Chapter 4 Notes
Diunggah oleh
Shirly GeorgeDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 4 Notes
Diunggah oleh
Shirly GeorgeHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
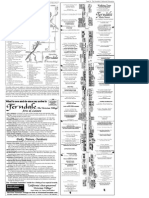
CHAPTER 4 : INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND ENVIRONMENT
Symbiosis
Example: owl and snake compete for same food (rat). Three types : (a) Commensalism Relationship between two organisms which one partner (commensal) get benefits while the other(host) does not get any harm or benefit. Example : a remora fish attached under a shark, getting free transport and food from shark without harming the shark. (b) Mutualism Interaction between two organisms which benefits each other. Example : green alga and fungus form a lichen. The alga produces food and fungus provides shelter. : Rhizobium bacteria in the root of leguminous plant convert gaseous nitrogen to nitrogenous compounds for usage of the plant while the plant in return provide food and shelter for the bacteria. (c) Parasitism The parasite (living outside of inside the host) get benefits while the host get harmed/maybe killed by parasite. Examples : Ticks (parasite) live on skin of mammals and suck blood from the mammals (host). : Tapeworms(parasite) living in intestines of human (host).
ECOSYSTEM Various communities living in the same habitat as well as the non-living components COMMUNITY (physical factors such as light, temperature). POPULATIONS The differentSPECIES of organisms populations A group of organisms of the same species. A group of similar organisms that can interbreed among themselves to produce fertile offspring.
A balanced ecosystem 1. Various organisms live together and are interdependent of one another. 2. A balanced ecosystem does not change over a period of time. Size of each populations remain the same over time through a steady supply of basic needs like oxygen, food, shelter and breeding partners. Interaction between living organisms
Prey-predator
Predators which are normally bigger size kills and feeds smaller animals (prey). Predators- good vision, sharp claws, good sense of smell, carnivores Preys- sharp eyes to detect predators, have body colours that blend well with surrounding, omnivores/herbivores. Examples: lion and zebra, snake and frog, Venus flytrap and fly.
Biological control -Prey-predator relationship applied . -Use living organism to control population of pest in certain area by feeding/killing the pest. - Example: Owls and snakes use to controls rats(pest) in oil palm plantation. Points to consider Ecological imbalance Results Interaction of living organisms Competition Explanation Living organisms compete for their needs- shelter, food, breeding partners. Pollution Pest resistance Biological control Few Takes a longer time bit usually long lasting None None or rare Chemical control A lot Very fast but usually is temporary and may need repeated treatments A lot Common
- In Malaysia, increase in number of crows (used to control Hawk Moth caterpillar) had posed problem to people living in Klang. With food scraps available at Klang, the crow population increased and become a nuisance Food web Food chain demonstrates feeding relationship between living organisms in an ecosystem. Produce r Green plant Paddy plants Primary consumer caterpillars rats Secondary consumer birds snakes Tertiary consumer snakes eagles
Example of pyramid numbers
- Organisms with highest number placed at the bottom of the pyramid. - The number of producers always bigger than the number of consumers so that there is enough food. - If there is a big increase in the number of snakes, balance of nature is affected as frogs will quickly disappear from the ecosystem. Energy flow in a food web Producers obtain energy directly/ indirectly from Sun through photosynthesis Chemical energy stored in green plants passed on to primary consumers Energy then flow to secondary consumers and tertiary consumers - amount of energy that transferred from one consumer to another decreases along the food chain. - energy at every level is lost as heat due to evaporation, respiration, excretion and other life processes. Photosynthesis - Process which green plants make food (glucose) in the presence of light.
