Chapter 12 - Motivation and Work
Diunggah oleh
Maddy TienDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 12 - Motivation and Work
Diunggah oleh
Maddy TienHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 12 Motivation and Work
Physiological readiness Sexual Disorders- problems that consistently impair sexual arousal or functioning In Men Premature ejaculation- ejaculation before they or their partners wish Impotence- inability to have or maintain erection In Women Orgasmic disorder- infrequent or absent orgasms Sexual Orientation- an enduring sexual attraction toward members of wither ones own gender (homosexual orientation) or the other gender (heterosexual orientation) Sexually explicit material may lead people to perceive their partners ascomparatively less appealing and to devalue their relationships. Sexually coercive material tends to increase viewers acceptance of rape andviolence toward women. In combination with the internal hormonal push and the external pull of sexualstimuli, fantasies (imagined stimuli) influence sexual arousal. The stimuli inside our headsour imaginationcan influence sexual arousal anddesire. hormones PYY- fullness hormone secreted by digestive tract Ghrelin- hunger hormone secreted by empty stomach
Orexin- hunger-triggering hormone secreted by hypothalamus Leptin- protein secreted by fat cells; increases metabolism Insulin- controls blood glucose secreted by pancreas Adolescent Sexuality Adolescents physical maturation fosters a sexual dimension to their emergingidentity, but rates of teen intercourse vary from culture to culture. In the twentieth century increased teen sexual activity in North America wasreflected in increased rates of adolescent pregnancies. teen pregnancy 1/3 of sexually active teen males use condoms regularly American teens have less sex than Euro. teens, but use less contraception, andso have more babies and abortions TJ 5 reasons people don't use contraceptives: 1. ignorance 2. guilt related to sexual activity 3. minimum communication about birth control (awkward conversation!) 4. alcohol use (too drunk to remember) 5. mass media norms of unprotected promiscuity Sexually Transmitted Infections STIssexually transmitted infections, such as the human papilloma virus, AIDS,and othershave spread rapidly.
People under the age of 25 accounts for two-thirds of such infections, and teenagegirls seem especially vulnerable because of their less mature bodies and lower levels of protective antibodies. Attempts to protect teens through comprehensive sex-education programs includea greater emphasis on teen abstinence. High intelligence, religiosity, father presence and participation in service learning programs tend to be predictors of teen sexual restraint. Sexual Orientation Sexual orientationan enduring sexual attraction toward members of either onesown sex (homosexual orientation) or the other sex (heterosexual orientation). Studies indicate that about 3 or 4 percent of men and 1 or 2 percent of women arehomosexual, and that sexual orientation is enduring. Research does not support cause-effect links between homosexuality and any of the following; A childs relationships with parents, father-absent homes, fear or hatred of peopleof the other gender, childhood sexual experiences, peer relationship, or datingexperiences. Evidence supporting the likelihood of a biological component of homosexuality isfound in studies of same-sex behavior in several hundred species, straight-gaydifferences in body and brain characteristics, genetic studies of family membersand twins, and the effect of exposure to certain hormones during critical periodsof prenatal development. The cell cluster was reliably larger in heterosexual men than I women andhomosexual men. Achievement Motivation- a desire for significant accomplishment For mastery of things, people, or ideas For attaining a high standard McClelland and Atkinson believed fantasies would reflect achievement concerns TJ
