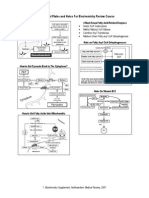
Signal Trans Duct Ion
Diunggah oleh
Prasath ThevarajahDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Signal Trans Duct Ion
Diunggah oleh
Prasath ThevarajahHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Signal transduction
\\\\ The effects of acetylcholine on the postsynaptic ion channel are mainly due to: \\\ protein cleavage (proteolysis). \\ protein conformational changes. \\\ protein phosphorylation. \\\ protein synthesis. \\\\ Protein kinase A (PKA) is: \\\ activated by covalent binding of cyclic AMP. \\ allosterically activated by cyclic AMP. \\\ competitively inhibited by cyclic AMP. \\\ noncompetitively inhibited by cyclic AMP. \\\\ Which of the following is not involved in signal transduction by the beta-adrenergic receptor pathway? \\\ ATP \\\ Cyclic AMP \\ Cyclic GMP \\\ GTP \\\\ Which of the following does not involve cyclic AMP? \\\ Regulation of glycogen breakdown \\\ Regulation of glycolysis \\ Signaling by acetylcholine \\\ Signaling by glucagon \\\\ Hormone-activated phospholipase C can convert phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate to: \\ diacylglycerol + inositol triphosphate. \\\ glycerol + inositol + phosphate. \\\ glycerol + phosphoserine. \\\ phosphatidyl glycerol + inositol + phosphate. \\\\ What is Calmodulin? \\\ allosteric activator of calcium-dependent enzymes. \\\ allosteric inhibitor of calcium-dependent enzymes. \\\ cell surface calcium receptor. \\ regulatory subunit of calcium-dependent enzymes. \\\\ Which of the following is a general characteristic of all chemical messengers? \\\ They are secreted by one cell, enter the blood, and act on a distant target cell. \\\ To achieve a coordinated response, each messenger is secreted by several types of cells. \\ Each messenger binds to a specific protein receptor in a target cell. \\\ Chemical messengers must enter cells to transmit their message. \\\\ Which of the following is a characteristic of chemical messengers that bind to intracellular transcription factor receptors? \\\ They are usually cytokines or polypeptide hormones. \\\ They exert rapid actions in cells. \\ They are transported through the blood bound to proteins. \\\ They are always present in high concentrations in the blood. \\\\ SH2 domains on proteins are specific for which of the following sites? \\ Certain sequences of amino acids containing a phosphotyrosine residue \\\ PI-3,4,5 trisphosphate in the membrane \\\ Ca2+-calmodulin \\\ Receptor domains containing phosphoserine residues
\\\\ Which of the following is incorrect for acetylcholine receptor? \\\ It is gatedion channel receptor \\ It is gene-specific transcriptional factor \\\ binding of acetylcholine to the receptor opens the closed conformation. \\\ irritation of the receptor in the nerve-muscular synapses results in muscle contraction \\\\ Which of the following is the first messenger? \\\ cAMP \\\ DAG \\ epinephrine \\\ IP3 \\\\ Which of the following is the second messenger? \\ cAMP \\\ insulin \\\ epinephrine \\\ glucagon \\\\ Which of the following is cytoplasmic receptor? \\\ gated ion channel receptor \\ gene-specific transcriptional factor \\\ Heptahelical receptor \\\ Tyrosine-kinase receptor \\\\ Which of the following statements is not characteristic for protein phosphatases? \\\ Protein phosphatases remove phosphate groups from proteins that have been phosphorylated \\\ Insulin activates protein phosphatases and removes phosphate groups added by the cAMP cascade \\\ The cAMP cascade can inhibit phosphatases \\ It takes a long time for the phosphatases to reverse the action of the cAMP cascade \\\\ G.M. has been fasting (500 kcal/day) for several days. Which one from the following statements would be decreased? \\\ Cyclic-AMP in adipose tissue \\\ The activity of hormone sensitive lipase in adipose tissue \\ The concentration of glycerol phosphate in adipose tissue \\\ The amount of free fatty acid entering the liver mitochondria \\\\ Which of the following is the first messenger? \\\ GMP \\\ DAG \\ glucagon \\\ IP3 \\\\ Which of the following is the second messenger? \\ DAG \\\ cortisole \\\ insulin \\\ epinephrine \\\\ Which of the following does not involve cyclic AMP? \\\ regulation of glycogen breakdown \\\ regulation of glycolysis \\\ signaling by glucagon \\ signaling by alpha-adrenergic receptors \\\\ In which pathway of signal transduction the signal molecule is carried by the blood in a long distance? \\ Endocrine
