Brain Abscess
Diunggah oleh
Eugene Briagas RoqueDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Brain Abscess
Diunggah oleh
Eugene Briagas RoqueHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
BRAIN ABSCESS
DEFINITION A brain abscess is a collection of infectious material within the tissue of the brain.Bacteria is the most common causative organisms.The most common predisposing factors for abscess among immunocompetant people are ottitis media and sinusitis.
ETIOLOGY
o o o o
Ottitis media and sinusitis. Intracranial surgery ,penetrating injury or tongue piercing. Wound or intra abdominal infection. Ottitis media, sinusitis,mastoiditis,dental infections and systemic
infections. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
o o
Head ache usually worse in the morning Fever,vomiting and focal neurological deficits.(weakness and Increased ICP and decreased level of consciousness
decreasing vision reflects the area which is involved)
o
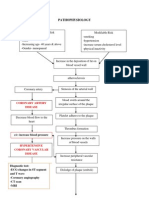
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
The mechanisms to the entry of the micro organisms are as follows:
o
Direct extension-Infections stemming from the sinus,middle ear or
mastoid may gain access into the venous drainage of the brain via valveless emissary veins and drain into this region. Because of the antibiotic therapy for this infections incidence rate due to this type of spread has been decreased to a greater extent
o o
Haematogenous spread-This includes the spread via blood Following penetrating head injury or neurosurgery-Most cases
can also occur as a result of penetrating head injury or trauma. ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSTIC FINDINGS
o o o
History collection and physical examination MRI and CT scan demonstrates a ring around the hypodense area. Aspiration of the abscess guided by CT scan or mRI helps to Blood cultures if the origin of the abscess is from a distant sourse Chest X-ray to rule out predisposing lung infections CT Scan to evaluate the bony structure of the ear and the sinus
identify the organism
o o o
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
o
The goal of the treatment is to drain the abscess and to provide Large IV doses of antibiotics are given to penetrate the blood brain The choice of the antibiotic depends on the causative organism Corticosteroids are prescribed to reduce the inflammatory cerebral Antiseizure medications(Phenytoin and phenobarbitone )is
antibiotic therapy for the infection detected.
o
barrier and to reach the site of infection.
o
being identified by culture.
o
edema.
o
prescribed to prevent or to reduce seizure. NURSING MANAGEMENT
Nursing care focuses on the assessment of neurological
status,administering the medication,assessing the response to the treatment and providing supportive care.
o
Blood laboratory test results especiallyblood glucose and serum Administration of insulin or electrolyte replacement is required to The level of consciousness and the physical status has to be Observe for neurological deficits like hemiparesis,seizures,visual
potassium levels has to be monitored and corticosteroids are prescribed.
o
return this values to the normal state.
o
monitored constantly
o
deficits etc..
Cerebral Edema - Is an increase in the water content of the brain tissue. When cerebral edema occurs as a result of trauma, hemorrhage, tumor, abscess or ischemia, an increase in ICP occurs. Herniation - When the pressure exerted by a mass in the brain is not equally divided, result in shifting or herniation of the brain from one compartment of high pressure to one of lower pressure. Clinical Manifestations
- Change in level of consciousness is the most sensitive and important indicator of neuro status - Early signs may be nonspecific: restlessness, irritability, generalized lethargy - Determine the level of stimulus needed to arouse the patient (verbal, touch, shaking?) - Content of consciousness: orientation - Speech: clear, coherent, slurred, distorted, aphasic, incomprehensible sounds, no effort to speak - Report changes immediately. - Changes in vital signs- Increasing systolic blood pressure - Widening pulse pressure - Bradycardia - Pulse slowing and is bounding
- Irregular respiratory pattern - May also have a change in temperature - Ocular signs - Pupil changes are from pressure on third cranial oculomotor nerve result in dilation of pupil - Pupils become sluggish, unequal. This is because of brain shift. May also be pressure on other cranial nerves - A fixed, unilaterally dilated pupil indicates herniation of the brain - Motor ability is controlled by nerve tracks originating in the frontal lobes of the brain. - Distortion of brain tissue along these pathways can cause motor dysfunction. - Patient may exhibit localization to painful stimulus or withdraw from it. - Motor strength and tone are assessed in all 4 extremities. - Decorticate posturing now called abnormal flexion, - Decerebrate posturing now called abnormal extension. - Decrease in motor function - May have hemiparesis or hemiplegia - May see posturing either decorticate or decerebrate - Decerebrate more serious from damage in midbrain and brainstem - Decorticate from interruption of voluntary motor tracts - Headache - From compression on the walls of cranial nerves, arteries and veins - Straining and movement makes worse - Vomiting - NOT preceded by nausea- unexpected - May be projectile Diagnostic Tests - CT - MRI - Cerebral angiography - EEG - No lumbar puncture if there is ICP because sudden release of pressure can cause brain to herniate - ABGs keep O2 at 100% and PCO2 as related to ICP (25-35) Drug Therapy - Mannitol Rapid short acting diuretic that decreases ICP. Decreases total brain water content - Watch fluids and electrolytes closely (I and O and labs) - Dont give in cases of renal failure or if serum osmolality increased Drug Therapy - Barbiturates causes decrease in metabolism and ICP. Causes reduction in cerebral edema and blood flow to brain. - Skeletal muscle paralyzers may be used (Pavulon) - Antiseizure drugs Dilantin - Loop diuretics reduce blood volume and tissue volume Nutrition - Fluid balance is controversial - Give saline either .45% or normal saline not glucose to help prevent additional cerebral edema - Watch sodium if on Mannitol may need to give additional salt.
