Sri Lanka
Diunggah oleh
Harshadewa AriyasingheHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sri Lanka
Diunggah oleh
Harshadewa AriyasingheHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2.
1: Country/Economy Profiles
Part 2A.r2
8/31/09
10:32 AM
Page 286
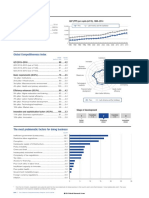
Sri Lanka
Key indicators
GDP (PPP intl $) per capita, 19802008
Population (millions), 2008.......................................19.4
GDP (US$ billions), 2008...........................................39.6
GDP per capita (US$), 2008 ................................1,971.8
GDP (PPP) as share (%) of world total, 2008 .......0.13
5,000
Sri Lanka
South Asia
4,000
3,000
2,000
1,000
0
1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008
Global Competitiveness Index
Rank
(out of 133)
Stage of development
Score
(17)
GCI 20092010.........................................................79 ......4.0
Transition
12
GCI 20082009 (out of 134)..................................................77 ........4.0
GCI 20072008 (out of 131)..................................................70 ........4.0
Factor
driven
Basic requirements.............................................................89 ........4.1
1st pillar: Institutions ...........................................................73 ........3.8
2nd pillar: Infrastructure.....................................................64 ........3.9
3rd pillar: Macroeconomic stability................................128 ........2.8
4th pillar: Health and primary education .........................47 ........5.7
286
Transition
23
Efficiency
driven
Innovation
driven
Institutions
7
Innovation
6
5
Business
sophistication
Efficiency enhancers..........................................................74 ........3.9
5th pillar: Higher education and training .........................64 ........4.0
6th pillar: Goods market efficiency...................................45 ........4.5
7th pillar: Labor market efficiency ..................................111 ........3.9
8th pillar: Financial market sophistication.......................65 ........4.2
9th pillar: Technological readiness...................................85 ........3.3
10th pillar: Market size........................................................63 ........3.8
Infrastructure
Macroeconomic
stability
4
3
2
Market size
Health and
primary
education
Higher education
and training
Technological
readiness
Innovation and sophistication factors ............................44 ........4.0
11th pillar: Business sophistication..................................42 ........4.5
12th pillar: Innovation..........................................................46 ........3.4
Financial market
sophistication
Goods market
efficiency
Labor market efficiency
Sri Lanka
Factor-driven economies
The most problematic factors for doing business
Tax regulations ..............................................................14.6
Access to financing ......................................................14.2
Tax rates .........................................................................12.5
Inflation ...........................................................................11.8
Inefficient government bureaucracy...........................7.7
Inadequate supply of infrastructure ............................7.5
Policy instability...............................................................7.4
Corruption.........................................................................7.1
Restrictive labor regulations .........................................4.4
Foreign currency regulations........................................3.7
Poor work ethic in national labor force ......................3.4
Inadequately educated workforce...............................2.0
Government instability/coups .......................................1.5
Crime and theft ................................................................1.4
Poor public health ...........................................................0.7
0
10
15
20
25
Percent of responses
Note: From a list of 15 factors, respondents were asked to select the five most problematic for doing business in their country/economy and to rank them
between 1 (most problematic) and 5. The bars in the figure show the responses weighted according to their rankings.
The Global Competitiveness Report 2009-2010 2009 World Economic Forum
30
8/31/09
10:32 AM
Page 287
Sri Lanka
The Global Competitiveness Index in detail
INDICATOR
Competitive Advantage
RANK/133
INDICATOR
1st pillar: Institutions
1.01
1.02
1.03
1.04
1.05
1.06
1.07
1.08
1.09
1.10
1.11
1.12
1.13
1.14
1.15
1.16
1.17
1.18
1.19
Property rights .............................................................68 ........
Intellectual property protection....................................63 ........
Diversion of public funds .............................................73 ........
Public trust of politicians..............................................81 ........
Judicial independence .................................................50 ........
Favoritism in decisions of government officials ..........79 ........
Wastefulness of government spending.......................74 ........
Burden of government regulation................................81 ........
Efficiency of legal framework in settling disputes.......51 ........
Efficiency of legal framework in challenging regs .......58 ........
Transparency of government policymaking .................98 ........
Business costs of terrorism.......................................132 ........
Business costs of crime and violence .........................99 ........
Organized crime...........................................................87 ........
Reliability of police services.......................................102 ........
Ethical behavior of firms ..............................................85 ........
Strength of auditing and reporting standards ..............44 ........
Efficacy of corporate boards ........................................27 ........
