Chapter 1
Diunggah oleh
ZKordubaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 1
Diunggah oleh
ZKordubaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter1
Friday,January27,2012
ZR
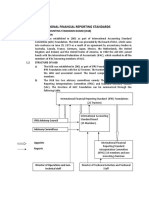
Introduction - Regulatory framework deals with financial reporting It is the rules and regulations that apply to the preparation of financial statements - Financial reporting General purpose financial statement and other financial reports issued for public consumption - Users of financial statements Shareholders Equity - your own money you Creditors put into the business Employees Liability - the money you have Tax authorities borrowed Sources of Regulation - Legislation EU Directives; SEC - Accounting standards Generally Accepted Accounting Practice (GAAP) IASB (IFRS), FASB (FAB) - Stock exchange regulations NYSE; LSE Generally Accepted Accounting Practice / Principles (GAAP) - GAAP is the complete set of accounting regulations (from all sources) and accounting conventions that apply in a certain jurisdiction (e.g. UK GAAP, US GAAP etc.) - The IASB is developing a set of standards that may form the basis of 'international GAAP' The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) - IASB Issues IFRS International Accounting standards (IAS's) (IASC) Consists of 14 members (12 full-time, 2 part-time) - IASC Foundation Standards Advisory Council (SAC) International Accounting Standards Board IFR Interpretations Committee
K
Accounting Page 1
The Standard-setting process - Due process Identification and review of issues pertaining to topic IASB conceptual framework Study of national accounting requirements Consultation of SAC Publication of discussion document for public Consideration for comments received Publication of exposure draft Consideration for comments received Publication for the standard The structure of an international standard - Introduction - Objectives of the standard - Scope of the standard - Definitions of terms used in standard - Body of the standard - Effective date and transitional provisions - Application guidance - Approval and dissenting opinions by IASB members
ZR
The purpose of accounting standards - Standards reduce variation in accounting practice and introduce a degree of uniformity into financial reporting - Standards make it more likely that financial statements will provide a faithful representation for an entity's financial performance and financial position - Meaningful comparisons may be drawn over time and between entities Worldwide use of international standards - over 100 counties use IFRS in one form of the other - European Union - Canada (2011) Mexico (2012) South Korea - China; Japan - United States? Memorandum of understanding between FASB and IASB Convergence of standards Reconciliation of IFRS to US GAAP eliminated SEC Roadmap to adoption (see AICPA Backgrounder)
K
Accounting Page 2
Fist time adoption of international standards - 'reporting date' is the date which falls at the end of the period covered by the first IFRS statements - 'date of transition' is the date at the start of the period for which comparatives are provided in the first IFRS statements - Need to prepare an opening IFRS balance sheet as at the date of transitions - Must use the same accounting policies in the opening IFRS balance sheet and in all periods presented in the first IFRS statements; these policies must comply with all international standards in force at the reporting date - Certain reconciliation are required Reconciliation - the explanation of differences between two items
ZR
Accounting Page 3
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ifrs Vs PfrsDokumen16 halamanIfrs Vs PfrsDenisse Dela Cruz100% (1)
- IFRS Simplified: A fast and easy-to-understand overview of the new International Financial Reporting StandardsDari EverandIFRS Simplified: A fast and easy-to-understand overview of the new International Financial Reporting StandardsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (11)
- FA - Financial Accounting: Chapter 2 - Regulatory FrameworkDokumen23 halamanFA - Financial Accounting: Chapter 2 - Regulatory FrameworkSumiya YousefBelum ada peringkat
- Iso 28598-1-2017Dokumen36 halamanIso 28598-1-2017Best Look100% (1)
- International Convergence of Financial Reporting Ch3Dokumen18 halamanInternational Convergence of Financial Reporting Ch3Margareth SilvianaBelum ada peringkat
- International Harmonization of Financial ReportingDokumen8 halamanInternational Harmonization of Financial ReportingRajipah Osman100% (1)
- BSBWHS412 AT1 QuestioningDokumen7 halamanBSBWHS412 AT1 Questioningkavan patelBelum ada peringkat
- Sait - Admission ApplicationDokumen2 halamanSait - Admission ApplicationshakBelum ada peringkat
- The Wave Condos - ByLawsDokumen16 halamanThe Wave Condos - ByLawsTeena Post/Laughton100% (3)
- International Financial Reporting StandardsDokumen11 halamanInternational Financial Reporting Standardscreepy444Belum ada peringkat
