CH 47
Diunggah oleh
Kripa PatelDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CH 47
Diunggah oleh
Kripa PatelHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 47.
Neurological Function, Assessment, and Therapeutic Measures
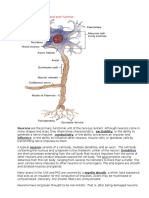
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What part of the brain initiates voluntary movement? a. Parietal lobe b. Hypothalamus c. Cerebellum d. Frontal lobe 2. What part of a neuron carries impulses toward the cell body? a. Dendrite b. Schwann cell c. Axon d. Myelin sheath 3. What part of the brain regulates heart rate and blood pressure? a. Medulla b. Hypothalamus c. Cerebrum d. Cerebellum 4. Motor neurons compose which spinal nerve root? a. Lateral b. Dorsal c. Ventral d. Medial 5. Which of the following carries nerve impulses at synapses? a. Schwanns cells b. Depolarizations c. Cell membrane d. Neurotransmitters 6. What types of neurons transmit impulses from receptors in the internal organs to the central nervous system? a. Somatic sensory neurons b. Visceral sensory neurons c. Interneurons d. Efferent neurons 7. What structure electrically insulates neurons? a. Gray matter b. Myelin sheath c. Interneurons d. Astrocytes 8. What part of the brain regulates coordination and muscle tone? a. Cerebellum b. Medulla c. Frontal lobes d. Hypothalamus
____
____
____
____
____
____
____
____
9. Which of the following structures and functions describes the ascending tracts of the spinal cord? a. They are made of white matter and carry motor impulses. b. They are made of gray matter and carry motor impulses. c. They are made of white matter and carry sensory impulses. d. They are made of gray matter and carry sensory impulses.
____ 10. The nurse is caring for an individual with a head injury and notes unequal pupils. Which of the following terms would be used to document this finding? a. Anisocoria b. Aphasia c. Nystagmus d. Ophthalmoplegia ____ 11. The nurse is caring for a patient admitted to the emergency room after a motor vehicle accident. Which of the following assessments is most important to carry out? a. Visual analogue scale b. Romberg test c. Glasgow Coma Scale d. Babinski test ____ 12. The nurse is assessing a patients pupils for reactivity to light. Which cranial nerve (CN) is being tested? a. CN III b. CN IV c. CN VI d. CN XII ____ 13. A neurologist has a patient stick out the tongue to test which cranial nerve (CN)? a. I (olfactory) b. IV (trochlear) c. VII (facial) d. XII (hypoglossal) ____ 14. A man narrowly misses another car while driving through a busy intersection. His sympathetic nervous system is activated; his heart pounds and his breathing is rapid. As he calms down, his heart rate and breathing return to normal. Which neurotransmitter is in charge now that the excitement is over and he is calmed down? a. Norepinephrine b. Acetylcholine c. Prostaglandin d. Serotonin ____ 15. The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with a cerebral tumor. The nurse anticipates abnormal findings when assessing which functions? a. Heart rate and respiratory rate b. Coordination and posture c. Reflex movement d. Movement and speech ____ 16. The nurse is caring for a 22-year-old female patient who is 2 days post craniotomy for a brain tumor. She was doing well until 2 a.m., when she begins crying and asks for her mother. She has a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) of 15, and pupils are equal and reactive. Her mother is sleeping in the visitors lounge. What nursing action would be most appropriate at this time? a. Administer an as-needed sedative to calm the patient.
b. Notify the neurosurgeon that the patient is upset and crying. c. Ask the mother to come and stay with the patient. d. Reassure the patient, and sit with her until she falls back asleep. ____ 17. The nurse is caring for a patient who has impaired functioning of the left glossopharyngeal (IX) nerve and the vagus (X) nerve. What intervention should the nurse plan to maintain the patients safety while diagnostic testing is being completed? a. Withhold oral fluid or foods. b. Insert an oral airway. c. Apply eye patches to keep the eyes closed. d. Obtain a picture board and a Magic Slate. ____ 18. The nurse is caring for a patient who is scheduled for a computed tomography (CT) scan of the brain because of new onset of headaches. Which statement by the nurse is most accurate when preparing the patient for the scan? a. You must shampoo your hair thoroughly tonight to remove oil and dirt. b. You may take fluids until about 8 a.m. Then we will give you a special radiopaque drink. c. We will partially shave your head tonight so that electrodes can be attached securely to your scalp. d. You will need to hold your head completely still during the examination. ____ 19. The nurse is preparing a patient for an electroencephalogram (EEG). What information should be given to the patient? a. The hair at the temporal area will have to be shaved. b. Little needles will be stuck into the scalp. c. The hair must be clean and dry before the test. d. The patient must withhold fluids and food for 12 hours before the test. ____ 20. The nurse is assisting a neurologist with assessment of a patient with facial muscle weakness. When the neurologist asks the patient to identify different odors, which nerve is being tested? a. I (olfactory) b. II (optic) c. VIII (acoustic) d. X (vagus) ____ 21. The nurse is preparing a patient for a lumbar puncture. Which action is appropriate? a. Administer enemas until clear. b. Remove all metal jewelry. c. Assist the patient into a side-lying position. d. Remove the patients dentures. ____ 22. The nurse is providing post-procedure care for a patient who has had a lumbar puncture. Which of the following orders does the nurse anticipate? a. Have the patient lie flat for 6 hours. b. Keep the patient NPO for 4 hours. c. Monitor the patients pedal pulses every 4 hours. d. Keep the head of the bed elevated 30 degrees for 8 hours. ____ 23. The nurse is caring for a patient who is scheduled for a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. What explanation should be provided to the patient and family? a. An MRI measures muscle contraction after stimulation by tiny needle electrodes. b. An MRI uses electrodes placed on the scalp to measure activity of the brain.