Protection of minority shareholders interests ............40 ........
2.01
2.02
2.03
2.04
2.05
2.06
2.07
2.08
Quality of overall infrastructure....................................63 ........
Quality of roads............................................................60 ........
Quality of railroad infrastructure ..................................44 ........
Quality of port infrastructure........................................43 ........
Quality of air transport infrastructure...........................64 ........
Available seat kilometers* ...........................................66 ........
Quality of electricity supply .........................................72 ........
Telephone lines* ..........................................................69 ........
3.01
3.02
3.03
3.04
3.05
Government surplus/deficit* .....................................129 ........
National savings rate*..................................................73 ........
Inflation* ....................................................................125 ........
Interest rate spread* ...................................................93 ........
Government debt*.....................................................115 ........
4.01
4.02
4.03
4.04
4.05
4.06
4.07
4.08
4.09
4.10
4.11
Business impact of malaria..........................................82 ........
Malaria incidence* .......................................................81 ........
Business impact of tuberculosis..................................63 ........
Tuberculosis incidence*...............................................73 ........
Business impact of HIV/AIDS ......................................51 ........
HIV prevalence*.............................................................1 ........
Infant mortality*...........................................................54 ........
Life expectancy*..........................................................80 ........
Quality of primary education........................................33 ........
Primary enrollment* ....................................................40 ........
Education expenditure* .............................................114 ........
2nd pillar: Infrastructure
3rd pillar: Macroeconomic stability
Competitive Disadvantage
RANK/133
6th pillar: Goods market efficiency
6.01
6.02
6.03
6.04
6.05
6.06
6.07
6.08
6.09
6.10
6.11
6.12
6.13
6.14
6.15
Intensity of local competition ......................................36 ........
Extent of market dominance .......................................38 ........
Effectiveness of anti-monopoly policy .........................46 ........
Extent and effect of taxation .......................................79 ........
Total tax rate* ............................................................113 ........
No. of procedures required to start a business* ...........8 ........
Time required to start a business* ..............................96 ........
Agricultural policy costs ...............................................69 ........
Prevalence of trade barriers.......................................105 ........
Tariff barriers* ..............................................................88 ........
Prevalence of foreign ownership .................................73 ........
Business impact of rules on FDI .................................29 ........
Burden of customs procedures ...................................85 ........
Degree of customer orientation ..................................32 ........
Buyer sophistication ....................................................32 ........
7th pillar: Labor market efficiency
7.01
7.02
7.03
7.04
7.05
7.06
7.07
7.08
7.09
Cooperation in labor-employer relations ......................74 ........
Flexibility of wage determination.................................78 ........
Rigidity of employment*..............................................43 ........
Hiring and firing practices ............................................84 ........
Firing costs* ..............................................................124 ........
Pay and productivity.....................................................59 ........
Reliance on professional management .......................40 ........
Brain drain ....................................................................52 ........
Female participation in labor force*...........................105 ........
8.01
8.02
8.03
8.04
8.05
8.06
8.07
8.08
8.09
Financial market sophistication....................................55 ........
Financing through local equity market.........................34 ........
Ease of access to loans ...............................................51 ........
Venture capital availability ............................................60 ........
Restriction on capital flows .........................................79 ........
Strength of investor protection*..................................55 ........
Soundness of banks ....................................................60 ........
Regulation of securities exchanges .............................31 ........
Legal rights index*.......................................................83 ........
9.01
9.02
9.03
9.04
9.05
9.06
9.07
9.08
Availability of latest technologies.................................58 ........
Firm-level technology absorption.................................46 ........
Laws relating to ICT.....................................................53 ........
FDI and technology transfer ........................................39 ........
Mobile telephone subscriptions*.................................96 ........
Internet users* ..........................................................107 ........
Personal computers* ...................................................92 ........
Broadband Internet subscribers*.................................90 ........
8th pillar: Financial market sophistication
4th pillar: Health and primary education
5th pillar: Higher education and training
5.01
5.02
5.03
5.04
5.05
5.06
5.07
5.08
Secondary enrollment* ................................................71 ........
Tertiary enrollment* .....................................................92 ........
Quality of the educational system ...............................41 ........
Quality of math and science education .......................44 ........
Quality of management schools ..................................40 ........
Internet access in schools ...........................................74 ........
Local availability of research and training services ......46 ........
Extent of staff training .................................................68 ........
9th pillar: Technological readiness
10th pillar: Market size
10.01 Domestic market size index* ......................................61 ........
10.02 Foreign market size index*..........................................75 ........
11th pillar: Business sophistication
11.01
11.02
11.03
11.04
11.05
11.06
11.07
11.08
11.09
Local supplier quantity .................................................56 ........
