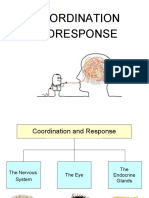
Chapter 2 Body Coordination
Diunggah oleh
ZekZanaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 2 Body Coordination
Diunggah oleh
ZekZanaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
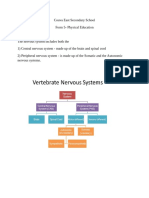
B: Neuron (Neurone)
1. Neuron ialah unit asas system saraf
(Neurone is a basic unit of the nervous system) Sel badan (Cell body) Mengawal semua aktiviti neuron (Controls all the activities of neurons) Dendron (Dendrone) Menerima impuls dan menghantarnya ke arah badan sel Receives impulses and transmits them to the cell body Dendrit (Dendrite) Menerima impuls dan menghantarnya ke arah dendron (Receives impulses and transmits them to the dendrone)
2. Fungsinya ialah membawa impuls ( It
function is to carry impulses)
3. Struktur neuron dan fungsinya (Structure
of neurone and their function is) Nukleus (Nucleus) Mengawal semua aktiviti sel badan (Controls all the activities of cell body) Salut mielin (Mylien sheath) -Penebat akson untuk mengelakkan kebocoran impuls. (Axon insulator to prevent leakage of impulses) -Mempercepatkan penghantaran impuls. (Increases the speed of impulse transmission) Akson (Axon) Menghantar impuls keluar dari badan sel (Transmits impulses out of the cell body)
Hujung saraf (Nerve end)
4. Terdapat tiga jenis neuron dalam badan manusia. (There are three types of neurones in a human
body)
Neuron deria (sensory neurone) dendrit (dendrite) body) sel badan (cell
Neuron perantaraan (relay neurone) dendrit (dendrite) dendron (dendrone) sitoplasma (cytoplasm)
Nukleus (nucleus) Akson (axon) Reseptor (receptor)
Fungsi: Membawa impuls dari organ deria/reseptor ke sistem saraf pusat. (Carries impulses from the sensory organ/receptor to the central nervous system)
sel badan (cell body) Fungsi: Menghantar impuls dari neuron deria ke neuron motor. (Transmits impulses from the sensory neurone to the motor neurone)
Neuron motor (motor neurone) Nukleus (nucleus)
Akson (axon)
Hujung saraf (nerve end)
Dendrit (dendrite) Salut myelin (myelin sheath) Sel badan (cell body)
Dendron (dendrone)
Fungsi: Membawa impuls dari sistem saraf pusat ke efektor (Carries impulses from the central nervous system to the effector) .
2.3
Menganalisis Koordinasi Saraf (Analysing Nervous Coordination) impuls dalam sistem saraf
2. Efektor ialah organ yang bergerak balas
terhadap ransangan contohnya otot dan kelenjar. (Effector is an organ which responds to the stimuli, example muscle and gland)
A: Lintasan
manusia (Pathway of impulse in the human nervous System)
3. Rajah di bawah menunjukkan perkaitan 1. Reseptor ialah satu sel dalam organ deria
yang mengesan ransangan dan menghasilkan impuls (Receptor is a cell in the sensory organs which receive stimuli and will generate impulses) antara reseptor, neuron dan efektor dalam sistem saraf manusia . (Figure below shows the relationship between receptors, neurons and effectors in the human nervous system)
Ransangan (stimuli)
Ransangan (stimuli)
Organ reseptor (dalam organ deria) Receptor organ (in sensory organ)
Neuron deria (sensory neurone)
Neuron peraantaraan ( relay neurone)
Neuron motor (motor neurone)
Organ efektor (otot atau kelenjar) Effector organs (muscle or gland)
B: Tindakan Refleks ( Reflex Action)
1. Tindakan Refleks merupakan gerak balas
yang berlaku dengan pantas, automatik terhadap ransangan (A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response towards a stimulus)
(a) Tangan
terangkat
bila
tersentuh
seterika panas ( withdrawing hand when touching a hot iron)
(b) Mengalihkan kaki sepantas mungkin
apabila terpijak paku di atas Iantai (We jerk our foot away immediately when we accidentally step on a nail)
2. Tindakan ini adalah luar kawal dan tidak
boleh dikawal oleh otak , contohnya (It is involuntary and cannot be controlled by the brain ; Example)