\\\ Paracrine \\\ Sinaptic \\\ Autocrine \\\\ Which signal molecules target cells receptor has the high affinity to the ligand? \\\ Local mediators \\\ Neurotransmitters \\\ Hormones \\\ Large polipeptide growth factors \\\\ Which of the following molecule cant cross the cell plasma membrane? \\\ Steroid hormone \\ Growth factor \\\ Thyroid hormone \\\ Retinoic acid \\\\ Which of the following is lipid second messenger? \\\ cAMP \\ diacylglycerol (DAG) \\\ cGMP \\\ Ca2+ \\\\ Which enzymes catalyze proteins phosphorylation in the intracellular signal transduction? \\\ Phosphodiestherases \\\ Protein phosphatases \\ Protein kinases \\\ Phosphohydrolases \\\\ What is desensitization? \\ Loss of sensitivity of target cells receptors towards agonists \\\ The starting step of signal transduction \\\ Receptors increased affinity towards agonist \\\ Signal propagation inside the cell \\\\ Which description is correct concerning G protein cycle? \\\ In basal state G proteins are homotrimeres \\ Alpha subunit has GTP-ase activity \\\ Alpha- GTP is inactive conformation towards effector \\\ Alpha- GDP is active conformation towards effector \\\\ Which of the following is the major messenger in the relaxation process of blood vessels? \\\ DAG \\\ PIP3 \\\ cAMP \\ cGMP \\\\ What is called the type of intercellular signaling, when it occurs between the distant cell? \\\ Autocrine \\ Endocrine \\\ Contact-dependent \\\ Paracrine \\\\ Which statement is correct concerning intracellular receptors? \\\ As a rule they connect to hydrophilic ligands \\\ They are situated in the cytosol in complex with protein \\ After connecting to ligand, they regulate gene transcription \\\ Have ability to connect DNA specific consequences without connection to ligand
\\\\ Which of the following is correct concerning membrane receptor? \\\ It connects only with large molecules \\ After binding to ligand it activates enzyme cascade \\\ After binding to fat-soluble ligands opens the ionic channels \\\ Produces second messengers without binding with proteins \\\\ Which statement opposites of the signal transduction pathway based on the protein phosphorylation? \\ Tyrosin kinase is always part of receptor protein \\\ Phosphorylation may go on Serine or Threonine \\\ protein kinase cascade causes signal amplification \\\ phosphorylation changes protein structure and function \\\\ How the termination of signal transduction go with help of cell membrane receptors? \\\ With increasing agonist concentration \\ With internalization and degradation of receptor-agonist complex \\\ With increasing the receptor sensitivity towards agonist \\\ With increasing the amount receptors \\\\ What is Calmodulin? \\\ Nonspecific kinase \\ Ca2+-binding protein \\\ Second messenger \\\ Protein channel which is activator of Ca+ influx \\\\ Which statement is correct about G protein? \\\ G protein is directly bound to the hormone on the cell surface \\ Alpha subunits may have stimulatory activity, as well as inhibiting activity \\\ Hydrolysis of GTP is essential for separation of GTP \\\ in the resting state GTP is bound with G-protein \\\\ Which amino acids radicals are the subjects of phosphorylaton during protein kinase cascade? \\\ Glycine and valine \\\ Proline and methionine \\\ Tripthopan and phenylalanine \\ Serine and threonine \\\\ Which amino acid radical is the subject of phosphorylaton during protein kinase cascade? \\\ Valine \\\ Phenylalanine \\\ Tripthopan \\ Tyrosin \\\\ What is not thought in the termination mechanism of signal transduction? \\\ Decreasing the agonist concentration in the environment \\\ Internalization of agonist-receptor complex \\\ Receptor inactivation \\ increasing affinity between agonist and receptor \\\\ What is not characteristic for tyrosin kinase receptors? \\ Existence of several transmembrane domeins \\\ Dimerization after binding with ligand \\\ Autophosphorylation \\\ Binding to intracellular specific proteins with recognizing site \\\\ High affinity of target cells receptors towards hormones provides: \\\ Formation of contact dependent transduction of signal
\\\ Binding of any hormone despite of their concentration in the blood \\ Specific binding of any hormone even in case of their low concentration in the blood \\\ Easy dissociation of hormone from hormone-receptor complex \\\\ Which is not second messenger? \\ Epinephrine \\\ cAMP \\\ diacylglycerol \\\ PIP3 \\\\ Which signal molecules are used for signal transduction in synaptic way? \\\ Citokines \\ Neurotransmitters \\\ Steroid hormones \\\ Prostaglandines \\\\ From the following which one has no intracellular receptors? \\\ Derivatives of Vit.D3 \\ Epinephrine \\\ Thyroid hormones \\\ Steroid hormones \\\\ Which statement is correct concerning second messengers? \\ They are small sized molecules, which are generating after binding agonist with receptor and provide signal intracellular transduction \\\ They are large sized molecules, which transmit signals to target cells \\\ All of them are water soluble \\\ All of them are organic molecules \\\\ Which signal molecule is responsible for