Types of Hardware Devices
Diunggah oleh
anon_678973145Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Types of Hardware Devices
Diunggah oleh
anon_678973145Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IWC: Computer Fundamental What is Computer?
A machine that can be programmed to accept data, process it into useful information, and store it away Data: raw facts representing people and events (e.g. Your name, Address,..) Information: Data that is organized, meaningful, and useful (e.g. Your name, address etc all together makes an Information.) What is the main function of Computer? Computer has 4 basic functions, Input computer gathers data from users Process data is converted into information Storage data or information is stored for future use Output data or information is retrieved from the computer Computer Hardware and its types All physical parts of the computer (or everything that we can touch) are known as hardware. Types of hardware devices include: 1. System Unit 2. Storage Devices 3. Input Devices 4. Output Devices 5. Hybrid Devices
Types of Hardware Devices
System Unit/Devices Motherboard Its the main board which hold all the hardware's. We can also say It holds hardware, electrical power supply, disk drives, circuit cards, ports for connecting other hardware and the motherboard (system board) Name of Motherboard Manufacturer: Intel, GigaByte, MSI, ASUS The motherboard holds 2 very important parts: Processor (CPU) Memory (RAM, ROM) Central processing Unit (CPU) CPU is the brain of the computer that controls all the commands and tasks of the computer. The CPU is Also Known as 1. Processor 2. Microprocessor 3. Central processor 4. Brains of the computer CPU/Processor - Main 3 Parts It has 3 basic main parts: Control Unit: Manages all resources of a computer (It receive instructions from the computers memory and interprets these instructions and executes them) Arithmetic-Logic Unit (ALU): Performs all the arithmetic (math operations) and logical (comparisons) operations for the computer. Registers: A small set of temporary storage cells used to store data and instructions needed frequently. Clock Speed & Processor Unit Processor speed is measured by clock speed/rate. Processor clock speed measured unit is hertz. The clock rate/speed is the rate in cycles/bits per second (measured in hertz) for the frequency of the clock in CPU. Example for understanding What is the weight of this book? (Ans: 2 kg) What is the clock speed/rate of this processor? (Ans: 2.1 GHz) Processor 2.17GHz indicate that it can execute 2.17x109 cycles per second Name of processors: Pentium, Celeron, Centrino (by Intel Corporation), Athlon, Sempron, Turion (by Advanced Micro Devices Storage Devices
It used to store data and information. It is mainly divided into two parts. They are, Primary Storage RAM (Random Access Memory) ROM (Read-only-memory) Cache Memory Secondary Storage Magnetic storage HDD (Hard disk Drive), FDD, (Floppy Disk Drive), Zip Drive, Tape Secondary Storage Optical/Removable storage : CD-R (Compact Disc-Recordable) CD-RW (Compact Disc-ReWritable) DVD-R (Digital Versatile Disk - Recordable) DVD-RW (Digital Versatile Disk Read Writable) Flash memory Flash drives, USB Drive, SD(Secure Digital) Card Primary Memory Holds: Data raw facts for processing Instructions rules for processing data Information processed data Two basic types of memory include: Random Access Memory (RAM) It is the temporary memory inside CPU 1. Volatile part of memory that stores information temporarily 2. Data will be lost as soon as power is lost 3. RAM is read /write memory 4. Processing speed is very high. 5. Much Expensive Example: 256MB RAM is 256x106 bytes of Random Access Memory. The amount of primary working memory available. Read-Only Memory (ROM) It is the permanent memory inside CPU 1. Non-volatile part of memory on which data is prerecorded 2. Data will not be lost as soon as power is lost 3. ROM is read only memory 4. Processing speed is very low compare to RAM. 5. Less Expensive Cache Memory are used for temporarily retaining data in order to achieve high speed read/write operations. Advantages: Processing speed is very fast. Cache is faster then RAM also. CPU used it for read and write. Disadvantage: Price is very high. (Higher then RAM) Memory is measured by its size in bytes, kilobytes (thousands), megabytes (millions), and gigabytes (billions) Bit (Binary Digit) the smallest unit represent with only 0s and 1s Byte represents a 1 character consists of 8 bits Word a group of bytes. Vary from 16 bits (2 bytes), 32 bits ( 4 bytes) or even 64 bits (8 bytes) ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) one of the coding schemes used to represent characters in 8-bit bytes. Can represent a maximum of 256 characters (incl.uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and special symbols)
