Essential elements of contracts and business law questions
Diunggah oleh
rramadanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Essential elements of contracts and business law questions
Diunggah oleh
rramadanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Year wise question solution Business Law
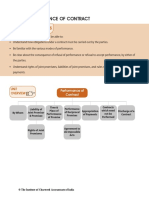
Q1. What is contract / what is meant by contract? (May -02, Nov-03) The word contract means that to be agreement on something. Generally when an agreement comes in to existence, one or more person promise to one or others to do or not to do some thing- is called contract. The agreement must be enforceable by law. So, from the above discussion we find out that a contract bust be: An agreement; The agreement must be enforceable by law. According to contract Act 1872, sec 2 (h) an agreement enforceable by a law is a contract. Q2. Explain the essential elements of a contract? (May-02) Or All agreement are not contract but all contract are not agreement -discuses the statement explaining elements of a valid contract? Or What are the characteristics of valid contract? The word contract means that to be agreement on some things. When an agreement comes in to existence one or more person promise to one another to do or not to do some things is called contract. The agreement must be enforceable by law. The essential elements of valid contract are explain below: 1. Offers & Acceptance: There must be lawful offer be one party and lawful acceptance of another party. 2. Intention to create legal relationship: There must be an intention that the agreement shall result in or create legal relationship. 3. Lawful consideration: In a valid contract there must be a lawful consideration between the related parties. 4. Lawful object: The object for which the agreement has been entered into must not be illegal. 5. Capacity to control: The parties to an agreement must be legally capable of entering in to an agreement otherwise it cannot be enforceable by law. 6. Free consent: In order to be enforceable, an agreement must be based on the free consent of all the parties. 7. Certainty: It must be possible to ascertain the meaning of the agreement, otherwise it cannot be enforced. 8. Possibility of performance: An agreement must be capable to perform. 9. Written & registered:
Page 1 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
A valid contract should be written and registered. The elements mentioned above must all be present in a contract. If any of them is absent, the agreement does not become a valid contract. An agreement which fulfills all the essential elements is enforceable by law and is called a contract. From this it follows that, every contract is an agreement but all agreement are not contract.
Q3. The contract Acts specially declares certain agreements to be void. You are required to list such agreement? (May-02) Void agreement: According to contract act 1872 section 2(g) an agreement which is not enforceable by law is called void agreement. A void agreement has no legal effect. List of the void agreement: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. An agreement with minor & mad. An agreement unlawful consideration. An agreement unlawful object. Except some exception on agreement with out consideration. An agreement of uncertain meanings. An agreement by the way of wager. Impossible Acts. (May 01, May
Q4. Distinguish between contract and an agreement? 05)
The distinguish between contract and an agreement are as follows: Contract An agreement enforceable by law is a contract. A legal contract must enforceable by law. Agreement Every promise and every set of promises, forming the Definition consideration for each other is an agreement. be Agreement does not Enforceable by enforceable by law. law Consideration Consideration is not essential in all kind of agreement. There is no legal obligation s that an agreement should be registered. All agreement are not contract. Subject
Each contract must have certain lawful consideration. A contract may be registered.
Registered Every contract agreement. is an Nature
Q5. When the communication of proposal and acceptance complete? How and when can they be revoked? (May- 01) Communication of proposal:
Page 2 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
The communication of proposal is competing when it comes to the knowledge of the person to whom it is made. (Sec- 4). Illustration: Zahid proposed by a letter to sale a house to Tazmilur at Tk 15 lac. The communication of proposal is complete when Tazmilur received & come to know about this matter. Communication of acceptance: Communication of acceptance is complete when acceptor, accept it & it comes to the knowledge of the proposer/ offeror. Illustration: Rony accept Baris proposal by the post. The communication of acceptance is complete when Bari knows that Rony accepted his proposal. Revocation of communication proposal: 1. If the offeror give the notice of revocation to the other party, 2. If the offeror gives a fixed time to accept & if the time is over, 3. If the acceptor fail to fulfill the condition of the offer. 4. If the acceptor give a counter offer. 5. If the acceptor refuse the proposal. 6. When acceptor refuses his duties before the time of performance is due. Q6. Define offer and acceptance. (Nov 05) When are offer and acceptance deemed to be complete, if made through post? Offer: An offer involves the making of proposal, when one person signifies to another his willingness to do or not to do anything is called offer. The people who give an offer is called offer or or promis or. Offer can be made by specific person class or people at large, and may be conditional. But it must be intention to established lawful relationship. Illustration: Sami says to Sheri will you buy my house for TK.50,000? This is an offer. Acceptance: When one party give a lawful offer to another party and if another party accept it then is called acceptance or promise. Illustration: Mr. Enam says to Mr. Sakil, will you buy my car at the price of Tk. 100,000? This is an offer. If Mr. Sakli says yes, the offer is completed and a contract is formed. Offer and acceptance by post: An offer may be made by post. An offer may also be accepted by post, if there is no other mode of acceptance specially prescribed by the proposer. The letter of acceptance duly addressed and posted is sufficient acceptance even through the letter does not actually reach the proposer. Therefore the letter must be actually posted. Q7. State how offer is made revoked and accepted .what are the rules when offer is made through post office and over the telephone? Offer: When one person signifies to another his willingness to do or not to do anything is called offer. But the offer must be intention to established lawful relationship. Illustration: Sami says to Sheri will you buy my house for TK.50,000? This is an offer.
Page 3 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Revocation of an offer: An offer comes to an end, and is no longer open to acceptance under the following circumstances: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. If If If If If the the the the the offeror give notice of revocation to the other party. offeror give a specific time to accept and if the time is over. acceptor fail to fulfill the condition of the offer. acceptor give a counter offer. acceptor refuse the proposal.
Acceptance: When one party gives a lawful offer to another party and if another party accept it then is called acceptance or promise. Illustration: Mr. Enam says to Mr. Sakil, will you buy my car at the price of Tk. 100,000? This is an offer. If Mr. Sakli says yes, the offer is completed and a contract is formed. Rules regarding an offer is made through post office and over the telephone: Q8. Define the term Acceptance? What are the essentials of a valid acceptance? Acceptance: When one party gives a lawful offer to another party and if another party accept it then is called acceptance or promise. Illustration: Mr. Enam says to Mr. Sakil, will you buy my car at the price of Tk. 100,000? This is an offer. If Mr. Sakli says yes, the offer is completed and a contract is formed. Essential of a valid Acceptance: 1. Acceptance must be unqualified and absolute, 2. Conditional Acceptance, 3. Acceptance must be communicated, 4. Mental acceptance does not result in a contract, 5. When acceptance is complete, 6. Acceptance must be done within the prescribed time. Q9. What do you understand by counter offer? (Nov-02) Counter Offer: When one person signifies to another his willingness to do or not to do anything is called offer. If the other party does not accept the offer, but give another offer to the offeror including one or more condition that is called counter offer. Q10. What are the characteristics/essential factors of consideration? (May-03) The characteristics or essential factors of consideration discuss in below: 1. Desire/ Request of the promisor is essential: Consideration means when at the desire or request of the promisor, the promisee or any other person has done from doing something. So, without request is a voluntary act and does not come within the definition of consideration. 2. Consideration must be real:
Page 4 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
The consideration must have some value in the eye of law. It must not be fraud or misleading. 3. Consideration needs not to be adequate: In a contract consideration need no to be adequate. For Illustration, Patu agrees to sell a house worth tk.50,000 for tk.5,000. Patus consent to the agreement was freely given. The agreement is a contract notwithstanding the inadequacy of the consideration. 4. Consider may be present, past or future: As per agreement of the contract consideration may be at present, past or in future, i.e. as per prescribed terms. 5. Consideration must not be illegal, immortal or opposed to public policy: If the consideration of the object of the agreement is illegal, immoral or opposed to public policy, the agreement cannot be enforce. 6. Consideration may be move from promise or from any other person. Q11. Information of a contract, consideration must be real but need not be adequate- Explain? (May-02, May05) Information of a contract, consideration must he real. It must not fraud or misleading. The impossible acts and illusory cannot support a contract. Therefore, real consideration comes from good consideration. Illustration: Titu promise to Anu to supply of one tola fold from sun. The consideration is Shaw and illusory so, there is no contract. So, information of a valid contract the consideration must be real, but to make a real consideration it should not be adequate. By inadequate consideration a contract also may be formed. But the inadequacy of the consideration may be grant when the consent to the promisor was freely given. Illustration: Rifu aggress to sell a horse worth tk.10,000 for tk.1,000 to Jafor. Rifus consent to the agreement was freely given. So, the agreement is a contract notwithstanding the inadequacy of the consideration. So, from the above discussion we know that Information of a contract consideration must be real but need not to e adequate.