inflammatory and immune response? \\\ Neurotransmitter \\\ Protein hormones \\ Cytokines \\\ Steroid hormones \\\\ Which statement is not true concerning heterotrimeric G protein? \\\ It is coupled with 7 transmembrane containing receptor \\\ Contains alpha, beta, gama subunits \\\ Alpha subunit has guanin nucleotide-binding and GTP-ase acitvity \\ s subunits of Gs proteins inhibit adenylatcyclase \\\\ Which enzyme increases intracellular concentration of cAMP? \\\ Phosphoprotein phosphatases \\ Adenylate cyclase \\\ Guanylate cyclase \\\ Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase \\\\ To which enzymes activity is connected with NO? \\ Soluble guanylate cyclase \\\ AMP-dependent protein kinase \\\ cAMP-dependent protein kinase \\\ adenylate cyclase \\\\ Which neurotransmitter regulates anion-selective receptors? \\ Acetylcholine \\\ Gama- aminobutirate \\\ Glutamate
\\\ serotonine \\\\ Which does not belong to plasma membrane receptors? \\\ Ion-channel type receptors \\ Gene-specific transcriptional factor \\\ Heptahelical receptors \\\ Tyrosin kinase receptors \\\\ Which receptor does not respond to epinephrine with activation of cAMP cascade? \\\ Beta1-adrenergic receptor \\\ Beta2-adrenergic receptor \\ Alpha1-adrenergic receptor \\\ Beta3-adrenergic receptor \\\\ Which is the second messenger? \\ cAMP \\\ Cortisole \\\ Insulin \\\ Epinephrin \\\\ Functioning of PIP system starts with phospholipase C activation, what initiates the proceeding of concequent events. Which of the following is not relevant for this process? \\ IP3 releases with help of phophatase \\\ Increase concentration of intracellular Ca2+ \\\ Activation of proteinkinase C \\\ phophorylation of cytoplasmic proteins
\\\\ Cell signaling means all of the following except: \\\ intercellular communication. \\ export of cellular waste products. \\\ environmental monitoring. \\\ response to stimuli. \\\\ If you break liver cells by homogenization, separate the broken cell membranes (particulate) from the cytoplasm (soluble), and add epinephrine to the soluble portion, the result will be: \\\ the production of cAMP. \\\ binding of the epinephrine to its receptor. \\\ activation of adenylyl cyclase. \\ None of these are correct. \\\\ Glucagon binds to the glucagon receptor, which interacts with a membrane-bound G protein, whichs alpha subunit releases GDP and binds GTP. The alpha subunit then dissociates from the G protein and diffuses to a membrane-bound adenylyl cyclase which produces cAMP. In this scenario, name the (1) transducer, (2) effector, (3) first messenger, and (4) second messenger \\\ (1) glucagon (2) cAMP (3) G protein (4) GTP \\ (1) G protein (2) adenylyl cyclase (3) glucagon (4) cAMP \\\ (1) G protein (2) GTP (3) glucagon (4) cAMP \\\ (1) glucagon (2) G protein (3) adenylyl cyclase (4) cAMP \\\\ G proteins are said to be self-inactivating. What G-protein function accounts for this? \\ GTPase activity of the alpha subunit \\\ activation of the effector \\\ binding to the receptor \\\ dissociation of the subunits
\\\\ People who suffer from thyroid adenomas have constitutively activated G proteins in some cells of the thyroid gland. Tumor cells not only secrete copious quantities of thyroid hormones but also divide and grow excessively. Based on these observations, in what kind(s) of signal transduction pathways do the mutant G proteins participate? \\\ cAMP-regulated pathways \\\ MAP kinase pathways \\ both cAMP and MAP kinase pathways \\\ neither cAMP nor MAP kinase pathways \\\\ What factors are responsible for the specificity of G protein-coupled responses? \\ Protein kinases can phosphorylate different proteins in different cells. \\\ Receptors can exist as isoforms. \\\ G-protein subunits can exist as isoforms. \\\ All of these are correct. \\\\ Ryanodine and IP3 receptors are found on ---------- membranes, whereas epinephrine and glucagon receptors are found on ---------- membranes. \\\ plasma, intracellular \\ intracellular, plasma \\\ mitochondrial, endoplasmic reticulum \\\ outer, inner \\\\ Depending on the cell, increase in intracellular Ca2+ can do all of the following except: \\\ stimulate the increase of intracellular calcium. \\\ stimulate the removal of intracellular calcium. \\\ stimulate the opening of ryanodine receptors. \\ stimulate the deactivation of calmodulin. \\\\ Which mutant form of Ras is likely to cause malignancy? \\ ras that cannot hydrolyze GTP \\\ ras that cannot bind to GTP \\\ ras that cannot bind to Grb2 or Sos \\\ ras that cannot bind to Raf \\\\ What second messenger has been implicated in blood pressure regulation? \\\ cAMP \\ NO \\\ CO \\\ IP3 \\\\ Amplification of a chemical signal occurs when \\ a receptor in the plasma membrane activates several G protein molecules while a signal molecule is bound to it. \\\ a cAMP molecule activates one protein kinase molecule before being converted to AMP. \\\ phosphorylase and phosphatase activities are balanced. \\\ receptor tyrosine kinases dimerize upon ligand binding. \\\\ Consider this pathway: epinephrine Gproteinlinked receptor adenylyl cyclase cAMP. Identify the second messenger. \\ cAMP \\\ G protein \\\ GTP G protein