c. A scan of the brain will be done after injection of a radioisotope. d. An MRI is a noninvasive test that uses magnetic energy to visualize internal parts. ____ 24. A patient who is severely brain damaged has decerebrate posturing with extended extremities. The nurse understands that damage most likely occurred in which area of the brain? a. Cerebellum b. Cerebrum c. Brain stem d. Hypothalamus ____ 25. The nurse is caring for a patient who has had a stroke (brain attack). The patient is unable to understand what the nurse is saying and appears frustrated. What term should the nurse document to describe this finding? a. Dysphagia b. Expressive aphasia c. Receptive aphasia d. Confusion ____ 26. The nurse is assisting as a neurosurgeon examines a patient who has a positive Babinski reflex. What assessment finding would the nurse expect to observe? a. The leg flexes when the patellar tendon is struck. b. The leg extends when the patellar tendon is struck. c. Toes curl downward when the sole of the foot is stroked. d. The big toe extends when the sole of the foot is stroked. ____ 27. The nurse is providing care for patients on the neurological step-down unit and notices a patient startle when the alarm rings for a fire drill. After reassuring the patient that there is no danger, an assessment is completed. The nurse recognizes which of the following findings may be related to a sympathetic response? a. Diminished bowel sounds b. Wheezing c. Confusion d. Incontinence ____ 28. When the nurse shines a light in a patients left pupil, both of the pupils constrict. What type of response should the nurse document? a. Direct b. Abnormal c. Accommodation d. Consensual ____ 29. The nurse is providing care for an 87-year-old woman who is recovering from a cerebral vascular accident. Which of the following precautions should the nurse take after noting the patient has a positive Romberg test? a. Provide small, frequent meals. b. Institute fall-risk precautions. c. Darken the room and reduce stimuli. d. Request a footboard and splints. ____ 30. The nurse is providing care for a client admitted to the hospital after a motor vehicle accident. After being informed by family members that the patient is deaf-mute, which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Utilize a three-point scale to grade muscle strength. b. Consider the Babinski response invalid. c. Avoid use of the Glascow Coma Scale. d. Perform the Romberg test with the patient in a seated position.
Multiple Response Identify one or more choices that best complete the statement or answer the question. ____ 31. Which finding is abnormal in an aging patient and should be reported to the physician? (Select all that apply.) a. Altered sleep patterns b. Depression c. Forgetfulness d. Decreased postural stability e. Decreased problem-solving ability f. Fine motor tremors of the hands ____ 32. The nurse is providing care for a patient with a history of aspirating. Which of the following foods would the nurse remove from patients tray? (Select all that apply.) a. Bread with butter b. Ground chicken c. Coffee d. Fruit juice e. Ice cream f. Applesauce ____ 33. Which of the following occur during a sympathetic nervous system response? (Select all that apply.) a. Dilation of bronchioles b. Decrease in peristalsis c. Increase in salivary gland secretion d. Decrease in heart rate to normal e. Relaxation of bladder ____ 34. The nurse is caring for a patient scheduled to undergo a computed tomography (CT) scan with contrast. Which of the following should be included in preprocedure preparation? (Select all that apply.) a. Question the patient about allergies to dye, shellfish, or iodine. b. Determine if the patient has aneurysm clips or metal pins in the body. c. Check blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels. d. Explain to the patient that a sensation of warmth may be felt when dye is injected. e. Tell the patient to report any nausea, itchiness, or difficulty breathing during the scan. ____ 35. Which of the following are functions of the hypothalamus? (Select all that apply.) a. Regulation of body temperature b. Production of growth hormone c. Regulation of food and liquid intake d. Production of epinephrine e. Production of antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin f. Regulation of serum calcium levels ____ 36. The nurse is caring for a patient who is scheduled for a lumbar puncture. Which of the following nursing interventions should the nurse anticipate providing? (Select all that apply.) a. Ensure that the patient has given informed consent to the procedure. b. Position the patient prone on the bed. c. Keep the patient on bedrest with the head of the bed flat for 6 hours after the procedure. d. Limit fluid intake. e. Assess movement and sensation of lower extremities frequently for several hours after the
f.
procedure. Check the puncture site for swelling or drainage.