Q12. No consideration no contract- explain? (Nov03, Nov04) Or A contract without consideration is void explain? Or Importance of consideration Or Insufficiency of consideration is immaterial but an agreement without consideration is void explain? Consideration is an essential element of valid contract. So, valid contract does not made without consideration. We know that by promise one party give or sacrifice something and other party take something. This type of give and take or sacrifice is called consideration by the eye of law.
Page 5 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
If someone give promise without any consideration that is called gift. On the other hand give premise exchange of any consideration that is called contract. Illustration: Alim promise to give tk.5,000 to build mosque. It is not contract because there is no consideration. Consideration may be paid in future and it is not sufficient but in a contract must have consideration. So, it is clear that no consideration no contract. Q13. Distinguish between void agreements and void able agreements? (May- 02) Void Agreement Void able Agreement An agreement not enforceable by law A void able agreement is one which is said to be void agreement. can be avoided, i.e. set a side by some of the parties to it. A void agreement has no legal effect, In the case of void able agreement no right and create no obligation on the rights and obligations of the any person. parties concerned are present unless it becomes void. For a void agreement it is not In the case of void able agreement necessary for the effected party to the effected party needs to call the declare the agreement void. agreement void. In case of void agreement the party is But in the case of void able not bound to refund the benefit agreement the party may refund the received to the other party. benefit to the other party, if the agreement void later on. A void agreement originates by an A void able agreement originates by agreement made by a minor, contracts brought about by endue agreements without consideration, influence, misrepresentation. illegal objectives.
Q14. Distinguish between contingent contract and wagering contract? (May-03; Nov-03) Contingent contract Contingent contract is a valid contract. Contingent contract is enforceable by law. Contingent contract depends happening or non happening of an event, Wagering contract Wagering contract is a void contract. Wagering contract is not enforceable by law. Wagering contract depends success and failure of an event.
Q15. Explain the difference between a void and illegal transaction with reference to collateral transactions? An illegal agreement is void, but a void agreement is not necessarily illegal. An agreement, the terms of which are uncertain is void but such a contract is not illegal. When an agreement is illegal, other agreements which are incidental or collateral to it are void. So, if the main agreement is void, (but not illegal) agreements which are incidental or collateral to it may be valid.
Page 6 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Illustration: Rana enters into a wagering agreement and borrows tk.500 for the purpose. The main agreement i.e. wagering is void but the loan transaction being merely collateral to it is valid even though the creditor is aware of the purpose of the loan. Q16. Void able agreement and unenforceable agreement? Void able agreement: Under section 2 (i) an agreement which is enforceable by law at the option of one or more of the parties thereto, but not at the option of the other or others, is a void able contract. We can say it also in another way; a void able agreement is one, which can be avoided, i.e. set a side by some of the parties to it. A void able agreement originates by contracts brought about by undue influence, misrepresentation or fraud. Unenforceable Agreements: Sometimes an agreement is not enforceable by law for some lawful defect. These agreements are called unenforceable contract or unenforceable agreement. Illustration: Zahid made a contract with Kanta to sell a house. But the contract was not registered or written. It is an unenforceable contract. Q17. What do you understand by supervening impossibility? How it may occur? (Nov-03, May-03, Nov-01, Nov02) Supervening Impossibility: A contract after made becomes impossible to perform or by reason of some event which the promisor could not prevent. Unlawful in these cases the contract becomes void. This is called the supervening impossibility. Supervening impossibility may occur many ways, some of which are explained below: 1. Destruction of an object: In the contract which performance depends on the existence of a given person or thing, and the supervening impossibility arise by the destruction of the person or thing or object necessary for the performance of the contract. 2. Change of law: By a subsequent change of law the performance of a contract become unlawful and it become void. Illustration: Moni sold to Nadia a specific parcel of wheat in a wear house. Before delivery the wheat was requisitioned by the Govt. under statutory power. The delivery is now legally impossible, so the contract was discharged. 3. Failure of precondition: When a contract is entered in to on the basis of some conditions, the contract is discharged if the conditions fail or changes. Illustrations: Zaman & Juli contract to marry each other, before the time fixed for the marriage, Zaman goes mad. The contract becomes void. 4. Death or Incapacity for personal services:
Page 7 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Where the personal qualification of a party is the basis of contract, the contract is discharged in cases of death or personal incapacity. Illustration: A seaman was entered owing to war; his contract of services was discharged. 5. War: A contract entered into during war with an alien enemy is void. A contract entered in to before the war start between citizens of countries, the contract remains suspended during the time of the war. Q18. What do you understand by frustration of contract by supervening impossibility? What are the legal consequences of a contract, which has been frustrated due to supervening impossibility? (Nov-02) Frustration of contract: Frustration of contract may occur by the supervening impossibility of the contract. When a contract offer made becomes impossible to perform or by reason of some event, which the promisor could not prevent, then the contract become void and unlawful and the court may declare the contract to be at an end. Legal consequences of a contract, which has been frustrated due to supervening impossibility: Or The effect of frustration due to supervening impossibility: The legal consequences of a contract which has been frustrated due to supervening impossibility are discussed in below: 1. When the performance of a contract becomes supervening impossible or frustrated or illegal, the contract becomes void. 2. When the promisor of a contract know that the performance of the promise is not possible or illegal, and which the promisee did not know to be impossible or unlawful, such promisor is liable for any loss which such promisee effected through the non performance of the promise. 3. When a contract becomes void by the supervening impossibility any person who has received any advantages under it must restore to the person who he received it. Illustration: Enam pays Zahid tk.2,000 in consideration of Zahids promising to marry Geet, Enams daughter Geet is dead at the time of the promise. The agreement is void but Zahid must repay Enam tk. 2,000. Q19. Distinguish between a contract of guarantee and a contract of indemnity? (Nov-01) Contract of guarantee: A contract of guarantee is a contract to perform the promise, or discharge the liability of a third person in case of his default. Contract of indemnity: A contract by which one party promise to save other party from loss caused to him by the conduct of any other person is called contract of indemnity. More distinguish discuss in below:
Page 8 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Contract of guarantee In a contract of guarantee there are three parties: (1) The creditors (2) The principle debtors (3) The surety It is necessary to have three contracts between the parties; the creditors, the principle debtors and the surety. The liability of the surety is secondary.