- Also may need additional free water if dehydrated watch I and O closely. Nursing Interventions - Airway and respiratory suction only as needed and for 10 seconds at a time, only 2 passes. Give 100% O2 prior to suctioning. - Avoid abdominal distention may need NG tube to decompress stomach - Sedate with care if not on a ventilator, use sedation that will not interfere with respiration or mask any neuro changes * Posture and head position Avoid jugular vein compression - Head should be in neutral position - Cervical collars should not be too tight Elevation of the head and trunk may improve jugular venous return. - Keep head in alignment to prevent cutting off venous flow from the head - Dont elevate knees this will increase intrathoracic pressure - Turn gently from side to side if turning raises ICP, client will need to stay on back - If client is posturing frequently during care, will need to sedate first and then do only one thing at a time. Minimize stimulation - These clients can become agitated and aggressive avoid over stimulating them - Restraining them will make them MORE AGITATED and RAISE THEIR ICP! - NO TV IN ROOM - Keep room darkened if needed - Hyperventilation (PaCO2 < 35 mmHg) works by decreasing blood flow and should be reserved for emergency treatment and only for brief periods - May need eye drops to moisten eyes - Client may benefit from rehab to help him adapt and progress - Keep body temperature within normal limits - Do not use ice on client - Prevent infection - Protect from injury - Avoid factors that increase ICP - Psychological support
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Intracranial (Inside The Skull) Hemorrhage (Bleeding)Dokumen41 halamanIntracranial (Inside The Skull) Hemorrhage (Bleeding)MASIIBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study 1 FinalDokumen28 halamanCase Study 1 Finalapi-3905968320% (1)
- A Case Study Presentation On Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Presented byDokumen78 halamanA Case Study Presentation On Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Presented byNinaBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDokumen4 halamanCerebrovascular DiseasekathyfacaBelum ada peringkat
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDokumen12 halamanHemorrhagic StrokeManggara Surya DharmaBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 112 MidtermDokumen25 halamanNCM 112 MidtermJan Charlie Sophia100% (1)
- Exam FinalsDokumen7 halamanExam FinalsMaria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia IIBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Dokumen3 halamanPediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Jonah MaasinBelum ada peringkat
- Cushing's SyndromeDokumen5 halamanCushing's SyndromesummerduskBelum ada peringkat
- Medical-Surgical Nursing 3Dokumen2 halamanMedical-Surgical Nursing 3Charissa Magistrado De LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiDokumen12 halamanCase Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiHarlene Joyce ReyBelum ada peringkat
- PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanPathophysiologyHazel PalomaresBelum ada peringkat
- Brain AbscessDokumen4 halamanBrain AbscessTamil VillardoBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes, Fractures, and Heart Disease Diagnostic TestDokumen32 halamanDiabetes, Fractures, and Heart Disease Diagnostic TestNebawBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Hospital Equipment ChecklistDokumen2 halamanEssential Hospital Equipment ChecklistMhOt AmAdBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter60 Assessment of Neurologic FunctionDokumen25 halamanChapter60 Assessment of Neurologic FunctionAhmed 123Belum ada peringkat
- Myocardial Infarction (Diseases For Oral Revalida)Dokumen12 halamanMyocardial Infarction (Diseases For Oral Revalida)Suzette PipoBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrocephalus Nursing CareDokumen27 halamanHydrocephalus Nursing CareyounggirldavidBelum ada peringkat