Note: 1 KILOBYTE = 103 BYTE 1 MEGABYTE = 106 BYTE = 103 KB 1 GIGABYTE = 109 BYTE = 103 MB 1 TERABYTE = 1012 BYTE = 103 GB 1 PETABYTE = 1015 BYTE = 103 TB Secondary Memory/Storage Used to store data and information permanently Magnetic storage: uses sectors that divide tracks to store data E.g. hard disks, tapes, floppy disks, zip disks Optical storage: also uses tracks and sectors but data is saved using a laser beam E.g.Compact discs (CDs), digital video discs (DVDs) Flash memory: Uses solid-state technology which is completely electronic and has no moving mechanical parts. E.g. Flash drives (memory sticks), cards used in digital cameras, MP3 players, etc Storage devices are measured in bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, Gigabytes Magnetic Vs. Optical Storage Speed: Magnetic disk storage has been optimized for high speeds. Optical Disk (DVDs and CDs) access data fast enough to play movies and music, but are much slower than a magnetic disk. Portability: Most magnetic disks, while lightweight, are meant to stay inside the computer. Since the optical disk is small, light and removable, optical media is portable. Cost: Neither magnetic hard disks nor optical disk drives are expensive. Relatively same. Storage: Magnetic disk: 80GB - 2 Exabyte (1 Exabyte = 1000 Peta byte). Optical disks: 700MB 15GB (Exabyte>Petabyte) Purpose: Magnetic disks have been a workhorse technology for computers since the 1950s. They're the main place to keep files and software. Optical disks are handy media for portable data, movies and music. Input Device Used to enter data into the computer for processing Examples include: Keyboard: It is the primary input device for computers. Uses the following types of keys to send data to the computer Alphanumeric keys (A,B,Ca,b,c, 1,2,3.), Control keys (Ctrl, Alt, Tab, ), Function keys (F1,F2.), Cursor control keys (,,, ), Toggle and other keys (Insert, Num Lock, Caps Lock), Multimedia and Internet control keys - available on most modern keyboards. Standard Keyboard - Desktop computer keyboards Laptop-size Keyboard - The keyboards on laptops have a shorter travel distance and (usually) a reduced set of keys. Thumb-sized Keyboard - Smaller keyboards have been introduced for laptops, PDAs, smartphones, or users who have a limited workspace. Mouse: Control a pointer on the monitor which is used to select buttons, menus, links Mouse is the most common pointing device Type of mouse: Mechanical: The ball-mouse replaced the external wheels Optical Mouse: uses a light-emitting diode and photodiodes to detect movement Connectivity: Serial Post, PS/2, USB, Wireless Scanner: Flatbed Scanner: This is smaller scanner that will fit on top of a desk. Flatbed scanners produce medium quality images. Less expensive. Allow to scan up to a 8 x 11 inch sheet of paper. Accept between 1200dpi and 2400 dpi. Can be connected via a Parallel Port or a USB Port. Business Card Scanner: A card-reading device allows to you to capture information on business cards.
Finger Print Scanner: A device allows to you to scan your fingerprint for security sensitive applications. Hand-Held Scanner: This device allows to you to capture information by waving the scanner over the document or image you wish. Optical Bar Code Scanner: This device allows to you to capture barcode information on articles. Microphone: Convert sound into digital format Digital camera: Image recorded digitally to memory Web camera: Capture images for broadcast on Internet Touch Pad: Special monitor that allows selecting by touching screen directly Joysticks: Popular for computer games Bar Code Reader: Photoelectric scanner that reads bar codes and used normally in grocery stores, retail stores Light Pen Graphics Tablet Output Device Display processed data from a computer. Output can be: Text, graphics, photos, audio, video Common output devices Monitor: Most frequently used output device whose size is measured by diagonal of screen. Common sizes: 15, 17, 19, 21 inches. Clarity is indicated by resolution measured in pixels. More pixels = better clarity. Pixels: The smallest discrete component of an image or picture on a CRT screen (usually a colored dot); "the greater the number of pixels per inch the greater the resolution. Cathode Ray tubes (CRT) can be curved or flat and relatively inexpensive. Flat-panel/LCD monitors use liquid crystal display (LCD) technology and are much slimmer and expensive Printer: It produces hard copy output. Printers can be divided into 2 ways, 1. Impact Printer A type of printer that works banging a head or needle against an ink ribbon to make a mark on the paper. Example Dot Matrix Printer 2. Non-Impact Printer A type of printer that does not operate by striking a head against a ribbon. Example Inkjet Printer, Laser printer Printers are usually specified by the speed of printing, number of pages printed per minute (ppm) and by their printing resolution, dots per inch (dpi). To be suitable for printing, need a minimum resolution of 300 dpi. This means that there should be at least 300 dots per one inch. Dot Matrix Printers: Advantages Allows you to print long banners Low purchase cost. Cheap to operate, just new ribbons. Low repair cost. Disadvantages Noisy. Take long time print. Produce low-quality print (You can see the dots making up each character) Not all can do color. Color looks faded and streaky. Any type of printer can jam, but dot matrix printers are more flat to jamming Ink jet Printers: Advantages Noiseless Less Expensive than Laser Printers Excellent print quality for both text and picture Capable of producing good quality.
