Chapter 20 Rate of Reaction (Extension)
Diunggah oleh
sliversniper0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
88 tayangan5 halamanZinc reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. When the hydrogen gas is allowed to escape, the mass of the reaction mixture decreases over time. Zinc reacts with copper(II) sulphate solution and copper metal.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
20
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniZinc reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. When the hydrogen gas is allowed to escape, the mass of the reaction mixture decreases over time. Zinc reacts with copper(II) sulphate solution and copper metal.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
88 tayangan5 halamanChapter 20 Rate of Reaction (Extension)
Diunggah oleh
sliversniperZinc reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. When the hydrogen gas is allowed to escape, the mass of the reaction mixture decreases over time. Zinc reacts with copper(II) sulphate solution and copper metal.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 5
56 Part 4
Chapter 20 Rate of Reaction (Extension)
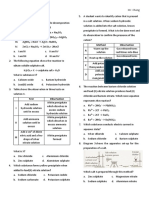
A. Multiple Choice Questions 3. (a) Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq)
ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
1. A. Reaction between magnesium Method 1 : Measuring the mass of
chloride solution and sodium the reaction mixture
carbonate solution Zinc reacts with dilute hydrochloric
2. D. Reaction between powdered acid to form zinc chloride and
limestone and 2 M hydrochloric acid hydrogen gas. When the hydrogen
3. B. S2O32(aq) + 2H+(aq) gas is allowed to escape, the mass of
SO2(g) + S(s) + H2O(l) the reaction mixture decreases over
4. C. (1), (2) and (4) only time.
5. A. (1) and (3) only Method 2 : Measuring the volume
6. D. The time for completion of reaction of gas produced
in beaker A is half of that in beaker Zinc reacts with dilute hydrochloric
B. acid to form zinc chloride and
hydrogen gas. The volume of
B. Fill in the Blanks hydrogen gas produced increases
over time.
(b) Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq)
1. Rate of reaction, product
Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq)
2. reactant, product
Method 1 : Measuring the
3. concentration, surface area, temperature
concentration of product Zinc reacts
with copper(II) sulphate solution to
C. Comprehensive Questions form zinc sulphate solution and
copper metal. The concentrations of
1. (a) Fast the products, zinc sulphate solution
(b) Fast and copper, increase over time.
(c) Steady Method 2 : Measuring the colour
(d) Fast intensity of the reaction mixture
(e) Fast and instantaneous Zinc reacts with copper(II) sulphate
solution to form zinc sulphate
2. (a) Reaction between zinc and copper(II) solution and copper metal. In the
sulphate solution reaction, copper(II) ions are one of
(b) Reaction between magnesium and the reactants and only copper(II) ions
dilute sulphuric acid are coloured. Throughout the reaction,
(c) Rusting of iron the concentration of copper(II) ion
(d) Reaction between dilute and the colour intensity of the
hydrochloric acid and dilute sodium reaction mixture decrease.
hydroxide solution (i.e.
neutralization)
Chapter 20 Solutions (EE).doc
Chapter 20 57
(c) NH4Cl(aq) + NaOH(aq) (c) Zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric
NaCl(aq) + NH3(g) + H2O(l) acid to form zinc sulphate and
Method 1 : Measuring the mass of hydrogen gas. When the hydrogen
the reaction mixture gas is allowed to escape, the mass of
Ammonium chloride reacts with the reaction mixture decreases over
dilute sodium hydroxide solution to time.
form sodium chloride, ammonia gas Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq)
and water. When the ammonia gas ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
is allowed to escape, the mass of the Observable change(s): Zinc
reaction mixture decreases over dissolves and colourless gas bubbles
time. evolve.
Method 2 : Measuring the volume (d) Sodium hydrogencarbonate reacts
of gas produced with dilute hydrochloric acid to
Ammonium chloride reacts with form sodium chloride, carbon
dilute sodium hydroxide solution to dioxide gas and water. The volume
form sodium chloride, ammonia gas of carbon dioxide gas produced
and water. The volume of ammonia increases over time.
gas produced increases over time. NaHCO3(s) + HCl(aq)
NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
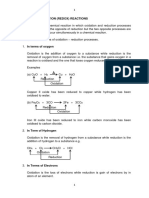
4. (a) When ethanol is heated with an Observable change(s): Sodium
oxidizing agent (e.g. acidified hydrogencarbonate dissolves and
potassium permanganate solution), colourless gas bubbles evolve.