- Low Back Pain Numbness: Strain SciaticaDokumen5 halamanLow Back Pain Numbness: Strain SciaticaCarol KayasBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction - MIDokumen10 halamanIntroduction - MIkhimiiiBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Concepts of Psyche PPt-gapuz OutlineDokumen104 halamanBasic Concepts of Psyche PPt-gapuz OutlineIbrahim RegachoBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Fractures, Traction, and Hip Dislocation SignsDokumen3 halamanTypes of Fractures, Traction, and Hip Dislocation SignsDoyTanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study of FractureDokumen3 halamanDrug Study of FractureMarijune Caban ViloriaBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Worksheet for Stroke PatientDokumen6 halamanClinical Worksheet for Stroke PatientJackie GriffisBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 100 Case AnaDokumen3 halamanNCM 100 Case AnaCharissa Magistrado De LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Compre Ho PsychDokumen114 halamanCompre Ho PsychRyan Mae Tutor GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- TP4Dokumen14 halamanTP4Asdfghjl0% (1)
- Emergency Cardiac Medications for ArrhythmiasDokumen14 halamanEmergency Cardiac Medications for ArrhythmiasRomzy BasañesBelum ada peringkat
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Dokumen5 halamanSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDokumen79 halamanCerebrovascular AccidentKathy B. AbuanBelum ada peringkat
- Nurse Licensure Exam CBQs on Renal and Cardiovascular SystemsDokumen2 halamanNurse Licensure Exam CBQs on Renal and Cardiovascular SystemsJhannBelum ada peringkat
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanBelum ada peringkat
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDokumen39 halamanAcute TonsillopharyngitisCin AtianzarBelum ada peringkat
- InTech-Diabetic Foot and GangreneDokumen25 halamanInTech-Diabetic Foot and GangrenePutu Reza Sandhya PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- MS 3 Case Analysis DownloadableDokumen1 halamanMS 3 Case Analysis DownloadableCharissa Magistrado De LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Grand Case Presentation Repaired)Dokumen45 halamanGrand Case Presentation Repaired)hulaanmuakoBelum ada peringkat
- PPPDokumen3 halamanPPPJack BangcoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing DiagnosisDokumen10 halamanNursing DiagnosisZaty ChaiyOkk100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASEDokumen2 halamanPATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASEPamela DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- Tarlac State University College of Nursing case study on choledocholithiasisDokumen53 halamanTarlac State University College of Nursing case study on choledocholithiasisCzarina ManinangBelum ada peringkat
- Intracranial HemorrhageDokumen41 halamanIntracranial Hemorrhagedoctormussieaberra100% (1)
- Endocrine System Nursing ReviewDokumen7 halamanEndocrine System Nursing ReviewMeiJoyFlamianoIIBelum ada peringkat
- Spinal Cord InjuryDokumen50 halamanSpinal Cord InjuryVINCHRISTINEBelum ada peringkat
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus (Report) - 2Dokumen27 halamanHerniated Nucleus Pulposus (Report) - 2Angelu Gabrielle CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Activity IntoleranceDokumen6 halamanActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanBelum ada peringkat
- Recap Obstetrics Day 1 Post TestDokumen1 halamanRecap Obstetrics Day 1 Post TestJANEL BUENAVENTURABelum ada peringkat
- CBQ Legal Ethical MNGTDokumen23 halamanCBQ Legal Ethical MNGTyzak jouleBelum ada peringkat
- Path o PhysiologyDokumen9 halamanPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersBelum ada peringkat
- Herniated Nucleus PulposusDokumen5 halamanHerniated Nucleus PulposusPeterzen ManaigBelum ada peringkat
- Nebulization Nursing Procedure at Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDokumen9 halamanNebulization Nursing Procedure at Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityMitzi BelamideBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Diseasejonel lorenzoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP CvaDokumen4 halamanNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeBelum ada peringkat
- German MeaslesDokumen8 halamanGerman MeaslesYdynn Parejas GavinaBelum ada peringkat
- nursing assessment 1Dokumen6 halamannursing assessment 1Kedir AliyiBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Client With Neurologic Trauma Anatomy of The CraniumDokumen17 halamanManagement of Client With Neurologic Trauma Anatomy of The CraniumGoldie Reroma GelagaBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Patients with Neurologic DysfunctionDokumen9 halamanManagement of Patients with Neurologic DysfunctionDinarkram Rabreca EculBelum ada peringkat