(c) Mengerdipkan mata secara automatik
apabila ternampak serangga kecil berterbangan ke arah mata. (We blink
automatically when a small insect flies towards our eyes)
3. Laluan impuls dalam tindakan reflex
dikenali sebagai Arka reflex. (The sequence of pathways taken by impulses in a reflex action is known as a reflex arc)
(d) Bersin apabila hidung rasa jengkel
(We sneeze when something irritates the nose)
Contoh: Arka reflex bila tersentuh paku tajam (Exampel: Reflex arc when a sharp nail is touched) Ringkasan Arka Refleks (Summary of Reflex Arc) _______________________ _______________ ______________ ____________ _____________ ___________
2.4
Memahami
Peranan
Reseptor
Regang
dalam
Mengekalkan
Keseimbangan
dan
Koordinasi (Understanding The Role of Proprioceptors in Maintaining Balance and Coordination) A: Deria Kinestesis (Kinaesthetic sense) 1. Deria Kinestesis ialah deria yang membantu untuk mengesan kedudukan anggota tubuh badan. ( Kinaesthetic sense is a sense which can helps to conscious of the position and the posture of our body)
1. Reseptor regang ialah organ deria bertindak sebagai deria
kinestesis. ( Proprioceptors are sensory organs which act as Contoh (example) (a) (b) Berjalan di atas tali tegang. (walking on thight ropes) Mengikat melihat (c) Menaip tali (tying tanpa kasut tanpa shoelaces papan kinaesthetic sense)
2. disambungkan dengan neuron deria yang terdapat pada otot
dan tendon, ligamen, dan sendi. (that are connected to sensory neurons) and are found in muscles and tendons, ligaments and joints.)
without looking at it)
DERIA KINESTESIS (KINAESTHETIC SENSE)
melihat
kekunci ( typing without looking at the keyboard)
Kepentingan (Importance)
1. Mengetahui kedudukan anggota badan tanpa melihat . ( conscious of position and body posture without
using our eyes)
2. Mengimbangkan kedudukan dan koordinasi badan (balance the posture and coordination of the body)
B:
Rajah menunjukkan reseptor regang yang terlibat dalam deria kinestesis ( Diagram shows the proprioceptor which proprioceptor which act as kinaesthetic sense
2.5Memahami Otak Manusia dan Kerencamannya (Understanding Human Brain and Its Complexity) A: Struktur Otak Manusia Structure of Human Brain) (The
dalam. (The white matter consists of mainly nerve fibres (axons) which forms the inner layer.)
4. Otak dilindungi oleh tengkorak kranium.
(The brain is protected by the cranium of the skull)
1. Otak manusia terdiri daripada 2 jenis tisu
iaitu jirim kelabu dan jirim putih. (The human brain is made up of two parts of tissues, namely grey matter and white matter.)
5. Otak serebrum manusia berlipat-lipat
untuk menempatkan lebih banyak neuron. (The human cerebral cortex is folded to increase the surface area so that more neurones can be stored).
2.
Jirim kelabu mengandungi badan sel neuron yang membentuk lapisan luar. (The grey matter consists of cell bodies of neurones, which forms the outer layer.)
6.
Tiga
bahagian terdiri
penfing daripada
dalam
otak
manusia
serebrum,
serebelum, dan medula oblongata.(The three main regions of the brain are the cerebrum, oblongata) cerebellum and medulla
3. Jirim putih pula mengandungi genfian
saraf (akson) yang membentuk lapisan
B: Fungsi Bahagian Otak Manusia (Function of each parts of human brain)
1. Serebrum ialah bahagian terbesar otak. Fungsi serebrum ialah: (The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain. It has the following functions) a) Mengawal aktiviti mental , deria dan aktiviti terkawal (Controls mental , sensory and voluntary activities) 2. Serebelum terletak di bahagian bawah dan di helakang serebrum. Fungsi serebelum ialah: (The cerebellum is located below and behind the cerebrum. It has the following functions)
(a) Mengkoordinasikan
movement).
pergerakan
otot. (It coordinates muscular
(b) Mengekalkan postur badan dan
keseimbangan. (It maintains pergerakan body posture and balance).
