Drug Study
Diunggah oleh
Czarinah Ela MesiasDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Drug Study
Diunggah oleh
Czarinah Ela MesiasHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
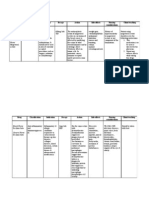
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
Indication
Contraindicati on
Adverse effect
Nursing alert
Omeprazole
Classification: Benzimidazole and a Gastric acid pump inhibitor.
Dosage
PO: 40 mg tab OD
Omeprazole is converted to active metabolites that irreversibly bind and inhibit H+-K+ATPase (an enzyme on the surface of gastric parietal cells). It inhibits transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen. Omeprazole increases the gastric pH and reduces gastric acid formation
This medication was given to our patient Because his on NPO Diet which means the stomach of our patient continuously producing hydrochloric acid so to stop it the physician ordered omeprazole.
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to omeprazole or its components
CNS: He a da c he , dizziness, asthenia, vertigo,insomnia, apathy,anxiety, paresthesias,drea m abnormalities Dermatologic: Rash,inflammation , urticaria, pruritus,alopecia, dry skin GI: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, drymouth,
- Give before meals Rationale: to avoid stomach upset - Do not crush or chew tablets, swallow whole Rationale: chewed tablets and opened capsules decreased the effectiveness of drugs - Evaluate for therapeutic response like relief of Gastrointestinal symptoms Question if Gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea occurs. Rationale: The patient is continually
28
tongueatrophy Respiratory: URI symptoms, c ough, epistaxis
evaluated for therapeutic response and the occurrence of drug side effects for evaluation of both the effectiveness and toxicity of the drug - when taking omeprazole be careful while driving or operating machinery because Dizziness may occur (avoid driving or performing hazardous tasks);headache (request medications); nausea,vomiting, diarrhea (maintain proper nutrition);symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection,cough (do not selfmedicate; consult with your health care provider if
29
Prescribed given: September 17, 2011
uncomfortable). Rationale: Omeprazole generally does not cause any problems with your ability to drive a car or operate machinery. However, as with many other medicines, it could be dangerous if you were not fully alert
29
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
Indication
Contraindicatio n
Adverse effect
Nursing alert
Paracetamol
Classification : antipyretics, nonopioid analgesics
Dosage
PO: 500 mg q4 hours PRN for fever
Inhibits prostaglandi n synthesis in the CNS and blocks the pain impulse through a peripheral action. It acts on the hypothalamic heatregulating center, producing peripheral vasodilation. It results in antipyresis
This medication was given to our patient to Temporarily relieve pain and discomfort from fever, minor muscular aches, overexertion,
Paracetamol is contraindicated in hypersensitivity, analgesic nephropathy, renal and hepatic impairment.
Early signs of toxicity: Anorex ia, nausea, diaphoresis (excessive sweating), generalized weakness within the first 12-24 hours.
- Assess patients pain or temperature before therapy and regularly thereafter Rationale: To indicate baseline data and monitor drugs effectiveness - Asses patients drug history and calculate total daily dosage accordingly Rationale: To prevent over dosage that could lead to toxicity and liver damage. - Be alert for signs of reactions and drug
28
Late signs of toxicity: Vomiti ng, right upper quadrant tenderness, elevated liver function tests within 48-72
and produces analgesic effect.
hours after ingestion. Antidote: Acetylcysteine.
interactions. Rationale: To establish proper preca utionary measures and management for possible adverse effects of drug. -Assess patients and familys knowledge of drug therapy.
Prescribed given: August 13,2011
Rationale: To determine the level of understanding of the patient and her family about the drug therapy
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse effect
Nursing alert
Ascorbic acid
Assists in collagen formation, tissue repair; involved in oxidation reduction
Vitamin C is used boosting our patients
Previous hypersensitivity; products containing
GI: Nausea,
-May give without regard to food. -Assess for clinical
28
Classification: reactions, other metabolic Vitamin reactions. Vitamin C is involved in metabolism; carbohydrate utilization; Dosage synthesis of lipids, PO: 500 mg BID proteins, carnitine. It also preserves blood vessel integrity.
immune system.
alcohol, aspartame, saccharin, sugar, or tartrazine (FDC yellow dye #5) should be avoided in patients who have hypersensitivity or intolerance to these compounds.
