A Bone Fracture
Diunggah oleh
Markimz AligaenDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
A Bone Fracture
Diunggah oleh
Markimz AligaenHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
A bone fracture (sometimes abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the
bone. A bone fracture can be the result of high force impact or stress, or trivial injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathological fracture. Nursing goal for a patient with fracture is to relieve pain, education about upcoming surgery, promote comfort and promote healing.
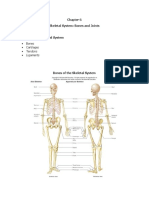
Types of Fractures:
Complete fracture: A fracture in which bone fragments separate completely. Incomplete fracture: A fracture in which the bone fragments are still partially joined. Linear fracture: A fracture that is parallel to the bones long axis. Transverse fracture: A fracture that is at a right angle to the bones long axis. Oblique fracture: A fracture that is diagonal to a bones long axis. Spiral fracture: A fracture where at least one part of the bone has been twisted. Comminuted fracture: A fracture in which the bone has broken into a number of pieces. Compacted fracture: A fracture caused when bone fragments are driven into each other.
Pathophysiology
The natural process of healing a fracture starts when the injured bone and surrounding tissues bleed, forming a fracture Hematoma. The blood coagulates to form a blood clot situated between the broken fragments. Within a few days blood vessels grow into the jelly-like matrix of the blood clot. The new blood vessels bring phagocytes to the area, which gradually remove the non-viable material. The blood vessels also bring fibroblasts in the walls of the vessels and these multiply and produce collagen fibers. In this way the blood clot is replaced by a matrix of collagen. Collagens rubbery consistency allows bone fragments to move only a small amount unless severe or persistent force is applied. At this stage, some of the fibroblasts begin to lay down bone matrix (calcium hydroxyapatite) in the form of insoluble crystals. This mineralization of the collagen matrix stiffens it and transforms it into bone. In fact, bone is a mineralized collagen matrix; if the mineral is dissolved out of bone, it becomes rubbery. Healing bone callus is on average sufficiently mineralized to show up on X-ray within 6 weeks in adults and less in children. This initial woven bone does not have the strong mechanical properties of mature bone. By a process of remodeling, the woven bone is replaced by mature lamellar bone. The whole process can take up to 18 months, but in adults the strength of the healing bone is usually 80% of normal by 3 months after the injury. Several factors can help or hinder the bone healing process. For example, any form of nicotine hinders the process of bone healing, and adequate nutrition (including calcium intake) will help the bone healing process. Weight-bearing stress on bone, after the bone has healed sufficiently to bear the weight, also builds bone strength. The bone shards can also embed in the muscle causing great pain. Although there are theoretical concerns about NSAIDs slowing the rate of healing, there is not enough evidence to warrant withholding the use of this type analgesic in simple fractures Fracture Nursing Care Plans
Cholecystolithiasis: Presence of one or more gallstones in the gallbladder. [chole- + G. kystis, bladder, + lithos, stone]
Gallstones are a common condition of the biliary tract of the digestive system. Gallstones are hard deposits that are similar to pebbles or stones that can develop in the gallbladder. They can be tiny, like a grain of sand, to quite large in size, such as a golf ball.
Symptoms of Gallstones
The list of signs and symptoms mentioned in various sources for Gallstones includes the 26 symptoms listed below:
No symptoms - many people don't know they have gallstones. These "silent stones" are often found by accident from x-rays for other medical reasons. These stones may or may not require treatment. Abdominal pain Nausea Vomiting Indigestion Abdominal bloating Fatty food intolerance Biliary Colic Belching Gas Indigestion Certain symptoms are particularly dangerous and require urgent medical attention: o Fever o Sweating o Chills o Jaundice o Yellow eyes o Yellow skin o Persistent pain o Clay-colored stools
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Fracture: BY: Ma. Elizabeth C. JardiolinDokumen47 halamanFracture: BY: Ma. Elizabeth C. JardiolinEdmonLagartoBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Skeletal SystemDokumen32 halaman02 Skeletal SystemHarshika KDGBelum ada peringkat
- HANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Dokumen40 halamanHANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Abia Annieson A. LorenzoBelum ada peringkat
- All About FractureDokumen59 halamanAll About FractureJohn John Torres100% (1)
- NCSBN - Pharmacology and ParenteralDokumen36 halamanNCSBN - Pharmacology and ParenteralKarissa May Cortez92% (12)