\\\ Gproteinlinked receptor \\\\ Binding of a signal molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of anions and/or cations on opposite sides of the membrane? \\\ receptor tyrosine kinase \\\ Gproteinlinked receptor \\\ phosphorylated receptor tyrosine kinase dimer \\ ligandgated ion channel \\\\ Protein phosphorylation is commonly involved with all of the following except \\\ regulation of transcription by extracellular signal molecules. \\ activation of Gproteinlinked receptors. \\\ activation of receptor tyrosine kinases. \\\ activation of protein kinase molecules. \\\\ Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because \\\ they are species specific. \\\ they always lead to the same cellular response. \\ they amplify the original signal manyfold. \\\ the number of molecules used is small and fixed. \\\\ The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases is always characterized by \\ dimerization and phosphorylation. \\\ IP3 binding. \\\ GTP hydrolysis. \\\ channel protein conformational change. \\\\ Which of the following reactions is catalyzed by the enzyme adenylate cyclase? \\ The conversion of ATP to cyclic AMP. \\\ The conversion of cyclic AMP to AMP. \\\ The conversion of cyclic AMP to ATP. \\\ The conversion of AMP to cyclic AMP. \\\\ Which of the following statements is true for diacylglycerol (DG) formed in the following reaction PIP2 --- DAG+IP3 ? \\ It is a hydrophobic molecule. \\\ It moves into the cytoplasm. \\\ It deactivates an enzyme called protein kinase C. \\\ It is not a secondary messenger. \\\\ Which of the following statements is true for inositol triphosphate (IP3) formed in the reaction PIP2 ---DAG+IP3? \\\ It is a hydrophobic molecule. \\ It moves into the cytoplasm to activate the release of calcium ions. \\\ It deactivates the release of calcium ions. \\\ It is not a secondary messenger. \\\\ Which of the following statements is untrue about G-proteins? \\ G-proteins consist of four protein subunits. \\\ G-Proteins act as signal proteins. \\\ G-Proteins interact with receptors.
\\\ G-Proteins bind GDP in the resting state. \\\\ Which of the following is true when a G-protein interacts with a receptor? \\\ The G-protein is split into a gama-subunit and an alpha, beta-dimer \\\ The G-protein is split into a beta-subunit and an alpha, gama-dimer \\ The G-protein is split into an alpha-subunit and a beta, gama-dimer \\\ The G-protein is split into its component protein subunits \\\\ Which of the following subunits activates adenylate cyclase? \\\ The alphai-subunit \\ The alphas-subunit \\\ The alphaq-subunit \\\ The alphao-subunit \\\\ Which of the following is untrue with respect to small G-proteins? \\\ Small G-proteins consist of a single protein. \\\ Ras is an example of a small G-protein. \\\ Small G-proteins bind GDP in the resting state. \\ Small G-proteins are the same as G-proteins, but have a lower molecular weight. \\\\ Which of the following statements is true about calmodulin \\ It is a protein which binds calcium ions and activates protein kinases. \\\ It is a protein which binds calcium ions and binds to DNA to activate transcription. \\\ It is a protein which transports calcium ions across the cell membrane. \\\ It is a protein which modifies calcium ion concentration within the cell. \\\\ Which of the following statements is true about a G-protein coupled receptor? \\\ It contains five transmembrane hydrophobic sections. \\\ There are more extracellular loops than intracellular loops. \\\ The binding region for the G-protein involves two extracellular loops. \\ The N-terminal chain is extracellular and the C-terminal chain is intracellular. \\\\ Which of the following reactions is catalysed by a protein kinase? \\ The phosphorylation of hydroxyl- groups in protein substrates. \\\ The hydrolysis of phosphate groups in protein substrates. \\\ The cleavage of blood plasma proteins. \\\ The hydrolysis of phosphate groups in ATP and GTP. \\\\ Which of the following statements is true about a tyrosine kinase linked receptor? \\\ It is situated in the cytoplasm. \\\ The N-terminal chain is intracellular. \\ The ligand binding site is in the N-terminal chain. \\\ It has two hydrophobic transmembrane regions. \\\\ Which of the following is not a typical messenger for a tyrosine kinase linked receptor? \\\ insulin \\ acetylcholine \\\ growth factors \\\ cytokines \\\\ What is second messenger?