Local supplier quality ...................................................50 ........
State of cluster development ......................................31 ........
Nature of competitive advantage ................................37 ........
Value chain breadth......................................................34 ........
Control of international distribution .............................18 ........
Production process sophistication ...............................51 ........
Extent of marketing .....................................................40 ........
Willingness to delegate authority ................................44 ........
12.01
12.02
12.03
12.04
12.05
12.06
12.07
Capacity for innovation ................................................49 ........
Quality of scientific research institutions.....................45 ........
Company spending on R&D ........................................41 ........
University-industry collaboration in R&D .....................51 ........
Govt procurement of advanced tech products ...........52 ........
Availability of scientists and engineers ........................44 ........
Utility patents*.............................................................82 ........
12th pillar: Innovation
* Hard data
Note: For further details and explanation, please refer to the section How to
Read the Country/Economy Profiles at the beginning of this chapter.
2.1: Country/Economy Profiles
Part 2A.r2
The Global Competitiveness Report 2009-2010 2009 World Economic Forum
287
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Groth Competitiveness IndexDokumen2 halamanGroth Competitiveness IndexsulthanhakimBelum ada peringkat
- Singapore: Key Indicators, 2014Dokumen2 halamanSingapore: Key Indicators, 2014Siddhant AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Hong Kong SAR: Key Indicators, 2013Dokumen2 halamanHong Kong SAR: Key Indicators, 2013huznmh8334Belum ada peringkat
- Taiwan, China: Key Indicators, 2012Dokumen4 halamanTaiwan, China: Key Indicators, 2012Santiago MilesBelum ada peringkat
- Ranking de Competitividad PerúDokumen2 halamanRanking de Competitividad PerúCarlos Alexander Espinoza HBelum ada peringkat
- FinlandDokumen2 halamanFinlandFrancesco SaviozziBelum ada peringkat
- Romania Global Competitive IndexDokumen2 halamanRomania Global Competitive IndexAnda MărășescuBelum ada peringkat
- QatarDokumen2 halamanQatarshabina921Belum ada peringkat
- BMI Vietnam Consumer Electronics Report Q3 2013Dokumen52 halamanBMI Vietnam Consumer Electronics Report Q3 2013chip12384Belum ada peringkat
- COmpetitividad España 2013 PDFDokumen2 halamanCOmpetitividad España 2013 PDFcroquetoideBelum ada peringkat
- Chile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Dokumen1 halamanChile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Víctor Alfonso Castillo VillchezBelum ada peringkat
- Sector Statistics Report Q4 2021 2022Dokumen28 halamanSector Statistics Report Q4 2021 2022iganjo mutahiBelum ada peringkat
- Argentina: Key Indicators, 2010Dokumen2 halamanArgentina: Key Indicators, 2010Stephen HartantoBelum ada peringkat
- ACER Market Monitoring Report 2018 - Electricity Wholesale Markets VolumeDokumen71 halamanACER Market Monitoring Report 2018 - Electricity Wholesale Markets VolumeMartin Javier Molina GodoyBelum ada peringkat
- 8th Pillar: Tourism InfrastructureDokumen2 halaman8th Pillar: Tourism Infrastructureapi-25966334Belum ada peringkat
- Malaysia: Key IndicatorsDokumen2 halamanMalaysia: Key Indicatorszindagi5323Belum ada peringkat
- JICA Roadmap For Transport Infra DevtDokumen160 halamanJICA Roadmap For Transport Infra DevtPortCalls100% (2)
- Print World ForumPortugalDokumen2 halamanPrint World ForumPortugalbiles1234Belum ada peringkat
- Arts College Value Chain 2011 - Copy - Docx 1111Dokumen40 halamanArts College Value Chain 2011 - Copy - Docx 1111Awetahegn HagosBelum ada peringkat
- Ocde ChileDokumen137 halamanOcde Chiledalton850Belum ada peringkat
- BMI Vietnam Information Technology Report Q2 2014 PDFDokumen84 halamanBMI Vietnam Information Technology Report Q2 2014 PDFBiểnLêBelum ada peringkat