(c) Menyelaraskan
terkawal. (It promotes smooth voluntary movements). A: Kawasan motor (Motor area) 3. Medula oblongata ialah pusat refleks yang penting. (Medulla B: Kawasan deria (kulit dan otot) Sensory oblongata is an area (skin and muscles) important reflex centre). (a) Ia mengawal kebanyakan tindakan luar kawal seperti C: Pertuturan Speech homeostasis, denyutan jantung, dan peristalsis. (It controls D: Bau dan rasa Smell as taste many involuntary actions, suchandhomeostasis, heartbeat
Setiap bahagian pada serebrum mempunyai fungsi berlainan ( Each parts of cerebrum having different functions)
and peristalsis) E: Penglihatan Vision
Kedudukan kawasan kawalan otak (Location of different controlling parts of the brain) F: Pendengaran Hearing
C: Perbandingan dan perbezaan Tindakan Terkawal dan Tindakan Luar Kawal (Comparison and differences between voluntary action and involuntary action) 1. Tindakan terkawal ialah tindakan yang disedari dan di bawah kawalan mengikut kehendak sendiri. Tindakan mi dikawal oleh sistem saraf somatik. (A voluntary action is a conscious action that is under the control of the
will. It is controlled by the somatic nervous system). 2. Tindakan luar kawal pula ialah tindakan yang tidak disedari dan tidak boleh dikawal mengikut kehendak sendiri. Tindakan ini dikawal oleh sistem saraf autonomi. (An involuntary action is an unconscious action that is not under the control of the will. It is controlled by the autonomic nervous system).
Tindakan (Action) Sistem saraf terlibat (Nervous sytem involved) Dikawal mengikut kehendak (controlled by desire) Bahagian otak yang mengawal tindakan (part of brain in control of action) Laluan pergerakan impuls (pathway of impuls) Kecepatan gerak balas (the speed of response) Contoh tindakbalas ( example)
Terkawal (voluntary) Sistem saraf soma (somatic nervous system) Ya (yes) Serebrum (cerebrum)
Luar Kawal (Involuntary) Sistem saraf autonomi (autonomic nervous sytem) Tidak (No) Medula oblongata (medulla oblongata)
Impuls mengalir melalui serebrum (Impuls flows through cerebrum) Dapat dilambatkan atau dicepatkan (Can be slowed down or speeded up) 1. Menulis (writing) 2. Bercakap(talking)
Impuls mengalir melalui medula oblongata (Impuls flows through medulla oblongata) Cepat (fast)
1. Denyutan jantung
(heart beat) 2. Pencernaan makanan (food digestion)
2.6
Memahami Koordinasi Kimia dalam Badan (Understanding Hormonal Coordination In Body)
Apakah Kelenjar maksud tanpa bahan kelenjar duktus kimia endokrin? yang (hormon) (hormones) bloodstream). directly into the
1.
(What is an endocrine gland?) merembeskan
2. Rajah di bawah menungjukkan kelenjarkelanjar endokrin pada manusia dan fungsinya (The diagram below shows the Endocrine glands and its function)
terus ke dalam aliran darah. (A gland without ducts that secretes chemicals
A : Kelenjar Pituitary (Pituitary gland)kelenjar utama (master gland)
B: Kelenjar Tiroid (Thyroid gland)
(a) Mengawal
(a) Mengawal proses penyerapan air dari
ginjal (To control water absorption from the kidneys)
kadar metabolism control the rate of metabolism) growth)
badan
(To
(b) Merangsangkan pertumbuhan (To stimulate
(b) Sebagai
kelenjar induk yang merangsang kelenjar endokrin lain.(As the main gland that stimulates other endocrine glands)
D: Kelenjar Adrenal (Adrenal gland)
(a) Menyelaraskan badan untuk
C: Kelenjar Pankreas (Pancreas gland) Mengawal aras gula dalam darah (To control the level of blood sugar)
menghadapi kecemasan (To prepare the body to meet greater demands) (b) Menambahkan kadar denyutan jantung dan respirasi (To increase the rate of heartbeats and respiration)
E: Kelenjar testis(lelaki) -Testes gland (Male)
F: Kelenjar Ovari (perempuan) -Ovary gland (Female)
(a) Mengawal ciri-ciri seks sekunder (To
control secondary characteristic) sexual
(a) Mengawal ciri-ciri seks sekunder (To control
secondary sexual characteristics)
(b) Mengawal penghasilan sperma. (To
(b) Mengawal kitar haid (To control menstrual
cycle)
Hormon dan kesan terhadap badan apabila hormon itu dirembeskan dalam amaun yang terlalu sedikit atau terlalu banyak. (The hormones and their effects on the body when their secretion are too little or too much)