Contract of indemnity In a contract of indemnity there are two parties: (1) The indemnifier (2) Indemnity holder. It is necessary to have only one contract between indemnifier and the indemnity-holder.
The liability of the indemnifier is primary. According to cheating law of England According to general law of England the guarantee is necessary to written. the contract of indemnity may be written or oral.
Q20. What is continuing guarantee? (May 03) A guarantee, which extended to a series of transaction, is called a continuing guarantee. Q21. Distinguish between bailment and pledge? (May-01) Bailment: Bailment is the delivery of goods by one person to another for some purpose, upon a contract that they shall, when the purpose is accomplished be returned or otherwise disposed of according to the direction of the person delivering them. So, the Bailment means act of delivering goods for a specific purpose on trust. Pledge: Pledge means, the bailment of goods as security for payment of a debt or performance of a promise. More distinguish between the bailment and pledge shown in below: Bailment Pledge The purpose of bailment are repair, The purpose of pledge is to provide safe custody etc. security for a debt. In the case of bailment, the ownership In the case of pledge special does not handover to bailee. ownership hand over to pledge /pawn. Bailment must create by a certain There may no contract between contract between bailee and bailor. pladgee and pledgor. Bailment can perform as an agent on But pledge can not do that. certain factors. Q22. Discuss about the extent of authority of an agent? (May-02) Authority of agent: The authority of an agent may be expressed or implied. The authority is said to be expressed when it is given by words spoken or written. The authority is implied when it is to be determined from the circumstances from the case.
Page 9 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Extent of authority of an agent: The extent of authority of an agent discuss below: 1. An agent having an authority to do an act has authority to do every lawful thing which is necessary in order to do such act. 2. An agent having an authority to carry on a business has authority to do every lawful thing necessary for the purpose of such business. 3. An agent has authority, in an emergency to do all such acts for the purpose of practicing his principal from any loss, in his own case, under similar circumstances. Illustration: An agent for sale may have goods repaired if it be necessary. Q23. Write down the Agent duty to the principal Vs principal duly to the agent? (May-02) Agent duty to the principal: 1. Duty to do act according principals direction: An agent is bound to conduct the business of his principal according to the directions or in the absence of any such directions. 2. Maintaining proper books of accounts: An agent is bound to maintain the books of accounts of his principal properly. 3. Communicate with principal take direction: It is the duty of an agent in case of difficulty, communicate with his principal and take direction. 4. Principals death or insanity: Agency may terminate by the principals dying or unsound mind, then agent is bound to take on behalf of the representative of his late principal. 5. Pay sums received for principal: The agent is bound to pay to his principals all sum received on behalf of the principal. More duties to the principals of an agent are: Inform all information; Agent not to deal on his own account, etc. Principals duty to the agent: 1. Agent to be indemnified against consequences of lawful acts. 2. Agents to be indemnified against consequences of acts done in good faith. 3. Principals not bound to indemnify the agent for any criminal acts. 4. Agent to be indemnified in respect of any injury by the principals neglect or want of skill. Q24. What are the limitations of a wife as an agent in binding her husband? (May-01) Limitations of a wife as agent in binding her husband: A wife could be an agent of her husband. If the husband gives her a sufficient allowance, she has no authority to pledge his credit and can never be the agent of necessity.
Page 10 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
This will be clearer to us from the following illustrations. Illustration: (i) A shopkeeper supplied a cloth at the price of tk.200 to a wife. The shopkeeper sued the husband to recover his amount. The court declared that the husband was not liable to pay the amount. Illustration: (ii) A shopkeeper supplied a cloth at the price of tk.200 to a wife. The shop keeper sued the husband to recover it. The court declared that the husband is liable for that money. From the above two illustrations we saw that from illustration (i) the husband is not liable to pay the money because it was investigated that the husband give to his wife tk.500 yearly as allowance. So the husband is not liable to pay the money to the shopkeeper. But in illustration (ii) it is investigated that after the transaction between the wife and the shopkeeper the husband divorced to his wife do not give any allowances her. So for this case, the husband is liable to pay the shopkeepers money. Q 25.What is agency necessity? (Nov-03) Agency of necessity: An authority which act some work without declaration is called agency of necessity. When a person to act on behalf of another without any express authority from him, in such cases an agency of necessity created. Illustration: The captain of a ship finds himself in a distant port without money. The owner cannot be communicated with. The captain pledged the ship for obtaining money. He will be considered the agent of the owner by necessity. Q26. The general rule is that No seller of goods can give the buyer of goods a better title to the goods than he himself has-Explain? (Nov-02, 03) The general rule is that only the owner of goods can sale the goods. No one convey to a transfer to a better title than he himself has. If a person transfer articles not belonging to him, the transferee gets no title. The principal is expressed by the Latin phrase Nemo quod qui non habet which means none can give who does not himself posses. This rule applies to both movable and immovable property. Q27. Distinguish between condition and warranty? (May02) Distinguish between condition and warranty is given below: Consideration A condition is a stipulation essential to the main purpose of the contract, the breach of which gives rise to a right to treat the contract. To perform a contract condition is necessary. trend Warranty Warranty is a stipulation collateral to the main purpose of the contract, the breach of which gives rise to claim for damage but not right to reject the goods and treat the contract. of Trend of warranty is not essential but is duty to perform all parties.
Page 11 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Condition may be treated as warranty under certain circumstances. Condition is treated as pillar in the contract of goods sale.
Warranty can not becomes a condition. Warranty is treated as a secondary element in the contract of sale of goods.
Q28. Distinguish between sale and agreement to sale. When does an agreement to sale become sale? (Nov-01) Distinguish between sale and agreement to sale are narrated below in different point of view: Sale In the case of sale ownership of the goods transfer to buyer as soon as transaction is complete. Sale is an existing good. Sales are an executed contract. In the case of sale, the unpaid seller can lien, stoppage in transit and re-sale the goods. Agreement to sale In the case of agreement to 1) Ownership sale ownership of goods is transfer not transfer. 2) Goods 3) Nature 4) Remedy Agreement is a future goods. Agreement is an executory contract. In the case of agreement to sale, seller remedy for breach of contract by the buyer suit for damage. Subject
An agreement to sale becomes sale: An agreement to sell becomes a sale when the prescribed time, conditions and terms of agreements are fulfilling properly. Illustration: Zahid agrees to by some fruits after arrive a certain ship; this is an agreement to sale after arrival the ship Zahid bought some fruits. Here the agreement to sale becomes sale. Q29. When does the property in goods sold pass from the seller to the buyer? (Nov-02) a) In the case of Ascertain goods: 1. Where the goods in a deliverable state as soon as the contract is made. 2. Whether the goods are not deliverable state the seller has to do something until such things are done and the buyer has notice thereof. 3. Where the goods are deliverable state but the seller is bound to weigh measure that or do something for ascertaining price until such things are done and the buyer has notice thereof. 4. Where goods are delivered to the buyer on terms i.e. sale on approval and sale on return: When buyer signifies his approval. After expiry of reasonable time. b) In case of uncertain goods: Until and unless the goods are ascertained or made specific. c) Future goods: Until and unless the time is determined.