Completion Complete each statement. 37. A patient who opens the eyes to painful stimuli, makes incomprehensible sounds, and withdraws from pain has a Glasgow Coma Scale score of ____________________. 38. A Glasgow Coma Scale score of less than ____________________ indicates a comatose state. 39. A patient who experiences swaying or leaning to one side when standing with feet together and eyes closed for ____________________ seconds is said to have a positive Romberg test result.
40. The human body has ____________________ pairs of spinal nerves.
Chapter 47. Neurological Function, Assessment, and Therapeutic Measures Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: D The frontal lobes contain the motor areas that generate the impulses that bring about voluntary movement. Each motor area controls movement on the opposite side of the body. The parietal lobes contain the general sensory areas for the cutaneous senses, conscious muscle sense (proprioception), and taste (gustation). The hypothalamus has varied functions. The functions of the cerebellum are concerned with the involuntary aspects of voluntary movement: coordination, the appropriate direction and endpoint of movements, and the maintenance of posture and balance or equilibrium. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1117 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 2. ANS: A A neuron may have one or many dendrites, which are extensions that carry impulses toward the cell body. A neuron has one axon that transmits impulses away from the cell body. In the peripheral nervous system, axons and dendrites are wrapped in specialized neuroglial cells called Schwann cells. The concentric layers of cell membrane of a Schwann cells plasma membrane form the myelin sheath. Myelin is a phospholipid that electrically insulates neurons from one another. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1112 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 3. ANS: A Within the medulla are cardiac centers that regulate heart rate, respiratory centers that regulate breathing, and vasomotor centers that regulate the diameter of blood vessels and therefore blood pressure. The hypothalamus and cerebrum have varied functions. The functions of the cerebellum are concerned with the involuntary aspects of voluntary movement: coordination, the appropriate direction and endpoint of movements, and the maintenance of posture and balance or equilibrium. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1116 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 4. ANS: C Each spinal nerve has two roots, which are neurons entering or leaving the spinal cord. The dorsal root is made of sensory neurons that carry impulses into the spinal cord. The dorsal root ganglion is an enlargement of this root that contains the cell bodies of these sensory neurons. The ventral root is the motor root; it is made of motor neurons that carry impulses from the spinal cord to muscles or glands. (Their cell bodies are in the gray matter of the spinal cord.) When the two roots merge, the nerve thus formed is a mixed nerve. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1115 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 1 5. ANS: D
The end of the axon (the presynaptic neuron) is called the synaptic end bulb and contains a chemical neurotransmitter that is released into the synapse by the arrival of the electrical impulse. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse and combines with specific receptor sites on the postsynaptic membrane. At excitatory synapses, the neurotransmitter makes the postsynaptic membrane more permeable to sodium ions, which rush into the cell, initiating an electrical impulse on the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron. Schwann cells, depolarization, and cell membranes are part of the neuron and its function, not the synapse. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1118 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 6. ANS: B Sensory neurons from receptors in the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints are called somatic; those from receptors in internal organs are called visceral sensory neurons. Motor (efferent) neurons transmit impulses from the central nervous system to effectorsthat is, muscles and glands. Motor neurons to skeletal muscle are called somatic; those to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands are called visceral. Interneurons are found entirely within the central nervous system. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1114 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 7. ANS: B Myelin is a phospholipid sheath that electrically insulates neurons from one another. The gray matter is where the cell bodies of motor neurons and interneurons are located. Astrocytes are part of the neuroglia. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1114 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 1 8. ANS: A The functions of the cerebellum are concerned with the involuntary aspects of voluntary movement: coordination, the appropriate direction and endpoint of movements, and the maintenance of posture and balance or equilibrium. The frontal lobes contain the motor areas that generate the impulses that bring about voluntary movement. Each motor area controls movement on the opposite side of the body. The frontal lobes contain the motor areas that generate the impulses that bring about voluntary movement. The hypothalamus has many functions. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1116 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 9. ANS: C The gray matter is where the cell bodies of motor neurons and interneurons are located. The white matter is the myelinated axons. These nerve fibers are arranged in tracts based on their functions; ascending tracts transmit sensory impulses to the brain, and descending tracts transmit motor impulses from the brain to motor neurons. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1114 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 1 10. ANS: A Anisocoria describes unequal pupils. Aphasia is difficulty speaking or communicating. Nystagmus is involuntary movement of the eyes. Some patients may be unable to move one or both eyes in a specific direction; this is called ophthalmoplegia. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1124 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Integrated Processes: Communication and Documentation | Question to Guide Your Learning: 4
