NUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping Instructor
Diunggah oleh
Amber EssmanDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping Instructor
Diunggah oleh
Amber EssmanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
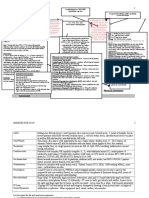
RETS College - School of Nursing NUR 129
Concept Mapping Endocrine
Disorders of the Anterior Pituitary Gigantism
Overproduction of growth hormone GH in the childhood
Great height Increased muscle and visceral development Increased weight Normal body proportions Weakness
Dwarfism
Underproduction of growth hormone in childhood
1. Abnormally short height 2. Normal body proportion 3. Appear younger than age 4. Dental problems due to underdeveloped jaws 5. Delayed sexual development
Acromegaly 1. Assess ability to perform ADLs
2. 3. 4. 5. Soft, easy-to-chew diet Encourage Fluids Analgesics Visual disturbances a. Risk for injury- Keep environment free from clutter b. Self-Esteem issues c. Family coping d. Cardiac dysrhythmias enlarged heart
Overproduction of growth hormone GH in the adult
Irreversible physical changes Assessment Muscle weakness Hypertrophy of the joints with pain and stiffness Femalesdeepened voice, increased facial hair, amenorrhea Partial or complete blindness with pressure on the optic nerve due to tumor Severe headaches Malocclusion of teeth
NUR129 Summer 2009
[1]
Instructor: Amber Essman RN BSN CFRN
RETS College - School of Nursing NUR 129
Concept Mapping Endocrine
Disorders of the Posterior Pituitary Diabetes Insipidus
Manifests - polydipsia and polyuria Deficiency in antidiuretic hormone (ADH) 1. Strict Intake and Output 2. Daily Weight 3. Vital Signs 4. Monitor Electrolytes Sodium levels
5. urine specific gravity <
SIADH
Excessive Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) 1. Monitor Intake and Output, Daily Weight 2. Monitor blood chemistries Hyponatremia 3. Neurological Exam 4. Restrict Fluids Fluid Restriction 800-1000 ml/day. If Hyponatremia is severe, than 500 ml/day Hypertonic Saline Solution will be ordered at a slow rate (need to avoid too rapid of rise in sodium) Need to correct sodium imbalance and pull water out of edematous brain cells
1.005 (Normal 1.003 to 1.030) 6. Limit Caffeine secondary to its diuretic properties FLUID Volume Deficit Risk for Hypernatremia
NUR129 Summer 2009
[2]
Instructor: Amber Essman RN BSN CFRN
RETS College - School of Nursing NUR 129
Concept Mapping Endocrine
Disorders of the Thyroid Gland Hypothyroidism Underproduction of thyroid hormones
Assessment: Depression, constipation, bradycardia, hypotension, fatigue, Weakness Diagnostic Tests Radioactive iodine uptake test (RAIU). Medical Management: Synthroid Know client teaching 1. Imbalanced Nutrition, more than body requirements. 1. Low calorie diet 2. Provide warm environment 3. Fluids and fiber for constipation 4. Monitor depression 5. fatigue activity intolerance
Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis)
Overproduction of the thyroid hormones
Medications block production of thyroid hormones Propylthiouracil Methimazole Radioactive iodine non-pregnant patients Subtotal hemorrhage, hypoparathyroidism, vocal cord paralysis)
1. Provide a cool environment 2. Monitor vital signs 3. eye drops for exophthalmos Subtotal Thyroidectomy: Positioning, complications, monitoring for thyroid crisis, inadvertent removal of the parathyroid glands.
NUR129 Summer 2009
[3]
Instructor: Amber Essman RN BSN CFRN
RETS College - School of Nursing NUR 129
Concept Mapping Endocrine
Disorders of the Parathyroid Gland Hypoparathyroidism
Decreased parathyroid hormone Hypocalcemia Neuromuscular hyperexcitability Involuntary and uncontrollable muscle spasms Tetany, Laryngeal spasms, Stridor, Cyanosis Calcium gluconate or calcium chloride IV slowly Vitamin D Chvosteks (an abnormal spasm of the facial muscles elicited by light taps on the facial nerve in patients who are hypocalcemic) Trousseaus signs assesses for latent tetany; carpal spasm is induced by inflating a sphygmomanometer cuff on the upper arm to a pressure exceeding systolic blood pressure for 3 minutes; a positive result may be seen in hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia patients.