\\\ a protein that is capable of speeding up specific chemical reactions by lowering the required activation energy \\ a small molecule or ion that carries the message from a receptor on the target cell surface into the cytoplasm \\\ derivative compound resulted from the removal of a phosphate group, usually by a phosphatase enzyme. \\\ a highly specific cell-surface receptor embedded in a cell membrane that responds only to a specific messenger molecule \\\\ What is receptor protein? \\\ a protein that is capable of speeding up specific chemical reactions by lowering the required activation energy \\\ lipid molecule modified within the Golgi Complex by having a short sugar chain (polysaccharide) attached \\\ derivative compound after removal of a phosphate group, usually by a phosphatase enzyme \\ a highly specific cell-surface receptor embedded in a cell membrane that responds only to a specific messenger molecule \\\\ Which of the following is correct about cyclic AMP (cAMP)? \\\ Any of a class of protein kinases that activate transcription factors to alter gene expression. A mitogen is any molecule that stimulates cell division. MAP kinases are activated by kinase cascades. \\\ one of a large group of transmembrane proteins that contain a ca+2-mediated binding between cells; these protiens are responsible for the cell-to-cell adhesion between cells of the same type \\ a form of adenosine monophospate (AMP) in which the atoms of the phosphate group form a ring; found in almost all organisms, this molecule functions as an intracellular second messenger that regulates a diverse array of metabolic activities. \\\ a protein that functions to link transcriptional activators to the transcription complex consisting of RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors \\\\ Which of the following is correct concerning enzymes? \\ a protein that is capable of speeding up specific chemical reactions by lowering the required activation energy \\\ lipid molecule modified within the Golgi Complex by having a short sugar chain (polysaccharide) attached \\\ a cell surface protein that binds a signal molecule and converts the extracellular signal into an intracellular one \\\ a small molecule or ion that carries the message from a receptor on the target cell surface into the cytoplasm \\\\ Which of the following is correct concerning receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)? \\\ It is consequence of events that occur within a cell on the receipt of a signal, ligand binding to a receptor protein. Signal transduction pathways produce the cellular response to a signaling molecule \\ It is a diverse group of membrane receptors that when activated have kinase enzymatic activity. Specifically, they phosphorylate proteins on tyrosine. Their activation can lead to diverse cellular responses \\\ It is a protein that functions to link transcriptional activators to the transcription complex consisting of RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors \\\ It is a receptor that acts through a heterotrimeric (three component) G protein to activate effector proteins then function as enzymes to produce second messenger such as cAMP or IP3 \\\\ Which of the following is correct concerning signal transduction?
\\\ It is a receptor that acts through a heterotrimeric (three component) G protein to activate effector proteins then function as enzymes to produce second messenger such as cAMP or IP3. \\\ It is a protein that functions to link transcriptional activators to the transcription complex consisting of RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors \\ It is the consequence of events that occur within a cell on the receipt of a signal, ligand binding to a receptor protein. Signal transduction pathways produce the cellular response to a signaling molecule \\\ It is a protein that binds guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and assists in the function of cell-surface receptors. When the receptor binds its signal molecule, the _______ binds GTP and is activated to start a chain of events within the cell \\\\ What is paracrine signaling? \\\ lipid molecule modified within the Golgi Complex by having a short sugar chain (polysaccharide) attached \\ a type of chemical signaling between cells in which the effects are local and short-lived \\\ any of a number of enzymes that removes a phosphate group from a protein, reversing the action of a kinase \\\ a highly specific cell-surface receptor embedded in a cell membrane that responds only to a specific messenger molecule \\\\ What is phosphorylation? \\\ intracellular receptors are found in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The site of action in the hormone- receptor complex is in the nucleus where they modify gene expression \\\ a molecule, usually a peptide or a steroid, that is produced in one part of the organism and triggers a specific cellular reaction in target tissues and organs some distance away \\\ a diverse group of membrane receptors that when activated have kinase enzymatic activity. Specifically, they phosphorylate proteins on tyrosine. Their activation can lead to diverse cellular responses \\ chemical reaction reacting in the addition of a phosphate group to an organic molecule. because of this process ADP makes ATP. Many proteins can be activated or deactivated by it. \\\\ What is true about hydrophilic hormones? \\\ Form a micelle \\ Bind to receptors on the cell surface \\\ Bind to G proteins \\\ Are chemically altered \\\\ All of the following are important aspects of normal signal transduction except: \\\ Responds to changes in environment \\\ Signal amplification \\ Tumor formation \\\ Signals are short-lived \\\\ How do most hydrophobic chemical messengers get transported to a target cell? \\\ They dissolve easily in the circulatory fluids. \\\ They bind to hormones in the blood. \\\ They move from cell to cell through gap junctions. \\ They bind to carrier proteins in the blood. \\\\ How does a ligand-gated ion channel work? \\\ When a ligand binds to an ion channel, an enzyme facilitates the passage of ions across the membrane.