- Course Syllabus (Sample)Dokumen11 halamanCourse Syllabus (Sample)Gelaie Salangsang100% (3)
- Enteral Feeding Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanEnteral Feeding Nursing Care PlanChebz Zy0% (1)
- Fracture Nursing Care PlansDokumen10 halamanFracture Nursing Care Plansheron_bayanin_15Belum ada peringkat
- ICU LogbookDokumen37 halamanICU Logbookrinus5100% (1)
- NCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseDokumen9 halamanNCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseJavieBelum ada peringkat
- Journal article analyzes relationship between facial type and occlusal forcesDokumen8 halamanJournal article analyzes relationship between facial type and occlusal forcesAlexandra FocaBelum ada peringkat
- Reading All That Jazz - Body ClockDokumen4 halamanReading All That Jazz - Body ClockMehran EltBelum ada peringkat
- Types of FractureDokumen6 halamanTypes of FractureChristine Marie Barce MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- A Bone Fracture... ZarateDokumen8 halamanA Bone Fracture... ZarateRose SalviejoBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal - Break A LegDokumen9 halamanSkeletal - Break A LegShannon SandersBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair: Break A LegDokumen8 halamanLesson 3: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair: Break A LegEduardo SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Bones and Soft Tissue - Clinical GateDokumen10 halamanBones and Soft Tissue - Clinical GateAkira MasumiBelum ada peringkat
- Week 6 Bone Case StudyDokumen7 halamanWeek 6 Bone Case StudyAndriBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Tissue: Supportive Connective Tissue: CellsDokumen52 halamanBone Tissue: Supportive Connective Tissue: CellsCalin PopaBelum ada peringkat
- Four Types of Cells in BoneDokumen5 halamanFour Types of Cells in BoneTazrian Islam FarihaBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Fracture Diagnosis and ClassificationDokumen26 halamanBone Fracture Diagnosis and ClassificationNiningRahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Musculoskeletal Pathology NotesDokumen20 halamanMusculoskeletal Pathology Notesdinia fitrianiBelum ada peringkat
- Musculoskeletal Pathology Notes PDFDokumen20 halamanMusculoskeletal Pathology Notes PDFvevestephaniBelum ada peringkat
- Vertebrates Nervous System Muscles Cardiac MuscleDokumen2 halamanVertebrates Nervous System Muscles Cardiac MuscleChristopher MasseyBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of The BoneDokumen12 halamanAnatomy of The BoneOpen Sea Ever CapturedBelum ada peringkat
- Tricald 130524041738 Phpapp01Dokumen57 halamanTricald 130524041738 Phpapp01Vishwas U MadanBelum ada peringkat
- Ch6Bone StudentDokumen66 halamanCh6Bone Studentbhattiareeba13Belum ada peringkat
- Patho FinalDokumen25 halamanPatho FinalSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Pathological FracturesDokumen48 halamanPathological FracturesHafidah RakhmatinaBelum ada peringkat
- SkeletAl SystemDokumen18 halamanSkeletAl SystemYen BailadoBelum ada peringkat
- OsteoporosisDokumen19 halamanOsteoporosisTsedhonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3Dokumen12 halamanChapter 3Deolita BadiangBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Fracture & RemodellingDokumen39 halamanBone Fracture & Remodellingokware rodrickBelum ada peringkat
- Functions of The Musculoskeletal SystemDokumen9 halamanFunctions of The Musculoskeletal SystemLinda XueBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Dokumen13 halamanLecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Muhammad FaizBelum ada peringkat
- FRACTURESDokumen35 halamanFRACTURESMichelle DuBelum ada peringkat
- Ch6Bone StudentDokumen67 halamanCh6Bone Studentbhattiareeba13Belum ada peringkat
- Skeletal System: CartilageDokumen20 halamanSkeletal System: CartilageGrace PascualBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 HomeworkDokumen4 halamanModule 4 HomeworkCj LinceBelum ada peringkat
- CH 06 Lecture OutlineDokumen6 halamanCH 06 Lecture OutlineTameka HedgepethBelum ada peringkat
- Osteoblast & Synovial JointDokumen18 halamanOsteoblast & Synovial JointDeviBelum ada peringkat
- Module-5-The Skeletal SystemDokumen13 halamanModule-5-The Skeletal SystemMARIA CORAZON CONTANTEBelum ada peringkat
- 4 OsteoporosisDokumen6 halaman4 OsteoporosisLilianna Ireen Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- BoneDokumen25 halamanBoneDark EnoughBelum ada peringkat
- The Skeletal System HDokumen23 halamanThe Skeletal System HRajorshi MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Last Updated Thu 30 March 2017 by Christian Nordqvist Reviewed by William Morrison, MDDokumen5 halamanLast Updated Thu 30 March 2017 by Christian Nordqvist Reviewed by William Morrison, MDScarlett EscamillaBelum ada peringkat
- Bone 2Dokumen4 halamanBone 2Elyka Alivan Valdez PolonioBelum ada peringkat
- Bone 1Dokumen4 halamanBone 1Elyka Alivan Valdez PolonioBelum ada peringkat
- Fracture Healing and BonegraftingDokumen76 halamanFracture Healing and BonegraftingJio AmurBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Fracture": Jea N. Daligdig BSN-3Dokumen7 halamanBone Fracture": Jea N. Daligdig BSN-3pjcolitaBelum ada peringkat