Hyperparathyroidism Excessive parathyroid hormone hypertension, psychosis, muscle weakness, renal calculi Hypercalcemia 1. Increase fluids 2. Weight bearing ambulation 3. Monitor ECG
NUR129 Summer 2009
[4]
Instructor: Amber Essman RN BSN CFRN
RETS College - School of Nursing NUR 129
Concept Mapping Endocrine
Disorders of the Adrenal Gland Adrenal hyperfunction (Cushings) Adrenal Hypofunction (Addisons)
Excessive Cortisol Moonface, buffalo hump weakness,
easily bruised, poor wound healing, glycosuria
Adrenal glands do not secrete adequate amounts of glucocorticoids and Mineralocorticoids Adrenalectomy Long-standing steroid therapy observe for postural hypotension, syncope, Addisonian crisis
Nursing Interventions and Patient Teaching
Deficient knowledge secondary to repeated hospital admissions, 2. Disturbed body image secondary to increased androgens, abnormal fat distribution, and muscle wasting, 3. Risk for injury secondary to poor wound healing, decreased bone density, and capillary fragility. 4. Risk for fluid volume excess secondary to sodium and H2O retention from excessive glucorticords. 5. Diet low in sodium and High in Potassium
Diet high in sodium and low in potassium Steroids for adrenal crisis Orthostatic Hypotension
NUR129 Summer 2009
[5]
Instructor: Amber Essman RN BSN CFRN
RETS College - School of Nursing NUR 129
Concept Mapping Endocrine
Disorders of the Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine/Norepinephrine Avoid Stress
Pheochromocytoma-Chromaffin cell tumor
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. LOW SODIUM DIET Avoid Stress Monitor Blood pressure Administer Anti hypertensives Avoid Stimulants
Disorders of the Pancreas Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM) Type I
NUR129 Summer 2009 [6]
Diabetes Mellitus- Type II
Instructor: Amber Essman RN BSN CFRN
RETS College - School of Nursing NUR 129
Concept Mapping Endocrine
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
(HHNC)
Hypoglycemia
Hyperglycemia
NUR129 Summer 2009
[7]
Instructor: Amber Essman RN BSN CFRN
RETS College - School of Nursing NUR 129
Concept Mapping Endocrine
Hunger Shakiness Nausea Irritability Anxiety Rapid pulse Pale, cool skin Hypotension Sweating
Insulin Monitor storage and expiration of insulin Monitor and maintain a record of blood glucose readings as prescribed Monitor food intake Oral Hypoglycemics Administer with food Assess diet and exercise Monitor for hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia Assess for side effects
NUR129 Summer 2009
[8]
Instructor: Amber Essman RN BSN CFRN
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Description: Congestive Heart FailureDokumen22 halamanDescription: Congestive Heart FailurePinklet Arleena CubianBelum ada peringkat
- Completed Concept MapDokumen4 halamanCompleted Concept Mapapi-607361848Belum ada peringkat
- n360 Concept Map Care Plan Week 3 Sheryl SatoDokumen15 halamann360 Concept Map Care Plan Week 3 Sheryl Satoapi-283363983Belum ada peringkat
- Concept MapDokumen5 halamanConcept Mapapi-546509005Belum ada peringkat
- Mnemonics PDFDokumen15 halamanMnemonics PDFbeingfiredBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Signs, Diagnosis, TreatmentDokumen10 halamanAcute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Signs, Diagnosis, TreatmentBianca Watanabe - RatillaBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Map TemplateDokumen16 halamanConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsBelum ada peringkat
- Head To Toe AssessmentDokumen2 halamanHead To Toe AssessmentMichelle Myca Rosauro100% (1)
- Clinical Case Study - Online Discussion Form Fall 2020-1Dokumen14 halamanClinical Case Study - Online Discussion Form Fall 2020-1Sabrina Odies100% (1)
- Flashcards 2601-2800Dokumen191 halamanFlashcards 2601-2800kkenBelum ada peringkat
- Main drug therapy for ulcerative colitis is sulfa for one yearDokumen4 halamanMain drug therapy for ulcerative colitis is sulfa for one yearcathyBelum ada peringkat
- IVY TECH NURSING LAB INFORMATIONDokumen7 halamanIVY TECH NURSING LAB INFORMATIONSethBelum ada peringkat
- HA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusDokumen4 halamanHA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusJULIE ANNE CORTEZBelum ada peringkat