\\\ When a ligand binds to an ion channel, the channel interacts with a G-protein that subsequently opens another ion channel nearby, allowing ions to cross the membrane. \\\ A ligand-gated ion channel is generally open and allows ions to cross the membrane. However, in the presence of a ligand, an ion channel will close. \\ When a ligand binds to an ion channel, the channel changes conformation and the ion channel opens, allowing ions to cross the membrane. \\\\ Which of the following statements about receptors with enzymatic activity is false? \\\ A receptor-enzyme has an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular catalytic (enzyme) domain. \\\ Three types of receptor-enzymes found in animals are 1) receptor guanylate cyclases 2) receptor tyrosine kinases, and 3) receptor serine/threonine kinases. \\\ The signal transduction pathways of receptor-enzymes involve phosphorylation cascades. \\ Receptor-enzymes interact with an intracellular protein called a "G-protein". \\\\ _____________ rely on ___________, such as Ca2+, cyclic GMP, phosphatidylinositol, and cyclic AMP, to activate (or inactivate) a variety of pathways within the cell. \\\ Intracellular receptors; ligands \\ G-protein-coupled receptors; second messengers \\\ Receptor-enzymes; G-proteins \\\ G-protein-coupled receptors; G-proteins \\\\ Which of the following statements about G-protein signaling pathways is false? \\\ cAMP is the second messenger. \\\ Most Ca2+ -mediated signal transduction cascades act through the protein calmodulin, a Ca2+ binding protein that is present in every eukaryotic cell. \\ Receptor serine/threonine kinases directly activate G-proteins, which in turn activate second messengers. \\\ Inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglyerol (DAG) act as second messenger in two branches of the phosphatidylinositol signaling pathway. \\\\ The autocrine/paracrine signaling system has a ____________signaling distance and ___________duration of response. \\\ short; long \\\ long; long \\\ long; short \\ short; short \\\\ Because steroids generally act by _______________, their effects are typically _______________ than the effects of peptide hormones. \\ regulating transcription; slower \\\ activating second messengers; slower \\\ opening ion channels; faster \\\ regulating transcription; faster \\\\ cAMP acts as a second messenger that goes on to interact with and activate which of the following molecule? \\ Protein kinase A \\\ AMP-activated protein kinase \\\ Protein kinase CG \\\ protein-coupled receptor kinase
\\\\ Besides differentiation and survival, what is the result of activation of Ras signalling?. \\\ Cell cycle \\ Cell growth \\\ Cell nucleus \\\ Mitosis \\\\ Which of the following is correct about Steroid hormones? \\\ bind cell surface receptors. \\\ are insoluble in blood. \\\ have a very rapid effect (within seconds) on target cells. \\\ mediate their effects through second messengers. \\\\ Which of the following is correct about Ion channels? \\\ allow the flow of ions only down their electrochemical gradient. \\\ are always open. \\\ allow the simultaneous flow of anions and cations. \\\ are ATPases. \\\\ Activation of a G protein-coupled receptor causes stimulatory G protein (Gs) to: \\\ replace its bound GDP with GTP. \\\ dissociate from adenylyl cyclase. \\\ combine all three subunits of G-protein. \\\ generate cGMP. \\\\ What is the role of SH2 domains in proteins? \\\ They contain phosphorylation sites that create docking sites for other proteins. \\\ They are needed for the phosphorylation of target proteins at specific Tyr residues. \\\ They activate protein kinases. \\ They bind to proteins that contain P-Tyr residues.
102 tests
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Lecture 8-CAMP and Cell SignallingDokumen7 halamanLecture 8-CAMP and Cell Signallingjosphat nzuvaBelum ada peringkat
- Cyclic Adenosine MonophosphateDokumen3 halamanCyclic Adenosine Monophosphatek.n.e.d.Belum ada peringkat
- 2 Mechanism of Action of Steroid HormonesDokumen25 halaman2 Mechanism of Action of Steroid HormonesRana AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Cell SignalingDokumen75 halamanCell SignalingjhanvisBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanism of Hormone Action: DR Jehad Al-ShuneigatDokumen47 halamanMechanism of Hormone Action: DR Jehad Al-Shuneigatyousef sarairehBelum ada peringkat
- FisWan Pertemuan Ke 3. OkDokumen24 halamanFisWan Pertemuan Ke 3. OkEria MarinaBelum ada peringkat
- CDD Is 2013151 ADokumen10 halamanCDD Is 2013151 ADalton JLBelum ada peringkat
- Intraneuronal Signalling Pathways: Chair Person: Dr. S. Kiran Kumar Presenter: Dr. G - Sangha MitraDokumen20 halamanIntraneuronal Signalling Pathways: Chair Person: Dr. S. Kiran Kumar Presenter: Dr. G - Sangha Mitrasangha_mitra_2Belum ada peringkat
