2CO3. CO2 + H 2O H 2 CO3 Aluminum carbonate, A12(CO3)3, can be used as an antacid (not the best choice however!). How many grams of aluminum carbonate can be formed from combination of 10.0 L of CO2(g) at STP with 500. mL of 0.543 M A1(OH)3 which react by the following unbalanced equation? Al (OH )3 + H 2CO3 Al2 (CO3 )3 + H2 O
3 Name__________________________________ 2. (15 points) Given the following: H fo (C2 H 2 (g)) = 227 kJ/mole H fo (CO2 (g)) = -393 kJ/mole H fo (H 2O(l )) = -286 kJ/mole H fo (C2 H 4 (g)) = 52.3 kJ/mole (a) Calculate the heat of combustion of C2 H 2 (g) . (b) How much heat in kJ would be evolved in combustion of 1.00 g C2 H 2 (g)?
4 Name__________________________________ Part II Place Answers on Cover Page
1.
A mixture of 1.00 g of HCl and enough water to give 1.00 x 102 mL of solution will have what molarity? (a) 0.274 M (b) 0.548 M (c) 0.0100 M (d) 0.0274 M (e) 0.0548 M
2.
A 10. mL solution of 1.0 M NaOH is required to react completely with how many mL of a 0.25 M solution of H2SO4? (a) 40. mL (b) 160 mL (c) 4.0 mL (d) 10. mL (e) 20. mL
3.
The net ionic equation for the neutralization of sulfuric acid with sodium hydroxide is:
2 (a) SO4 ( aq) + 2 Na + ( aq) Na2 SO4 ( aq) 2 (b) SO4 ( aq) + 2 Na + ( aq) Na2 SO4 ( s )
(c) H 2 SO4 (aq ) + 2OH (aq ) 2 H2 O (l ) + SO42 ( aq) (d) H + ( aq) + NaOH ( aq) H 2O (l ) + Na+ (aq ) (e) H + ( aq) + OH (aq) H 2O (l )
4.
o The H f for CO2(g) is -393 kJ/mole and H rxn for the reaction
2CO(g) + O 2 (g) 2CO2 (g) is -560 kJ. The H o for CO(g) is (in kJ/mole) f (a) +113 (b) -673 (c) -113 (d) -209 (e) -226
5 Name__________________________________ 5. For the reaction 2H 2 (g) + O2 (g) 2H2 O(g) which of the following is true? (a) (b) (c) (d) All reactants and products are in their standard state. o The H f for H2O(g) is -484 kJ/mole. The reaction is exothermic. o The H f for H2O() would be less negative. H = -484 kJ
o o (e) You would need H f (H2(g)) to calculate H f (O2(g)).
6.
Two identical flasks contain O2 and H2 gas, respectively, at the same temperature and pressure. In comparing the two flasks, which of the following is not a true statement. (a) The total mass of each gas is different. (b) The average speed of H2 molecules is greater than that of O2 molecules. (c) The average kinetic energy of H2 is greater than that of O2. (d) The number of molecules of H2 and O2 is the same. (e) The number of moles of H2 and O2 is the same.
7.
If the pressure in a helium-filled balloon is 4.4 atm when filled to 5.0 x 102 L, what volume is occupied by the helium-filled balloon when the pressure is reduced to 1.1 atm? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2.0 x 102 L 2.5 x 102 L 2.2 x 102 L 2.0 x 103 L 3.0 x 102 L
6 Name__________________________________
8.
What is the temperature (K) for 0.500 moles of an ideal gas at 2.00 atm in a 22.4 L container? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 0K 273 K 1.09 x 103 K 68.3 K 546 K
9.
How many different orbitals can have the principal quantum number n = 3? (a) 4 (b) 9 (c) 6 (d) 5 (e) 18
10.
Which of the following properties is associated with the value of the quantum number? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) The number of electrons in an orbital. The size of an orbital. The orientation in space of an orbital. The energy of an orbital. The shape of an orbital.
11.
The number of 5d electrons in the electronic configuration of element 75 (Re) is: (a) 10 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 5 (e) 7
12.
Which of the following is not a permitted set of quantum numbers for an orbital in an atom? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) n = 2, = 2, m = 1 n = 3, = 1, m = -1 n = 1, = 0, m = 0 n = 6, = 1, m = 0 n = 5, = 4, m = -4
7 Name__________________________________
13.
Which of the following represents the electron configuration of an atom of tin (Sn)?