Kelenjar endokrin (endocrine glands) Pituitari (Pituitary) Tiroid (Thyroid) Pankreas (Pancreas) Adrenal (Adrenal) Adrenalin (Adrenaline) Kebolehan untuk menangani tekanan berkurangan (decrease the ability to overcome stress) Testis (Testes) Testeosteron (Testesterone) Ciri-ciri seks sekunder tidak berkembang baik (Secondary sexual characteristic PERSAMAAN Ciri-ciri seks sekunder berkembang baik (Secondary sexual characteristic overdevelop) Insulin (Insuline) Hormon pertumbuhan (Growth hormone) Tiroksina (Thyroxine) (too little) Pertumbuhan terbantut (Stunted growth) Pertumbuhan terbantut (Stunted growth) Diabetes mellitus-kencing manis Aras gula dalam darah rendah (Lower the blood sugar level) Tekanan darah tinggi (Higher blood pressure) Goiter-beguk (Goitre) Hormon (Hormones) Kesan apabila rembesan hormone (Effect when hormone secretion is) Terlalu sedikit/kekurangan Terlalu banyak/berlebihan (too much) Kegergasian (Gigantism)
KOORDINASI SARAF Ovari (Ovary) Estrogen dan (NERVOUS progesterone COORDINATION)
(Oestrogene and
(similarity) not well develop)
Ciri-ciri seks sekunder tidak berkembang baik (Secondary sexual characteristic
KOORDINASI HORMON Ciri-ciri seks sekunder (HORMONAL COORDINATION) berkembang baik
(Secondary sexual
Mengawal dan mengkoordinasi fungsi serta aktiviti organ dalam progesterone) not well develop) characteristic overdevelop) badan (To control and coordinate functions and activities of organs in the body) PERBEZAAN (differences)
2.7
Terdiri daripada (Consists Menganalisis koordinasi antara sistem saraf dengan sistem endokrin Kelenjar tanpa duktus ( ductless of) Saraf (nerves) (Analysing coordination between the nervous system and the endocrine system) glands)
Saraf (nerves)
Mesej dihantar melalui (Messages are sent through)
Aliran darah (hormone) Bloodstream (hormones) Perlahan (slow) Jangka panjang (long term) Luas (wide) Lambat (slow)
Sangat cepat (very fast) Jangka pendek (short term) Terhad (limited) Serta-merta (Immediate)
Kelajuan penghantaran (Speed of transmission) Kesan (Effects) Kawasan sasaran (Target) Gerakbalas (Response)
2.8
Menilai kesan penyalahgunaan dadah terhadap koordinasi badan dan kesihatan (Evaluating the effects of drug abuse on body coordination and health)
chemical substances that can change the functions of the body) 2. 5 jenis dadah berbahaya ialah stimulan, narkotik, depresan, halusinogen dan inhalan.(5 types dangerous drugs are stimulants, depressants, narcotics, hallucinogens and inhalants) Contoh dadah (example of drugs)
-amfetamin (amphetamines) -kafein (caffeine) -kokain (cocaine) -barbiturat (barbiturates) -pil tidur (sleeping pills)
1. Dadah ialah bahan kimia psikoaktif yang boleh mengubah fungsi badan. (Drug is defined as psychoactive Jenis dadah (Types of drugs)
Stimulan (stimulant) metabolic rate) -sentiasa aktif (stay awake or active) Depresan (depressants)
kesan dadah (Effects of drugs)
-Meningkatkan kadar metabolism (increase
-melambatkan gerak balas terhadap ransangan (delay reaction toward stimuli) -membantu untuk menenangkan (help people to calm down)
Narkotik (narcotic) opiat Halusinogen (hallucinogens) Inhalan (inhalants)
-mengurangkan sakit (relieve pain) -menidurkan (induce sleep) -halusinasi (hallucination)
-heroin (heroin) -morfin (morphine) -Kanabis (cannabis) -ganja (marijuana) -LSD
-halusinasi (hallucination) -merosakkan organ badan ( damage the body organs)
-pelarut pencuci (cleaning solvent) -gam (glue) -pelarut cat (paint thinner)
3. Penyalahgunaan
yang boleh
dadah kesan
ialah buruk
drugs excessively or in ways that will harm our body).
menggunakan dadah secara berlebihan membawa kepada badan ( Drug abuse means to use
4. Kesan penyalahgunaan dadah terhadap kesihatan ( Effects of drug abuse on health) 1. Ketagihan (addiction) 2. penagih dadah akan menunjukkan simptom (drug addicts will show withdrawal symptoms) -mengantuk, berpeluh, kepenatan, demam, menggigil, sakit tulang dan sendi, sakit kepala, loya, muntah dan cirit-birit (yawning, sweating,
restlessness, fever, shivering, aching bones and joints, headaches, nausea, vomiting and diarhoea).