- Essentials of Bone Densitometru For The Medical PhysicistDokumen10 halamanEssentials of Bone Densitometru For The Medical PhysicistAmanda Farias FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Formation: Blood Calcium Level - Calcium HydroxyapatiteDokumen13 halamanFormation: Blood Calcium Level - Calcium HydroxyapatiteClarissa IsuriñaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Bone BiologyDokumen3 halamanBasic Bone BiologyRuxandra Maria100% (1)
- Types of Bone Fractures and Clinical ManifestationsDokumen10 halamanTypes of Bone Fractures and Clinical ManifestationsFryam BellsBelum ada peringkat
- Osteomyelitis LaikaDokumen4 halamanOsteomyelitis LaikaAl Lai KaBelum ada peringkat
- A. Skeletal System (Structure, Function, and Diseases)Dokumen8 halamanA. Skeletal System (Structure, Function, and Diseases)Kim LiatBelum ada peringkat
- Fractures BasicDokumen10 halamanFractures BasicAnish BishwakarmaBelum ada peringkat
- Lec. 4 Bone FractureDokumen11 halamanLec. 4 Bone Fracturebtwlalbwdy16Belum ada peringkat
- Reactions of Musculoskeletal Tissues To Disorders and InjuriesDokumen24 halamanReactions of Musculoskeletal Tissues To Disorders and Injurieschristian sihiteBelum ada peringkat
- Fracture Fixation and ArthroplastyDokumen39 halamanFracture Fixation and Arthroplastyzony khanBelum ada peringkat
- 2) Development and Growth of The BonesDokumen3 halaman2) Development and Growth of The BonesAris PaparisBelum ada peringkat
- Secondary bone healing prognosis factorsDokumen4 halamanSecondary bone healing prognosis factorsYuva RajaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathologic Bone FractureDokumen5 halamanPathologic Bone FractureJaysellePuguonTabijeBelum ada peringkat
- Bones As A Living Dynamic TissueDokumen13 halamanBones As A Living Dynamic TissueSanish Basnet100% (1)
- Dr. Sassia Lecture Bone Histology Part II July 4 2023Dokumen39 halamanDr. Sassia Lecture Bone Histology Part II July 4 2023Ali ELKARGHALYBelum ada peringkat
- Avn On ScriptDokumen13 halamanAvn On Scriptclaire.deveraBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing Pulse Oximetry (Performance Checklist) : Iloilo Doctors' College College of NursingDokumen1 halamanAssessing Pulse Oximetry (Performance Checklist) : Iloilo Doctors' College College of NursingJemy Tamaño MorongBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Hashimoto's Disease?Dokumen6 halamanWhat Is Hashimoto's Disease?Novia MentariBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen9 halamanDrug StudyStephanie ValerioBelum ada peringkat
- ActonelDokumen42 halamanActonelSimon JonatanBelum ada peringkat
- What Do Language Disorders Reveal About Brain-Language Relationships? From Classic Models To Network ApproachesDokumen14 halamanWhat Do Language Disorders Reveal About Brain-Language Relationships? From Classic Models To Network ApproachesvalentinepoulainBelum ada peringkat
- GlossectomyDokumen68 halamanGlossectomyRohan GroverBelum ada peringkat
- Terapi Cairan PD Syok KardiogenikDokumen27 halamanTerapi Cairan PD Syok KardiogenikSri AsmawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Sophie Griswold Recc Letter Mary OconnellDokumen1 halamanSophie Griswold Recc Letter Mary Oconnellapi-356127291Belum ada peringkat
- Or JournalDokumen5 halamanOr JournalEchanique, James F.Belum ada peringkat
- New Fixed Acrylic Bite Plane for Deep Bite CorrectionDokumen6 halamanNew Fixed Acrylic Bite Plane for Deep Bite CorrectionFisaBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Imaging of The Pharynx and Esophagus: Key PointsDokumen33 halamanDiagnostic Imaging of The Pharynx and Esophagus: Key PointsChutcharwan JintasoponBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Peritoneal Lavage (DPL)Dokumen10 halamanDiagnostic Peritoneal Lavage (DPL)hatem alsrour100% (2)
- Worldwide Trends in Diabetes Since 1980Dokumen484 halamanWorldwide Trends in Diabetes Since 1980L P Lozada MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Rhopalurus Junceus: and The Treatment of CancerDokumen17 halamanRhopalurus Junceus: and The Treatment of CancerAmalia Tri UtamiBelum ada peringkat
- Current JobsDokumen24 halamanCurrent JobsFatima SajidBelum ada peringkat
- CasuitryDokumen3 halamanCasuitrySoufiane ElabedBelum ada peringkat
- Dehydration PPDokumen17 halamanDehydration PPApol PenBelum ada peringkat
- Chandak Myocardial PDFDokumen12 halamanChandak Myocardial PDFAugustusBelum ada peringkat
- Toxic and Metabolic Disorders of The Nervous SystemDokumen7 halamanToxic and Metabolic Disorders of The Nervous SystemBenj Ricafrente IIIBelum ada peringkat
- International Guidelines For Groin Hernia ManagementDokumen165 halamanInternational Guidelines For Groin Hernia ManagementDina100% (1)
- ANNEX F (Page 1of 3)Dokumen12 halamanANNEX F (Page 1of 3)elmersgluethebombBelum ada peringkat
- Health Benefits Tai ChiDokumen2 halamanHealth Benefits Tai Chiapi-300486677Belum ada peringkat
- Bailey ResumeeDokumen3 halamanBailey Resumeeapi-314996796Belum ada peringkat