11. ANS: C The Glasgow Coma Scale is an international scale used to assess level of consciousness and document findings and would be the highest priority. A visual analog scale is often used to measure pain level. Babinski and Romberg tests assess muscle function. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1122 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 4 12. ANS: A CN III controls movement of the eyeball and constriction of the pupil for bright light or near vision. CN IV and VI control eyeball movement. CN XII controls tongue movement. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1118 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 4 13. ANS: D CN XII controls tongue movement. CN I controls sense of smell, IV is eyeball movement, and VII is taste and facial muscles. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1118 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 4 14. ANS: B Acetylcholine mediates parasympathetic (peaceful) function. Norepinephrine mediates the sympathetic stress response. Prostaglandins are involved in pain sensation, and serotonin affects mood. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1118 KEY: Client Need: PHYSPhysiological Adaptation | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 15. ANS: D The frontal lobes of the cerebrum contain the motor areas that generate the impulses that bring about voluntary movement. Each motor area controls movement on the opposite side of the body. Also in the frontal lobe, usually only the left lobe is Brocas motor speech area, which controls the movements involved in speaking. The medulla controls heart and respiratory rates; the cerebellum controls coordination and posture; and reflexes are controlled at the spinal cord level. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1117 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 4 16. ANS: C A GCS of 15 and other assessment findings show the patient is stable. She has been through tremendous stress and wants her mother. There is no reason not to ask the mother to come and stay with her. A sedative is not indicated and may mask assessment findings. There is no reason to contact the surgeon. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1122 KEY: Client Need: PHYSBasic Care and Comfort | Cognitive Level: Analysis | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 7 17. ANS: A The patients swallowing and gag reflexes are impaired and could lead to aspiration if food or fluids are given. Cranial nerves (CNs) IX and X do not affect the airway, the eyes, or the ability to communicate.
PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: Page 1118 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Analysis | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 6 18. ANS: D No special preparation is required for a head CT. Shampoo is done before electroencephalogram (EEG). Restricting fluids and radiopaque drinks is done prior to gastrointestinal tests. Electrodes are for EEGs, but shaving is not necessary. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1127 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Teaching and Learning | Question to Guide Your Learning: 6 19. ANS: C Evaluation of the electrical activity of the brain is obtained through an EEG. Electrodes are attached to the scalp with an adhesive. Before the test, make sure that the patients hair is clean and dry. Shaving and fluid restriction are not necessary. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1128 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 6 20. ANS: A The olfactory nerve controls the sense of smell. The optic nerve controls sight. The acoustic nerve controls hearing and equilibrium. The vagus nerve controls some autonomic functions. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1118 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 5 21. ANS: C For a lumbar puncture, the nurse assists the patient into a side-lying position with his or her back as close to the edge of the bed nearest the practitioner as possible. Depending on the patients condition, the nurse may need to help the patient flex his or her knees up to the chest. Enemas are for gastrointestinal (GI) tests, metal must be removed for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and dentures are removed for surgeries or endoscopic procedures. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1126 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 6 22. ANS: A After the lumbar puncture is completed, instruct the patient to remain on bedrest with the head of the bed flat for 6 to 8 hours, as ordered by the physician, and to increase oral intake of fluids. Keeping the head flat decreases the likelihood of leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the puncture site, which can result in a severe headache. Pedal pulses are important for angiograms. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1126 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 6 23. ANS: D MRI uses magnetic energy to visualize soft tissues. A describes an electromyogram (EMG). B describes an electroencephalogram (EEG). C is a brain scan.
PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1127 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Teaching and Learning | Question to Guide Your Learning: 6 24. ANS: C Abnormal extension posturing, or decerebrate posturing, indicates damage in the area of the brain stem. Decorticate posturing indicates significant impairment of cerebral functioning. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1116 KEY: Client Need: PHYSPhysiological Adaptation | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 4 25. ANS: C Receptive aphasia affects the patients ability to understand spoken language. Expressive aphasia is difficulty or inability to communicate verbally with others. Dysphagia is difficulty swallowing. A patient who is unable to communicate is not necessarily confused. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1130 KEY: Client Need: PHYSBasic Care and Comfort | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Communication and Documentation | Question to Guide Your Learning: 4 26. ANS: D Babinski reflex is tested by firmly stroking the sole of the foot. Normal response is flexion of the great toe. If the great toe extends and the other toes fan out, neurological dysfunction should be suspected if the patient is more than 6 months old. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1125 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 5 27. ANS: A The sympathetic division is dominant in stressful situations such as fear, anger, anxiety, and exercise, and the responses it brings about involve preparedness for physical activity, whether or not it is actually needed. The heart rate increases, vasodilation in skeletal muscles supplies them with more oxygen, the bronchioles dilate to take in more air, and the liver changes glycogen to glucose to provide energy. Relatively less important activities such as digestion are slowed, and vasoconstriction in the skin and viscera permits greater blood flow to more vital organs such as the brain, heart, and muscles. The urethral sphincter contracts to prevent urination. PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: Page 1118 KEY: Client Need: PHYSPhysiological Adaptation | Cognitive Level: Analysis | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 28. ANS: D A consensual response means that when one pupil is exposed to direct light, the other pupil also constricts. This is a normal response. A direct response means the pupil exposed to light constricts. Accommodation is the process of visual focusing from far to near. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1124 KEY: Client Need: PHYSPhysiological Adaptation | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Integrated Processes: Communication and Documentation | Question to Guide Your Learning: 3 29. ANS: B A positive Romberg test in an older adult is expected as a result of normal aging changes in the cerebellum. Be sure to protect the patient with a positive result from falls. A gait belt may be helpful when assisting the patient with ambulation.
PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: Page 1125 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 7 30. ANS: C A limitation of the Glascow Coma scale is that if one of the three components cannot be measured, the resulting score is of no use. Because it is not possible to fully evaluate verbal responses for this patient, the scale should not be used. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1122 KEY: Client Need: PHYSPhysiological Adaptation | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Integrated Processes: Communication and Documentation | Question to Guide Your Learning: 7 MULTIPLE RESPONSE 31. ANS: B, F With age the brain loses neurons, but this is only a small percentage of the total and is not the usual cause of mental impairment in the elderly; far more common causes of mental changes include depression, malnutrition, hypotension, and the side effects of medications. Some forgetfulness is to be expected, however, as is a decreased ability for problem solving, altered sleep patterns, and a decrease in postural stability. Fine motor tremors in the hands are a symptom of Parkinsons disease and is considered an abnormal finding. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1120 KEY: Client Need: Health Promotion and Maintenance | Cognitive Level: Comprehension | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 3 32. ANS: C, D Patients with swallowing difficulty (dysphagia) may have better success with foods or thick liquids rather than thin fluids. Thin fluids are more easily aspirated and should be altered (thickened) prior to drinking. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1130 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 7 33. ANS: A, B, E When the sympathetic nervous system is activated, the heart rate increases, vasodilation in skeletal muscles supplies them with more oxygen, the bronchioles dilate to take in more air, and the liver changes glycogen to glucose to provide energy. Relatively less important activities such as digestion (and salivation) are slowed, and vasoconstriction in the skin and viscera permits greater blood flow to more vital organs such as the brain, heart, and muscles. The bladder muscle relaxes, and the sphincter constricts to prevent urination. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1120 KEY: Client Need: PHYSPhysiological Adaptation | Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 34. ANS: A, C, D, E