vomiting, heartburn, diarrhea. Hematologic: Acute hemolytic anemia (patients with deficiency of G6PD); sickle cellcrisis. CNS: Headache (high doses). Urogenital: Arthritis, dysuria, crystalluria (high doses)
improvement (improved sense of well-being and sleep patterns). -Observe for reversal of deficiency symptoms (gingivitis, bleeding gums, poor wound healing, digestive difficulties, joint pain). Patient Teachings for Clients Taking Vitamin C -Abrupt vitamin C withdrawal may produce rebound deficiency. - Take large doses of vitamin C in divided amounts Rationale: the body uses only what is needed at a particular time and excretes the rest in urine
28
Prescribed given: August 15, 2011
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse effect
Nursing alert
Tramadol
Tramadol binds to -opiate receptors and inhibits Classification: reuptake of norepinephrine Analgesic. and serotonin. It reduces intensity
Tramadol is prescribed to our patient to treat moderate to moderately
should not be administered to patients who have previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to tramadol, any
agitation, hallucinations, fever, fast heart rate, overactive reflexes, nausea, vomiting,
* For ambulatory patients: Be careful in rising and walking. Avoid driving and other potentially hazardous activities that require mental
28
of pain stimuli incoming from sensory nerve endings, altering pain perception and emotional response to pain. Dosage
severe pain.
other component of this product or opioids.
diarrhea, loss of coordination, fainting; seizure (convulsions); a red, blistering, peeling skin rash; or shallow breathing, weak...
alertness until drugs CNS effects are known. * Avoid giving tramadol to patients with acute abdominal conditions Rationale: because it may mask evidence and disrupt assessment of the abdomen. * Monitor patient for drug dependence. Rationale: Drug can produce dependence similar to that of codeine or dextropropoxyphene and thus has potential for abuse.
PO: 50mg q12 hours
Prescribed given August 23, 2011
29
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
Indication
Contraindicatio n
Adverse effect
Nursing alert
Ketorolac
Classification: :Antipyretic NS AID
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity; inhibits prostaglan dins and leukotrienesynthes is
Short-term management of pain (up to 5days)
Contraindicated with significant renal impairment, during labor and delivery , lactation, aspirin allergy, recent GI bleed or
CNS: headache, dizziness, somnolence, insomnia, fatigue,
- Patients who have asthma, aspirininduced allergy, and nasal polyps are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Assess for rhinitis, asthma, and
28
perforation
dizziness, tinnitus ,ophthalmologic effects
Dosage 30g I.V q8 hours
Prescribed given: August 12, 2011
urticaria. - Ketorolac therapy should always be given initially by the IM or IV route. Oral therapy should be used only as a continuation of parenteral therapy. - Advise patient to consult if rash, itching, visual disturbances, tinnitus, weight gain, edema, black stools, persistent headche, or influenza-like syndromes (chills,fever,muscles aches, pain) occur. - Effectiveness of therapy can be demonstrated by decrease in severity of pain. Patients who do not respond to one NSAIDs may respond to another.
29
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
Indication
Contraindicatio n
Adverse effect
Nursing alert
Cefuroxime
Classification: secondgeneration cephalosporin and antibiotic
Cefuroxime binds to bacterial membranes. It inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall.
Cefuroxime is used to our patient to prevent infection due to the Gunshot Wound.
*Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug. * Use cautiously in patients hypersensitive to penicillin because of possibility of cross-sensitivity with other beta-
CV: phlebitis, thrombophlebitis GI: pseudomembran ous colitis, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea Hematologic: transient
-Question for history of hypersensitivity to this drugs , particularly cephalosporins and penicillins. Rationale: to avoid allergy -Give without regards
28
lactam antibiotics.
Dosage
IV: 750 mg every 8 hours post operative
Prescribed given: August 12, 2011
neutropenia, eosinophilia, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopeni a Skin: maculopapular and erythematous rashes, urticaria, pain, induration, sterile abscesses, temperature elevation, tissue sloughing at intramuscular injection site Other: hypersensitivity reactions, serum sickness, anaphylaxis.
to meals. If GI upset occurs give with food or milk. -Avoid crushing tablets due to bitter taste. Rationale: chewed tablets decreased the effectiveness of drugs - Intramuscular injections must be administered deep IM rationale: to minimize discomfort. -Discomfort may occur with IM injection. -Doses should be evenly spaced. -Continue antibiotic therapy for full length of treatment.
29
29
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
Indication
Contraindica tion
Adverse effect
Nursing alert
Ciprofloxacin
Classification: Fluoroquinolon e and an Antiinfective
Ciprofloxacin inhibits DNA enzyme in susceptible microorganisms . It interferes with bacterial DNA replication. Ciprofloxacin is also bactericidal.