- Brain DeathDokumen43 halamanBrain Deathanimesh pandaBelum ada peringkat
- Head TraumaDokumen4 halamanHead TraumaDinarkram Rabreca EculBelum ada peringkat
- Causes and Management of Syncope in DentistryDokumen27 halamanCauses and Management of Syncope in DentistrySelvarathi KandhaswamyBelum ada peringkat
- Stroke: A.K.A. Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) & Brain AttackDokumen81 halamanStroke: A.K.A. Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) & Brain AttackNovianty GliceriaBelum ada peringkat
- Modeling Vessel Impacts for Lock Wall DesignDokumen15 halamanModeling Vessel Impacts for Lock Wall DesignSalam FaithBelum ada peringkat
- Terminal BlockDokumen12 halamanTerminal BlockAlmaforBelum ada peringkat
- Proceedings of National Conference on Landslides held in LudhianaDokumen8 halamanProceedings of National Conference on Landslides held in LudhianaAniket PawarBelum ada peringkat
- Inakyd 3623-X-70Dokumen2 halamanInakyd 3623-X-70roybombomBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Edition February 2013: Ec2 Guide For Reinforced Concrete Design For Test and Final ExaminationDokumen41 halaman3 Edition February 2013: Ec2 Guide For Reinforced Concrete Design For Test and Final ExaminationDark StingyBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 The Truth About Air TravelDokumen14 halaman3.1 The Truth About Air TravelСвітлана Свирид0% (1)
- Carta Psicrometrica PDFDokumen2 halamanCarta Psicrometrica PDFJuliethBelum ada peringkat
- PCS PADDLE SHIFTER INSTALL GUIDEDokumen21 halamanPCS PADDLE SHIFTER INSTALL GUIDEAndreas T P ManurungBelum ada peringkat
- Unit explores Christian morality and conscienceDokumen1 halamanUnit explores Christian morality and conscienceRose Angela Mislang Uligan100% (1)
- The LM393Dokumen2 halamanThe LM393mayron vasquezBelum ada peringkat
- SXMDokumen7 halamanSXMLi NearBelum ada peringkat
- Dimensions and Relations of The Dentogingival Junction in Humans. Gargiulo 1961Dokumen7 halamanDimensions and Relations of The Dentogingival Junction in Humans. Gargiulo 1961Linda Garcia PBelum ada peringkat
- Infinera Product BrochureDokumen4 halamanInfinera Product Brochurebarry_fieldBelum ada peringkat
- NTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesDokumen2 halamanNTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesFreddy SarabiaBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics 5 Q1 W10Dokumen31 halamanMathematics 5 Q1 W10Aices Jasmin Melgar BongaoBelum ada peringkat
- Prom 2Dokumen3 halamanProm 2arvindBelum ada peringkat
- Ch1 PDFDokumen54 halamanCh1 PDFChristian Jegues100% (2)
- Quant One Analyser – endless possibilitiesDokumen6 halamanQuant One Analyser – endless possibilitiesSamuel SuBelum ada peringkat
- Tramadol Drug StudyDokumen1 halamanTramadol Drug Studymilkv82% (11)
- Nest Installation GuideDokumen8 halamanNest Installation GuideOzzyBelum ada peringkat
- 89HPES24T3G2 Hardware Design Guide: NotesDokumen10 halaman89HPES24T3G2 Hardware Design Guide: NotesDavidBelum ada peringkat
- Booster Pump Service ManualDokumen11 halamanBooster Pump Service ManualSGI AUTOMOTIVE PVT LTDBelum ada peringkat
- Deam Edan M8 Monitor - User ManualDokumen248 halamanDeam Edan M8 Monitor - User Manualvelasquez diazBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Alloys and Compounds: Wei Li, Zhijun Xu, Ruiqing Chu, Peng Fu, Guozhong ZangDokumen4 halamanJournal of Alloys and Compounds: Wei Li, Zhijun Xu, Ruiqing Chu, Peng Fu, Guozhong ZangSamah SamahBelum ada peringkat
- CEFIC Guidelines Transport Equipment Packed Cargo (2010)Dokumen7 halamanCEFIC Guidelines Transport Equipment Packed Cargo (2010)sl1828Belum ada peringkat
- Polycab HT XlpeDokumen33 halamanPolycab HT Xlpezafrikhan875Belum ada peringkat
- English Test 6Dokumen87 halamanEnglish Test 6Ha PhanBelum ada peringkat
- Soal ReadingDokumen3 halamanSoal ReadingSendi PuspaBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer preference towards branded milk: A comparative analysis of Verka milk and Amul milkDokumen12 halamanConsumer preference towards branded milk: A comparative analysis of Verka milk and Amul milkBhawna RehanBelum ada peringkat
- 1830PSS R36 QuickReferenceGuide 8DG60888JAAADokumen66 halaman1830PSS R36 QuickReferenceGuide 8DG60888JAAAFelippe CanatoBelum ada peringkat