3. Risiko
mendapat
AIDS
kerana
berkongsi jarum suntikan ( major risk to get AIDS by sharing injection needles)
4. Rupa fizikal- pucat, kurus, kotor dan
kadang-kadang agresif ( Physical appearance- pale, thin, poor hygiene and sometime become aggressive).
2.9
Menganalisis kesan pengambilan alkohol yang berlebihan terhadap koordinasi badan dan kesihatan (Analysing the effects of excessive consumption of alcohol on body coordination and health) Alkohol (Alcohol) Mengandungi: Etanol (Contain: Ethanol) contoh: Wiski, brandi, bir, wain (examples: Whisky, brandy, beer, wine) Kesan mengambil alkohol yang berlebihan: ( Effects of excessive alcohol consumption: ) (a) Melambatkan gerak balas seseorang terhadap keadaan kecemasan.( Slows down the respond during emergencie) (b) Menyebabkan penglihatan seseorang kurang baik, pendengaran menjadi kurang tepat dan masaFaktor balas menjadi lambat. gerak (Factor): 1. Luaran (external) (Causes bad eyesight, less accurate hearing a. Faktor social tekanan and slows down the reflex time) di tempat kerja atau perasaan
di rumah dan konflik dengan Definasi (Definition) rakan-rakan (Social conditionKeupayaan otak untuk berfikir dan pressure in family , stress at menaakul . (The ability of the brain to work and conflics with think colleagues) 2.10 Menyedari kepentingan minda yang sihat dan baik (Realising the importance of and reason) a healthy and sound mind) b. Faktor persekitaran- kesesakan Minda sihat (healthy mind) lalulintas, pencemaran bunyi Contoh: dan pengudaraan yang tidak MINDA baik. (Environmentbusy 1. Penyayang (loving) (THE MIND) traffic, noise pollution and poor 2. berfikiran rasional (think ventilation) rationally) 3. bertanggungjawab( responsible) 2. Dalaman (internal) 4. mengambil berat ( awareness) 1. Ketidakseimbangan hormone (Imbalance of hormones) Minda tidak sihat 2. Penyalahgunaan dadah (drug abuse) Contoh: 3. Pengambilan alkohol yang 1. Cepat marah (short-tampered berlebihan (excessive 2. tidak bertanggungjawab consumption of alcohol) (irresponsible) 3. saling membenci ( hatred)
SCIENCE FORM 4/ SAINS TINGKATAN 4 BAB 3: VARIASI DAN KETURUNAN (CHAPTER 3: HERIDITY AND VARIATION)
PERKARA Learning Objectives/ Objektif pembelajaran 3.1 Understanding cell division Learning Outcomes/ hasil pembelajaran At the end of the lesson, a student is able to, a. state what genes, deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) and chromosomes are, b. describe the relationship between gene, DNA and chromosome, c. state what mitosis is, d. describe the process of mitosis, e. state what meiosis is, f. describe the process of meiosis, g. compare and contrast mitosis with meiosis, h. explain the importance of mitosis and meiosis Learning Objectives/ Objektif pembelajaran 3.2 Understanding the principles and mechanism of inheritance Learrning Outcomes/ hasil pembelajaran At the end of the lesson, a student is able to, a. explain what dominant genes and recessive genes are, b. identify dominant traits andrecessive traits in human, c. llustrate the mechanism of inheritance of traits using a schematic diagram, d. predict the genotype and phenotype ratios of a monohybrid cross. Learning Objectives/ Objektif pembelajaran 3.3 Understanding sex Determination and the occurrence of twins in human beings Learning Outcomes/ hasil pembelajaran At the end of the lesson, a student is able to, a. explain what sex chromosomes are, b. explain how sex is determined, c. explain the formation of identical and non-identical twins, d. compare and contrast identical with non-identical twins, e. explain what siamese twins are. Learning Objectives/ Objektif pembelajaran 3.4 Understanding mutation Learning Outcomes/ hasil pembelajaran At the end of the lesson, a student is able to, a. state what mutation is, b. state the types of mutation, c. list examples of mutation, d. identify causes of mutation, Learning Objectives/ Objektif pembelajaran 3.5 Evaluating the effects of genetic research on human life Learning Outcomes/ hasil pembelajaran At the end of the lesson, a student is able to, a. list the contributions of genetic research in various fields, b. explain selective breeding in plants and livestock, c. state the importance of selective breeding in plants and livestock, d. describe the technology used for selective breeding, e. present arguments for and against genetic research. Learning Objectives/ Objektif pembelajaran 3. 6 Analysing variation among living things Learning Outcomes/ hasil pembelajaran
Sangat baik
TAHAP PENGUASAAN memuaska baik n
Tidak baik
Sangat baik
baik
memuaska n
Tidak baik
Sangat baik
baik
memuaska n
Tidak baik
Sangat baik
baik
memuaska n
Tidak baik
Sangat baik
baik
memuaska n
Tidak baik
Sangat baik
baik
memuaska n
Tidak baik
At the end of the lesson, a student is able to, a. state what variation is, b. list variation in humans, c. classify variation into continuous and discontinuous variation, d. compare and contrast continuous and discontinuous variation, e. identify factors that cause variation, f. explain the importance of variation. Learning Objectives/ Objektif pembelajaran 3. 7 Realising the need to adhere to a code of ethics in genetic research Learning Outcomes/ hasil pembelajaran At the end of the lesson, a student is able to, a. explain how the misuse of knowledge in the field of genetics can endanger life, b. describe the importance of establishing and adhering to ethics and morals in scientific research for the benefit of mankind.