Ciprofloxacin is used to prevent infection to our patient
Dosage PO: 500 mg 1 tab BID
Ciprofloxacin should be avoided by pregnant women as well as by lactating mothers since it could harm the baby. This drug is contraindicate d in patients who have shown hypersensitivit y to ciprofloxacin or to any other quinolones.
-severe dizziness, fainting, fast or pounding heartbeats -sudden pain, snapping or popping sound, bruising, swelling, tenderness, stiffness, or loss of movement in any of your joints; -diarrhea that is watery or bloody; -confusion, hallucinations, depression, unusual thoughts or behavior; -seizure (convulsions);
-Patients taking ciprofloxacin usually develop sensitivity of the skin to direct sunlight therefore these patients need to avoid direct exposure to the sun. -The medication should also be used with strict precautions in patients with history of seizures Rationale: it has been reported that this drug causes seizures.
Prescribed given:
-pale or yellowed skin, dark colored
30
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
Indication
Contraindicatio Adverse effect n
Nursing alert
28
Methylcobal
Classification: Nootropics & Neurotonics/ Neurotrophics
Methycobal is a mecobalamin drug, a co-enzyme of Vitamin B that transpires in the blood and the cerebrospinal fluid. It is utilized by the nerve tissue more broadly than other homologues of vitamin B12.
Methycobal Tablets are administere d for treating peripheral neuropathie s.
Dosage
PO: 500 mg 1 tab TID
The drug is contraindicated to patients who has a known allergy to Mecobalamin. The drug is not recommended also with persons whoa re taking multiple medications. In such cases, it may be taken cautiously or unless if the drug is prescribed by your physician.
-Headache -Heat sensation -Feeling warm (general). -Pain around the intramuscular injection site -Pain at the intramuscular injection site -induration at the intramuscular injection site -A hardened mass forms within the muscle at the intramuscular injection site.
- While taking the drug Mecobalamin, it is not advised by the doctor to drink any alcoholic beverages because of the effects it produces on the drug. Patients with pernicious anemia may have to take the drug for the rest of his/her life to -Avoid irrevocable damage to the spinal cord. It is necessary to check your blood every three to six months to monitor progress.
29
Prescribed given: Setember 14, 2011
29
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
Indication
Contraindicati on
Adverse effect
Nursing alert
Etoricoxib
The mechanism of action of this drug is a COX-2 selective Classification: inhibitor. This drug selectively inhibits Analgesic isoform 2 of cyclooxyginase enzymes /NSAID (COX-2). This reduces the generation of prostaglandins (PGs) from Dosage arachidonic acid. PO: 120 mg 1 Among the different cap OD for functions exerted by pain PGs, their role in the inflammation cascade should be highlighted. This drug non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Prescribed COX is involved in given: producing prostaglandins, in August 23, response to certain 2011 diseases and injury.
-This medication is a nonsteroidal antiinflammator y drug (NSAID), prescribed for osteoarthriti s, rheumatoid arthritis and gouty arthritis. -relief of chronic musculoskel etal pain -relief of acute pain
Contraindicated in patients with peptic ulcer, severe heart disease, stroke, and hypersensitivity.
Central Nervous Systemnervousness, depression, drowsiness, insomnia, vertigo and ringing in the ear. Heart- Chest pain, high blood pressure and fluid retention. Metabolic- Taste disturbances, mouth ulcer, loss of appetite and weight loss. MiscellaneousKidney damage, fever, GI disorders, muscle pain and influenza-like syndrome.