ethanoic acid is produced. (e) Magnesium reacts with copper(II)
[O] sulphate solution to form
CH3CH2OH(aq) CH3COOH(aq) magnesium sulphate solution and
ethanol ethanoic acid copper metal. In the reaction,
copper(II) ions are one of the
[ O ] : acidified potassium reactants and only copper(II) ions
permanganate solution are coloured. Throughout the
Observable change(s): The solution reaction, the concentration of
changes from purple to colourless / copper(II) ion and the colour
pale pink. intensity of reaction mixture
(b) When ethanal is heated with an decrease.
oxidizing agent (e.g. acidified Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq)
potassium permanganate solution), (blue)
ethanoic acid is produced. Cu(s) + MgSO4(aq)
(colourless)
[O] Observable change(s): Magnesium
CH3CHO(aq) CH3COOH(aq) dissolves and brown solid is formed.
ethanal ethanoic acid The solution changes from blue to
[ O ] : acidified potassium colourless / The blue solution
permanganate solution becomes paler.
Observable change(s): The solution (f) Dichromate ions react with
changes from purple to colourless / hydrogen ions and iron(II) ions to
pale pink. form chromate(III) ions, iron(III)
Chapter 20 Solutions (EE).doc
58 Part 4
ions and water. The concentration of concentration of the reaction
hydrogen ions decreases over time. mixture. Therefore, the rate of the
Hence, the pH of the reaction reaction decreases.
mixture increases. (e) The rate of the reaction increases
Cr2O72(aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6Fe2+(aq) since a higher concentration of
2Cr3+(aq) + 6Fe3+(aq) + hydrochloric acid is used. This
7H2O(l) allows the reactant particles to
Observable change(s): The solution contact with each other more easily,
changes from orange to yellowish and thus a faster reaction is resulted.
green.
(g) Copper(II) chloride reacts with 6. HKCEE Question
silver nitrate solution to form
copper(II) nitrate solution and silver 7. (a) Fe(s) + H2SO4(aq)
chloride. The silver chloride formed FeSO4(aq) + H2(g)
is a white solid and it makes the (b)
reaction mixture cloudy.
CuCl2(aq) + 2AgNO3(aq)
Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2AgCl(s)
Observable change(s): A white solid
is formed over time.
5. (a) The rate of the reaction increases.
This is because powdered limestone
has a larger surface area than
limestone chip. The larger surface
area allows the reactant particles to
contact with each other more easily
and this usually causes a faster (c) 3 minutes
reaction. (d) 50 cm3
(b) The rate of the reaction decreases. (e)
This is because decreasing the
temperature decreases the kinetic
energy of reactants, so they collide
at a lower rate. Thus, the reaction
rate decreases.
(c) The rate of the reaction does not
change. Using a large volume of
hydrochloric acid of the same
molarity does not change the
concentration of hydrogen ions.
Therefore, the rate of the reaction
will not change.
(d) The rate of the reaction decreases.
Addition of water to the reaction
mixture will decrease the
Chapter 20 Solutions (EE).doc
Chapter 20 59
The reaction rate of Test 2 is the (e)
same as that of Test 1. This is
because increasing the volume of
sulphuric acid does not increase the
concentration of hydrogen ions.
Thus, the reaction rate remains
unchanged.
The reaction rate of Test 3 is lower
than that of Test 1. This is because
decreasing of sulphuric acid
decreases the concentration of
hydrogen ions. Thus, the reaction
rate decreases.
The reaction rate of Test 4 is higher
than that of Test 1. This is because
iron powder has a larger surface area
than iron wire, so the reaction rate of The reaction rate of Test 2 is the
Test 4 is higher. same as that of Test 1. This is
because increasing the volume of
8. (a) CaCO3(s) + 2HNO3(aq) nitric acid does not increase the
Ca(NO3)2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) concentration of hydrogen ions.
(b) Thus, the reaction rate remains
unchanged.
The reaction rate of Test 3 is higher
than that of Test 1. This is because
increasing the concentration of nitric
acid increases the concentration of
hydrogen ions. Thus, the reaction
rate increases.
The reaction rate of Test 4 is higher
than that of Test 1. This is because
powdered limestone has a larger
surface area than limestone chips.