Patients who are receiving dye should be warned that they may feel a sensation of warmth following the injection; warmth in the groin area may make them feel as though they have been incontinent of urine. Nausea, diaphoresis, itching, or difficulty breathing may indicate allergy to the dye and should be reported immediately to the physician or nurse practitioner. Sedation may be required for patients who are agitated or disoriented. Patients who are in pain may require pain medication before the examination. The patient should be questioned about any allergies to contrast material, iodine, or shellfish. The BUN and creatinine levels should be checked before administration of contrast material because it is excreted through the kidneys. Patients with elevated BUN and creatinine or known renal disease may be unable to tolerate the contrast material. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1127 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 5 35. ANS: A, C, E The hypothalamus produces antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin; these hormones are then stored in the posterior pituitary gland. It produces growth hormonereleasing hormone (GHRH), not growth hormone (GH). It regulates food and fluid intake; it is believed to respond to changes in blood nutrient levels or chemicals secreted by adipose tissue and brings about feelings of hunger or fullness. It regulates body temperature by promoting responses such as shivering in a cold environment or sweating in a warm environment. Epinephrine is secreted by the adrenal medulla. Serum calcium levels are controlled by the parathyroid glands. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1116 KEY: Client Need: PHYSPhysiological Adaptation | Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 2 36. ANS: A, C, E, F Ensure that informed consent has been obtained prior to the procedure. Assist the patient into a side-lying (not prone) position with his or her back as close to the edge of the bed nearest the practitioner as possible. After the lumbar puncture is completed, instruct the patient to remain on bedrest with the head of the bed flat for 6 to 8 hours, as ordered by the physician, and to increase (not limit) oral intake of fluids. Keeping the head flat decreases the likelihood of leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the puncture site, which can result in a severe headache. Increasing fluid intake promotes replacement of the fluid that was removed. Check the puncture site for swelling or drainage of cerebrospinal fluid and report any leakage to the health-care provider. Assess the movement and sensation to the lower extremities frequently for the first 4 hours after the procedure. Assess the patient for headache, and if necessary, obtain an order for analgesia. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1126 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 6 COMPLETION 37. ANS: 8 eight Responds to painful stimuli 2 + makes incomprehensible sounds 2 + withdraws from pain 4 = 8. PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: Page 1122 KEY: Client Need: PHYSPhysiological Adaptation | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Communication and Documentation | Question to Guide Your Learning: 4 38. ANS: seven
7 A score of less than 7 indicates a comatose patient, and a score of 15 indicates the patient is fully alert and oriented. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1122 KEY: Client Need: PHYSPhysiological Adaptation | Cognitive Level: Application | Integrated Processes: Communication and Documentation | Question to Guide Your Learning: 3 39. ANS: twenty 20 A negative Romberg test means that the patient experiences minimal swaying for up to 20 seconds. A patient who experiences swaying or who leans to one side is said to have a positive Romberg test. PTS: 1 DIF: Medium REF: Page 1125 KEY: Client Need: PHYSReduction of Risk Potential | Cognitive Level: Recall | Integrated Processes: Clinical Problem-Solving Process | Question to Guide Your Learning: 4 40. ANS: thirty one 31 There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, named according to their respective vertebrae: 8 cervical pairs, 12 thoracic pairs, 5 lumbar pairs, 5 sacral pairs, and 1 very small coccygeal pair. PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 1114 KEY: Cognitive Level: Recall | Question to Guide Your Learning: 1
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- F.A. 5 Health AssessmentDokumen6 halamanF.A. 5 Health AssessmentYep YepBelum ada peringkat