Light weight and compact (they don't take up too much space) Faster then Dot Matrix Printer. Good for Small Offices Disadvantages Expensive ink cartridges Slower then Laser printer. So fail in high volume printing. Inkjet cartridges get clogged or dirty. You can't use all types of paper with an inkjet. Not good for Business use Laser Printers: Advantages Very fast in printing Prints very high and very accurate. For high volume printing, It cheaper to run. Printing is fast so they can handle large volumes. Disadvantages Price is high compared to an inkjet. Larger and heavier as they need to contain the imaging drum and laser technology. Output Device: Deference's between Impact & Non-Impact Printers: 1. Non-impact printers are quieter and produce better quality print than impact printers. 2. Non-impact printers, the characters and images are form without any direct physical contact of the paper. 3. Impact printers are noisily because of the hitting activity 4. Non-impact printers are usually more expensive than impact printers. 5. In non-impact printers the text or image is formed without any physical contact of the paper and the printer head. But in impact printers the paper and the printer head come in contact and hence the text or image is formed. Projectors Speakers Hybrid Devices Hybrid devices are those which at different times can be both input and output devices. Such items as; floppy disks, hard disks, Optical media (rewritable CDs and DVDs) Important Terms A: Floppy disk C: Local disk D: Local disk (partition) E: Optical Drive AGP = Accelerated Graphics Port. ATA = Advanced Technology Attachment. ATM = Asynchronous Transfer Mode. CMOS= Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor BIOS= Basic Input/Output System DDR Memory= Double Data Rate Memory IDE is has no abbreviation. Its a popular standard for internal hard drives and CD-ROM drives of IBM-compatible systems. PCI= Peripheral Component Interconnect PCMCIA= Personal Computer Memory Card International Association SDRAM= Synchronous DRAM TFT= Thin Film Transistor SATA= Serial ATA SCSI: Small Computer System Interface VGA: Video Graphics Array
Different Types Of Computers Micro Computers (Personal Computers): computers that fits on a desk and runs on power from an electrical wall outlet. The CPU can be housed in either a vertical or a horizontal case. Has separate components (keyboard, mouse, etc.) that are each plugged into the computer. Desktop PC: Desktop computers Also known as PCs, microcomputers, or home computer. Three types of Desktop PC are available. They are, Low-end computers Fine for home users, word processing, simple games, Internet access Fully powered computers Good for heavy use of graphics, programming, or action-oriented games Workstations Very high-end computers used by engineers, financial traders, and graphic designers Notebook PC: Notebook a small compact portable computer. Advantages: Lightweight Computer; Small in Size, Easy to carry Low consumption Small comparative to desktop You can do lot with it (Internet, office, games, photo editing, CAD) Disadvantages: Expensive compare to Desktop PC Hard to upgrades; expensive to upgrades. Hardware and Software limitation It loses over the time performance Some generate allot of heat, some hardware limitations Laptop PC: A portable computer small enough to use in your lap. Advantages: Laptops are portable. Can carry anywhere. Compact - Small, less space required. Disadvantages: Slower than a desktop compare to price. Can't upgrade as much as a desktop. Sensitivity - easy to break, low resistance. More expensive than a desktop. Server Computers: Powerful desktop computer designed for specialized tasks. They can tackle tasks that require a lot of processing speed and they can also be an ordinary personal computer attached to a LAN (local area network). Server Types: Web Servers - uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTP) to serve static content to a web browser by loading a file from a disk and serving it across the network to a users web browser Application Servers Handles all application operations between users and a database Mail Servers Move and store mail over corporate networks and across the Internet Database Servers A server that performs tasks such as data analysis and storage Audio/Video Servers Enable websites to broadcast streaming and multimedia content
Chat Servers Enable a large number of users to exchange information in an environment similar to Internet newsgroups that offer real-time discussion Print Server - Shares and maintains network printers Mini (Midrange) Computers: Hundreds or thousands of users can be connected in Mini Computer. These are multi-user computers designed to serve the needs of medium-sized organizations, Collages and are used for inventory, order-entry and other company-wide applications. This computer offers less than mainframe in work and performance. Mainframe Computers: These are very large and powerful computers capable of processing billions of instructions per second and can handle billions of characters of data. They are used to store, manage, and process large amounts of data that need to be reliable, secure, and centralized. Often used for applications with many users. This is normally too expensive and out of reach from a salary-based person who wants a computer for his home. Commonly used in big hospitals, air line reservations companies (many other huge companies prefer mainframe because of its capability of retrieving data on a huge basis) Super Computers: A computer that was the fastest in the world at the time it was constructed. These are the fastest and most powerful computers very Capable of processing trillions of instructions per second and can tackle tasks that would not be practical for other computers. They are used for very sophisticated applications requiring mammoth data manipulation, e.g Weather forecasting, Weapons research, Special effects for movies, Breaking codes, Bigger in Size. They are the most expensive computers. Software Part Operating System Operating systems software is a special type of program that loads automatically when you start your computer. It allows you to use the advanced features of a modern computer without having to learn all the details of how the hardware works. It gives the link between the hardware and you, the user and makes the computer easy to use without having to understand bits and bytes A Graphical User Interface (GUI) is simply an additional part of the operating system that displays windows and drop down menus, and also enables you to drive your computer using a mouse. Data Backup What is backup? backup is part of a larger domain called data security: Store Data, Integrity and protection of Data, availability Why Backup? Software and Hardware failures are a common thing in the computer world. Any number of occurrences can cause loss of valuable data. Types of failures: Power failures (software/hardware failure) Natural disasters (fire, flood) Security incidents (theft) Hardware Failures (disk crash) User error Social issues (stolen data) Backup Strategy This is driven by many variables. Such as: How long can you be offline before your org disappears? Do you have legal responsibilities?