(c) 3 minutes Thus, the reaction rate of Test 4 is
(d) 50 cm3 higher.
The reaction rate of Test 5 is lower
than that of Test 1. This is because
decreasing the temperature
decreases the kinetic energy of the
reactants, so they collide at a lower
rate. Thus, the reaction rate
decreases.
9 10. HKCEE Questions
Chapter 20 Solutions (EE).doc
60 Part 4
D. Essay-type Question sulphate solution used, the reaction is
carried out at different temperatures (e.g
1. Effect of concentration on the rate of 25 oC, 35 oC and 45 oC). For each reaction
the reaction between zinc and copper(II) mixture, the time required for the
sulphate solution: completion of the reaction is recorded.
At the same temperature and pressure, an The rate of the reaction between zinc and
equal mass of zinc is used to react with copper(II) sulphate solution increases
different concentrations of copper(II) when the temperature of the reaction
sulphate solution (e.g. 1 M, 2 M, 5 M and mixture increases.
10 M). In each of the reaction mixture, the
zinc strip dissolves and some reddish
brown solids (i.e. copper) are deposited.
Also, the solution becomes paler. For each
reaction mixture, the time required for the
completion of the reaction is recorded.
From 10 M copper(II) sulphate solution to
1 M copper(II) sulphate solution, the time
for the completion of reaction increases.
To conclude, when the concentration of
copper(II) sulphate solution increases and
other factors are kept the same, the rate of
the reaction increases.
Effect of surface area on the rate of the
reaction between zinc and copper(II)
sulphate solution:
At the same temperature and pressure, the
same mass of zinc strips and zinc powder
is used to react with the same volume of
copper(II) sulphate solution which is in
excess. For each reaction mixture, the
time required for the completion of the
reaction is recorded. The time for
completion of the reaction for zinc powder
is shorter than that for zinc strips. With the
same mass, zinc powder has a larger total
surface area than zinc strips. To conclude,
when the surface area of zinc increases
and other factors are kept the same, the
rate of the reaction increases.
Effect of temperature on the rate of the
reaction between zinc and copper(II)
sulphate solution:
With the same mass of zinc and same
concentration and volume of copper(II)
Chapter 20 Solutions (EE).doc
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Part IV Acids and Alkalis: LQ 01 (Answer) Properties of Acids and AlkalisDokumen12 halamanPart IV Acids and Alkalis: LQ 01 (Answer) Properties of Acids and AlkalisCharmine HolmesBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT CHEM01 Q:AsDokumen5 halamanNCERT CHEM01 Q:Asvivekabala13Belum ada peringkat
- CBSE Grade 10 Chemistry ExperimentsDokumen9 halamanCBSE Grade 10 Chemistry Experimentsclass10b iisBelum ada peringkat
- Salts: Quick Check (Page 214)Dokumen3 halamanSalts: Quick Check (Page 214)何小霞Belum ada peringkat
- DPP6 Salt Analysis Advanced-20210817095236189649Dokumen5 halamanDPP6 Salt Analysis Advanced-20210817095236189649safarisurf688Belum ada peringkat
- Action of Metals With Water: O-LevelDokumen3 halamanAction of Metals With Water: O-Levelleticia karungiBelum ada peringkat
- Module A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsDokumen13 halamanModule A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsJOANNA MAGDALIN A/P JOSEPH MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Part IV Acids and Alkalis: MC 01 (Answers)Dokumen12 halamanPart IV Acids and Alkalis: MC 01 (Answers)Charmine HolmesBelum ada peringkat
- All in One SCIENCE 10 Activity CH 2Dokumen8 halamanAll in One SCIENCE 10 Activity CH 2Shanthosh100% (1)
- Acids, Bases - Salts 4 QPDokumen8 halamanAcids, Bases - Salts 4 QPANIKA DHANIKACHALAMBelum ada peringkat
- ch-1 TestDokumen8 halamanch-1 TestGURANSH DEEPBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Equation NotesDokumen2 halamanChemical Equation NotesSarah WongBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Experiment 1Dokumen3 halamanChemistry Experiment 1Tanishq UppalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 Reactivity of MetalsDokumen2 halamanChapter 10 Reactivity of MetalssliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- Purification & Characterisation of Organic CompoundsDokumen14 halamanPurification & Characterisation of Organic CompoundsEzhil MukilBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE-X Chapterwise (Previous Years) Qs - Science - SOL-min PDFDokumen60 halamanCBSE-X Chapterwise (Previous Years) Qs - Science - SOL-min PDFmathanagopal balasundram100% (1)