Page 12 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Q30. What are the features of a contract of a sale of goods? (May-02) The features of a contract for the sale of goods are discuss below: 1. Moveable Goods: The sale of goods act deals only with movable goods, except actionable claims and money. 2. Movable Goods for money: For a contract of sale of goods there must be money consideration. But it has been held that if an exchange is made partly for goods and partly for money. 3. Two Parties: A contract of sale involves a change of ownership, that means the buyer and the seller must be different person. But there is an exception in law, that is a part owner can sell goods to another part owner. 4. Formation of the contract of sale: A contract of sale is made by an offer to buy or sell goods for a price and the acceptance of such offer. 5. Method of forming the contract: A contract of sale may be in writing, or by word of month, or may be implied. 6. The terms of contract: The parties may agree upon any term concerning the time, place and mode of delivery. The terms may be two type and these are (i) Essential (ii) Non essential. Q31. What do you understand by caveat emptor? (May-03, May04) Caveat emptor: Caveat Emptor is a Latin expression which means buyers beware. The doctrine of caveat emptor means that, ordinarily a buyer must buy goods after satisfying himself of their quality and fitness. If he made a bad choice he can not balm the seller or recover damages from him. Illustration: Kanta bought a television at the price of tk.10,000 from Zahid after testing its quality and fitness with his satisfaction, but when she took it to home she saw that the television do not servicing well as her satisfactory, then she could not liable Zahid for that. Q32. What is an unpaid seller of goods? (Nov-03) Unpaid seller: 1. When price has not been received or tendered. 2. When negotiable instrument has been received but the same has been dishonored. On the above cases seller can be said as unpaid seller. Illustration: Enam sold a good to Zahid at the price of tk.500. Zahid gave a cheque of tk.500 to Enam for that purpose. But the cheque was dishonored. In the case Enam is an unpaid seller. Q33. What is the right of a unpaid seller against the buyer? (May-03)
Page 13 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
The right of an unpaid seller against the buyer explained in below: 1. Right to sue for price: Where under a contract of sale the property has passed to the buyer and the buyer wrongfully neglects or refuse to pay for the goods according to the terms of contract, the seller may sue him for the price of the goods. 2. Damage for non acceptance of goods: Where the buyer wrongfully neglects or refuse to accept and pay for the goods, the seller may sue him for damages for non- acceptance. 3. Claim for interest and special damages: The seller may recover interest or special damages in any case where by law interest or special damages may be recoverable. Q34. What is the meaning of vendors lien? (May-03) Vendors lien involves in the following terms: Where the goods have been sold without any credit; Where the goods have been sold on credit but the term of credit has expired; and Where the buyers become insolvent. Q35. What do you understand by partnership at will? (May-03) A partnership is called a partnership at will when: 1. The partnership is not for a fixed period of time; and 2. No provision is made as to when and how the partnership will come to an end. Q36. What are the effects of non registration of a firm? (May-03) The registration of a partnership is not compulsory. But an unregistered firm suffers from certain disabilities and therefore registration is necessary for carrying on business. An unregistered firm and the partners suffer from certain disabilities: 1. A partner of an unregistered firm can not file a suit against the firm or any other partner. 2. No suit can be filed against any third party. 3. An unregistered firm can not claim a set off in suit. Q37. What are the 10 important elements of a standard partnership deed? (Nov-02) Important elements of a standard partnership deed are as follows: 1. Name of the partnership firm; 2. Address of the firm; 3. Nature, object and scope of the firm; 4. Permanency of the firm/duration of the firm; 5. Name, address and occupation of the partners; 6. Total capital of the firm; 7. Profit distribution method and ratio; 8. Maintain and management procedure of the firm; 9. Details of partners right, liabilities and duties; 10. Admission procedure of a new partner; 11. Good will valuation procedure of firm; and 12. Dissolution procedure of firm.
Page 14 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Q38. Can you spell act the procedure for registration of a firm? (Nov02) Procedure for registration of a firm: The registration of a firm may be affected at any time by sending by post or delivering to the register of firms of the locality a statement in the prescribed form and accompanied by the prescribed fee, stating the following particulars: 1) The firms name; 2) Head office address of the firm; 3) Branch office address of the firm; 4) Objectives of the firm; 5) Date of commencement of the firm; 6) Name, address and occupations of the partners; 7) The date when each partner joined the firm; and 8) The duration of the firm. The statement shall be signed and verified by all the partners or their agents. On receipt of the statement and fees the registration made registration of the firm. Q39. What is registration of a partnership firm? Is it mandatory for a firm to register? (Nov-02) Registration of partnership firm means the enlisted of firms name in registered office. The registration of partnership is not compulsory. Therefore an unregistered firm is not illegal association. But an unregistered firm suffers from certain disabilities and therefore registration is necessary for carrying on business. Q40. What are the essential elements of partnership? (May-02) Partnership is the relationship between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all. The essential element of partnership is as follows: 1) There must be an agreement entered in to by two or more person. A partnership can not be formed with more than ten persons in banking business and twenty persons in other business. 2) The agreement must be to share the profit of a business. 3) The agreement must be carried on by all or any of them acting for all. Q41. Happening of certain contingencies may lead to dissolution of partnership-what are those? (May-02) A partnership may lead to discussion by happening of certain contingenciesthose are as follows: 1) If constitute for fixed term, by the expiry of that term. 2) If constitute to carry out one or more adventures or undertaking by the completion thereof. 3) By the death of partner. 4) By the adjudication of the partner as an insolvent. Q42. Spell out the grounds on which a court may dissolve a partnership firm on a suit filed by a partner? (May-02) Grounds of dissolution: A firm may be dissolved on any of the following grounds:
Page 15 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
1) By agreement: A firm may dissolved any time with the consent of all the partners of the firm. 2) o o o Compulsory dissolution: By the adjudication of all the partners. If all partners insolvent except one partner. By the happening of any event which makes the business of the firm unlawful.
3) On the happening of certain contingencies: Subject to contract between the partners, a firm is dissolved:o If constitute for fixed term, by the expiry of that term. o If constitute to carry out one or more adventures undertaking, by the completion thereof. o By the death of partner. o By the adjudication of the partner as an insolvent. 4) Dissolution by notice: Where the partnership at will, the firm may be dissolved by any partner giving notice in writing to all another partners of his intentions to dissolve the firm. 5) Dissolution by the court: At the suit of a partner, the court may dissolve a firm on any one of the following grounds:
o Unsound mind: If a partner becomes unsound mind. o Permanent incapacity: If a partner becomes permanently incapable
of performing his duties as a partner.
o Guilty conduct: If a partner is guilty of conduct. o Persistent breach of agreement: If a partner persistently breach of
the partnership agreement.
o Transfer of whole interest: If a partner has transferred whole of his
interest to an outsider. o Loss: If the business of the firm cannot be carried on except at a loss.