Levels of backup planned: Daily Weekly Monthly Quarterly Semi-annually Annually How long must you keep the data? How do you restore the data? A robust, strong and secure business back-up plan should include activities such as taking of regular back-ups, storage of back-ups off site together with the testing of the backups in order to ensure that the data can be restored from them. The business should have such a plan in place in case of data loss or corruption, physical damage to the computers or computer building, and to ensure that data may be restored for future use. Protection Of Business Data The use of passwords, which prevents others without the password from accessing data. The installation of a firewall, which helps prevent unauthorized external access Use of anti-virus software which may help prevent data corruption Internet Fundamentals Introduction The World Wide Web (WWW): The World Wide Web (WWW) is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. WWW is a hypertext-based system. Hypertext allows users to click on buttons or highlighted text using a mouse to go to other Web pages containing text, sound, pictures, or video. A vast collection of information is accessible through the Internet using connections called hyperlinks. We can view the WWW resources through a program called a Web Browser, such as: Mozilla Firefox Internet Explorer Netscape Navigator Google Chrome The Internet: A large system of interconnected computer networks spanning the globe. The Internet is a worldwide network of connected computers. This allows the sharing of electronic information and resources and world wide communication through standards Services available through the Internet: Email (Discussion groups,Chat Rooms, etc.) Information search (including research) Education (Online courses; virtual colleges) Entertainment, News, and more... Finding Information on the Web (Using Effective Search Strategies) Often confused...URL or Email Address? URL - Uniform Resource Locator or Web Address Example:http://www.weather.com Used by Browsers to locate sites Often confused with Email addresseslike johndoe@netscape.net Uniform Resource Locators (Web Addresses) Each part of the URL directs the browser to the correct web page.
http://library.sullivan.edu/datainfo.html
Hypertext transfer protocol(http)
Network Domain
File name
Different Domains on the WWW .edu - educational .gov Government sites in the United States at any level, city, county, state, federal etc. .org Organization or individuals .com Commercial (for profit) .net Network providers How to Access Web Pages Here are three ways to access a web page: 1. Type the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) in the address box. 2. Click on hypertext links on a web page. 3. Use a search tool such as a keyword search engine or web directory. Use a Search Tool. Examples of search tools include: Google, AltaVista, Yahoo!, Lycos Email What is Email and Why is it Popular? An electronic message sent from one computer to another. Email saves money and time compared to regular mail. An email message takes seconds to reach destination. How does Email Work? 1. Email travels via the Internet from one computer to another. 2. Computers known as mail servers direct outgoing mail and store incoming the mail. 3. Once email reaches your mail server, it waits in an electronic mail box, the "Inbox for you to collect it. Things You Can Do with Email Compose and Send: write an email and send it to others. To Cc BCc Attachment Body Send Reply: reply to an email that you received. Forward: pass on an email that you received to others. Attachment: You can send files with your email such as: pictures, music, software and documents Web Browsers Software programs used to access the World Wide Web Internet Fundamentals Using a Web Browser Starting and stopping the Browser The Web Browsers window Getting around a page and the WWW Saving, printing, and mailing items from the WWW Bookmarks - Keeping track of favorite sites Setting preferences and options We find Information on the Web, using
Directories Search Engines Searching the Web Guess Domain Names such as:ibm.com or weather.com, maps.com or abcnews.com Performing Keyword Searches Search Engines What is a Search Engine ? Is a program that connects you to a data base or Web address used to perform a thorough search Some Popular Search Engines Alta Vista, Excite, Hotbot, Lycos, InforSeek, etc. Random Browsing (takes too much time) Mark Favorite Sites (bookmark the sites) Use several Search Engines for a thorough search Whats the difference? Search Engine - allows you to collect and then browse information from more sources (Excite, AltaVista, InfoSeek, etc.) Directory - generally doesnt include every single web page or resource. Organizes resources of web pages by categories. Web Browsers: A browser lets you access the WWW and browse the Internet for information. You use the browser to maneuver through web pages. The browser takes all that text and uses it to