- NCM NEURO DISORDERS ASSIGN - QDokumen14 halamanNCM NEURO DISORDERS ASSIGN - QDanica Joy Vinluan JacobaBelum ada peringkat
- The Nurse in The Emergency Department Is Caring For A Patient With A PartialDokumen13 halamanThe Nurse in The Emergency Department Is Caring For A Patient With A Partialhasan ahmdBelum ada peringkat
- 50 NEuro Tutorial Week 5ADokumen6 halaman50 NEuro Tutorial Week 5AChristian Versola-Macapulay ValleBelum ada peringkat
- Neurosensory test knowledge questionnaire 3Dokumen5 halamanNeurosensory test knowledge questionnaire 3Ebenezer Manguerra Diala Gube Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Nervous System.Dokumen10 halamanNervous System.Nurse UtopiaBelum ada peringkat
- Question NEURODokumen39 halamanQuestion NEUROjondelacruz19100% (1)
- Analytical QuestionsDokumen29 halamanAnalytical Questionsfujoji92Belum ada peringkat
- 68 Quetion of Nervou Ytem NewDokumen13 halaman68 Quetion of Nervou Ytem NewYash RamawatBelum ada peringkat
- Page - 1Dokumen21 halamanPage - 1AnnizaBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Questions Nursing ReviewDokumen4 halamanSample Questions Nursing ReviewJenny TorredaBelum ada peringkat
- Neurologic Disorder PostDokumen8 halamanNeurologic Disorder PostGwenn SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Neurological System Questions Part 2Dokumen35 halamanNeurological System Questions Part 2luna nguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Ca IiDokumen40 halamanCa IiAbigael Patricia GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 3 lv4Dokumen4 halamanExam 3 lv4Omph IcuBelum ada peringkat
- Neurology, Fluid and Electrolytes and Disaster Nursing: General InstructionsDokumen14 halamanNeurology, Fluid and Electrolytes and Disaster Nursing: General InstructionsJj DelacruzBelum ada peringkat
- When Assessi-WPS OfficeDokumen7 halamanWhen Assessi-WPS OfficeJocelyn AndresBelum ada peringkat
- Final Coaching NP4 Set 2Dokumen18 halamanFinal Coaching NP4 Set 2STEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 57test1 AnswerkeyDokumen31 halamanChapter 57test1 AnswerkeyGwenn SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- SEO - Revision 0905Dokumen77 halamanSEO - Revision 0905Ezah ZiedalBelum ada peringkat
- Week 5 NCLEX QuestionsDokumen6 halamanWeek 5 NCLEX QuestionsGwenn SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 104 Midterm Exams - 1Dokumen21 halamanNCM 104 Midterm Exams - 1Bing58Belum ada peringkat
- Neuromuscular and Nervous System Q OnlyDokumen11 halamanNeuromuscular and Nervous System Q OnlyWenzy CruzBelum ada peringkat
- MSDokumen8 halamanMSVin BaniquedBelum ada peringkat
- PERCEPTION-COORDINATION-PRE-TEST RationalizationDokumen11 halamanPERCEPTION-COORDINATION-PRE-TEST Rationalizationdrei yanBelum ada peringkat
- Health Assessment QuizDokumen3 halamanHealth Assessment QuizSamantha Joy VidalBelum ada peringkat
- Test QuestionsDokumen28 halamanTest QuestionsJerson CastroBelum ada peringkat
- NCA3Dokumen11 halamanNCA3Ley BeltranBelum ada peringkat
- Neuro Study GuideDokumen11 halamanNeuro Study GuideEllen Hennings100% (1)
- Giles Set CDokumen45 halamanGiles Set CPrinting CoBelum ada peringkat
- Neurological Dysfunction Exercises-HIZONDokumen16 halamanNeurological Dysfunction Exercises-HIZONDan HizonBelum ada peringkat
- The Nervous System: An SEO-Optimized TitleDokumen6 halamanThe Nervous System: An SEO-Optimized TitlemaeBelum ada peringkat
- Neuromuscular and Nervous System 2010 With AnswersDokumen13 halamanNeuromuscular and Nervous System 2010 With AnswersWenzy CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Neurologic NCLEX Practice Test Part 1Dokumen10 halamanNeurologic NCLEX Practice Test Part 1mpasague100% (2)
- PosttestDokumen6 halamanPosttestBelleBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 13: Central and Peripheral Nervous System Disorders: Multiple ChoiceDokumen5 halamanChapter 13: Central and Peripheral Nervous System Disorders: Multiple ChoiceJamieBelum ada peringkat
- Haad 1Dokumen23 halamanHaad 1Badet KimBelum ada peringkat
- RLE Exam L4Dokumen10 halamanRLE Exam L4d1choosen100% (1)
- Maternal Child Nursing Care Optimizing Outcomes For Mothers Children and FamiliesDokumen36 halamanMaternal Child Nursing Care Optimizing Outcomes For Mothers Children and Familiesfrankishhobblycnvf46100% (39)
- Neurosensory Disorders: Symptoms, Tests, and Nursing CareDokumen13 halamanNeurosensory Disorders: Symptoms, Tests, and Nursing CarePaul Lexus Gomez LorenzoBelum ada peringkat
- FUNDA Part 1Dokumen5 halamanFUNDA Part 1Jo Hn Vengz100% (1)
- Chapter 08 - Neurologic ProblemsDokumen12 halamanChapter 08 - Neurologic Problemscari100% (1)
- Neuro Nursing Diagnosis and CareDokumen47 halamanNeuro Nursing Diagnosis and CareMeredith Caitlyn Fernandez100% (1)
- MS Exam SampleDokumen17 halamanMS Exam SampleAllen Bugarin CabadingBelum ada peringkat
- NCLEX Neurology Practice Test Part IDokumen6 halamanNCLEX Neurology Practice Test Part IAngelica Superable Nacion100% (2)
- Neurologic ProblemsDokumen11 halamanNeurologic ProblemsFilipino Nurses Central67% (3)