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
[Xe]5s24d105p3 [Kr]5s24d105p3 [Kr]4s23d104p3 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d95p3 [Kr]5s24d105p2
Some Potentially Useful Equations for General Chemistry Examinations
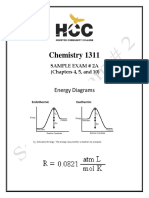
MM is molar mass PV = nRT P x MM ( g / mol ) = dRT PVi PV2 i = 2 Ti T2 U = q + w, H = q p for a constant pressure process q = m x C(per gram) x T
v = c
E = hv
h p
p = momentum = mass x velocity for matter
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: xp x
h 4 Energy levels for the hydrogen atom: 2.179 x 1018 J En = n2
H o = nH o (products) - mH o (reactants) f f
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Redox Review With ANSWERS - 4Dokumen13 halamanRedox Review With ANSWERS - 4AYESHA NAAZBelum ada peringkat
- Year End Practice DiplomaDokumen22 halamanYear End Practice DiplomaAYESHA NAAZBelum ada peringkat
- CHemistry TEST 2 Mole Concept 4ADokumen3 halamanCHemistry TEST 2 Mole Concept 4AMinorBelum ada peringkat
- Nelson Grade 11 Chemistry ReviewDokumen10 halamanNelson Grade 11 Chemistry Reviewexhalait67% (3)
- Practice Exam 2Dokumen10 halamanPractice Exam 2Niomi ButtermilkBelum ada peringkat
- Post Market Surveillance SOPDokumen8 halamanPost Market Surveillance SOPgopinathBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan - Organization and ManagementDokumen5 halamanLesson Plan - Organization and ManagementBilly Joe80% (15)
- Thetford c250 InstallationDokumen19 halamanThetford c250 InstallationCatalin Bejan100% (1)
- Samsung LN55C610N1FXZA Fast Track Guide (SM)Dokumen4 halamanSamsung LN55C610N1FXZA Fast Track Guide (SM)Carlos OdilonBelum ada peringkat
- 2009 Practice Exam 2 With Answers HighlightedDokumen6 halaman2009 Practice Exam 2 With Answers HighlightedTricia Lee CairnsBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Exam in ChemDokumen12 halamanSample Exam in ChemDiane GuilaranBelum ada peringkat
- Review For Test 2 ch3 and ch4Dokumen5 halamanReview For Test 2 ch3 and ch4Alison VelázquezBelum ada peringkat
- UNSCO 2014 ExamDokumen8 halamanUNSCO 2014 ExamwakuserBelum ada peringkat
- SCH4U Exam ReviewDokumen3 halamanSCH4U Exam Reviewtaya guyBelum ada peringkat
- Che101 Exam 2a KeyDokumen11 halamanChe101 Exam 2a KeyKartikeBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 1100 and 1110 Exam 2 October 28 2009 Answer KeyDokumen8 halamanChem 1100 and 1110 Exam 2 October 28 2009 Answer KeyElizabeth McKennaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry 151 Study Session For Exam 3 KeyDokumen5 halamanChemistry 151 Study Session For Exam 3 KeymiketolBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry 101 SPRING 2005: Final Form B SECTIONS 501-511 Dr. Keeney-KennicuttDokumen15 halamanChemistry 101 SPRING 2005: Final Form B SECTIONS 501-511 Dr. Keeney-KennicuttKalaiarasu SelvarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Soal ElectrochemistryDokumen3 halamanSoal ElectrochemistryHerlinda OktaBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions To Problem Set 2Dokumen5 halamanSolutions To Problem Set 2Andy Nguyen100% (1)
- 5.2 (152 Marks) : 1. (1 Mark)Dokumen42 halaman5.2 (152 Marks) : 1. (1 Mark)Semwezi EnockBelum ada peringkat
- CHE 110 Exam 2 F'13 v1Dokumen6 halamanCHE 110 Exam 2 F'13 v1MicahBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Gen A. 2016 KeyDokumen4 halamanFinal Exam Gen A. 2016 KeyAbdelfattah Mohamed OufBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 1 & 2Dokumen4 halamanChem 1 & 2Fashola AbdulhamidBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Practise QuestionDokumen12 halamanChemistry Practise Questiong24n3950Belum ada peringkat
- Exam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1Dokumen10 halamanExam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1asjawolverineBelum ada peringkat
- DPP # 1 - 8 Physical ChemistryDokumen5 halamanDPP # 1 - 8 Physical ChemistrySankar KumarasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 ElectrolysisDokumen8 halamanChapter 4 ElectrolysisPremBelum ada peringkat