Intrinsic Motivation- desire to perform a behavior for its own sake or to beeffective Extrinsic Motivation- desire to perform a behavior due to promised rewards or threats of punishment Industrial/Organizational (I/O) Psychology- sub-field of psychology that studiesand advises on workplace behavior I/O Psychologists-help organizations select and train employees, boost moraleand productivity, and design products and assess responses to them Task Leadership- goal-oriented leadership that sets standards, organizes work,and focuses attention on goals Social Leadership-group-oriented leadership that builds teamwork, mediatesconflict, and offers support Theory X Assumes that workers are basically lazy, error-prone, and extrinsically motivated by money Should be directed from above Theory Y Assumes that, given challenge and freedom, workers are motivated to achieveself-esteem and to demonstrate their competence and creativity
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Psychosexual A. Physiological Aspects of Human Sexuality: ExampleDokumen11 halamanPsychosexual A. Physiological Aspects of Human Sexuality: ExampleJuanaly Badiola100% (1)
- Brand Plan For Dienogest by Saqib AltafDokumen13 halamanBrand Plan For Dienogest by Saqib AltafSakib ZabooBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 12Dokumen3 halamanChap 12Kevin CorpBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatry SeminarDokumen152 halamanPsychiatry SeminarMichael GebreamlakBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Outline Itp.Dokumen8 halamanLearning Outline Itp.Darlyn JabiniaoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 Motivation BasicDokumen31 halamanChapter 11 Motivation Basicosrah_gBelum ada peringkat
- Dimensions of Human SexualityDokumen43 halamanDimensions of Human SexualityFroilan Tindugan100% (1)
- Chapter 12 MotivationDokumen7 halamanChapter 12 MotivationAazmeer RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding of The Self - Sexual SelfDokumen53 halamanUnderstanding of The Self - Sexual SelfDANE PIAMONTEBelum ada peringkat
- Sexualtiy and Sexual HealthDokumen51 halamanSexualtiy and Sexual HealthRashmi GoswamiBelum ada peringkat
- Sexuality and Sexual HealthDokumen87 halamanSexuality and Sexual HealthFroilan TinduganBelum ada peringkat
- Physical and Cognitive Development in Emerging and Young AdulthoodDokumen17 halamanPhysical and Cognitive Development in Emerging and Young AdulthoodLouise Nicole AlcobaBelum ada peringkat
- Safeguarding of MinorsDokumen50 halamanSafeguarding of MinorsNgan NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Theories of Personality: DR Owolabi Shakirah Psychiatry Department AkthDokumen51 halamanTheories of Personality: DR Owolabi Shakirah Psychiatry Department AkthKomal TalrejaBelum ada peringkat
- Nature of Human SexualityDokumen20 halamanNature of Human Sexualitysunil518100% (1)
- Sexuality and Sexual HealthDokumen80 halamanSexuality and Sexual HealthKishore RathoreBelum ada peringkat
- Family Health 1Dokumen19 halamanFamily Health 1Melvita FabiaBelum ada peringkat
- 6+ +sexualityDokumen113 halaman6+ +sexualityalieraongaco100% (1)
- II. Sex, Gender and SexualityDokumen56 halamanII. Sex, Gender and SexualityJohn Raymund100% (1)
- Ch08 - PPTs - Morris101chapter 8Dokumen57 halamanCh08 - PPTs - Morris101chapter 8Annie KwonBelum ada peringkat
- The Sexual SelfDokumen25 halamanThe Sexual Selfkristinebea22Belum ada peringkat
- Human SexualityDokumen113 halamanHuman SexualityCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligBelum ada peringkat
- NCM105 8th Psychosexual DisordersDokumen6 halamanNCM105 8th Psychosexual DisordersKamx MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Psyc311 CH 11-12 AdolescenceDokumen78 halamanPsyc311 CH 11-12 Adolescencedanish5_2020Belum ada peringkat