Sangat baik
baik
memuaska n
Tidak baik
BAB 3: VARIASI DAN KETURUNAN (CHAPTER 3: HERIDITY AND VARIATION)
3.1 PEMBAHAGIAN SEL ( CELL DIVISION)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 2.1 Body Coordination. Koordinasi BadanDokumen20 halaman2.1 Body Coordination. Koordinasi BadanElly EllynaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Nervous SystemDokumen6 halamanHuman Nervous SystemI Kadek Adi Putra Suandana 2005Belum ada peringkat
- Control and CoordinationDokumen22 halamanControl and CoordinationMozibor RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Co OrdinationDokumen4 halamanCo OrdinationBalakrishnan MarappanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen18 halamanChapter 1wakaopakao2Belum ada peringkat
- Science 8 PDFDokumen172 halamanScience 8 PDFaftab khanBelum ada peringkat
- 1630 4245 1 PBDokumen18 halaman1630 4245 1 PBDyah AnindyaBelum ada peringkat
- Cls 10 Control and CoordinationDokumen5 halamanCls 10 Control and CoordinationpokeyballBelum ada peringkat
- SKEMA Modul PDPR SAINS T3Dokumen55 halamanSKEMA Modul PDPR SAINS T3nur fadhilah100% (1)
- Science-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Dokumen5 halamanScience-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Marl Rina EsperanzaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Regulatory SystemDokumen23 halamanHuman Regulatory SystemNina WirdiyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Organisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Dokumen24 halamanOrganisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Mei QiiBelum ada peringkat
- Chart Showing The Classification of Human Nervous SystemDokumen6 halamanChart Showing The Classification of Human Nervous Systemamala raviBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen11 halamanEndocrine SystemAnanya MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Coordination & ResponseDokumen152 halamanCoordination & ResponseChan Chiew WairBelum ada peringkat
- Science Chapter 2 Form 4Dokumen16 halamanScience Chapter 2 Form 4Muhammad Akmal Kamaluddin75% (4)
- 2.1 Body CoordinationDokumen25 halaman2.1 Body CoordinationSri ViineshBelum ada peringkat
- The Nervous SystemDokumen14 halamanThe Nervous SystemGrace JosephBelum ada peringkat
- IM AnSci 111 Module 3Dokumen21 halamanIM AnSci 111 Module 3Riza Mae Duran RangasBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System Notes #2Dokumen7 halamanNervous System Notes #2LeoBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDokumen13 halamanUnit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsIrene Caballero PicazoBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System Written Report 2Dokumen24 halamanNervous System Written Report 2Noronisa PendalidayBelum ada peringkat
- The Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanThe Nervous SystemananthBelum ada peringkat
- Neuronas y Musculos SternDokumen18 halamanNeuronas y Musculos SternAuelillaBelum ada peringkat
- The Nervous SystemDokumen43 halamanThe Nervous SystemmalakbasahalBelum ada peringkat
- TopicDokumen2 halamanTopicmaria maturanaBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Science Notes - Body CoordinationDokumen12 halamanSPM Science Notes - Body CoordinationSPM98% (50)
- Control and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesDokumen45 halamanControl and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesPriyanshu ManwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Samar Deb Easy and Interesting ADokumen846 halamanSamar Deb Easy and Interesting ACharlieBelum ada peringkat
- Axon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyDokumen6 halamanAxon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyshashwatthegamerytBelum ada peringkat
- 1630 4245 1 PBDokumen12 halaman1630 4245 1 PBAnjar JuliyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Ingles Medico Ii - TP 4Dokumen4 halamanIngles Medico Ii - TP 4Rodrigo Anelli De OliveiraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 Control and CoordinationDokumen8 halamanChapter 7 Control and CoordinationS. KishoreBelum ada peringkat
- Class Notes CH7 Control and CoordinationDokumen4 halamanClass Notes CH7 Control and CoordinationArya tyagiBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen23 halamanNervous SystemPatricia BonganayBelum ada peringkat