- 2-Hormonal Signal Transduction 2 2Dokumen33 halaman2-Hormonal Signal Transduction 2 2Mohammed Mansour AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- BiochemDokumen5 halamanBiochemUzair MughalBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Signal Transduction: The Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department of CMUDokumen98 halamanCellular Signal Transduction: The Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department of CMUKrisda JitrakbumrungBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanism of Hormone ActionDokumen54 halamanMechanism of Hormone ActionDr. Tapan Kr. Dutta100% (1)
- Second Messenger Action, cAMP & CGMPDokumen27 halamanSecond Messenger Action, cAMP & CGMPSandraBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem - Hormone and Signal TransductionDokumen36 halamanBiochem - Hormone and Signal TransductionPrincess Jeyan PagatpatanBelum ada peringkat
- Day 22 Signaling 1: General Concepts and cAMP Pathway: - You Should Be Able To ExplainDokumen20 halamanDay 22 Signaling 1: General Concepts and cAMP Pathway: - You Should Be Able To Explainshouq huusainBelum ada peringkat
- Faisal Institute of Health Sciences: Assignment Department/ Class: DPT Semester: 4Dokumen14 halamanFaisal Institute of Health Sciences: Assignment Department/ Class: DPT Semester: 4Ansa MalikBelum ada peringkat
- With The Name of Allah The Most Gracious and The Most MercifulDokumen23 halamanWith The Name of Allah The Most Gracious and The Most MercifulMohammad Noman AkramBelum ada peringkat
- Mech of Action HormonesDokumen25 halamanMech of Action HormonesVurla PrabhavathiBelum ada peringkat
- Original Article: Macroenzyme Detection by Polyethylene Glycol PrecipitationDokumen7 halamanOriginal Article: Macroenzyme Detection by Polyethylene Glycol PrecipitationMWBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Signaling by Chemical Messengers: Dr. Maha Sallam Professor of BiohemistryDokumen117 halamanCell Signaling by Chemical Messengers: Dr. Maha Sallam Professor of BiohemistryFaizBelum ada peringkat
- Second MessengersDokumen42 halamanSecond MessengersYunonBelum ada peringkat
- CAMP PathwayDokumen14 halamanCAMP PathwaySree Lakshmi NBelum ada peringkat
- Second Messenger Signaling SystemsDokumen42 halamanSecond Messenger Signaling SystemsMirza Shaharyar BaigBelum ada peringkat
- SECOND MESSENGER SIGNALSDokumen8 halamanSECOND MESSENGER SIGNALSdebkantha gopeBelum ada peringkat
- Rac1/Pi3K/Pkb-Dependent Caspase-1 Activation Release Through Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibition Induces Il-1Dokumen12 halamanRac1/Pi3K/Pkb-Dependent Caspase-1 Activation Release Through Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibition Induces Il-1Josse BouwhuisBelum ada peringkat
- CAMPing in The Immune System - News & Announcements - Cayman ChemicalDokumen3 halamanCAMPing in The Immune System - News & Announcements - Cayman ChemicalRovin RamphalBelum ada peringkat
- Cell SignallingDokumen37 halamanCell SignallingSreekarWunnava100% (1)
- Intracellular Signal TransductionDokumen42 halamanIntracellular Signal TransductionYunita FatmalaBelum ada peringkat
- BiochemistryDokumen82 halamanBiochemistryAmritzz Paul83% (6)
- Lecture 4 GPCR-AA MetabolitesDokumen22 halamanLecture 4 GPCR-AA MetabolitesDr. Sagheer AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Biosignaling 1Dokumen52 halamanBiosignaling 1Javeria DawoodBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry 1Dokumen4 halamanBiochemistry 1Beatriz SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemical Signalling - 2 G Proteins and GPCRS: Shoba RanganathanDokumen23 halamanBiochemical Signalling - 2 G Proteins and GPCRS: Shoba RanganathanshaheenBelum ada peringkat
- Cyclic AMP Signalling PathwayDokumen5 halamanCyclic AMP Signalling Pathwayrawatpooran05Belum ada peringkat
- G-protein receptors overviewDokumen18 halamanG-protein receptors overviewLaura RossiBelum ada peringkat
- Use of Vasopressors and InotropesDokumen29 halamanUse of Vasopressors and InotropesAmaliahHarumiKarimBelum ada peringkat
- Signal Transduction in Cells: An Overview of Key ConceptsDokumen25 halamanSignal Transduction in Cells: An Overview of Key ConceptsSadaf BegBelum ada peringkat
- Secondary MessengerDokumen50 halamanSecondary MessengerFlorlin Grace YradBelum ada peringkat
- AMPK Phosphorylation Assay KitDokumen3 halamanAMPK Phosphorylation Assay KitBioAssay 2015Belum ada peringkat
- Hormone FinalDokumen36 halamanHormone FinalRajkishor YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 4 QuickiesDokumen40 halamanPaper 4 QuickiesRobin KeaneBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Revesion PDFDokumen80 halaman7 Revesion PDFMd Sakil AminBelum ada peringkat
- DR - Imran Ali: (AP Biochemistry)Dokumen118 halamanDR - Imran Ali: (AP Biochemistry)Aliya KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Line : Interplay of Ca and cAMP Signaling in The Insulin-Secreting Min6Dokumen9 halamanCell Line : Interplay of Ca and cAMP Signaling in The Insulin-Secreting Min6sofia03Belum ada peringkat
- Overview of Course Topics: Section/Module IDokumen61 halamanOverview of Course Topics: Section/Module IVidelicit89Belum ada peringkat