- Acyfar 1 NotesDokumen7 halamanAcyfar 1 Noteskate santosBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Ifrs Ias 1-AccaDokumen265 halaman1 Ifrs Ias 1-AccaSabrina Aeni100% (1)
- Acc 101 Topic 1 2024 (Autosaved)Dokumen83 halamanAcc 101 Topic 1 2024 (Autosaved)severinmsangiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen15 halamanChapter 1Dora RaytchevaBelum ada peringkat
- BBM 304 Study NotesDokumen97 halamanBBM 304 Study Notesmuriithialex2030Belum ada peringkat
- Matching of Indian Accounting Standard With International AccountingDokumen21 halamanMatching of Indian Accounting Standard With International AccountingSwati Rawat25% (4)
- Chapter-1 of Advanced AccountingDokumen4 halamanChapter-1 of Advanced AccountingAsif AliBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting Standards (IAS & IFRS) For CMA F1Dokumen369 halamanAccounting Standards (IAS & IFRS) For CMA F1khanali45955Belum ada peringkat
- Module 1 - Intro and Conceptual Framework S2 2023Dokumen42 halamanModule 1 - Intro and Conceptual Framework S2 2023Mark S.PBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 01 (8553)Dokumen30 halamanUnit 01 (8553)naseer ahmedBelum ada peringkat
- Financial and Accounting Regulatory LandscapeDokumen7 halamanFinancial and Accounting Regulatory LandscapeDiana Mindru StrenerBelum ada peringkat
- DipIFR TextbookDokumen375 halamanDipIFR TextbookEmin SaftarovBelum ada peringkat
- International Business Management: AssignmentDokumen16 halamanInternational Business Management: AssignmentkeshavBelum ada peringkat
- Objective: Session 01 - International Financial Reporting StandardsDokumen18 halamanObjective: Session 01 - International Financial Reporting StandardsVladlenaAlekseenkoBelum ada peringkat
- Rule Based-Principal BasedDokumen10 halamanRule Based-Principal BasedYuri AnnisaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8: Global Accounting and Auditing StandardsDokumen32 halamanChapter 8: Global Accounting and Auditing Standardsapi-241660930Belum ada peringkat
- IASB3Dokumen3 halamanIASB3Altessa Lyn ContigaBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting Standard-1 and Its Legal Implications in The Corporate WorldDokumen32 halamanAccounting Standard-1 and Its Legal Implications in The Corporate Worldlove_djBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 Introduction - ACCT6001 - S2 2022Dokumen42 halamanTopic 1 Introduction - ACCT6001 - S2 2022AbigailBelum ada peringkat
- IFRS BasicsDokumen86 halamanIFRS BasicsManisha DeyBelum ada peringkat
- Deloitte IFRS 1 First Time Implementation GuideDokumen84 halamanDeloitte IFRS 1 First Time Implementation GuideRaymond M Reed100% (1)
- International Financial Reporting Standards and Philippine Financial Reporting StandardsDokumen12 halamanInternational Financial Reporting Standards and Philippine Financial Reporting StandardsLilian LagrimasBelum ada peringkat
- PP (A) - Lect 1-Reporting FrameworkDokumen33 halamanPP (A) - Lect 1-Reporting Frameworkkevin digumberBelum ada peringkat
- US Gaap Vs IFRSDokumen76 halamanUS Gaap Vs IFRSmittaldivya167889100% (1)
- Harmonizing Financial Reporting A Study of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)Dokumen57 halamanHarmonizing Financial Reporting A Study of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)pomater270Belum ada peringkat
- International Accounting Standard IAS1 PDFDokumen22 halamanInternational Accounting Standard IAS1 PDFsafa haddadBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - 2 Accounting StandardDokumen28 halamanUnit - 2 Accounting StandardShivam ChandraBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 1-The Regulatory FrameworkDokumen2 halamanCHAPTER 1-The Regulatory FrameworkMuchakunda GooraBelum ada peringkat
- Present at in On IFRSDokumen7 halamanPresent at in On IFRSRamendra SinghBelum ada peringkat
- IFRSDokumen11 halamanIFRSSagar PanchalBelum ada peringkat
- Gaap Vs IfrsDokumen6 halamanGaap Vs IfrsCy WallBelum ada peringkat
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsDokumen2 halamanConceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsJoy KimBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-01: An Introduction To International Financial Reporting StandardsDokumen9 halamanChapter-01: An Introduction To International Financial Reporting StandardsMominul MominBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-01: An Introduction To International Financial Reporting StandardsDokumen9 halamanChapter-01: An Introduction To International Financial Reporting StandardsMominul MominBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting Standards S.ClementDokumen109 halamanAccounting Standards S.Clementabhi_chess22Belum ada peringkat
- Accounting StandardsDokumen109 halamanAccounting StandardsJugal Shah100% (1)
- 2011 Accounting Standards in NigeriaDokumen70 halaman2011 Accounting Standards in Nigeriaoluomo1100% (1)
- Group 1Dokumen8 halamanGroup 1Jason Leur BernabeBelum ada peringkat
- The Regulatory Framework of AccountingDokumen52 halamanThe Regulatory Framework of Accountingssentu100% (1)