- Form 5 Nervous SystemDokumen19 halamanForm 5 Nervous SystemJeanMichael VincentBelum ada peringkat
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemDokumen11 halamanSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemGraceEstoleCalo100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Science Form 4Dokumen26 halamanChapter 2 Science Form 4Shafie Buyamin100% (2)
- Coordinated Functions Nervoys SDokumen3 halamanCoordinated Functions Nervoys SGwency Ross Alvarez (Gwen)Belum ada peringkat
- Nervous Sys BiologyDokumen6 halamanNervous Sys Biologyalviayaan807Belum ada peringkat
- Control and CoordinationDokumen4 halamanControl and CoordinationdeveshigiricontactBelum ada peringkat
- Control and Co-Ordination in Animals Nervous System and Endocrine SystemDokumen12 halamanControl and Co-Ordination in Animals Nervous System and Endocrine SystemAgastya SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Nervous SystemDokumen7 halamanHuman Nervous Systemzainab umerBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen35 halamanChapter 2Amiey SehokBelum ada peringkat
- General Psychology: The Biological Basis of Psychological FunctioningDokumen62 halamanGeneral Psychology: The Biological Basis of Psychological Functioningtracy_jBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-7, Control and Coordination in Animals. NotesDokumen10 halamanCh-7, Control and Coordination in Animals. NotesHimanshi VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Saraf Manusia A.S. Muhammad Arhamar, 2023Dokumen9 halamanAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Saraf Manusia A.S. Muhammad Arhamar, 2023Vansh SayaniBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen5 halamanNervous Systemkmakabe78Belum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanNervous Systemvictory IsaacBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 - The Nervous System - Structure and Control of MovementDokumen37 halamanChapter 7 - The Nervous System - Structure and Control of MovementMjBelum ada peringkat
- 14.coordination and ResponseDokumen104 halaman14.coordination and ResponseAli MirzaBelum ada peringkat
- Memahami Sistem Saraf ManusiaDokumen20 halamanMemahami Sistem Saraf ManusiaCt Nazira ZailaniBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment #1: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDokumen4 halamanAssignment #1: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesMarvin ParasBelum ada peringkat
- Study Guide QuestionsDokumen4 halamanStudy Guide QuestionszaidaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Nervous SystemDokumen4 halamanHuman Nervous SystemUmair BasheerBelum ada peringkat
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyDari EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyBelum ada peringkat
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Nervous System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionDari EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Nervous System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.Dari EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.Belum ada peringkat
- Nervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesDari EverandNervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesBelum ada peringkat
- Lo SC Role in GroupDokumen5 halamanLo SC Role in GroupZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- Mastery Exercise 8.3:: Describe The Preparation of Soluble Salts of Na, K and NHDokumen1 halamanMastery Exercise 8.3:: Describe The Preparation of Soluble Salts of Na, K and NHZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- P A H P B C: Sodium, Potassium and Ammonium Salts (Na All Are Soluble Semua LarutDokumen1 halamanP A H P B C: Sodium, Potassium and Ammonium Salts (Na All Are Soluble Semua LarutZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment Plant and NutrientDokumen4 halamanExperiment Plant and NutrientZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Question P1Dokumen18 halamanChemistry Question P1ZekZana100% (1)
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1Dokumen27 halamanChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1ZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- CH 9 Microorganisms TCDokumen24 halamanCH 9 Microorganisms TCZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- CH 9 Microorganisms TCDokumen24 halamanCH 9 Microorganisms TCZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Topikal Chapter 1Dokumen7 halamanLatihan Topikal Chapter 1ZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- Yearly Lesson Plan ChemistryDokumen18 halamanYearly Lesson Plan ChemistryZekZanaBelum ada peringkat