- Cnhemistry 11 em Book Back One Mark Reduced SyllabusDokumen14 halamanCnhemistry 11 em Book Back One Mark Reduced Syllabuselavarasannatesan0Belum ada peringkat
- Monica Bedi: 12+ Years of Teaching Experience Trained Million+ Students - Top Ranker's Series (TRS)Dokumen65 halamanMonica Bedi: 12+ Years of Teaching Experience Trained Million+ Students - Top Ranker's Series (TRS)Alkash BaigBelum ada peringkat
- IIT-JEE - Previous Year Papers - CHEMISTRY (Mains) - 2005Dokumen7 halamanIIT-JEE - Previous Year Papers - CHEMISTRY (Mains) - 2005ShardaVermaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 11 Chemistry Exam ReviewDokumen11 halamanGrade 11 Chemistry Exam ReviewAshwin Baskaran25% (4)
- Psi-Ap-Chemistry-Equilibrium-Multiple-Choice 3Dokumen30 halamanPsi-Ap-Chemistry-Equilibrium-Multiple-Choice 3Tricyver ChienBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM101 172 Final SolvedDokumen12 halamanCHEM101 172 Final SolvedTorong VBelum ada peringkat
- CHEMISTRY F6 Pre-Mock 1 July 2022Dokumen5 halamanCHEMISTRY F6 Pre-Mock 1 July 2022Kelvin CharlesBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry, BT-2, SET-IDokumen6 halamanChemistry, BT-2, SET-ISoham NagBelum ada peringkat
- AP Summer Review PacketDokumen5 halamanAP Summer Review PacketAndreaMarkhamBelum ada peringkat
- Eamcet 2008 EnggDokumen15 halamanEamcet 2008 EnggjanmanchiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Science TestDokumen4 halamanChapter 3 Science TestNatalie VerstichelenBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 4 - ElectrochemistryDokumen3 halamanTutorial 4 - ElectrochemistryAnis IssabellaBelum ada peringkat
- XI Chemistry Open Book Test (Chap # 12 Electrochemistry)Dokumen2 halamanXI Chemistry Open Book Test (Chap # 12 Electrochemistry)Newton's InnBelum ada peringkat
- Test 001 Mole Concept and Atomic StructureDokumen6 halamanTest 001 Mole Concept and Atomic StructureDarsh ThiyagarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Number of Atoms in 558.5 Gram Fe (At. Wt. of Fe 55.85 G MolDokumen3 halamanNumber of Atoms in 558.5 Gram Fe (At. Wt. of Fe 55.85 G MolGowri ShankarBelum ada peringkat
- IJC H2 Paper 1 and 2 Answers (For Sharing)Dokumen9 halamanIJC H2 Paper 1 and 2 Answers (For Sharing)Sharon HowBelum ada peringkat
- AP 02 Multiple ChoiceDokumen16 halamanAP 02 Multiple ChoiceKat TomasBelum ada peringkat
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDokumen11 halamanMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionOw ZeeBelum ada peringkat
- 38 Daily Tutorial SheetDokumen7 halaman38 Daily Tutorial SheetMeera SarangapaniBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Pilot 1Dokumen3 halamanChemistry Pilot 1Kaung Wai HtetBelum ada peringkat
- 11-When The Following Equation Is Balanced, The Coefficient of Al Is. Al (S) + H 2 O (L) - Al (OH) 3 (S) + H 2 (G)Dokumen5 halaman11-When The Following Equation Is Balanced, The Coefficient of Al Is. Al (S) + H 2 O (L) - Al (OH) 3 (S) + H 2 (G)Nesrine LaradjiBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercitacion N1Dokumen3 halamanEjercitacion N1Seba PalopoliBelum ada peringkat
- NSEJS Camp Equilibrium AssignmentDokumen5 halamanNSEJS Camp Equilibrium Assignmentaryan aggarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Test A3 Chemistry 11500 Final Exam Total Points 300Dokumen19 halamanTest A3 Chemistry 11500 Final Exam Total Points 300baxterinathetrollBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Exam 2Dokumen9 halamanPractice Exam 2N193746Belum ada peringkat
- 01 Bitsat Test-Iv - CmsDokumen5 halaman01 Bitsat Test-Iv - CmsS RamalingamBelum ada peringkat
- Class P ChemDokumen79 halamanClass P Chemprashantyadavpky07Belum ada peringkat
- Practice Test 4Dokumen14 halamanPractice Test 4shreyshreyBelum ada peringkat