- IFRS Disclosure ChecklistDokumen133 halamanIFRS Disclosure Checklistmamme933311Belum ada peringkat
- Regulatory Framework: The Need For RegulationDokumen10 halamanRegulatory Framework: The Need For RegulationNazmul HaqueBelum ada peringkat
- DBFI302 Unit-01Dokumen28 halamanDBFI302 Unit-01Vibhor KhandelwalBelum ada peringkat
- International Accounting Standard Board (Iasb)Dokumen22 halamanInternational Accounting Standard Board (Iasb)Jeffry OR100% (1)
- Financial Reporting Lam LauDokumen21 halamanFinancial Reporting Lam LauElmiImiartiPurbaBelum ada peringkat
- Preface To IFRS StandardsDokumen14 halamanPreface To IFRS StandardsQBO CourseBelum ada peringkat
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)Dokumen74 halamanInternational Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)Ashutosh GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- International Accounting and Auditing Standards: by Dr. Ayesha RehanDokumen22 halamanInternational Accounting and Auditing Standards: by Dr. Ayesha Rehanabubakr zulfiqarBelum ada peringkat
- W06 IASB Governance New2021Dokumen58 halamanW06 IASB Governance New2021Marsha Sabrina LillahBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 1 FINANCIAL REPORTING AND ACCOUNTING STANDARDSsDokumen6 halamanMODULE 1 FINANCIAL REPORTING AND ACCOUNTING STANDARDSsVivo V27Belum ada peringkat
- معايير المحاسبة الدوليةDokumen38 halamanمعايير المحاسبة الدوليةcommander511Belum ada peringkat
- Managing the Transition to IFRS-Based Financial Reporting: A Practical Guide to Planning and Implementing a Transition to IFRS or National GAAPDari EverandManaging the Transition to IFRS-Based Financial Reporting: A Practical Guide to Planning and Implementing a Transition to IFRS or National GAAPBelum ada peringkat
- Cheniere FERC Application LNG Liquefaction Terminal in Sabine Pass LADokumen1.244 halamanCheniere FERC Application LNG Liquefaction Terminal in Sabine Pass LAdrewmx100% (1)
- Control Valves PDFDokumen6 halamanControl Valves PDFIlham Bayu TiasmoroBelum ada peringkat
- AGREEMENT CommerzbankDokumen8 halamanAGREEMENT CommerzbankDattatreya Jay NBelum ada peringkat
- California Apostile Info and HelpDokumen3 halamanCalifornia Apostile Info and HelpDiana0% (1)
- New Sti Ojt Moa TemplateDokumen4 halamanNew Sti Ojt Moa TemplateAnonymous Btn4CGyJtBelum ada peringkat
- Rules and Regulations - Neram Short Film FestDokumen3 halamanRules and Regulations - Neram Short Film FestRohit Mg KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- At - Prelim Rev (875 MCQS) Red Sirug ofDokumen100 halamanAt - Prelim Rev (875 MCQS) Red Sirug ofNicole Kyle AsisBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Companies ActDokumen25 halamanIndian Companies ActswesiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2: Anti-Competitive Agreements and Competition Law: 2.01 Legal FrameworkDokumen70 halamanChapter 2: Anti-Competitive Agreements and Competition Law: 2.01 Legal FrameworkyashBelum ada peringkat
- B Regulatorycapturereview 2006 2Dokumen24 halamanB Regulatorycapturereview 2006 2Julius TariganBelum ada peringkat
- CA Final Law Charts by CA Ravi Agarwal-3 PDFDokumen47 halamanCA Final Law Charts by CA Ravi Agarwal-3 PDFshiva arunBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Health and Safety PolicyDokumen19 halamanBasic Health and Safety PolicyMuhammad Zubair BhattiBelum ada peringkat
- Chartered Investment Counselor ProgramDokumen7 halamanChartered Investment Counselor ProgramAnuj Harshwardhan SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- 06 Province of Cagayan Vs Joseph Lasam LaraDokumen3 halaman06 Province of Cagayan Vs Joseph Lasam LaraJamaica Cabildo ManaligodBelum ada peringkat
- Regulatory Framework of Corporate GovernanceDokumen21 halamanRegulatory Framework of Corporate GovernanceKEVAL SHAHBelum ada peringkat
- 0 01 - Statutes GBDokumen37 halaman0 01 - Statutes GBTangsel ArcheryBelum ada peringkat
- Employment Agreement New PDFDokumen3 halamanEmployment Agreement New PDFAjay AroraBelum ada peringkat
- EGESIF - 14-0011 - Guidance On Audit StrategyDokumen23 halamanEGESIF - 14-0011 - Guidance On Audit StrategymedsBelum ada peringkat
- HPC 420Dokumen46 halamanHPC 420ejangel1Belum ada peringkat
- Employee Orientation Checklist Areas To Be Covered Description CompletedDokumen2 halamanEmployee Orientation Checklist Areas To Be Covered Description Completedeast100% (1)
- Doing Business in Tanzania Company RegistrationDokumen5 halamanDoing Business in Tanzania Company RegistrationMagezi KataBelum ada peringkat
- Floirendo Vs Metro BankDokumen2 halamanFloirendo Vs Metro BankBryce KingBelum ada peringkat
- Corporations Act 2001Dokumen15 halamanCorporations Act 2001Chbz NatBelum ada peringkat
- Creba Vs Romulo TaxDokumen3 halamanCreba Vs Romulo TaxNichole LanuzaBelum ada peringkat
- Improving Energy Market Regulation: Domestic and International IssuesDokumen20 halamanImproving Energy Market Regulation: Domestic and International IssuesFransiska Ardie YantiBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1-1Dokumen44 halamanLecture 1-1gunaj khuranaBelum ada peringkat