- Null PDFDokumen48 halamanNull PDFfaniar tasha almaraBelum ada peringkat
- Kelas A Materi I - Terapi Insulin BPJS 2015 (Dr. Makbul)Dokumen80 halamanKelas A Materi I - Terapi Insulin BPJS 2015 (Dr. Makbul)dr. arsinaBelum ada peringkat
- Niacinamide A4 8pp 2020Dokumen8 halamanNiacinamide A4 8pp 2020Joatan de SousaBelum ada peringkat
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM OverviewDokumen39 halamanENDOCRINE SYSTEM OverviewAnn M. Hinnen Sparks50% (2)
- Short Stature: - CausesDokumen18 halamanShort Stature: - CausesYusri ArifBelum ada peringkat
- Spironolactone-Induced Unilateral GynecomastiaDokumen3 halamanSpironolactone-Induced Unilateral GynecomastiaLabontu IustinaBelum ada peringkat
- 28 Day Hormone Balance Reset PlanDokumen112 halaman28 Day Hormone Balance Reset PlanKowsalya subbiah100% (2)
- Graded RecitationDokumen2 halamanGraded RecitationKath Belleza DebloisBelum ada peringkat
- Menstrual DisordersDokumen29 halamanMenstrual DisordersJesse EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Severe Hyperglycemia: Effects of Rehydration On Endocrine Derangements and Blood Glucose ConcentrationDokumen8 halamanSevere Hyperglycemia: Effects of Rehydration On Endocrine Derangements and Blood Glucose Concentrationmohamadafif_drBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus Zoology (UG Courses) Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009Dokumen24 halamanSyllabus Zoology (UG Courses) Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009Marumamula Santosh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Hyper para Thyroid Is MDokumen3 halamanHyper para Thyroid Is MAriefBelum ada peringkat
- T1DN Cheat Sheet For Family & FriendsDokumen2 halamanT1DN Cheat Sheet For Family & FriendsType 1 Diabetes NetworkBelum ada peringkat
- Infertilitylessonplan 180525104924Dokumen14 halamanInfertilitylessonplan 180525104924Kavi rajput100% (1)
- HYPERALDOSTERONISMDokumen7 halamanHYPERALDOSTERONISMMarnee Justine ColladoBelum ada peringkat
- General Zoology Laboratory 1Dokumen3 halamanGeneral Zoology Laboratory 1Luther Abaya MolinaBelum ada peringkat
- Physiological Functions of Male Sex Hormone: Presented By:mohammad AqdusDokumen10 halamanPhysiological Functions of Male Sex Hormone: Presented By:mohammad Aqdusabc abcBelum ada peringkat
- Vanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 16Th Edition Eric Widmaier All ChapterDokumen67 halamanVanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 16Th Edition Eric Widmaier All Chaptercharles.harmon235100% (5)
- Internal Regulation Multiple Choice QuizDokumen3 halamanInternal Regulation Multiple Choice Quizsbjon984924100% (1)
- LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Dokumen5 halamanLPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Vikas RathoreBelum ada peringkat
- WWW Biologycorner Com Worksheets Articles Corticosteroids HTMLDokumen3 halamanWWW Biologycorner Com Worksheets Articles Corticosteroids HTMLHugvhBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 008Dokumen11 halamanChapter 008api-281340024Belum ada peringkat
- Arterial Blood Pressure RegulationDokumen21 halamanArterial Blood Pressure Regulationnaresh sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Skims BSC Nursing Syllabus PDFDokumen153 halamanSkims BSC Nursing Syllabus PDFMohd Amir Bin Bashir0% (1)
- 3 Use Thyroid Gland Use TTDokumen55 halaman3 Use Thyroid Gland Use TTMathy MtenjeBelum ada peringkat
- Renin-Angiotensin System: I: (The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus)Dokumen1 halamanRenin-Angiotensin System: I: (The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus)reioctabianoBelum ada peringkat
- Science 10 - Reproductive SystemDokumen32 halamanScience 10 - Reproductive SystemHanabi Scarlet ShadowBelum ada peringkat
- Adrenal InsufficiencyDokumen10 halamanAdrenal InsufficiencyKhalil DiabBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Kishawi 1Dokumen4 halamanMCQ Kishawi 1درالجمانBelum ada peringkat
- PCOSDokumen15 halamanPCOSAndyan Adlu PrasetyajiBelum ada peringkat