- Quiz ChemDokumen4 halamanQuiz ChemCherryBelum ada peringkat
- Reactions of Metals With Dilute AcidsDokumen3 halamanReactions of Metals With Dilute AcidsDarshanaK 728714Belum ada peringkat
- CA DEM Y: Chapter - 2 - NOTESDokumen2 halamanCA DEM Y: Chapter - 2 - NOTESvarun puriBelum ada peringkat
- Class 9 Icse - Chemical Changes and Reactions - Part A - Lecture A.3Dokumen2 halamanClass 9 Icse - Chemical Changes and Reactions - Part A - Lecture A.3Vijay GautamBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 23 Redox Reactions: e Is A Strong Oxidizing AgentDokumen3 halamanChapter 23 Redox Reactions: e Is A Strong Oxidizing AgentsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- Salt Analysis (Exercise) - EngDokumen8 halamanSalt Analysis (Exercise) - Engjoxis70026Belum ada peringkat
- Chem Activity BK 1B (Answers)Dokumen40 halamanChem Activity BK 1B (Answers)trumpBelum ada peringkat
- 1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradDokumen12 halaman1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradKshitiz sharma100% (1)
- Final Worksheet-Chemical EquationsDokumen3 halamanFinal Worksheet-Chemical Equationsfindaryan28Belum ada peringkat
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDokumen6 halamanAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry MCQDokumen3 halamanChemistry MCQSharkBelum ada peringkat
- Oxidation Reduction LadDokumen8 halamanOxidation Reduction Ladprincess lastimosaBelum ada peringkat
- Science Class 10 Complete BooksDokumen76 halamanScience Class 10 Complete BooksTemsuyanger JamirBelum ada peringkat
- Test 3Dokumen9 halamanTest 3bhattaraisurya54Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 Part 2 (KSSM) - 231019 - 184442Dokumen16 halamanChapter 6 Part 2 (KSSM) - 231019 - 184442Pewdan AsianBelum ada peringkat
- MC Acids and AlkalisDokumen12 halamanMC Acids and Alkalisapi-3826629100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 5 KSSM: 8 February 2021Dokumen24 halamanChemistry Form 5 KSSM: 8 February 2021NurBelum ada peringkat
- Jee Main Hydrogen Important QuestionsDokumen11 halamanJee Main Hydrogen Important Questionskinshuk.pradhanBelum ada peringkat
- A Level Mathematics WorkDokumen25 halamanA Level Mathematics WorkSseguya Lubega YaqubBelum ada peringkat
- Objective QuestionsDokumen4 halamanObjective QuestionsJacelynBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Reactions QuestionsDokumen5 halamanChemical Reactions QuestionsZeeshan AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989564Dokumen6 halamanCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989564abiniveshofficial4708Belum ada peringkat
- Evoke Ch-1 AnswersDokumen6 halamanEvoke Ch-1 AnswersHimanshu SattiBelum ada peringkat
- HydrogenDokumen22 halamanHydrogenKeerthana MBelum ada peringkat
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613Dokumen7 halamanCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613abiniveshofficial4708Belum ada peringkat
- Acids and Bases: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 189)Dokumen3 halamanAcids and Bases: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 189)何小霞Belum ada peringkat
- 10 Science English 2020 21Dokumen296 halaman10 Science English 2020 21Daksh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 - Unit Test (Redox Reaction)Dokumen2 halamanChapter 7 - Unit Test (Redox Reaction)KazuYesBelum ada peringkat
- Science Worksheet - SolutionDokumen15 halamanScience Worksheet - SolutionZainul ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Dokumen29 halamanChemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Novah GurulooBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises Part A: MCQDokumen3 halamanExercises Part A: MCQNur Husnina HussinBelum ada peringkat