- Smart Cities KPI GuideDokumen42 halamanSmart Cities KPI GuideAlan CruzBelum ada peringkat
- EnglishDokumen265 halamanEnglishOpenFileTOBelum ada peringkat
- Profil SR 2012Dokumen2 halamanProfil SR 2012Dennik SMEBelum ada peringkat
- Economics PDFDokumen62 halamanEconomics PDFEd ZBelum ada peringkat
- Cyprus Travel Tourism Competitiveness Report 2011 - Country ProfileDokumen2 halamanCyprus Travel Tourism Competitiveness Report 2011 - Country ProfileetourismforumBelum ada peringkat
- Global Hydraulic Power Units MarketDokumen94 halamanGlobal Hydraulic Power Units MarketDragan LazicBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring the Emissions & Energy Footprint of the ICT SectorDokumen54 halamanMeasuring the Emissions & Energy Footprint of the ICT SectorStoleriu IulianBelum ada peringkat
- BMI Vietnam Autos Report Q2 2014Dokumen64 halamanBMI Vietnam Autos Report Q2 2014Phạm ThaoBelum ada peringkat
- Derivatives and Risk Management in Petroleum, NG and Electricity (2002)Dokumen96 halamanDerivatives and Risk Management in Petroleum, NG and Electricity (2002)lucianmolBelum ada peringkat
- Conso CEDEAO Et CEMAC-GBDokumen88 halamanConso CEDEAO Et CEMAC-GBalexdunodBelum ada peringkat
- Global Hydraulic Cylinders MarketDokumen115 halamanGlobal Hydraulic Cylinders MarketDragan LazicBelum ada peringkat
- Foreign Direct Investment in AgricultureDokumen90 halamanForeign Direct Investment in AgricultureSeiha KhBelum ada peringkat
- Romania Country/Economy Profile SummaryDokumen2 halamanRomania Country/Economy Profile SummaryCata FrincuBelum ada peringkat
- Ren21 GSR2011Dokumen116 halamanRen21 GSR2011David Avila CharryBelum ada peringkat
- Market and Policy Outlook For Renewable Energy in Europe and The CISDokumen74 halamanMarket and Policy Outlook For Renewable Energy in Europe and The CISUNDP in Europe and Central AsiaBelum ada peringkat
- ParaguayDokumen2 halamanParaguaymalonso1234Belum ada peringkat
- AEIEA2019001 OverviewDokumen86 halamanAEIEA2019001 OverviewAstri MagallanesBelum ada peringkat
- Libya Economic StrategyDokumen203 halamanLibya Economic Strategyklatifdg50% (4)
- Designing and Implementing Ethiopia's Rural Safety Net ProgramDokumen166 halamanDesigning and Implementing Ethiopia's Rural Safety Net ProgramGetachew A. AbegazBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Scenario Planning For The German Carsharing Industry in 2025 (Carolin Von Sethe, 2016)Dokumen114 halamanStrategic Scenario Planning For The German Carsharing Industry in 2025 (Carolin Von Sethe, 2016)taghavi1347Belum ada peringkat
- Assam Power Sector Capacity Development PlanDokumen162 halamanAssam Power Sector Capacity Development PlanMikealayBelum ada peringkat
- Blueprint XXIII Web PDFDokumen194 halamanBlueprint XXIII Web PDFBruegelBelum ada peringkat
- MamproposalDokumen20 halamanMamproposalmohammedBelum ada peringkat
- BusinessPlan BangadBakeroBagongSikatBagongBuhay 2Dokumen41 halamanBusinessPlan BangadBakeroBagongSikatBagongBuhay 2Clark WaganBelum ada peringkat
- JapanDokumen2 halamanJapanarchitectofskinBelum ada peringkat
- DDP Boheco-I 2016-2025Dokumen104 halamanDDP Boheco-I 2016-2025Gia CachoBelum ada peringkat
- Tanzania Governance Review 2012Dokumen122 halamanTanzania Governance Review 2012Policy ForumBelum ada peringkat
- PA00XKT9Dokumen56 halamanPA00XKT9ricardoindia2008Belum ada peringkat
- BMI Ghana Telecommunications Report Q3 2013 (1) 22145049Dokumen91 halamanBMI Ghana Telecommunications Report Q3 2013 (1) 22145049eugene123Belum ada peringkat
- CapstoneProjectFinalReport LukeJohnstonDokumen48 halamanCapstoneProjectFinalReport LukeJohnstonSameer KBelum ada peringkat
- RICERIA FinalruleDokumen247 halamanRICERIA Finalrulesisai12u242Belum ada peringkat
- Final Iloilo TTMP 2015march29Dokumen123 halamanFinal Iloilo TTMP 2015march29Mark Ian AllosoBelum ada peringkat
- Wcms 400598Dokumen76 halamanWcms 400598Irina AtudoreiBelum ada peringkat
- Country/Economy Profile of the PhilippinesDokumen1 halamanCountry/Economy Profile of the PhilippinesVeda MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Triple Play: Building the converged network for IP, VoIP and IPTVDari EverandTriple Play: Building the converged network for IP, VoIP and IPTVBelum ada peringkat