- Animals/consumers will eat more than one type of food. These form a food web as in diagram below: Paddy plant rat snake bird grasshopper Number of food chain : 3
frog
- Food web made up of several food chains. Producers Consumers Decomposers Green plants that can make their own food by converting suns light energy into chemical energy(food) during photosynthesis. Primary consumer - animals that eat plants (herbivores) Secondary consumer animals that eat primary consumers (carnivores) Tertiary consumer bigger carnivores feed on secondary consumers. Microorganisms feeding on dead plants and animals. Example : bacteria and fungi
Pyramid of numbers
Carbon dioxide is needed for photosynthesis Word equation: sunlight Carbon dioxide + water chlorophyll glucose + oxygen Variables Manipulated : presence of carbon dioxide Responding: presence of starch in leaf Constant :presence of light, chlorophyll, water Observation : The leaf from Plant B turns blue black when tested with iodine solution. Photosynthesis takes place. Chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis Variables Manipulated : presence of chlorophyll Responding: presence of starch in leaf Constant :presence of light, carbon dioxide, water Observation : Only green parts of the leaf which contain chlorophyll turn blue-black.
Requirement of photosynthesis: 1. Light 2. Chlorophyll 3. Carbon dioxide 4. Water
To know whether photosynthesis has taken place in a plant, we test for the presence of starch(food storage of plant) in the leaves.
Sunlight is needed for photosynthesis Variables Manipulated : presence of sunlight Responding: presence of starch in leaf Constant :presence of carbon dioxide, chlorophyll, water Observation : The covered portion of the leaf does not turn blue- black whereas the portion that is exposed to sunlight turns blue-black.
Leaf turns blue black if starch is present. This shows that photosynthesis has taken place.
Determining the requirements of photosynthesis
Importance of photosynthesis
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. -
It helps to keep the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere the same. It helps to keep the level of oxygen in the atmosphere the same. Source of carbon for other organisms. Enables green plants to make its own food. Carbon cycle : process which carbon dioxide removed and returned to the atmosphere. Involved photosynthesis and respiration. Carbon dioxide from atmosphere is removed as plants used it for photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide return back to atmosphere by respiration and burning. process which oxygen removed and returned to the atmosphere. Involved photosynthesis and respiration. Plants release oxygen to atmosphere during day tine when photosynthesis takes place. At same time, both plants and animals use oxygen for respiration.
effect, global warming ( )and thinning of ozone layer( ). Exploitation of nature resources, deforestation Use of pesticides Kill wildlife for food and clothing. Clearing forests for timber, raw materials Control pest Flash floods, organisms facing extinction (), landslides(
)
Pollution
6. Oxygen cycle :
Importance of maintaining a stable and balanced ecosystem -natural resources will be continuous available for the goodness of mankind and all other living things.
Conservation and preservation of organisms 1. Conservation and preservation are ways to protect ecosystem from destruction, depletion and endangered species. 2. Conservation : careful and systematic use of resources without bringing harm to living organisms and environment. 3. Preservation : steps taken to keep living things and their environment in their original and balanced state. 4. Steps taken : - Forest reserves : Example are Taman Negara at Pahang - Marine parks : Example are Pulau Redang at Terengganu - Orang-Utan Rehabilitation Centre in Sepilok, Sabah - Law implementation : Wildlife Protection Act - Practice 3Rs Reuse, Recycle and Reduce 5. support activities organised by various parties to preserve and conserve the living organisms. Role of human beings in maintaining the balance of nature Human activities Industrial development Reasons Factories produces goods Effects on nature Air, soil and water pollution resulting in acid rain, greenhouse
EXERCISES 1.What is a habitat? _________________________________________________________________________
2. Three main interactions between organisms :
3. Give one advantage of biological control.
4. Write down the word equation for photosynthesis :
5. Give the four requirements of photosynthesis :
6.