Q43. What is promissory note? How does it differ from bill of exchange? (Nov-02, 03; May-03) Promissory note: According to Negotiable Instrument Act 1881 u/s 4 A promissory note is an instrument in writing containing an unconditional undertaking signed by maker, to pay certain sum of money only to, or to order of a certain person or to the bearer of the instrument. There are two parties related in promissory note: (i) maker/ drawer, (ii) payee. We can differ it easily from bill of exchange by discuss the following terms: Promissory note Bill of exchange In a promissory note there are two In a bill of exchange there are three parties- the maker and the payee. parties- the drawer, the drawee and the payee. In a promissory note there is a In a bill of exchange there is an promise to pay. order to pay. Acceptance is not necessary for the Acceptance is necessary in a bill of
Page 16 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
promissory note. In the case of promissory note, notice of dishonor to the maker is not necessary. In a promissory note protest is not necessary.
exchange. In the case of non-payment or nonacceptance of a bill notice mist be give to all related parties. In the bill of exchange protest is necessary.
Q44. What is promissory note? Is the following a promissory note-I promise to pay B TK.50,000 and all other dues which shall be due to him. (Nov-01,02;May-03) I promise to pay TK 50,000 to B and all other dues which shall be due to himis not a promissory note because to be a promissory note a negotiable instrument must have contain the following elements, and it mist be fulfilled properly: 1) The instrument must be in writing; 2) The instrument must be signed by the maker; 3) The instrument must contain a promise to pay; 4) The promise to pay must be unconditional; 5) The maker of the instrument must be certain and definite; 6) The promissory note must be stamped; 7) The payment must be in legal tender money; 8) Payable to definite person; 9) The sum of money to be paid must be certain; and 10) The promissory note may payable on demand or after certain definite period of time. The above instrument did not fulfill the condition to be a promissory note, so it is not a promissory note. Q45. What is the effect of crossing a cheque with the words not negotiable written across its face? (May-01) A checked marked with the words not negotiable can be transferred or assigned by the payee. The transferee will get the same rights, as regards payment as the transferor had. But the transferee will not get the right of holder in due course. From the language of the section 130 it follows that the transferee of such cheque takes it at his own risk. Q46. Who can accept a bill of exchange? (May-03, Nov04) Only the following person can accept the bill of exchange: The drawee of the bill. The drawee in case of need. The legal representative, when drawee is dead. The official assignee or official receiver when the drawee has become insolvent. Q47. Define negotiable instruments as per negotiable instrument act 1881. Also spell out 4 to 5 characteristics of the negotiable instrument. (Nov-02; May-01) Negotiable instrument: As per negotiable instrument act 1881a negotiable instrument means a promissory note, bill of exchange or cheque payable either to order or to bearer
Page 17 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Characteristics of negotiable instrument: 1) The instrument must be in writing and signed by the maker. 2) Must certain a promise to pay. 3) The sum of money to be paid must be certain. 4) The money must be payable to a definite person or according to his order. 5) The transferee/receiver of a negotiable instrument, when he fulfils certain is called the holders in due course. The holder in due course gets a good title to the instrument even the title of the transferor/sender is defective. Q48. Distinguish between cheque and bill of exchange. (Nov-02, May02) Bill of exchange A bill of exchange can be drawn any person including a bank. A bill of exchange requires acceptance. A bill of exchange is not payable on demand here allowed a grace period of 3 days. There is on crossing facility in bill of exchange. A bill of exchange must be stamped. subject Drawer / maker Acceptance Payable on demand Crossed Stamped Cheque A cheque can be drawn only upon a bank. A cheque does not require any acceptance. A cheque is always payable on demand. A cheque may be crossed. A cheque does not require any stamp.
Q49. Who can cross a cheque? (Nov-03) A cheque can be crossed by the drawer, the holder and the Bank. Q50. When a bill of exchange is said to be dishonored? (Nov-03) When a drawee does not accept the bill of exchange in specific date and the drawee fail to or show disability to pay the bill amount after the maturity date of that bill then it is said dishonored of bill of exchange. A bill of exchange may be dishonored in two separate ways. These are: Dishonored by non acceptance; and Dishonored by non-payment. Dishonored by non acceptance: When the drawee is incompetent to contract or the acceptance is qualified , the bill may be treated as dishonored. Illustration: Mr. X prepared a bill of tk.10,000 and present it to Mr. Y for its acceptance, but Mr. Y does not accept it within 48 hours. So, it is called dishonored by no acceptance. Dishonored by non payment: When the holder represent a bill for payment to its drawee or acceptor, and the drawee fail to pay the amount of the bill then its called dishonored by non payment. Illustration: Mr. X makes a bill of tk.5,000 and Mr. Y accept the bill, but after the maturity date Mr. Y fail to pay the bill amount it is called dishonored by non payment.
Page 18 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Q51. What is acceptance for honor? (May-03) When a bill of exchange has been noted or protested for non acceptance or for better security, any person not already liable on the bill, may accept the bill for the honor of any party thereto, this is called acceptance for honor. Q52. What is meant by payment for honor? (May-03, Nov04) When a bill of exchange has been noted or protested for non-payment, any person may pay the same for the honor of any party liable to pay the same. Such payment is called payment for honor. Q53. What are the acts of insolvency? (Nov-02, May-02) An act of insolvency is some act of the debtor, which shows that he is financially embarrassed, and the debtor performer any act which to be considered acts of insolvency. The acts of insolvency are as follows: 1) If he makes a transfer of all or substantially all his property to a third person for the benefit of his creditors generally. 2) If he makes a transfer of his properly or any part thereof, with the intention to defraud or delay his creditors. 3) If he makes any transfer of his property or any part thereof it would under this (insolvency) or any other enactment for the time being in force, be void as a fraudulent performance if he were adjudged an insolvent. 4) If with intent to defeat or delay his creditors: a) He departs from or remains out of the country. b) He departs from his dwelling house or usual place of business or other wise absent himself. c) He secludes himself so as to deprive his creditors of the means of communicating with him. 5) If any of his property has been sold or attached for a period of not less than 21 days in execution of the decree of any court for the payment of the money. 6) If the petitions to be adjudged an insolvent. 7) If he gives notice to any of his creditors that he has suspended or that he is about to suspend, payment of his debt. 8) If he is imprisoned in execution of the decree of any court for the payment of money. 9) If a creditor has served an insolvency notice in respect of any decree or order for payment of money and if the debtor has not paid the money within the period specified in notice. Q 54. Discuss at length if the following can be insolvent: An infant, foreigner, a married women, joint debtor, company, lunatic (Nov-02) Foreigner: A foreigner can be adjudicated insolvent if he commits an act of insolvent in Bangladesh while resident here. A married woman: In Bangladesh a married women does not suffer from any contractual incapacity. She can own property any contract debts. Therefore she can be declared insolvent under appropriate circumstances.