create what you see on the screen. Different browsers have different translations. Although the web tries to be uniform, things may not always display the same. There are standards for the Web portion of the internet, but not all companies adhere to them. Internet Explorer: One of the most common browsers is Internet Explorer, it is what we have here in the library. Many other browsers exist and often people have strong opinions on which is best Sometimes the text sent to your computer requires MORE than just the HTML decoding by your browser Networking Basic Concepts Communications activity associated with distributing or exchanging information Telecommunications technology of communications at a distance that permits information to be created any where and used everywhere with little delay Today it, involves Data: digital and analog Voice: spoken word Video: telelcommunication imaging Essentials For Communications Must have a message Message must have a transmitter Message must have a medium Message must be understood Message must have some level of security Source Transmitter Transmission Receiver Destination
Network A network is a group of computers connected together in such a way as to allow Networks that are interconnected have proven to be low cost, reliable, and efficient means of communicating at a distance. Main Type Of Network
LAN: A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area such as home, school, computer laboratory, office building, or closely positioned group of buildings. MAN: A Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN) is a large computer network that usually spans a city or a large campus. WAN: A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network that covers a large geographic area such as a city, country, or spans even intercontinental distances, using a communications channel that combines many types of media such as telephone lines, cables, and air waves. Computer networks can be open to everyone or restricted to the chosen few. An example of a private access network is a companys network. Internet is a public access network. Network Terminology Explained Node: anything connected to the network, usually a computer, but it could be a printer or a scanner Segment: any portion of a network that is separated by a switch, bridge or a router from another part of a network. Backbone: the main cabling of a network that all of the segment connect to. Usually, the backbone is capable of carrying more information than the individual segments. Topology: The way each node is physically connected to the network Basic Components Sending device Communications link Receiving device Ways Of Transmission Simplex transmission sends data in one direction only. Example: television broadcasting Half-duplex transmission sends data in both directions, but only one way at a time Example: bank teller sends data about a deposit; after data received, a confirmation returns Full-duplex transmission allows transmission in both directions at same time. Example: a conversation over phone. Typically used for high-speed data communication Network Topologies The physical layout of a network is called a topology. Also known as layout of LAN There are three common topologies. Star Ring Bus Hybrid In a topology a component is called a node, which is usually a computer on a network or other peripheral devices such as a printer. Star Network Topology A STAR network has a central (hub) computer or connector that is responsible for managing the network. All messages are routed through the hub computer, which acts as a traffic controller. Advantages: Easy to install and wire. Does not have a single point failure Easy to detect faults and to remove parts. Disadvantages: Requires more cable length . If the hub or concentrator fails, nodes attached are disabled. Ring Network Topology The Ring network topology connects computers in a circular fashion. The data messages travel in only one direction around the ring. Advantages: There is no danger of data collision since data travels in only one direction Disadvantages:
If one node fails the ring is broken and the entire network fails. Also known as single point failure Bus Network Topology A Bus network has a single line (TRUNK) to which all the network nodes are attached. If a data collision occurs the sending node tries to send the data again. Advantages: Nodes can be attached or detached from the network without affecting the network. If one node fails , it does not affect the rest of the network. Disadvantages: It has a single point of failure, meaning if there is a problem anywhere along the trunk, the whole network fails. Hybrid Topology Hybrid network is the combination of different topologies such as star, Ring, Mesh, Bus etc. For example, if a department uses a Bus network, second department uses the ring network, third department uses the star network. All the networks can be connected together through a central hub Network Devices Gateway: A gateway is a collection of