- Types of ReceptorsDokumen78 halamanTypes of ReceptorsDrPallavi DBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry Book Additional PlatesDokumen8 halamanBiochemistry Book Additional PlatesKiana TehraniBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To Hormones - Dr. Magat FINALDokumen8 halamanIntro To Hormones - Dr. Magat FINALneutralmindBelum ada peringkat
- Gene RegulationsDokumen11 halamanGene Regulationsmahadi.infsduBelum ada peringkat
- Online - B.Sc. - Hons. - Zoology - Sem-VI - ReproductiveBiologyTheory - Endocrine - System - 30042020Dokumen80 halamanOnline - B.Sc. - Hons. - Zoology - Sem-VI - ReproductiveBiologyTheory - Endocrine - System - 30042020s vBelum ada peringkat
- Second Messenger SystemsModDokumen49 halamanSecond Messenger SystemsModganotBelum ada peringkat
- BCH 227 CompletedDokumen17 halamanBCH 227 Completedmf5k8bx5w6Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Signalling Basics Part 2Dokumen15 halamanCell Signalling Basics Part 26ypywxdqmkBelum ada peringkat
- HormonesDokumen31 halamanHormonesKhalid RefaeyBelum ada peringkat
- Signal TransductionDokumen30 halamanSignal Transductionpalak100% (1)
- Systems of Intercellaneous Int: 2. The EndocrineDokumen62 halamanSystems of Intercellaneous Int: 2. The EndocrineSardar jiBelum ada peringkat
- Signal Transduction Mechanisms: II Messengers and ReceptorsDokumen21 halamanSignal Transduction Mechanisms: II Messengers and ReceptorsAisyah G PermatasariBelum ada peringkat
- Cell SignallingDokumen72 halamanCell SignallingSheerin SulthanaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Modulators of Protein Misfolding and Neurodegenerative DiseaseDari EverandChemical Modulators of Protein Misfolding and Neurodegenerative DiseaseBelum ada peringkat
- The Spell Thief Playbook For Through Sunken LandsDokumen4 halamanThe Spell Thief Playbook For Through Sunken LandsJakub WójtowiczBelum ada peringkat
- Apextimer WiringDokumen4 halamanApextimer Wiringkatwat01100% (1)
- Nocturne (Live in Los Angeles) Scott Colley and Julian LageDokumen7 halamanNocturne (Live in Los Angeles) Scott Colley and Julian LageSaurabh ShivakumarBelum ada peringkat
- Trek Volunteer Info Packet 2015Dokumen6 halamanTrek Volunteer Info Packet 2015api-275865446Belum ada peringkat
- CharacterSheet 3Pgs CompleteDokumen3 halamanCharacterSheet 3Pgs CompleteNahum Villanueva LunaBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica (B) Inglés-Bachillerato A Tu Medida-01-2019Dokumen30 halamanPráctica (B) Inglés-Bachillerato A Tu Medida-01-2019Apoyo Educativo FacilBelum ada peringkat
- Glassix Walkthrough GuideDokumen5 halamanGlassix Walkthrough Guidesaga gaaraBelum ada peringkat
- MATERIAL BALANCE TITLEDokumen46 halamanMATERIAL BALANCE TITLEG Vamsee KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Return of The Runelords - Player's Guide PDFDokumen14 halamanReturn of The Runelords - Player's Guide PDFPablo Herrer100% (5)
- Iron Defender EnhancementsDokumen2 halamanIron Defender EnhancementsGideon Stefan MostertBelum ada peringkat
- 29CB-Injectors CUMMINS CATALOGO PDFDokumen15 halaman29CB-Injectors CUMMINS CATALOGO PDFDiegoD'AmbrosioBelum ada peringkat
- Leo Messi: Name: Akilan Aravinthan Class: 1 Genesis Subject: EnglishDokumen3 halamanLeo Messi: Name: Akilan Aravinthan Class: 1 Genesis Subject: EnglishSivamalar ThyagarajahBelum ada peringkat
- Granada (Free Tabs)Dokumen9 halamanGranada (Free Tabs)Rahmayuni ElsyaBelum ada peringkat
- TH 350Dokumen5 halamanTH 350omarBelum ada peringkat
- Valvulas Triveca PDFDokumen9 halamanValvulas Triveca PDFABRIL MILLANBelum ada peringkat
- SotDL - Spell Cards - SotDL PathDokumen18 halamanSotDL - Spell Cards - SotDL PathIzael Evangelista100% (1)
- Histology LabDokumen9 halamanHistology Labsidro123100% (1)
- WRJC 2011 Rigging Survey 111208Dokumen57 halamanWRJC 2011 Rigging Survey 111208Stephen AitkenBelum ada peringkat
- D&D 5e - Players Handbook - SmallDokumen4 halamanD&D 5e - Players Handbook - SmallAngelo Navarro2% (41)
- Philippine Folk Dance StepsDokumen10 halamanPhilippine Folk Dance StepsKersey BadocdocBelum ada peringkat
- (DejaScacchi) Hard Level IDokumen15 halaman(DejaScacchi) Hard Level IOscar Estay T.Belum ada peringkat
- Helmet: Personal Protective Equipment Inspection ChecklistDokumen3 halamanHelmet: Personal Protective Equipment Inspection ChecklistDlraje DlrajeBelum ada peringkat
- Earthdawn Extended Character Sheet 3eDokumen7 halamanEarthdawn Extended Character Sheet 3eBilly MottBelum ada peringkat
- Hoist Drum Assy 4100XPCDokumen3 halamanHoist Drum Assy 4100XPCFrancisco GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Fist Full of ZombiesDokumen2 halamanFist Full of Zombiesadlard_matthew100% (1)
- Bulgarian Method 1Dokumen9 halamanBulgarian Method 1TRASH SHUBHAMBelum ada peringkat
- Chess OpeningsDokumen9 halamanChess Openingsgassy9999100% (1)
- Math in Focus 3B WorksheetDokumen6 halamanMath in Focus 3B WorksheetBobbili PooliBelum ada peringkat
- Chiller Room Chiller Room: Entry Mep Room Entry Mep RoomDokumen1 halamanChiller Room Chiller Room: Entry Mep Room Entry Mep RoomBertha Vinola ChrisanBelum ada peringkat
- Variable Camshaft Timing - Variable Valve TimingDokumen85 halamanVariable Camshaft Timing - Variable Valve TiminglibertyplusBelum ada peringkat