How many food chains are there? List down all the food chains you can find in the diagram above.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem ReviewerDokumen4 halamanBiodiversity and Ecosystem ReviewerMichaelah Reinne Alcaraz ConvocarBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Ib Biology Ecology CourseworkDokumen6 halamanIb Biology Ecology Courseworkafaydebwo100% (2)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021Dokumen22 halamanIndia State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021Devaraj BillaBelum ada peringkat
- Response of Water Resources Systems To Climate ChangeDokumen355 halamanResponse of Water Resources Systems To Climate ChangePat Prodanovic100% (5)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- A2-Level Biology, Unit 4 NotesDokumen97 halamanA2-Level Biology, Unit 4 NotesBhanhee Kim100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Target Species - Species of European ConcernDokumen193 halamanTarget Species - Species of European ConcernJozef DozsaiBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Cultural Heritage of The PhilippinesDokumen38 halamanCultural Heritage of The PhilippinesLea Rose Jeorgia SalongaBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Algology Micology EngDokumen2 halamanAlgology Micology Engmihaela021988Belum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Pearson Revision Work Book Copy-Part-2Dokumen21 halamanPearson Revision Work Book Copy-Part-2Hannah YeungBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Mineral Resources From The Earth: The Philippine Mining IndustryDokumen27 halamanMineral Resources From The Earth: The Philippine Mining IndustryIyleBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Mind Map Year 6 (L.area)Dokumen7 halamanMind Map Year 6 (L.area)radenesBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Biodiversity and ConservationDokumen34 halamanBiodiversity and ConservationKarylle Jhoye CheBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- People and Nature - 2020 - Pe Er - Action Needed For The EU Common Agricultural Policy To Address Sustainability ChallengesDokumen12 halamanPeople and Nature - 2020 - Pe Er - Action Needed For The EU Common Agricultural Policy To Address Sustainability ChallengesnajmiBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Lesson 2 - EcologyDokumen59 halamanLesson 2 - EcologyApril Christine Mae ApuraBelum ada peringkat
- Rodriguez-Ferreretal - 2017 Marine RecorsDokumen4 halamanRodriguez-Ferreretal - 2017 Marine Recorsalyman_bBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Biodiversity Loss: The Effects of Habitat Destruction On The WorldDokumen4 halamanBiodiversity Loss: The Effects of Habitat Destruction On The WorldMax FieldBelum ada peringkat
- Hoya JosetteaeDokumen11 halamanHoya JosetteaeHisyamBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Flora 284 (2021) 151925Dokumen9 halamanFlora 284 (2021) 151925Ariadne Cristina De AntonioBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- EIA Ghorasal Unit Sept 14Dokumen406 halamanEIA Ghorasal Unit Sept 14Shafayat AhmmedBelum ada peringkat
- You May Choose From Threatened, Vulnerable, Endangered, Critically EndangeredDokumen6 halamanYou May Choose From Threatened, Vulnerable, Endangered, Critically Endangeredapi-550930401Belum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rayos Et Al. MobulaDokumen44 halamanRayos Et Al. Mobulavinrene parciaBelum ada peringkat
- Aarrttss & & Lleeiissuurree: ""Ccaalliiffoorrnniiaa'Ss Bbeesstt - Pprreesseerrvveedd V Viiccttoorriiaann V Viillllaaggee""Dokumen1 halamanAarrttss & & Lleeiissuurree: ""Ccaalliiffoorrnniiaa'Ss Bbeesstt - Pprreesseerrvveedd V Viiccttoorriiaann V Viillllaaggee""ferndaleenterpriseBelum ada peringkat
- Frigid ZoneDokumen17 halamanFrigid ZoneDeepthi ThomasBelum ada peringkat
- EVS AssignmentDokumen2 halamanEVS AssignmentshantaBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Dolphins - Beneath The Waves of WonderDokumen2 halamanDolphins - Beneath The Waves of WonderNATURE DENTALBelum ada peringkat
- Blanqueamineto Coral RapanuiDokumen18 halamanBlanqueamineto Coral RapanuiMare Del PacifícoBelum ada peringkat
- Jordan 3e Chapter3 PDFDokumen20 halamanJordan 3e Chapter3 PDFShane Franchezka GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Diversity, Abundance and Habitat Utilization of Birds in Periphery of The Mihintale SanctuaryDokumen1 halamanDiversity, Abundance and Habitat Utilization of Birds in Periphery of The Mihintale SanctuaryH.Krishantha Sameera de ZoysaBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Kajima's Three PolicyDokumen2 halamanKajima's Three PolicyBe Seang SeBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)