hardware and software resources that lets a node communicate with a computer on another dissimilar network. Bridge: A bridge is a product that connects a local area network (LAN) to another local area network that uses the same protocol (for example, Ethernet or token ring). A bridge examines each message on a LAN, "passing" those known to be within the same LAN, and forwarding those known to be on the other interconnected LAN (or LANs). Network Component Modem: A device that enables computers to communicate over the telephone systems. Hub: In a network environment a hub is a simple device which may contain several ports used for connecting nodes together. Switch: Unlike a hub a switch splits the network traffic and sends it to different destinations Router: A router is used to direct network traffic particularly when several networks are connected together. Nodes: The devices attached to the network, for example, computers and printers are often referred to as nodes. Firewall: a piece of hardware or software put on the network to prevent some communications forbidden by the network policy. What Is The Difference Between? Bridge: A device to interconnect two LANs that use the SAME logical link control protocol but may use different medium access control protocols. Router: A device to interconnect SIMILAR networks, e.g. similar protocols and workstations and servers. Gateway: device to interconnect DISSIMILAR protocols and servers, and Macintosh and IBM LANs and equipment Security Security Risk Sources The security risk to our computers and data come from a variety of sources such as : 1. Theft of data 2. Theft of hardware 3. Unauthorized access to data 4. Loss due to systems failure or power failure 5. Loss due to virus attack
6. Virus attack through internet 7. Many more What Is Security? Information security means protecting information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, perusal, inspection, recording or destruction. It Security Principles: Confidentiality: To prevent the disclosure of information to unauthorized individuals or systems Integrity: Data cannot be modified untraceably. The system continues to operate properly Availability: The information must be available when it is needed. So the computing systems are used to store and process the information whilst the security controls are used to protect it. The communication channels used to access it must be functioning correctly Authenticity: To ensure that the data, transactions, communications or documents (electronic or physical) are genuine. Data protection principles What are the eight principles of it? 1. Data must be kept secure; 2. Data stored must be relevant; 3. Data stored must be kept no longer than necessary; 4. Data stored must be kept accurate and up-to-date; 5. Data must be obtained and processed lawfully; 6. Data must be processed within the data subject rights; 7. Data must be obtained and specified for lawful purposes; 8. Data must not be transferred to countries without adequate data protection laws. Start With The Basics Securities Basic computer security is through technology is easy; use Firewall: the most useful tool in your bag of defenses. Prevents intruders from accessing services on your computer. Validates/normalizes network traffic. May provide reports and trend analysis. Available for all major operating systems usually for free! Anti-Virus Software: Stops viruses sent by email, attachments, downloads, etc. Detects malicious software through intelligent heuristics. Available for all major desktop and server operating systems. A requirement; not an option. Patch: your computer quickly;(Usually) free updates to your computer; can be downloaded from the Internet. Available before most exploits surface. Strong passwords! eeps you on-target with best practices. Is composed of 8 or more K characters and includes letters, numbers and 2 special characters, including !@#$%^&.-+-=|]{}:. Not based on any dictionary word from any language. Changes regularly; not shared. Network Manager A network manager is responsible for an organisation's computer network system. A network is designed to give staff in an organisation access to files, documents, business applications, corporate systems, email and internet as well as printers and other devices. Job Role Of A Network Manager 1. Designing, installing and testing networks 2. Maintaining the network and backing up data 3. Ensuring systems are secure to prevent unwanted users 4. System documentation managing technical staff working on the network 5. Controlling budgets and devising a disaster recovery plan.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Basic Hardware Units of A ComputerDokumen12 halamanBasic Hardware Units of A ComputerRobinson JoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- Meeting 2 OKDokumen15 halamanMeeting 2 OKMuhamad Irvan SBelum ada peringkat