- Some Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandDari EverandSome Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandBelum ada peringkat
- LTC2410 Datasheet and Product Info - Analog DevicesDokumen6 halamanLTC2410 Datasheet and Product Info - Analog DevicesdonatoBelum ada peringkat
- Metal Oxides Semiconductor CeramicsDokumen14 halamanMetal Oxides Semiconductor Ceramicsumarasad1100% (1)
- Frozen DessertDokumen3 halamanFrozen DessertcsqueilBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - The Empirical Beginnings and Basic Contents of Educational PsychologyDokumen9 halamanChapter 1 - The Empirical Beginnings and Basic Contents of Educational PsychologyJoshua Almuete71% (7)
- ES1 Work Panel DatasheetDokumen3 halamanES1 Work Panel DatasheetGerardo Alberto Navarro LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Haier's Performance Management in Other CulturesDokumen8 halamanHaier's Performance Management in Other CulturesSubhransu SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Vivaldi - Genuis of BaroqueDokumen279 halamanVivaldi - Genuis of Baroqueilcanto100% (4)
- Brochure HorticultureDokumen46 halamanBrochure HorticulturezulfiqaralimalikBelum ada peringkat
- Component 2 Learner Statement Y2Dokumen6 halamanComponent 2 Learner Statement Y2api-426152133Belum ada peringkat
- Educating The PosthumanDokumen50 halamanEducating The PosthumanCatherine BrugelBelum ada peringkat
- FD-BF-001 Foxboro FieldDevices 010715 LowRes PDFDokumen24 halamanFD-BF-001 Foxboro FieldDevices 010715 LowRes PDFThiago FernandesBelum ada peringkat
- MEC332-MA 3rd Sem - Development EconomicsDokumen9 halamanMEC332-MA 3rd Sem - Development EconomicsRITUPARNA KASHYAP 2239239Belum ada peringkat
- Assessing Khazaria-Serpent PeopleDokumen1 halamanAssessing Khazaria-Serpent PeopleJoao JoseBelum ada peringkat
- All Types of Switch CommandsDokumen11 halamanAll Types of Switch CommandsKunal SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Soil Testing Lab Results SummaryDokumen2 halamanSoil Testing Lab Results SummaryMd SohagBelum ada peringkat
- Pump IntakeDokumen6 halamanPump IntakeAnonymous CMS3dL1T100% (1)
- Manufacturing Tech-1Dokumen6 halamanManufacturing Tech-1Vikram Rao0% (1)
- 2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11Dokumen90 halaman2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11eko sulistyo75% (4)
- HYBT Series: Assembling Terminal BlockDokumen8 halamanHYBT Series: Assembling Terminal Blockanon_670965762Belum ada peringkat
- Thank you for purchasing your remap from HDI Tuning LtdDokumen2 halamanThank you for purchasing your remap from HDI Tuning LtdMaks LebanBelum ada peringkat
- Pressing and Finishing (Latest)Dokumen8 halamanPressing and Finishing (Latest)Imran TexBelum ada peringkat
- SBFP Timeline 2019Dokumen1 halamanSBFP Timeline 2019Marlon Berjolano Ere-erBelum ada peringkat
- Effectiveness of Using High Gas Pressure in A Blast Furnace As A Means of Intensifying The Smelting OperationDokumen10 halamanEffectiveness of Using High Gas Pressure in A Blast Furnace As A Means of Intensifying The Smelting Operationchandan kumar100% (1)
- User Manual - Numrolgy SoftwareDokumen14 halamanUser Manual - Numrolgy SoftwareComputershastriNoproblem0% (1)
- We Generally View Objects As Either Moving or Not MovingDokumen11 halamanWe Generally View Objects As Either Moving or Not MovingMarietoni D. QueseaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Starter WBDokumen88 halaman1 Starter WBHYOBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions ManualDokumen25 halamanIntroduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions ManualMaryJohnsonsmni100% (57)
- Big Band EraDokumen248 halamanBig Band Erashiloh32575% (4)
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan ElementaryDokumen3 halamanSemi Detailed Lesson Plan ElementaryJinky JunioBelum ada peringkat
- Resp Part 4Dokumen95 halamanResp Part 4Kristian CadaBelum ada peringkat