-Administer with foods rationale: to prevent GI upset. -Use cautiously in patients with renal/liver dysfunction Rationale: to monitor for hepatic Failure and impair renal function -advice patient to avoid alcohol intake Rationale: GI upset or Gastric ulcer may result. -Instruct the patient to report occurrences of side effects. Rationale: To establish proper prec autionary measures
29
30
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Paranoid Schizophrenia 2Dokumen49 halamanParanoid Schizophrenia 2gopscharan100% (1)
- Name of Drug Content Class and Mechanism of Action (MOA) Indication/s Contraindication/s Side Effects (Pere System) Nursing ConsiderationsDokumen8 halamanName of Drug Content Class and Mechanism of Action (MOA) Indication/s Contraindication/s Side Effects (Pere System) Nursing ConsiderationsJustin John NavarroBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug StudyBheiatriz de VeraBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study2Dokumen8 halamanDrug Study2zbestgurlBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanDrug StudyCharlayne AnneBelum ada peringkat
- Bipolar 2 DisorderDokumen49 halamanBipolar 2 DisorderJalishia Mae Dumduma100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug Studysnowyfingers100% (2)
- Drug StudyDokumen6 halamanDrug Studyuntoned100% (1)
- 11 Drug StudyDokumen11 halaman11 Drug Studygreench08Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Study (Room 104)Dokumen4 halamanDrug Study (Room 104)Maeshe Pryll TanamorBelum ada peringkat
- Medications To Avoid Before and After SurgeryDokumen3 halamanMedications To Avoid Before and After SurgeryIoana PirvulescuBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen16 halamanDrug StudyBadgal BazingaBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageDokumen2 halamanGeneric Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageKim SunooBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen34 halamanDrug StudyMarco MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- HydrocortisoneDokumen2 halamanHydrocortisoneRenz Ivan Funtilon100% (1)
- CeftriaxoneDokumen2 halamanCeftriaxoneFlora Angeli PastoresBelum ada peringkat
- KetorolacDokumen5 halamanKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study NursingDokumen27 halamanDrug Study Nursingbilliam123Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Study For SLEDokumen28 halamanDrug Study For SLERomwella May AlgoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen7 halamanDrug StudyRowland PascuaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: Vomiting, GIDokumen5 halamanDrug Study: Vomiting, GIJoyzelle CagandahanBelum ada peringkat
- MEROPENEMDokumen1 halamanMEROPENEMJust now0% (1)
- Drug StudyDokumen6 halamanDrug StudyRyan BancoloBelum ada peringkat
- DrugDokumen8 halamanDrugAlyzza DagoyBelum ada peringkat
- Medication Competency Questions For NursesDokumen13 halamanMedication Competency Questions For NursesAlex AndrewBelum ada peringkat
- TetracyclineDokumen5 halamanTetracyclineMichael Angelo SeñaBelum ada peringkat
- Name of Drug Dosage and Route Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokumen7 halamanName of Drug Dosage and Route Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTon AgustinBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen5 halamanDrug StudyryanBelum ada peringkat
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationDokumen2 halamanBrand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationChristine Pialan SalimbagatBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen6 halamanDrug Studyjohnclement_dcBelum ada peringkat
- AmikacinDokumen1 halamanAmikacinMuhammad ArsalanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study KeterolacDokumen2 halamanDrug Study KeterolacKillerBall RegioBelum ada peringkat
- HydroxyzineDokumen4 halamanHydroxyzineGeorge Smith AbeledaBelum ada peringkat
- ItraconazoleDokumen1 halamanItraconazoleMuhammad ArsalanBelum ada peringkat
- DRUGS Study OrigDokumen17 halamanDRUGS Study OrigKiersten Karen Policarpio Verina100% (1)
- Meropenem: Antibiotic ClassDokumen2 halamanMeropenem: Antibiotic ClassAynshbBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - CaseDokumen9 halamanDrug Study - CaseMay EvelynBelum ada peringkat
- AmloDokumen1 halamanAmloamy navajaBelum ada peringkat
- Linezolid (Zyvox)Dokumen1 halamanLinezolid (Zyvox)EBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen7 halamanDrug StudyCandace DarleneBelum ada peringkat
- Cefpodoxime Proxetil - Print VersionDokumen5 halamanCefpodoxime Proxetil - Print Versionchristina_1990Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Study (GBS)Dokumen16 halamanDrug Study (GBS)Mary Rose Verzosa LuisBelum ada peringkat
- CefuroximeDokumen11 halamanCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaBelum ada peringkat
- DRug Study PhenytoinDokumen1 halamanDRug Study Phenytoinmichelle marquezBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study of FluoxetineDokumen2 halamanDrug Study of FluoxetineLance De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen9 halamanDrug StudyCris SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Miglitol (Glyset)Dokumen1 halamanMiglitol (Glyset)EBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - CaDokumen3 halamanDrug Study - Casaint_ronald8Belum ada peringkat