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988039Dokumen5 halamanCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988039abiniveshofficial4708Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical Arithmetic and Reactions: ObjectivesDokumen24 halamanChemical Arithmetic and Reactions: Objectivesgoputs6386Belum ada peringkat
- My ChemistryDokumen3 halamanMy ChemistryLu WeeBelum ada peringkat
- Redox TestDokumen4 halamanRedox Testhishmah138Belum ada peringkat
- GRADE 10 Chemical ReactionsDokumen17 halamanGRADE 10 Chemical ReactionsDanny BlessyBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 S5 1st Exam AnswerDokumen8 halaman2021 S5 1st Exam Answerlala LuBelum ada peringkat
- Acids, Bases and Salts Activities Class 10 CbseDokumen8 halamanAcids, Bases and Salts Activities Class 10 CbseIqbal Singh87% (30)
- ReductionDokumen50 halamanReductionElvis NgandweBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDokumen9 halamanChemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDhilfa Eleyedath International Indian School - Abu DhabiBelum ada peringkat
- Yr 11 - Chem - Term 1 Revision WS - Jan 2023Dokumen7 halamanYr 11 - Chem - Term 1 Revision WS - Jan 2023troyrodrigues36Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDokumen3 halamanChemical Formulae and EquationsFatema KhatunBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionDari EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- 2005paper 2Dokumen13 halaman2005paper 2sliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 2006paper 1 MarkingDokumen11 halaman2006paper 1 MarkingsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- CE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)Dokumen13 halamanCE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)08150815whoimBelum ada peringkat
- 2006 Paper 1Dokumen28 halaman2006 Paper 1sliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 2004 Paper I Marking SchemeDokumen12 halaman2004 Paper I Marking SchemesliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 2004paper IIDokumen13 halaman2004paper IIsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 2005paper 1Dokumen16 halaman2005paper 1sliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 2002 Paper 1Dokumen20 halamanPhysics 2002 Paper 1api-3739499100% (2)
- 1997paper IIDokumen11 halaman1997paper IIsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 2003 Paper I Marking SchemeDokumen10 halaman2003 Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3700944Belum ada peringkat
- 2003paper IDokumen8 halaman2003paper IsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 2003 Paper IIDokumen14 halamanPhysics 2003 Paper IIapi-26423290Belum ada peringkat
- 2004paper IDokumen10 halaman2004paper IsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 2002 Paper IIDokumen25 halamanPhysics 2002 Paper IIapi-26423290Belum ada peringkat
- 2002 Paper I Marking SchemeDokumen9 halaman2002 Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3700944Belum ada peringkat
- Physics 2000 PaperIDokumen19 halamanPhysics 2000 PaperIapi-26423290Belum ada peringkat
- Physics 2000 PaperIIDokumen14 halamanPhysics 2000 PaperIIapi-26423290Belum ada peringkat
- Physics 1998 PaperIIDokumen13 halamanPhysics 1998 PaperIIapi-26423290Belum ada peringkat
- 1999paper IIDokumen12 halaman1999paper IIsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 1996paper IIDokumen11 halaman1996paper IIsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 1998 PaperIDokumen6 halamanPhysics 1998 PaperIapi-26423290Belum ada peringkat
- 1999paper IDokumen8 halaman1999paper IsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 1997paper IDokumen8 halaman1997paper IsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 1994paper I MarkingDokumen9 halaman1994paper I MarkingsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 1994paper IIDokumen11 halaman1994paper IIsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 1995paper I MarkingDokumen10 halaman1995paper I MarkingsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 1996paper IDokumen8 halaman1996paper IsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 1995paper IIDokumen11 halaman1995paper IIsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 1995paper IDokumen8 halaman1995paper IsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- 1994paper IDokumen8 halaman1994paper IsliversniperBelum ada peringkat