- 5-Chemistry 151 Final ExamDokumen9 halaman5-Chemistry 151 Final ExamNesrine LaradjiBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry (Ii) Assignment Chapter 5:) NaclDokumen3 halamanGeneral Chemistry (Ii) Assignment Chapter 5:) NaclBilal MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Que Bank 12 ChemDokumen8 halamanQue Bank 12 Chemtechblogger098Belum ada peringkat
- Past Paper Chemistry 1st Year BISE Lahore 2010Dokumen4 halamanPast Paper Chemistry 1st Year BISE Lahore 2010Mian EjazBelum ada peringkat
- Merination NotesDokumen34 halamanMerination NotesNarmadha RameshBelum ada peringkat
- CHEMISTRY-19-11-11th (PQRS) SpaceDokumen21 halamanCHEMISTRY-19-11-11th (PQRS) SpaceRaju SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Geol P 20 Paper II CHEMISTRY PDFDokumen32 halamanGeol P 20 Paper II CHEMISTRY PDFRambo FeverBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal Resuscitation ProgramDokumen6 halamanNeonatal Resuscitation ProgramRick Frea100% (5)
- Guidance UDI Compliance DatesDokumen13 halamanGuidance UDI Compliance DatesGigi EssegiBelum ada peringkat
- Progress Test-The 7-Th GradeDokumen2 halamanProgress Test-The 7-Th GradebabystelutaBelum ada peringkat
- Annex 1: Homeroom Guidance Monitoring Tool (School Level) Homeroom Guidance Monitoring ToolDokumen2 halamanAnnex 1: Homeroom Guidance Monitoring Tool (School Level) Homeroom Guidance Monitoring ToolMariel Gregore0% (1)
- CATL 34189-20AH Low Temperature Cell SpecificationDokumen17 halamanCATL 34189-20AH Low Temperature Cell Specificationxueziying741Belum ada peringkat
- Argumentative EssayDokumen7 halamanArgumentative EssayHoang Thi Huyen DieuBelum ada peringkat
- Cultivation and Horticulture of SandalwoodDokumen2 halamanCultivation and Horticulture of SandalwoodAnkitha goriBelum ada peringkat
- Chinese MedicineDokumen16 halamanChinese MedicineTrisBelum ada peringkat
- CongressWatch #197: RA 1337-Innovative Startup ActDokumen1 halamanCongressWatch #197: RA 1337-Innovative Startup ActMakati Business ClubBelum ada peringkat
- Nemo Outdoor 8.40 User Guide PDFDokumen392 halamanNemo Outdoor 8.40 User Guide PDFXxbugmenotxXBelum ada peringkat
- Durham E-ThesesDokumen203 halamanDurham E-ThesesH Man SharifBelum ada peringkat
- What Is StevedoringDokumen10 halamanWhat Is StevedoringMinhaj KmBelum ada peringkat
- Liebherr PR 712 Litronic Final DrivesDokumen8 halamanLiebherr PR 712 Litronic Final DrivesLiebherr75% (4)
- A Review of The Mental Workload LiteratureDokumen36 halamanA Review of The Mental Workload LiteratureArlene LaguaBelum ada peringkat
- Model Questions and Answers Macro EconomicsDokumen14 halamanModel Questions and Answers Macro EconomicsVrkBelum ada peringkat
- D6 Gamemasters Aid Screen Weg51019eOGLDokumen40 halamanD6 Gamemasters Aid Screen Weg51019eOGLMr DM100% (1)
- Assessment 3 Comparative Analysis Primary Vs Secondary SourcesDokumen5 halamanAssessment 3 Comparative Analysis Primary Vs Secondary SourcesMATOZA, YLJOE V.Belum ada peringkat
- ESUR Guidelines 10.0 Final VersionDokumen46 halamanESUR Guidelines 10.0 Final Versionkon shireBelum ada peringkat
- List of ErpDokumen2 halamanList of Erpnavyug vidyapeeth trust mahadBelum ada peringkat
- A Single-Stage Asymmetrical Half-Bridge Flyback CoDokumen16 halamanA Single-Stage Asymmetrical Half-Bridge Flyback CoSantosh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Pre-Socratic Pluralism AtomismDokumen1 halamanPre-Socratic Pluralism AtomismpresjmBelum ada peringkat
- Hot and Cold TherapyDokumen24 halamanHot and Cold TherapyJo Obs100% (1)
- Assignment 2 Management Perspective Son Leadership MotivationDokumen14 halamanAssignment 2 Management Perspective Son Leadership MotivationHoneyVasudevBelum ada peringkat
- Sector San Juan Guidance For RepoweringDokumen12 halamanSector San Juan Guidance For RepoweringTroy IveyBelum ada peringkat
- Vertical Transportation: Commercial, Hotel, Hospital, Etc)Dokumen5 halamanVertical Transportation: Commercial, Hotel, Hospital, Etc)fdarchitectBelum ada peringkat
- Kumleben Commission ReportDokumen232 halamanKumleben Commission ReportJulian Rademeyer100% (2)