- TrimetazidineDokumen2 halamanTrimetazidinemasheennavirgoBelum ada peringkat
- RibavirinDokumen2 halamanRibavirinAnonymous 6u2S47fbxnBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen6 halamanDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueBelum ada peringkat
- ParacetamolDokumen1 halamanParacetamolChelsy MurielBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramDokumen3 halamanDrug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramJear RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Drug 101Dokumen12 halamanDrug 101Alyzza DagoyBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study Form TJDokumen4 halamanDrug Study Form TJJasmin Santiago CarrilloBelum ada peringkat
- DRUG STUDY (Dextromethorphan)Dokumen2 halamanDRUG STUDY (Dextromethorphan)Avianna CalliopeBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanDrug Studypopoyoio100% (2)
- Emergency Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanEmergency Drug StudyGrace Santos MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Allegra FexofenadineDokumen3 halamanAllegra FexofenadineCassieBelum ada peringkat
- GentamicinDokumen2 halamanGentamicinDeprama Sutikti100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokumen1 halamanDrug Studykennethbote0% (1)
- Viii. Pharmacologic Intervention (Drug Study)Dokumen10 halamanViii. Pharmacologic Intervention (Drug Study)Cyril Jane Caanyagan AcutBelum ada peringkat
- Neuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyDokumen7 halamanNeuropathic Pain Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyJomabee TuArBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanDrug StudyJoel MadjosBelum ada peringkat
- AAFP Marijuana ResolutionsDokumen5 halamanAAFP Marijuana ResolutionsMarijuana MomentBelum ada peringkat
- Acne Eczema Scabies 2014Dokumen22 halamanAcne Eczema Scabies 2014Novita Dwi MardiningtyasBelum ada peringkat
- Submitted By:: Pankaj GuptaDokumen34 halamanSubmitted By:: Pankaj GuptaPushpendra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Drug IncompatibilityDokumen16 halamanDrug Incompatibilityant beeBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Information Leaflet Atarax TabletsDokumen5 halamanPatient Information Leaflet Atarax TabletsradicalaliBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen5 halamanNursing Care PlancnvfiguracionBelum ada peringkat
- Ket-Amen. A Ketamine Safe Use and Information LeafletDokumen2 halamanKet-Amen. A Ketamine Safe Use and Information LeafletAnonymous Gz86b5Belum ada peringkat
- Drug AddictionDokumen9 halamanDrug AddictionMD Ishtiaq IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Lola Susianti, Sppd-FinasimDokumen28 halamanDr. Lola Susianti, Sppd-Finasimfahmy_tampanBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment Nurse ChecklistDokumen3 halamanTreatment Nurse ChecklistAnonymous GC8uMx3Belum ada peringkat
- BCPT 12584Dokumen8 halamanBCPT 12584kelly88137Belum ada peringkat
- Quality TestDokumen8 halamanQuality TestsfgvsdfrbhBelum ada peringkat
- Hospitalpharmacy PDFDokumen13 halamanHospitalpharmacy PDFBhavin DesaiBelum ada peringkat
- Preventing Medication Errors in Pediatric and Neonatal PatientsDokumen55 halamanPreventing Medication Errors in Pediatric and Neonatal PatientsJanarth NanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Dosage Calc. GuidelinesDokumen5 halamanDrug Dosage Calc. GuidelinesJo NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Common Abbreviations Used in Medication Orders: Official "Do Not Use" ListDokumen2 halamanCommon Abbreviations Used in Medication Orders: Official "Do Not Use" ListHamid OkBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris Dangers of DrugsDokumen19 halamanMakalah Bahasa Inggris Dangers of DrugsAri100% (3)
- Institute For Safe Medication Practices 2011 ReportDokumen25 halamanInstitute For Safe Medication Practices 2011 ReportLaw Med BlogBelum ada peringkat
- FDA PhotostabilityDokumen8 halamanFDA PhotostabilityLina SakellariouBelum ada peringkat
- Amitriptili N Acarbose 100: Allopurino LDokumen12 halamanAmitriptili N Acarbose 100: Allopurino Lgudang farmasiBelum ada peringkat
- Capsule (Pharmacy) - WikipediaDokumen19 halamanCapsule (Pharmacy) - WikipediaMohammad Monjur HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Soapp R Sample WatermarkDokumen2 halamanSoapp R Sample Watermarkapi-351447133Belum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study Requirements For The Submission of Generic Drug Us EuDokumen14 halamanComparative Study Requirements For The Submission of Generic Drug Us Euvg_vvgBelum ada peringkat
- American Soc. of Addiction Medicine Naloxone StatementDokumen5 halamanAmerican Soc. of Addiction Medicine Naloxone Statementwebmaster@drugpolicy.orgBelum ada peringkat
- Human Drug IndexDokumen18 halamanHuman Drug IndexOliver GiroudBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Selection FrameworkDokumen47 halamanCustomer Selection FrameworkKshama ShahBelum ada peringkat