Page 19 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Joint debtor: When money is borrowed by two or more person jointly, all of them can be declared insolvent on a single petition provided some act of insolvent is committed by each of them or jointly by all. Company: A company cannot be declared insolvent. In case of insolvent companies the proper procedure is winding up. Lunatic: A lunatic can be adjudged insolvent for debts incurred by him while he was sane. It must be noted that a lunatic cannot commit those acts of insolvent, which involve enocious volition. Thus a lunatic cannot stay away from him place of business with intent to defeat & delay his creditors Arbitration Act 1940 Q 55. What matter cannot be referred to arbitration? (May-01) The following matter cannot be referred to arbitration: 1) Matrimonial matters like divorce; 2) Testamentary matter like the validity of a will; 3) Insolvency matters; 4) Matter relating to the guardianship of a minor; and 5) Criminal matters. Q 56. Discuss the grounds on which the court can- (May01) 1. Set a side an award; and 2. Remit an award for reconsideration under the arbitration act 1940 1. The court can set a side an award only in the following cases: 1) When an award be comes void or has been set a side; 2) When an award has been improperly procured or is other wise invalid; 3) An award can not be set a side or remitted on the ground of error of law; 4) When an arbitrator or umpire has misconduct himself. 2. The court can remit an award for reconsideration under the arbitration act 1940 on the basis of following ground: 1) When the award has left undetermined any of the matters referred to arbitration; 2) Where the award is so indefinite as to be incapable of execution; 3) Where an objection to the legality of the award is apparent; 4) Where any new evidence has been found; 5) Where the arbitrator admits his mistake & he asks that the award should be remitted. Q 57. State the essentials of an arbitration agreement? The essentials of an arbitration agreement are as following: 1) An arbitration agreement, to be valid & binding & if must be in written. 2) It must be shown that the parties agreed to settlement of disputes by arbitration. 3) It is not necessary that the name of the person who will act as the arbitrator. 4) Arbitration agreement may be refer to the settlement of present difference or possible future differences; 5) The agreement must satisfy all the essential elements of valid contract.
Page 20 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Q 58. Define legal misconduct consequences of misconduct?
by
an
arbitrator.
What
are
the
Legal misconduct: As per section 30(a) legal misconduct means bribery, undue partiality in favor of one party, arbitrator secretly acquiring an interest in the subject matter of the arbitration, wrongfully refusing to hear a witness of a party etc. Consequences of misconduct: The following consequences will be occurring against misconduct: If the arbitrator or umpire is guilty of misconduct the court will set a side the award. Q 59. Examine the circumstances when the court may modify or correct an award? The court can by order, modify or correct an award in the following cases: 1) Where the award has left undetermined any of the matters not referred to the arbitration & does not effect the decision on the matter referred. 2) Where the award is imperfect; 3) Where the award contains a clerical mistake or an error arising from an omission. Q 60. State under what circumstances the court can remove an arbitrator validity appointed by the parties? The court may on the application of a party, remove an arbitrator or umpire in the following cases: Delay: If the arbitrator or umpire to start proceeding with the reference & making an award. Misconduct: If the arbitrator or umpire has misconduct himself or the proceedings. Q 61. When the court may appoint an arbitrator? The court may appoint an arbitrator in the following cases: 1) Where the agreement provides the arbitrator or arbitrators shall be appointed by the consent of all parties & the all parties do not concur in the appointments. 2) If any appointed arbitrator neglects or refuses to work or is incapable of acting or dies & the arbitration agreement does not show any provision to fill the vacancy & the parties or the arbitrators as the case may be, does not supply the vacancy. 3) Where the parties or the arbitrators are required to appoint an umpire and do not appoint him.
Page 21 of 22
Year wise question solution Business Law
Page 22 of 22
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Going for Broke: Insolvency Tools to Support Cross-Border Asset Recovery in Corruption CasesDari EverandGoing for Broke: Insolvency Tools to Support Cross-Border Asset Recovery in Corruption CasesBelum ada peringkat
- General and Commercial Law Laws of ContractDokumen29 halamanGeneral and Commercial Law Laws of ContractBahadurMehediBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Understanding of Financial Investment, Book 6- For Teens and Young AdultsDari EverandBasic Understanding of Financial Investment, Book 6- For Teens and Young AdultsBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Goods Under Sales of Goods ACTDokumen22 halamanTypes of Goods Under Sales of Goods ACTAlka Singh100% (1)
- Legality of Consideration and ObjectDokumen13 halamanLegality of Consideration and ObjectvijiBelum ada peringkat
- Legal Aspects of Business Transactions: A Complete Guide to the Law Governing Business Organization, Financing, Transactions, and GovernanceDari EverandLegal Aspects of Business Transactions: A Complete Guide to the Law Governing Business Organization, Financing, Transactions, and GovernanceBelum ada peringkat
- Contract Act 4 PDFDokumen18 halamanContract Act 4 PDFyisjoxaBelum ada peringkat
- Law Oral PresntationDokumen2 halamanLaw Oral PresntationOmi RokrBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Contract: Contract: Contract Is An Agreement Enforceable by Law. Between Two orDokumen7 halamanTypes of Contract: Contract: Contract Is An Agreement Enforceable by Law. Between Two orHarinni SivaBelum ada peringkat
- Sem 7 Dissolution of FirmDokumen162 halamanSem 7 Dissolution of FirmPraveshBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Partnership Act EssentialsDokumen27 halamanIndian Partnership Act Essentialsshaleenpatni100% (1)
- Law of PartnershipDokumen63 halamanLaw of PartnershipAyieBelum ada peringkat
- International Sale of GoodsDokumen6 halamanInternational Sale of GoodsSarah HoddinottBelum ada peringkat
- Company Law Business Organisation FormsDokumen51 halamanCompany Law Business Organisation FormsAtiqah DalikBelum ada peringkat
- Commercial Law, Lecture Notes - Law - Prof Hellen Chirry 1Dokumen10 halamanCommercial Law, Lecture Notes - Law - Prof Hellen Chirry 1Anshu Saurabh100% (4)
- Bailment and PledgeDokumen20 halamanBailment and PledgeIndrajBelum ada peringkat
- MBA IB - International Business Laws Notes & Ebook - Second Year Sem 3 - Free PDF Download PDFDokumen319 halamanMBA IB - International Business Laws Notes & Ebook - Second Year Sem 3 - Free PDF Download PDFrohanBelum ada peringkat
- Winding Up of CompanyDokumen5 halamanWinding Up of Companyhrprt_sngh1Belum ada peringkat
- Legal Reasoning MethodsDokumen6 halamanLegal Reasoning MethodsBudget FriendlyBelum ada peringkat
- IP Due Diligence: Assessing Value and RisksDokumen2 halamanIP Due Diligence: Assessing Value and RisksRenu GothwalBelum ada peringkat
- Law of TortsDokumen22 halamanLaw of TortsIramPeerzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Business & Industrial Law Complete SlidesDokumen469 halamanBusiness & Industrial Law Complete SlidesKamran Ali AnsariBelum ada peringkat