- Quantity Estimation OHSRDokumen4 halamanQuantity Estimation OHSRPrashant GargBelum ada peringkat
- Widearea Eye/Face Washes G1724: Guardian EquipmentDokumen2 halamanWidearea Eye/Face Washes G1724: Guardian Equipmenteisenbarger5607Belum ada peringkat
- Co-Ordinate (Dative Covalent) BondingDokumen8 halamanCo-Ordinate (Dative Covalent) BondingAnshuman TagoreBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 1 PDFDokumen33 halamanChem 1 PDFJelena ZdravkovicBelum ada peringkat
- 142 BDokumen15 halaman142 BarunachalamBelum ada peringkat
- Ref. Batcoda 14 Sanitary InstallationDokumen30 halamanRef. Batcoda 14 Sanitary InstallationmekdiBelum ada peringkat
- Metallic BondingDokumen22 halamanMetallic BondingnkjkjkjBelum ada peringkat
- Sintesis Dan Karakterisasi Nanopartikel Aluminium Oxide (Al O) Dari Limbah Aluminium Untuk NanofluidaDokumen5 halamanSintesis Dan Karakterisasi Nanopartikel Aluminium Oxide (Al O) Dari Limbah Aluminium Untuk NanofluidaYulia Puspa DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Ultra-High-Performance Geopolymer Concrete A ReviewDokumen25 halamanUltra-High-Performance Geopolymer Concrete A ReviewShaker QaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Major Head Minor Head Detailed Head: ShimlaDokumen11 halamanMajor Head Minor Head Detailed Head: ShimlaRajat SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Royalthane 450GLDokumen2 halamanRoyalthane 450GLSyed FaridBelum ada peringkat
- Marine CoatingsDokumen145 halamanMarine CoatingsAlexander MaksaevBelum ada peringkat
- CladdingDokumen21 halamanCladdingVaibhav HireraddiBelum ada peringkat
- Ferrocote 6130: Blank-Washing Rust Preventive OilDokumen2 halamanFerrocote 6130: Blank-Washing Rust Preventive Oilsumit100% (1)
- UHS-620A Projection For WTP Plant 50LPSDokumen9 halamanUHS-620A Projection For WTP Plant 50LPSirwan_souk100% (1)
- Pavement Design For NR-1Dokumen50 halamanPavement Design For NR-1Phearüm PotBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Blocking AdditiveDokumen5 halamanAnti Blocking AdditiveSergey TrifonovBelum ada peringkat
- GF 200 Installation Manual: Combination Gas-Fired, Condensing Instantaneous Hot Water Heater and Space Heating Fan CoilDokumen40 halamanGF 200 Installation Manual: Combination Gas-Fired, Condensing Instantaneous Hot Water Heater and Space Heating Fan CoiljazuoneBelum ada peringkat
- Eni Dicrea SX 68Dokumen2 halamanEni Dicrea SX 68AMAZING AGBelum ada peringkat
- DLP PatentingDokumen7 halamanDLP PatentingAon HemmatadBelum ada peringkat
- Exxonmobil High Density Polyethylene Product Guide: Europe Asia Pacific Middle East AfricaDokumen6 halamanExxonmobil High Density Polyethylene Product Guide: Europe Asia Pacific Middle East Africasébastien cardinale0% (1)
- HomeGuard Installation Manual 5C 2015Dokumen112 halamanHomeGuard Installation Manual 5C 2015_Asylum_Belum ada peringkat
- Kerto® LVL Q-Panels Combine Excellent Technical Performance With Ease of UseDokumen3 halamanKerto® LVL Q-Panels Combine Excellent Technical Performance With Ease of UseMatheus FlorianiBelum ada peringkat
- Astm A490mDokumen1 halamanAstm A490mSyed Mohammad Shabber AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Hostapal MRN Liq C - eDokumen4 halamanHostapal MRN Liq C - eRobin felderBelum ada peringkat
- ASTM D4301 - 2005 (2019) Cloro TotalDokumen2 halamanASTM D4301 - 2005 (2019) Cloro TotalPablo OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- Balcony Glass Partition Calculation - JBRSDokumen63 halamanBalcony Glass Partition Calculation - JBRSahsan khan100% (1)
- Experiment 8. Salt AnalysisDokumen3 halamanExperiment 8. Salt AnalysisSankalp MeshramBelum ada peringkat
- Client: Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Ltd. Contractor: Narmada Offshore Constructions Pvt. Ltd. Doc. No.: NOCPL/HPCL/NWOT/RK/WPS/JP/01 Rev. 00Dokumen7 halamanClient: Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Ltd. Contractor: Narmada Offshore Constructions Pvt. Ltd. Doc. No.: NOCPL/HPCL/NWOT/RK/WPS/JP/01 Rev. 00Bhargav BbvsBelum ada peringkat
- THE Behaviour of The Lead Dioxide Electrode: W. H. Beck, K. P. SinghDokumen8 halamanTHE Behaviour of The Lead Dioxide Electrode: W. H. Beck, K. P. SinghbuhalnitaBelum ada peringkat