- Prof. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesDokumen5 halamanProf. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesIvy VillalobosBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Surgical NotesDokumen18 halamanMedical Surgical NotesshalomBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Renal Failure-Student-Rapid ReasoningDokumen4 halamanAcute Renal Failure-Student-Rapid Reasoningapi-268403950Belum ada peringkat
- Vital signs and medication reference tableDokumen1 halamanVital signs and medication reference tablejhenssineBelum ada peringkat
- Medsurg 2007Dokumen15 halamanMedsurg 2007WisdomIsMisery100% (1)
- HESI Women's Health:Newborn DrugsDokumen8 halamanHESI Women's Health:Newborn Drugsisapatrick8126Belum ada peringkat
- Brain Dump NUR 213 FINALDokumen37 halamanBrain Dump NUR 213 FINALkelsey jackson100% (1)
- ATI Medication Template RanitidineDokumen1 halamanATI Medication Template RanitidineSharee HaywoodBelum ada peringkat
- Different Positions Assumed by A Patient During A Physical Examination ProcedureDokumen14 halamanDifferent Positions Assumed by A Patient During A Physical Examination ProcedureAziil LiizaBelum ada peringkat
- AH2 Hesi ReviewDokumen46 halamanAH2 Hesi ReviewJamie Antonini Grant100% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDokumen9 halamanCongestive Heart Failure PDFSheryl Ann Mae BombalesBelum ada peringkat
- DigoxinDokumen2 halamanDigoxinNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (2)
- FNP Final TestDokumen10 halamanFNP Final TestNelson MandelaBelum ada peringkat
- NERVOUS SYSTEM Communicable Diseases LEPROSYDokumen3 halamanNERVOUS SYSTEM Communicable Diseases LEPROSYFreeNursingNotesBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids and Electrolytes ConceptDokumen31 halamanFluids and Electrolytes ConceptDarwin AndalBelum ada peringkat
- Med-Surg LEWIS 47 Final Foofed UpDokumen10 halamanMed-Surg LEWIS 47 Final Foofed Uphariniliaankhen100% (1)
- Pku 3 Concept MapDokumen3 halamanPku 3 Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Pharm Drugs ListDokumen14 halamanPharm Drugs ListHumbe Oshun100% (1)
- Summary Notes For Studying Fluid and ElectrolytesDokumen8 halamanSummary Notes For Studying Fluid and ElectrolytesCandace Mead100% (1)
- Health AssessmentDokumen15 halamanHealth AssessmentrlinaoBelum ada peringkat
- Shock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Dokumen41 halamanShock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Samjaisheel SamsonBelum ada peringkat
- GROUP 3 - CASE STUDY - TraumaDokumen5 halamanGROUP 3 - CASE STUDY - TraumaDinarkram Rabreca EculBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Map 1Dokumen5 halamanConcept Map 1api-396919069Belum ada peringkat
- Week 5 CareplanDokumen2 halamanWeek 5 CareplanRaenell Curry100% (1)
- Changing Mainline IV BagDokumen5 halamanChanging Mainline IV BagLorna PaghunasanBelum ada peringkat
- Comfort, rest, and sleep through pain managementDokumen17 halamanComfort, rest, and sleep through pain managementDyna TumbokonBelum ada peringkat
- Immunity 1Dokumen6 halamanImmunity 1Tori RolandBelum ada peringkat
- The Process of OxygenationDokumen7 halamanThe Process of OxygenationMich CercadoBelum ada peringkat
- Vancomycin Dosing and Monitoring in AdultsDokumen1 halamanVancomycin Dosing and Monitoring in AdultsjulialeoBelum ada peringkat
- Care PlanDokumen11 halamanCare PlanAlyssa CardinalBelum ada peringkat
- Sinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementDokumen4 halamanSinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementMargueretti Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolyte ImbalancesDokumen8 halamanElectrolyte Imbalancesdonna mae junioBelum ada peringkat
- Potential Complications Signs and SymptomsDokumen2 halamanPotential Complications Signs and SymptomsJessica GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Ch35 CardiovascularDokumen11 halamanCh35 CardiovascularJessie Jennings100% (3)
- Congestive Heart Failure OutlineDokumen4 halamanCongestive Heart Failure OutlineDominique PorterBelum ada peringkat
- ATI Prototype DrugsDokumen11 halamanATI Prototype Drugsjinnyduong100% (1)
- Maternal Ob NotesDokumen103 halamanMaternal Ob NotesBoris OrbetaBelum ada peringkat
- The Infant Should Always Be in A Rear-Facing Car Seat From Birth To 9.1 KGDokumen7 halamanThe Infant Should Always Be in A Rear-Facing Car Seat From Birth To 9.1 KGSabhi Sandhu100% (1)
- PN NCLEX PRACTICE TESTDokumen75 halamanPN NCLEX PRACTICE TESTjedisay1100% (1)
- Concept Map Et Al 11-04-15Dokumen7 halamanConcept Map Et Al 11-04-15api-353656227Belum ada peringkat