- INR-YEN CURRENCY SWAP AGREEMENTDokumen19 halamanINR-YEN CURRENCY SWAP AGREEMENTneha sharma100% (1)
- Portfolio Selection Markowitz ModelDokumen15 halamanPortfolio Selection Markowitz Modelgaurav112011Belum ada peringkat
- Sample Question On Contract LawDokumen6 halamanSample Question On Contract LawNik Nur Fatehah50% (2)
- 17 Chapter 7Dokumen33 halaman17 Chapter 7tabassum_rimi100Belum ada peringkat
- Invitation To OfferDokumen8 halamanInvitation To OfferEsha AmerBelum ada peringkat
- Importance of Contracts - Uday Sharma Ba LLBDokumen2 halamanImportance of Contracts - Uday Sharma Ba LLBshubhamBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Garnishee OrderDokumen5 halamanWhat Is A Garnishee Ordergazi faisalBelum ada peringkat
- Contract of Indemnity Contract of GuaranteeDokumen19 halamanContract of Indemnity Contract of Guaranteekalra_kamal12100% (2)
- Mercantile LawDokumen11 halamanMercantile LawNitesh Matta100% (1)
- Ema Ge Berk CF 2GE SG 23Dokumen12 halamanEma Ge Berk CF 2GE SG 23Sascha SaschaBelum ada peringkat
- Q. 16 Functions of A Merchant BankerDokumen3 halamanQ. 16 Functions of A Merchant BankerMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAKBelum ada peringkat
- Law of Agency in PakistanDokumen18 halamanLaw of Agency in PakistanDania RaheelBelum ada peringkat
- Discharge of Contract Unit 3Dokumen5 halamanDischarge of Contract Unit 3Shubham Jain ModiBelum ada peringkat
- LLB 1st Semester Business Organisation & Communication Notes by Richa GuptaDokumen33 halamanLLB 1st Semester Business Organisation & Communication Notes by Richa GuptaRishi tiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Ema Ge Berk CF 2GE SG 04Dokumen13 halamanEma Ge Berk CF 2GE SG 04Duygu ÇınarBelum ada peringkat
- TABL1710 Lecture Wk5 - Exclusion Clauses, Capacity, Privity, Vitiating ElementsDokumen10 halamanTABL1710 Lecture Wk5 - Exclusion Clauses, Capacity, Privity, Vitiating Elementsriders29Belum ada peringkat
- Defining A Joint Venture'S Scope of Business: Key Issues To ConsiderDokumen10 halamanDefining A Joint Venture'S Scope of Business: Key Issues To ConsiderFirman HamdanBelum ada peringkat
- BookDokumen235 halamanBookSyed HamdanBelum ada peringkat
- Company Law 1 NewDokumen62 halamanCompany Law 1 NewmuhumuzaBelum ada peringkat
- Contract Act 1872 PDFDokumen51 halamanContract Act 1872 PDFRana HumzaBelum ada peringkat
- Government Securities Market: Role and TradingDokumen11 halamanGovernment Securities Market: Role and TradingVikasDalal100% (2)
- Contract LecturesDokumen42 halamanContract LecturesFaysal FahimBelum ada peringkat
- Business Law Exam ReviewDokumen4 halamanBusiness Law Exam ReviewnishuBelum ada peringkat
- Securities Contracts Regulation Act 1956Dokumen32 halamanSecurities Contracts Regulation Act 1956Shetty_Suraj80% (5)
- Partnership Act., 1932Dokumen26 halamanPartnership Act., 1932Shoyeb Anwarul AzimBelum ada peringkat
- Law of Agency SlideDokumen20 halamanLaw of Agency SlidePacific Hunter JohnnyBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Chapter 5 Internal Reconstruction PDFDokumen22 halaman1 Chapter 5 Internal Reconstruction PDFAbhiramBelum ada peringkat
- Unconscionability A Unifying Theme in EquitDokumen3 halamanUnconscionability A Unifying Theme in EquitshanicebegumBelum ada peringkat
- Meetings and ProceedingsDokumen11 halamanMeetings and ProceedingssreeBelum ada peringkat
- Chuma Contract Law NotesDokumen38 halamanChuma Contract Law NotesDickson Tk Chuma Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes - ConsiderationDokumen3 halamanLecture Notes - ConsiderationAdam 'Fez' Ferris100% (4)
- Partnership Act 1932Dokumen32 halamanPartnership Act 1932Padma TotaBelum ada peringkat
- Business Law AssignmentDokumen12 halamanBusiness Law AssignmentReema Mamtani0% (1)
- For Journal, Ethiopia-Quwait BITDokumen6 halamanFor Journal, Ethiopia-Quwait BITTewachew100% (1)
- Chapter - 2 Conceptual Framework of DividendDokumen36 halamanChapter - 2 Conceptual Framework of DividendMadhavasadasivan PothiyilBelum ada peringkat
- CHARTER of The Co Regulates The External Affairs of The CoDokumen6 halamanCHARTER of The Co Regulates The External Affairs of The CoVidhya SagarBelum ada peringkat
- Business Law Instructor: Arbab Shujja Notes By: Munir Ahmed: Types of CodesDokumen35 halamanBusiness Law Instructor: Arbab Shujja Notes By: Munir Ahmed: Types of CodesIqra AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Red Book - 222 PDFDokumen353 halamanRed Book - 222 PDFrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- 1.2.23 Con Mix DesignDokumen1 halaman1.2.23 Con Mix DesignrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Circulating PumpDokumen22 halamanCirculating PumprramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Ah121 PDFDokumen48 halamanAh121 PDFAnonymous S9qBDVkyBelum ada peringkat
- Ascii Code.Dokumen1 halamanAscii Code.rramadanBelum ada peringkat
- HVAC Controls and Building Automation SystemsDokumen340 halamanHVAC Controls and Building Automation Systemsmthein870% (1)
- Chapter 6 - Water Supply and Distribution PDFDokumen16 halamanChapter 6 - Water Supply and Distribution PDFEngineering ESIIBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Hydraulics Russian PDFDokumen6 halamanBasic Hydraulics Russian PDFrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Ramzi 2018Dokumen12 halamanRamzi 2018rramadanBelum ada peringkat
- SMK Products Company InformationDokumen7 halamanSMK Products Company InformationrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Hydraulics Russian PDFDokumen6 halamanBasic Hydraulics Russian PDFrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- JBT 10830-2008 液压电磁换向座阀Dokumen15 halamanJBT 10830-2008 液压电磁换向座阀rramadanBelum ada peringkat
- FIDIC Model Ugovora o Pruzanju UslugaDokumen50 halamanFIDIC Model Ugovora o Pruzanju UslugaJelena Peric100% (7)
- JBT 10830-2008 液压电磁换向座阀 PDFDokumen11 halamanJBT 10830-2008 液压电磁换向座阀 PDFrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Viewcontent CgiDokumen8 halamanViewcontent CgiNurul Izzati Raihan RamziBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Concrete MixDokumen2 halamanDesign of Concrete MixLIM ChanthaBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Foods That Drain Your EnergyDokumen5 halaman3 Foods That Drain Your EnergyrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Implementing BS 8500-1 for Durable Concrete StructuresDokumen13 halamanImplementing BS 8500-1 for Durable Concrete StructuresJimmy Lopez100% (1)
- Studyproject 121230083452Dokumen39 halamanStudyproject 121230083452rramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Ufer GroundDokumen4 halamanUfer GroundjemayenBelum ada peringkat
- E Books StudioDokumen1 halamanE Books StudiorramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Hydraulics RussianDokumen6 halamanBasic Hydraulics RussianrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- E Books StudioDokumen1 halamanE Books StudiorramadanBelum ada peringkat
- SMK Products Company InformationDokumen7 halamanSMK Products Company InformationrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- قائمة الدول الأكثر والأقلDokumen1 halamanقائمة الدول الأكثر والأقلrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- SMK Products Company InformationDokumen7 halamanSMK Products Company InformationrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- BursaDokumen2 halamanBursarramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Fidic - Power Point PresentationDokumen46 halamanFidic - Power Point PresentationDragan Gligorov100% (1)