- Hardware and SoftwareDokumen13 halamanHardware and SoftwareMaajith MarzookBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To HardwareDokumen14 halamanIntroduction To HardwarePriya AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Fundamentals Module 3Dokumen129 halamanComputer Fundamentals Module 3Raghavendra.K.ABelum ada peringkat
- Meeting 2 Inside ComputerDokumen16 halamanMeeting 2 Inside ComputerFelix Rizky LesmanaBelum ada peringkat
- IT Infrastuctural Management NotesDokumen26 halamanIT Infrastuctural Management NotesAayush JainBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of ComputerDokumen59 halamanFundamentals of ComputergpsamBelum ada peringkat
- 105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Dokumen15 halaman105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Ahmad Thariq RahmatullahBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3Dokumen9 halamanModule 3bscomputersciencelsstiBelum ada peringkat
- IT For Managers: Lecture 3: Computer System and ComponentsDokumen39 halamanIT For Managers: Lecture 3: Computer System and ComponentsRaheel HussainBelum ada peringkat
- FCPIT Practical FileDokumen78 halamanFCPIT Practical Filekaushal2442100% (1)
- Diploma in Computer (A Excellent Beginners Guide)Dokumen61 halamanDiploma in Computer (A Excellent Beginners Guide)Lingaraj SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of ComputerDokumen55 halamanFundamentals of ComputerJSPAMore100% (1)
- Computer Basic - ADokumen72 halamanComputer Basic - AkdkozBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Has A Full FormDokumen48 halamanComputer Has A Full FormDeepak kr. patelBelum ada peringkat
- Computer AwernesDokumen145 halamanComputer AwernessekharBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris 4 Makalah (Discussion Hardware and Software)Dokumen10 halamanTugas Bahasa Inggris 4 Makalah (Discussion Hardware and Software)rikzy rulaiwan100% (1)
- Computer SystemDokumen72 halamanComputer SystemTsehayou SieleyBelum ada peringkat
- BasicComputerSkills NotesDokumen31 halamanBasicComputerSkills NotesVanamala MahathiBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Basics For AP Grama Sachivalayam ExamsDokumen7 halamanComputer Basics For AP Grama Sachivalayam ExamsSuresh Chandragiri0% (1)
- Module 2 and 3Dokumen12 halamanModule 2 and 3Jerome BarraBelum ada peringkat
- Information Technology As Level - Chapter 2Dokumen26 halamanInformation Technology As Level - Chapter 2Heena100% (1)
- ICT G10 - Chapter 1Dokumen17 halamanICT G10 - Chapter 1tonet enteaBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts of Information Technology: Computer SkillsDokumen116 halamanConcepts of Information Technology: Computer SkillsHabahbeh YaraBelum ada peringkat
- It WRKSDokumen10 halamanIt WRKSdh_kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Course Pack Understanding New Media BAVDokumen47 halamanCourse Pack Understanding New Media BAVAdit PujariBelum ada peringkat
- Multimedia Class 11 Chapter 1Dokumen26 halamanMultimedia Class 11 Chapter 1akshatsharma007100% (1)
- Different Hardware and Components of A ComputerDokumen6 halamanDifferent Hardware and Components of A ComputercpewanwanBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Overview of Computer SystemsDokumen17 halaman1.1 Overview of Computer SystemsAsanka KulasiriBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Computer?Dokumen17 halamanWhat Is Computer?Narender SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of ComputerDokumen53 halamanFundamentals of ComputerFrancis Polycarp DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Computer: Prof. Jhalak DuttaDokumen55 halamanFundamentals of Computer: Prof. Jhalak DuttaJhalak DuttaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer System OrganizationDokumen39 halamanComputer System Organizationiitiansrd2025Belum ada peringkat
- EthicsDokumen8 halamanEthicsjoygumalayBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Computer Hardware (IT FUNDAMNETALS)Dokumen6 halamanWhat Is Computer Hardware (IT FUNDAMNETALS)JSON AMARGABelum ada peringkat
- ITGS GlossaryDokumen108 halamanITGS GlossaryAbdullah NajiBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1Dokumen7 halamanWeek 1nothaia morilloBelum ada peringkat
- Basic ComputerDokumen115 halamanBasic ComputerAnteneh WalleBelum ada peringkat
- Block Diagram of ComputerDokumen6 halamanBlock Diagram of ComputerdevitoshBelum ada peringkat
- Welcome To Presentation On Computer Hardware: by R.Venkata Ramana Manager (IT)Dokumen21 halamanWelcome To Presentation On Computer Hardware: by R.Venkata Ramana Manager (IT)GomathiRachakonda100% (1)
- Computer SystemDokumen10 halamanComputer Systemdhirendra lamsalBelum ada peringkat
- New ICDL Quick ReferenceDokumen32 halamanNew ICDL Quick ReferenceicdlkingBelum ada peringkat
- Computer System OrganizationDokumen39 halamanComputer System Organizationiitiansrd2025Belum ada peringkat
- Computer and Its HardwareDokumen61 halamanComputer and Its Hardwaredendenlibero100% (1)
- Computer HardwareDokumen11 halamanComputer HardwareRodriguez NikkoBelum ada peringkat
