Sheet An A
Diunggah oleh
Bakir JaberDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sheet An A
Diunggah oleh
Bakir JaberHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sun 5/2/2012
Introduction to anatomy
Anatomical Introduction - Basic Terms :
Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts in the body.
* (ology ) is a suffix means science .
Physiology: the science that deals with the normal functions of living organisms and their systems Gross Anatomy: deals with structures visible with the unaided eye, also called "Macroscopic
anatomy". e.g : like observing the liver by your eyes only , see the size of it , the color of it and any other details that you can see only by your naked eye.
Histology: the study of the microscopic structure of tissues, also
Called "Microscopic anatomy". ((Histologymicroscopic))
Pathology : the science of diseases in the body ( study the diseases , and it causes , processes, developments
and consequences )
Cytology : the science of the cell ( structure , formation and function of the cell )
Clinical Anatomy: anatomy as applied to clinical practice.
Radiology : the science which uses the X-RAY radiation to study the skeletal system. Basic Anatomy: to study minimal structures and their relations to other structures. Clinical Anatomy : anatomy as applied to clinical particle
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
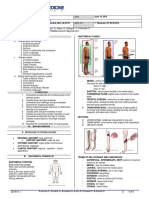
Anatomical terms : -Positions :
Anatomical position : a standard position used in anatomy and clinical medicine to allow accurate and consistent description of one body part in relation to another. Features: - Standing erect - The face directed anteriorly (looking forward), (abdominal wall=anterior, vertebral column = posterior) - palms of the hand facing forward - Feet together (or slightly separated) - the head is upwards (cephalic , superior ) - upper limps are away from the side of the body 1
Sun 5/2/2012
Introduction to anatomy
Supine position: lying on the back.
Prone position: lying face down.
Anatomical Planes :
1- Sagital : Mid sagittal plane (Median plane) , the vertical plane passing through the midline of the body and dividing it into right and .left halves Any plane parallel to this plane is termed paramedian or .sagittal plane 2-Horizontal (Transverse): divides the body into upper and lower parts 3-Coronal (Frontal): divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
Sun 5/2/2012
Introduction to anatomy
Anatomical terms of position :
Anterior (Ventral) In front of (nearer to the front of the body). e.g ; The liver is anterior to the kidneys. In back of nearer to the back of the body. e.g : Palmar surface of the hand is anterior in anatomical position, while the dorsal surface is posterior. Above e.g : The eyes are superior to the mouth. Below e.g : The nose is inferior to the eyes. nearer to the mid sagittal line (median line). away from the mid sagittal line (median line). nearer to the surface. e.g : Stomach is superficial in the abdominal cavity. away from the surface e.g : Kidneys are deep in the abdominal cavity. nearer to the origin of the limb (nearer to a specific point). e.g : Elbow joint is proximal whereas wrist joint is distal. away from the origin of the limb (farther from a specific point) e.g : whereas elbow joint is distal. Shoulder joint is proximal two parts of the body on the same side e.g : The right hand is ipsilateral to the right foot two parts of the body one on the right and the other on the left. e.g : The left hand is contralateral to the right foot. toward the inside. toward the outside.
Posterior (Dorsal)
Superior (Cephalic) Inferior (Caudal) Medial Lateral Superficial Deep Proximal
Distal
Ipsilateral Contralateral
Internal External
Sun 5/2/2012
Introduction to anatomy
Anatomical terms of movement
Flexion .to bend at a joint, or to reduce the angl
Extension Adduction
.to straighten at a joint, or to increase the angle .movement toward the midline
Abduction Supination
movement away from the midline .to rotate the forearm so that the palm faces forward
Pronation
to rotate the forearm so that the palm faces .backward .movement of part of the body around its long axis .to turn inward
Rotation Medial Rotation
Lateral Rotation Circumduction
to turn outward Movement of a part in a circular direction (a combination of flexion, adduction, extension, and .)abduction
Sun 5/2/2012
Introduction to anatomy
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- JustDokumen16 halamanJustBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s05 Ms 3Dokumen10 halaman0610 s05 Ms 3Bakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s05 Ir 5Dokumen8 halaman0610 s05 Ir 5Bakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s05 QP 5Dokumen8 halaman0610 s05 QP 5Bakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s05 Ms 1 PDFDokumen4 halaman0610 s05 Ms 1 PDFBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 4CH1 - 2C - Que - 20220118 IbrahimDokumen28 halaman4CH1 - 2C - Que - 20220118 IbrahimBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- Biology ............................................................................................................................ 2Dokumen15 halamanBiology ............................................................................................................................ 2Bakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- Tiki Taka Notes Final PDFDokumen104 halamanTiki Taka Notes Final PDFAditiSahak62Belum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 Ir 5 PDFDokumen8 halaman0610 s07 Ir 5 PDFBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question PaperDokumen3 halaman0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question PaperBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 QP 6 PDFDokumen12 halaman0610 s07 QP 6 PDFBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 QP 2 PDFDokumen24 halaman0610 s07 QP 2 PDFBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question PaperDokumen2 halaman9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question Paperkalpanaparikh20003331Belum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 ErDokumen27 halaman0610 s07 ErBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 QP 5 PDFDokumen8 halaman0610 s07 QP 5 PDFBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 QP 1 PDFDokumen16 halaman0610 s07 QP 1 PDFBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 Ms 3 PDFDokumen17 halaman0610 s07 Ms 3 PDFBakir Jaber100% (1)
- Physics Jan 2011 Unit 1 EdexcelDokumen24 halamanPhysics Jan 2011 Unit 1 EdexcelRatna ChowdhryBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 Ms 2 PDFDokumen7 halaman0610 s07 Ms 2 PDFBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 Ms 6 PDFDokumen4 halaman0610 s07 Ms 6 PDFBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- Najeeb PlanDokumen1 halamanNajeeb PlanBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s07 GT PDFDokumen1 halaman0610 s07 GT PDFBakir JaberBelum ada peringkat
- C1 January 2011Dokumen24 halamanC1 January 2011thivisantenBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel S1 QP Jan 2011Dokumen24 halamanEdexcel S1 QP Jan 2011Issam SaifBelum ada peringkat
- NCXZDokumen5 halamanNCXZNoraLambBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel S1 QP Jan 2011Dokumen24 halamanEdexcel S1 QP Jan 2011Issam SaifBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- CLASIFICACIÓN AO PEDIATRICA 2008-09-PediatricClassificationBrochureDokumen36 halamanCLASIFICACIÓN AO PEDIATRICA 2008-09-PediatricClassificationBrochurefjcrisafi100% (1)
- Fisiologi PenglihatanDokumen76 halamanFisiologi PenglihatanArsyil Ardiman MirwanBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Secondary Academy V Map GSE 32 40 Body and HealthDokumen1 halamanUpper Secondary Academy V Map GSE 32 40 Body and HealthАндрій ЮрківBelum ada peringkat
- 2. Atlas of Anatomy. Netter 3. An Atlas Of Surgical Anatomy Masquelet.pdf 4. Anatomie Sрringer.pdf 5. Anatomy Coloring Book Benjamin Cummings PDFDokumen2 halaman2. Atlas of Anatomy. Netter 3. An Atlas Of Surgical Anatomy Masquelet.pdf 4. Anatomie Sрringer.pdf 5. Anatomy Coloring Book Benjamin Cummings PDFmrmarcoguimaBelum ada peringkat
- Pocket Atlas of Radiographic Anatomy 21-30Dokumen10 halamanPocket Atlas of Radiographic Anatomy 21-30Ivan Alejandro Gonzalez DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Skin TractionDokumen10 halamanSkin Tractionpritinez2516100% (1)
- Neuroscience 4th Edition Lundy Test BankDokumen4 halamanNeuroscience 4th Edition Lundy Test Bankstrangstuprumczi100% (30)
- SRB Bedside ClinicDokumen592 halamanSRB Bedside ClinicAbinesh Kumar100% (1)
- AnatomyDokumen91 halamanAnatomysarahBelum ada peringkat
- Muscle CardsDokumen9 halamanMuscle Cardsapi-328688284Belum ada peringkat
- Occlusion, Articulators, FacebowDokumen40 halamanOcclusion, Articulators, FacebowMuaiyed Buzayan Akremy100% (1)
- Chapter 12 - HeartDokumen3 halamanChapter 12 - HeartAngelyka CabaloBelum ada peringkat
- NEET PG 2020 Questions: (Memory Based)Dokumen25 halamanNEET PG 2020 Questions: (Memory Based)Anmol KudalBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic UrethralDokumen2 halamanHydraulic UrethralMalgorzata LisowskaBelum ada peringkat
- Ruba Ali - Home Base GuideDokumen173 halamanRuba Ali - Home Base GuideShahenda El-MenshawyBelum ada peringkat
- Shoulder DysfociaDokumen92 halamanShoulder DysfociaKagomie SaskieBelum ada peringkat
- DOPS Revision - Orthopaedic TestingDokumen38 halamanDOPS Revision - Orthopaedic TestingDr-Syed Hammad Hussain-GilaniBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Lower Limb Assessment Flow SheetDokumen2 halamanBasic Lower Limb Assessment Flow Sheetمحمد نعمة جياد100% (1)
- Anatomy 1.2 Anatomy in MotionDokumen4 halamanAnatomy 1.2 Anatomy in Motionlovelots1234Belum ada peringkat
- Dumbbell Step-Up: ExecutionDokumen11 halamanDumbbell Step-Up: ExecutionDavid RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Head and Neck SurgeryDokumen92 halamanHead and Neck SurgeryAlbert GheorgheBelum ada peringkat
- Alberta Infant Motor Scale RecordsDokumen6 halamanAlberta Infant Motor Scale Recordsgrouch12153% (19)
- Esophageal Reconstruction With Large Intestine: 1. Vascular Anatomy of The ColonDokumen26 halamanEsophageal Reconstruction With Large Intestine: 1. Vascular Anatomy of The ColonCitra AryantiBelum ada peringkat
- Auricular Acupuncture 2013 SummerDokumen89 halamanAuricular Acupuncture 2013 Summerdoringrama100% (3)
- Zimede Medical Catalogue-SpanishDokumen16 halamanZimede Medical Catalogue-SpanishDerly PantojaBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 15 Sensory SystemDokumen23 halamanCh. 15 Sensory SystemJackieFernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Op&fdDokumen12 halamanOp&fdHazim Rhman AliBelum ada peringkat
- RTOG Breast Cancer Atlas For Radiation Therapy PlanningDokumen71 halamanRTOG Breast Cancer Atlas For Radiation Therapy Planningdoctordoctor80Belum ada peringkat
- DA Manual.3Dokumen14 halamanDA Manual.3Mayleen LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Ha&P - Semi ReviewerDokumen71 halamanHa&P - Semi ReviewerLittle StuartBelum ada peringkat