- Class 10 Module - 15v9 - FinalDokumen45 halamanClass 10 Module - 15v9 - FinalThanh Hang PhạmBelum ada peringkat
- Myers AP - Unit 09 NotesDokumen150 halamanMyers AP - Unit 09 NotesHuyen-Yen HoangBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment of PsychologyDokumen28 halamanAssignment of Psychologymadina100% (1)
- ParaphilicDokumen38 halamanParaphilicJerry GohBelum ada peringkat
- Modular Chpater Five Emotion and MotivationDokumen116 halamanModular Chpater Five Emotion and Motivationzekarias wondafrashBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts & Patterns of Human Behavior Mal Adap LecDokumen4 halamanConcepts & Patterns of Human Behavior Mal Adap LecAshtua MandixBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewerDokumen46 halamanPsychiatric Nursing ReviewerDick Morgan Ferrer100% (1)
- The Physical Side of Human SexualityDokumen5 halamanThe Physical Side of Human SexualityJunjun CaoliBelum ada peringkat
- HealthDokumen2 halamanHealthAerol QuizonBelum ada peringkat
- Supporting Gender Independent Children and Their FamiliesDokumen14 halamanSupporting Gender Independent Children and Their FamiliesGender SpectrumBelum ada peringkat
- Elmeida Effendy Psychiatric DepartmentDokumen35 halamanElmeida Effendy Psychiatric DepartmentputriBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Personality Disorder Seminar CGRDokumen61 halaman1 Personality Disorder Seminar CGRgautambobBelum ada peringkat
- Psyc 311Dokumen20 halamanPsyc 311laralesch2002Belum ada peringkat
- Gender and Human SexualityDokumen10 halamanGender and Human SexualityHarlene Dela Cruz Ozar100% (1)
- Fcos 201Dokumen97 halamanFcos 201joseckisecBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Mental Disorder in AdolescentDokumen20 halamanManagement of Mental Disorder in AdolescentMuhammad mukramBelum ada peringkat
- Health Promotion of The Adolescent and FamilyDokumen31 halamanHealth Promotion of The Adolescent and FamilyVanisa NurmaheriBelum ada peringkat
- Sexual Self PDFDokumen50 halamanSexual Self PDFyoeliyyBelum ada peringkat
- Child Abuse: Dr. B C Mutai, MBCHB, Mmed (Paeds & Child Health)Dokumen33 halamanChild Abuse: Dr. B C Mutai, MBCHB, Mmed (Paeds & Child Health)okwadha simionBelum ada peringkat
- Psyc311 CH 11-12 AdolescenceDokumen62 halamanPsyc311 CH 11-12 AdolescenceDanishwaran SundrasellanBelum ada peringkat
- Kastner Adol Psyc Dev Humbio 526 No Pics 2011Dokumen28 halamanKastner Adol Psyc Dev Humbio 526 No Pics 2011Zainul AbedeenBelum ada peringkat
- The Sexual SelfDokumen26 halamanThe Sexual SelfMalaika Aubrey Cao PalomoBelum ada peringkat
- The Sexual SelfDokumen33 halamanThe Sexual SelfEdrian Genesis SebleroBelum ada peringkat
- MCN 04 Sexual Health and Responsible ParenthoodDokumen35 halamanMCN 04 Sexual Health and Responsible ParenthoodBardiaga JmayBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 13Dokumen28 halamanChapter 13Kayelita Wu100% (2)
- Health8w1 210818165654Dokumen12 halamanHealth8w1 210818165654Joveena VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Harvey Milkman PowerpointDokumen234 halamanHarvey Milkman PowerpointHilux23Belum ada peringkat
- Sexology Lecture NotesDokumen32 halamanSexology Lecture NotesanaBelum ada peringkat
- The Sexual SelfDokumen67 halamanThe Sexual SelfJan Efraime Rian Sapla Marquez100% (2)
- K-2 Child & Adolescent 1Dokumen35 halamanK-2 Child & Adolescent 1santayohanaBelum ada peringkat
- SexualDokumen45 halamanSexualSharmela BrijmohanBelum ada peringkat
- Sexual DisorderDokumen10 halamanSexual Disorderbemina jaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6: Social InteractionDokumen89 halamanLecture 6: Social InteractionHoàng Bảo HânBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 - What Drives UsDokumen30 halamanChapter 11 - What Drives UsChristina CannilaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Patients' Sexual Problems: A Reference Handbook for Healthcare ProfessionalsDari EverandUnderstanding Patients' Sexual Problems: A Reference Handbook for Healthcare ProfessionalsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Teen Pregnancy - HoniaraDokumen33 halamanTeen Pregnancy - HoniaraMillenium Ayurveda80% (5)