- A-T-I Endocrine NotesDokumen3 halamanA-T-I Endocrine NotesKelseyAnnBarnesBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Map 2Dokumen1 halamanConcept Map 2lanrevoiceBelum ada peringkat
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseDari EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseBelum ada peringkat
- Prioritising HTA Funding: The Benefits and Challenges of Using Value of Information in AngerDokumen20 halamanPrioritising HTA Funding: The Benefits and Challenges of Using Value of Information in AngerHammad AjaBelum ada peringkat
- Download ebook Harrisons Principles Of Internal Medicine Self Assessment And Board Review 20Th Edition Pdf full chapter pdfDokumen67 halamanDownload ebook Harrisons Principles Of Internal Medicine Self Assessment And Board Review 20Th Edition Pdf full chapter pdfrebecca.vaughan926100% (24)
- Depression, lung function, and BODE index in COPDDokumen16 halamanDepression, lung function, and BODE index in COPDHera HeraBelum ada peringkat
- EndometritisDokumen6 halamanEndometritisandriansyah2110% (1)
- Dbms Project ProposalDokumen2 halamanDbms Project ProposalHoopeer Hoopeer0% (1)
- Anabolic Peptide Beta EbookDokumen226 halamanAnabolic Peptide Beta EbookMatei Cipri80% (5)
- Medical English ManualDokumen151 halamanMedical English ManualYobelkis PaulinoBelum ada peringkat
- DivocDokumen1 halamanDivocCarrackBelum ada peringkat
- Firda UsgDokumen19 halamanFirda UsgAnantaFxBelum ada peringkat
- Given: Required: SolutionDokumen2 halamanGiven: Required: SolutionChing KieBelum ada peringkat
- PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF VALSALVA AND IPPVDokumen27 halamanPHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF VALSALVA AND IPPVChaturika Bandara100% (1)
- Uterine ProlapseDokumen3 halamanUterine ProlapseKeshavprasad kurmi100% (1)
- Medical EthicsDokumen27 halamanMedical EthicsJuana Maria Garcia Espinoza67% (3)
- Ultrasound in Gynecology N ObstetricDokumen9 halamanUltrasound in Gynecology N ObstetricKarthik RajvBelum ada peringkat
- AIIMS Rajkot Webinar on Sleep & Polysomnography Basics to UpdatesDokumen4 halamanAIIMS Rajkot Webinar on Sleep & Polysomnography Basics to Updatesகார்த்திBelum ada peringkat
- Melioidosis.: Burkholderia PseudomalleiDokumen34 halamanMelioidosis.: Burkholderia Pseudomalleitummalapalli venkateswara raoBelum ada peringkat
- Hospital Infection ControlDokumen31 halamanHospital Infection ControlIndian Railways Knowledge PortalBelum ada peringkat
- NAMA PENYAKIT YANG HARUS DAPAT DITANGANI DI LAYANAN PRIMERDokumen5 halamanNAMA PENYAKIT YANG HARUS DAPAT DITANGANI DI LAYANAN PRIMERheru suhartoBelum ada peringkat
- Original Articles_ Comparison of Urinary Albumin-Creatinine Ratio and Albumin Excretion Rate in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial_Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications StudyDokumen16 halamanOriginal Articles_ Comparison of Urinary Albumin-Creatinine Ratio and Albumin Excretion Rate in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial_Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications StudyM Dwi SuprayogiBelum ada peringkat
- Priyadarshini, 2010Dokumen9 halamanPriyadarshini, 2010AmandaBelum ada peringkat
- Pedlatrlc Acupuncture Chinese Medicine KTCMDokumen363 halamanPedlatrlc Acupuncture Chinese Medicine KTCMSanté Kine Yoga-thérapieBelum ada peringkat
- Diphtheria 1Dokumen24 halamanDiphtheria 1Anam AbidBelum ada peringkat
- NURSING DIAGNOSIS #2 - HyperthermiaDokumen3 halamanNURSING DIAGNOSIS #2 - HyperthermiaEnerolisa ParedesBelum ada peringkat
- Contemporary Implant Dentistry: Chapter 14 of Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery By: DrarashkhojastehDokumen65 halamanContemporary Implant Dentistry: Chapter 14 of Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery By: DrarashkhojastehRawa Omar100% (1)
- 1.1 Role of Organic Drug Molecules Unit 1Dokumen16 halaman1.1 Role of Organic Drug Molecules Unit 1Amarnath SahBelum ada peringkat
- Semana UCLADokumen7 halamanSemana UCLAAndre BanhateBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen9 halamanDaftar Pustakaaajeng ftnyBelum ada peringkat
- Bisdorff2015 PDFDokumen10 halamanBisdorff2015 PDFLoreto González AguileraBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Pharmacy Lecture Notes - Doc LanchaDokumen36 halamanIntroduction To Pharmacy Lecture Notes - Doc LanchaMignot Ayenew100% (1)
- The Causes and Effects of Alzheimer's Disease: The Silent DiseaseDokumen35 halamanThe Causes and Effects of Alzheimer's Disease: The Silent DiseaseNina Canares100% (2)