- Computer System (Lesson 2)Dokumen10 halamanComputer System (Lesson 2)qshmkdjtuakrppwxetBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Computers: What Is A Computer?Dokumen14 halamanIntroduction To Computers: What Is A Computer?S.S. MeenaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Computers: Presented By: Engr. Leonides G. AgravanteDokumen38 halamanIntroduction To Computers: Presented By: Engr. Leonides G. Agravanteleonides agravanteBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A ComputerDokumen9 halamanWhat Is A Computerprishanifernando1981Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Computers: Presented by Muhammad Jaseem ID: 90 Section BDokumen15 halamanIntroduction To Computers: Presented by Muhammad Jaseem ID: 90 Section BmasroorimsBelum ada peringkat
- GEE2Dokumen15 halamanGEE2Ronimarie Nicole ZapataBelum ada peringkat
- Module IDokumen58 halamanModule IAhmed ZaidBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1.2 Components of A Computer System.Dokumen35 halamanUnit 1.2 Components of A Computer System.Sanie BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- PPS Complete NotesDokumen116 halamanPPS Complete NotesMOHAMMAD ANISHBelum ada peringkat
- The 8086 Computer Architectu Re and Hardware Compone NTS: Ronel CortezDokumen16 halamanThe 8086 Computer Architectu Re and Hardware Compone NTS: Ronel CortezRonel CortezBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To ComputersDokumen7 halamanIntroduction To ComputerskachaelvisBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Computer Course, For Beginners and Technology StudentsDari EverandBasic Computer Course, For Beginners and Technology StudentsBelum ada peringkat
- Data Transfer InstructionsDokumen5 halamanData Transfer InstructionsSaarah PatelBelum ada peringkat
- OCJP Notes Durga Classes PDFDokumen58 halamanOCJP Notes Durga Classes PDFSaurabh AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Module ICTDokumen9 halamanModule ICTMis She SalenBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Science Past Paper Igcse CambridgeDokumen11 halamanComputer Science Past Paper Igcse CambridgeAhmed0% (1)
- Pid ControlDokumen18 halamanPid Controlauntu_dhBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Metrics Casino 2Dokumen3 halamanPerformance Metrics Casino 2preetBelum ada peringkat
- Welcome To: Introduction To COBOL ProgrammingDokumen141 halamanWelcome To: Introduction To COBOL ProgrammingCarlosPrizBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan BinaryDokumen2 halamanLesson Plan Binaryapi-169562716100% (1)
- 330 - Visual Basic and C# Programming - R - 2020Dokumen17 halaman330 - Visual Basic and C# Programming - R - 2020avfg gfavdBelum ada peringkat
- IntrotocompengDokumen26 halamanIntrotocompengeng.tahaaslanBelum ada peringkat
- Introducation To ComputerDokumen42 halamanIntroducation To ComputerYul Delfin100% (1)
- Siemens: S7-CPUDokumen22 halamanSiemens: S7-CPUJulian AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- AdoptionDokumen7 halamanAdoptiondatateamBelum ada peringkat
- Requisition Import Whitepaper v1Dokumen39 halamanRequisition Import Whitepaper v1Sudhir PatilBelum ada peringkat
- An 120 Aliasing VCP Baud RatesDokumen18 halamanAn 120 Aliasing VCP Baud RatesMoZt WantTedBelum ada peringkat
- Familiarization With MDA8086 and MTS86C Microprocessor TrainersDokumen18 halamanFamiliarization With MDA8086 and MTS86C Microprocessor TrainersAnik Mazumder100% (1)
- Intro C ProgrammingDokumen29 halamanIntro C Programmingu2303083Belum ada peringkat
- Fortran NotesDokumen38 halamanFortran NotesSakar DotelBelum ada peringkat
- Desktop Info ManualDokumen56 halamanDesktop Info ManualJangdiniBelum ada peringkat
- Fanuc 30i 31i 32i Parameter ManualDokumen800 halamanFanuc 30i 31i 32i Parameter Manualg3gustavoBelum ada peringkat
- CSL101: Introduction To Computers and Programming: Lecture 1Dokumen79 halamanCSL101: Introduction To Computers and Programming: Lecture 1Ghilli TecBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 2 - Digital BasicsDokumen35 halamanLecture 2 - Digital BasicsAmelia Jasmin AzlanBelum ada peringkat
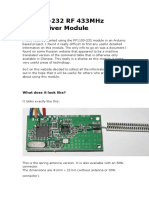
- Rf1100-232 RF 433Mhz Transceiver Module: What Does It Look Like?Dokumen9 halamanRf1100-232 RF 433Mhz Transceiver Module: What Does It Look Like?gezahegnBelum ada peringkat
- Test Items G8 TLE CSSDokumen2 halamanTest Items G8 TLE CSSrrBelum ada peringkat
- 8051 Learning BoardDokumen6 halaman8051 Learning BoardEmin KültürelBelum ada peringkat
- COT - 1 2023 Lesson Plan - Carryout Mensuration and CalculationDokumen5 halamanCOT - 1 2023 Lesson Plan - Carryout Mensuration and CalculationOtenciano50% (2)
- Computer Basics For KidsDokumen61 halamanComputer Basics For KidsDalya GomesBelum ada peringkat
- Latitude 3x10 Spec SheetDokumen7 halamanLatitude 3x10 Spec SheetFernando Mercedes GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Transforming Data Into InformationDokumen17 halamanTransforming Data Into InformationMuhammad Hussain Adenwala80% (5)
- EMV v4.3 Book 1Dokumen189 halamanEMV v4.3 Book 1p1nh3a6100% (2)