- Family PlanningDokumen32 halamanFamily Planningapi-263460114Belum ada peringkat
- 132 HealthwiseDokumen9 halaman132 Healthwisemichael.staffordBelum ada peringkat
- 20.04.2021 Testi-1-1Dokumen6 halaman20.04.2021 Testi-1-1Tanmay NainBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding in The Adolescent CME 2020Dokumen7 halamanAbnormal Uterine Bleeding in The Adolescent CME 2020Mariana HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Male SterilizationDokumen19 halamanMale SterilizationEggyDsBelum ada peringkat
- Progesterone (Crinone 8% Gel Vaginal)Dokumen7 halamanProgesterone (Crinone 8% Gel Vaginal)ddandan_2Belum ada peringkat
- Coitus InterruptusDokumen2 halamanCoitus InterruptusMaulana213Belum ada peringkat
- Frozen (Cryopreserved, Vitrified) Embryo TransferDokumen5 halamanFrozen (Cryopreserved, Vitrified) Embryo Transferandi hamatajBelum ada peringkat
- ASRM - Diagnostic Evaluation of The Infertile FemaleDokumen11 halamanASRM - Diagnostic Evaluation of The Infertile FemaleMina zhouBelum ada peringkat
- Repeat AbortionDokumen65 halamanRepeat AbortionLazyRittzBelum ada peringkat
- Maternal and Child HealthDokumen28 halamanMaternal and Child Health지창욱Belum ada peringkat
- Reproductive Pharmacology Lecturio ReflectionDokumen7 halamanReproductive Pharmacology Lecturio ReflectionNathaniel SolisBelum ada peringkat
- 2022-23 OBG MMed 2 - 3btest 1 - KeyDokumen12 halaman2022-23 OBG MMed 2 - 3btest 1 - KeyKenneth ChandaBelum ada peringkat
- Endometritis: R.N. Zainab Neamat JumaahDokumen19 halamanEndometritis: R.N. Zainab Neamat JumaahKevin Adrian WijayaBelum ada peringkat
- Hydatidiform MoleDokumen2 halamanHydatidiform MoleIrfan HardiBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Task 4 - Karen and William ConwayDokumen3 halamanWriting Task 4 - Karen and William Conwayprakash poudelBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 12 - Madhumayanti - 190701224political ScienceDokumen7 halamanTopic 12 - Madhumayanti - 190701224political ScienceMadhumayanti NandiBelum ada peringkat
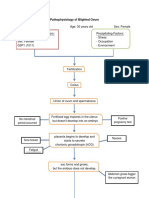
- Pathophysiology of Blighted OvumDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Blighted OvumFirmanFifa'FaizalBelum ada peringkat
- GyneDokumen43 halamanGyneNisreen Al-shareBelum ada peringkat
- PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME (PMS) - Rafael Costa Gouveia Mariz Group 01Dokumen15 halamanPREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME (PMS) - Rafael Costa Gouveia Mariz Group 01Rafael100% (1)
- CPM14th PCOS PDFDokumen9 halamanCPM14th PCOS PDFJapheth SalvanBelum ada peringkat
- Progesterone Medicinal PresentationDokumen14 halamanProgesterone Medicinal PresentationAsif KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of MenstruationDokumen11 halamanPhysiology of MenstruationDavid CalaloBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Guide To Bovine Reproduction Tcm95-44851 2Dokumen43 halamanPractical Guide To Bovine Reproduction Tcm95-44851 2rajkumar871992Belum ada peringkat
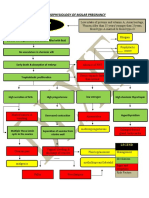
- Partial Mole or Complete Mole: Pathophysiology of Molar PregnancyDokumen1 halamanPartial Mole or Complete Mole: Pathophysiology of Molar PregnancyKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isBelum ada peringkat
- Sex EducationDokumen2 halamanSex EducationNur RozieBelum ada peringkat
- Position Paper New Rh971Dokumen2 halamanPosition Paper New Rh971David DueñasBelum ada peringkat
- Participate IN Various Programmes VasectomyDokumen6 halamanParticipate IN Various Programmes Vasectomyvenkat krishnanBelum ada peringkat