- Gebruiksaanwijzing enDokumen2 halamanGebruiksaanwijzing enrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Marine Transportation: SecurityDokumen1 halamanMarine Transportation: SecurityrramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Malouf Explores Complex Nature of IdentityDokumen1 halamanMalouf Explores Complex Nature of Identitymanoriii0% (1)
- HexaflexDokumen10 halamanHexaflexCharlie Williams100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Project Cost ManagementDokumen48 halamanChapter 7 Project Cost Managementafifah suyadiBelum ada peringkat
- Detect Organic Elements with Sodium FusionDokumen10 halamanDetect Organic Elements with Sodium FusionMukundBelum ada peringkat
- Determinants of Consumer BehaviourDokumen16 halamanDeterminants of Consumer BehaviouritistysondogBelum ada peringkat
- Operations Management Success FactorsDokumen147 halamanOperations Management Success Factorsabishakekoul100% (1)
- Day1 1Dokumen17 halamanDay1 1kaganp784Belum ada peringkat
- 11 Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis Caused by Food AllergyDokumen6 halaman11 Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis Caused by Food AllergyramaBelum ada peringkat
- Miranda V AgDokumen3 halamanMiranda V AgCARLO JOSE BACTOLBelum ada peringkat
- Ganzon Vs CADokumen3 halamanGanzon Vs CARaymond RoqueBelum ada peringkat
- TRU BRO 4pg-S120675R0 PDFDokumen2 halamanTRU BRO 4pg-S120675R0 PDFtomBelum ada peringkat
- Configure Windows 10 for Aloha POSDokumen7 halamanConfigure Windows 10 for Aloha POSBobbyMocorroBelum ada peringkat
- GUIA REPASO 8° BÁSICO INGLÉS (Unidades 1-2)Dokumen4 halamanGUIA REPASO 8° BÁSICO INGLÉS (Unidades 1-2)Anonymous lBA5lD100% (1)
- Ice Task 2Dokumen2 halamanIce Task 2nenelindelwa274Belum ada peringkat
- Sta. Ignacia High School: Philosophy 101Dokumen1 halamanSta. Ignacia High School: Philosophy 101Mira VeranoBelum ada peringkat
- A Systematic Literature Review of Empirical Research On ChatGPT in EducationDokumen23 halamanA Systematic Literature Review of Empirical Research On ChatGPT in Educationgraciduttra.profBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Notes and ReiewDokumen6 halamanChapter 1 Notes and ReiewTricia Mae Comia AtienzaBelum ada peringkat
- Cost-Benefit Analysis of The ATM Automatic DepositDokumen14 halamanCost-Benefit Analysis of The ATM Automatic DepositBhanupriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Linux OS MyanmarDokumen75 halamanLinux OS Myanmarweenyin100% (15)
- Statistics Machine Learning Python DraftDokumen319 halamanStatistics Machine Learning Python DraftnagBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Ethnic Foods: Angelina Rianti, Agnes E. Novenia, Alvin Christopher, Devi Lestari, Elfa K. ParassihDokumen6 halamanJournal of Ethnic Foods: Angelina Rianti, Agnes E. Novenia, Alvin Christopher, Devi Lestari, Elfa K. ParassihHerlinaBelum ada peringkat
- 1st PU Chemistry Test Sep 2014 PDFDokumen1 halaman1st PU Chemistry Test Sep 2014 PDFPrasad C M86% (7)
- Personal Branding dan Positioning Mempengaruhi Perilaku Pemilih di Kabupaten Bone BolangoDokumen17 halamanPersonal Branding dan Positioning Mempengaruhi Perilaku Pemilih di Kabupaten Bone BolangoMuhammad Irfan BasriBelum ada peringkat
- Edu 510 Final ProjectDokumen13 halamanEdu 510 Final Projectapi-324235159Belum ada peringkat
- Predict Y Scores Using Linear Regression EquationDokumen6 halamanPredict Y Scores Using Linear Regression EquationreebenthomasBelum ada peringkat
- B.A./B.Sc.: SyllabusDokumen185 halamanB.A./B.Sc.: SyllabusKaran VeerBelum ada peringkat
- New Titles List 2014, Issue 1Dokumen52 halamanNew Titles List 2014, Issue 1Worldwide Books CorporationBelum ada peringkat
- 202002Dokumen32 halaman202002Shyam SundarBelum ada peringkat
- Needs and Language Goals of Students, Creating Learning Environments andDokumen3 halamanNeeds and Language Goals of Students, Creating Learning Environments andapi-316528766Belum ada peringkat
- Fs Casas FinalDokumen55 halamanFs Casas FinalGwen Araña BalgomaBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsDari EverandA Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsBelum ada peringkat
- The Business of Broadway: An Insider's Guide to Working, Producing, and Investing in the World's Greatest Theatre CommunityDari EverandThe Business of Broadway: An Insider's Guide to Working, Producing, and Investing in the World's Greatest Theatre CommunityBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Theater for Nontechnical People: Second EditionDari EverandTechnical Theater for Nontechnical People: Second EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Broadway General Manager: Demystifying the Most Important and Least Understood Role in Show BusinessDari EverandBroadway General Manager: Demystifying the Most Important and Least Understood Role in Show BusinessBelum ada peringkat
- Learn the Essentials of Business Law in 15 DaysDari EverandLearn the Essentials of Business Law in 15 DaysPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (13)
- Fundamentals of Theatrical Design: A Guide to the Basics of Scenic, Costume, and Lighting DesignDari EverandFundamentals of Theatrical Design: A Guide to the Basics of Scenic, Costume, and Lighting DesignPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- Digital Technical Theater Simplified: High Tech Lighting, Audio, Video and More on a Low BudgetDari EverandDigital Technical Theater Simplified: High Tech Lighting, Audio, Video and More on a Low BudgetBelum ada peringkat
- What Are You Laughing At?: How to Write Humor for Screenplays, Stories, and MoreDari EverandWhat Are You Laughing At?: How to Write Humor for Screenplays, Stories, and MorePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Law of Contract Made Simple for LaymenDari EverandLaw of Contract Made Simple for LaymenPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (9)
- Crash Course Business Agreements and ContractsDari EverandCrash Course Business Agreements and ContractsPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (3)
- Contract Law for Serious Entrepreneurs: Know What the Attorneys KnowDari EverandContract Law for Serious Entrepreneurs: Know What the Attorneys KnowPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- How to Win Your Case In Traffic Court Without a LawyerDari EverandHow to Win Your Case In Traffic Court Without a LawyerPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- How to Win Your Case in Small Claims Court Without a LawyerDari EverandHow to Win Your Case in Small Claims Court Without a LawyerPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Reality Television Contracts: How to Negotiate the Best DealDari EverandReality Television Contracts: How to Negotiate the Best DealBelum ada peringkat
- Independent Film Producing: How to Produce a Low-Budget Feature FilmDari EverandIndependent Film Producing: How to Produce a Low-Budget Feature FilmBelum ada peringkat
- Starting Your Career as a Photo Stylist: A Comprehensive Guide to Photo Shoots, Marketing, Business, Fashion, Wardrobe, Off Figure, Product, Prop, Room Sets, and Food StylingDari EverandStarting Your Career as a Photo Stylist: A Comprehensive Guide to Photo Shoots, Marketing, Business, Fashion, Wardrobe, Off Figure, Product, Prop, Room Sets, and Food StylingPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- How to Improvise a Full-Length Play: The Art of Spontaneous TheaterDari EverandHow to Improvise a Full-Length Play: The Art of Spontaneous TheaterBelum ada peringkat
- The Perfect Stage Crew: The Complete Technical Guide for High School, College, and Community TheaterDari EverandThe Perfect Stage Crew: The Complete Technical Guide for High School, College, and Community TheaterBelum ada peringkat