- Oec 6-8Dokumen18 halamanOec 6-8Phil McLeanBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions Neuro1Dokumen13 halamanMedical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions Neuro1dee_day_80% (1)
- 4TH Year QuizbowlDokumen4 halaman4TH Year QuizbowlZoe Jeanne GarcianoBelum ada peringkat
- Funda 1Dokumen7 halamanFunda 1Kat Taasin100% (1)
- Basic Concepts in NursingDokumen9 halamanBasic Concepts in NursingLilian FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Risk Factors and Nursing Care for Neurological ConditionsDokumen4 halamanRisk Factors and Nursing Care for Neurological ConditionsKrizia R. PingkeBelum ada peringkat
- Neuro Nursing MCQ W AnswersDokumen12 halamanNeuro Nursing MCQ W AnswersSienaBelum ada peringkat
- 457 Cbt UpdatedDokumen82 halaman457 Cbt UpdatedDass DavidBelum ada peringkat
- P 1Dokumen9 halamanP 1Aijem RyanBelum ada peringkat
- Medsurg 3Dokumen22 halamanMedsurg 3eyesontheskyBelum ada peringkat
- VerA Ok-Prelim Ncm104 (Autosaved) VeraDokumen30 halamanVerA Ok-Prelim Ncm104 (Autosaved) Verajesperdomincilbayaua100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseDari EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseBelum ada peringkat
- A Brief Review: Explosive Exercises and Sports Performance: Strength and Conditioning Journal June 2001Dokumen9 halamanA Brief Review: Explosive Exercises and Sports Performance: Strength and Conditioning Journal June 2001Hams EletabBelum ada peringkat
- Parasympathetic Nervous SystemDokumen20 halamanParasympathetic Nervous SystemShahid Maqbool100% (1)
- Clinical Examination of Patients With Headache ComplaintsDokumen157 halamanClinical Examination of Patients With Headache ComplaintsrapannikaBelum ada peringkat
- Myasthenia Gravis Presentation and Treatment Variations: A Case Study ApproachDokumen5 halamanMyasthenia Gravis Presentation and Treatment Variations: A Case Study ApproachLiyasariBelum ada peringkat
- Temperature Control Using Neuro-Fuzzy Controllers With Compensatory Operations and Wavelet Neural NetworksDokumen14 halamanTemperature Control Using Neuro-Fuzzy Controllers With Compensatory Operations and Wavelet Neural NetworksDuc Thien NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11: Prognosis and Treatment PlanningDokumen10 halamanChapter 11: Prognosis and Treatment PlanningNikiBelum ada peringkat
- Arnold Chiari Malformation: Sharma A, K V Amrutha, Abraham JDokumen6 halamanArnold Chiari Malformation: Sharma A, K V Amrutha, Abraham JReyhan AristoBelum ada peringkat
- Dizziness, Unsteadiness, Visual Disturbances, and Sensorimotor Control in Traumatic Neck PainDokumen14 halamanDizziness, Unsteadiness, Visual Disturbances, and Sensorimotor Control in Traumatic Neck PainMarco NgBelum ada peringkat
- Final Study Guide Psyc101 Spring 2011Dokumen14 halamanFinal Study Guide Psyc101 Spring 2011FirstLady Williams100% (1)
- Ocular and Visual Physiology - Clinical ApplicationDokumen372 halamanOcular and Visual Physiology - Clinical ApplicationGrecia Sánchez RuízBelum ada peringkat
- Outcome Measure PresentationDokumen11 halamanOutcome Measure Presentationapi-547954700Belum ada peringkat
- Getting The Most From Your TherapyDokumen139 halamanGetting The Most From Your TherapyEjaz Ahmad100% (1)
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyDokumen4 halamanAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyJulia SalvioBelum ada peringkat
- SCIENCEDokumen6 halamanSCIENCEFerlyn SolimaBelum ada peringkat
- One and Half SindromeDokumen4 halamanOne and Half SindromeYulia DamayantiBelum ada peringkat
- Thera Neuromotor Approaches NirDokumen10 halamanThera Neuromotor Approaches NirCeline Kyla MalloBelum ada peringkat
- Ascending SystemDokumen104 halamanAscending SystemCharles OkohBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of Drugs on Indonesian Teenagers (39Dokumen5 halamanEffects of Drugs on Indonesian Teenagers (39Ieka AtiekaBelum ada peringkat
- Optic Neuritis: DR Rishi JhalaniDokumen64 halamanOptic Neuritis: DR Rishi JhalaniRishi Jhalani100% (1)
- Hindi Ocd BookletDokumen20 halamanHindi Ocd BookletAnonymous zNHxbrsETT100% (2)
- Ringer's Solution Stimulates The Blood Plasma of Frogs and Moistens The Exposed Muscle. Isotonic To Amphibians - Hypertonic To HumansDokumen2 halamanRinger's Solution Stimulates The Blood Plasma of Frogs and Moistens The Exposed Muscle. Isotonic To Amphibians - Hypertonic To Humansmaypeee100% (1)
- A. Neurological HistoryDokumen8 halamanA. Neurological HistoryShaneBelum ada peringkat
- Dementia Diagnosis and EvaluationDokumen32 halamanDementia Diagnosis and EvaluationShary AlickBelum ada peringkat
- Coordination Abilities in VolleyballDokumen9 halamanCoordination Abilities in VolleyballFernando Javier HuertaBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To ComaDokumen33 halamanApproach To ComaDương Đình ThuậnBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Training Limitless Brain Training Ryan CooperDokumen11 halamanBrain Training Limitless Brain Training Ryan CooperCarmen Resmerita50% (2)
- Integrative Neuroscience BringingDokumen269 halamanIntegrative Neuroscience BringinghalleyworldBelum ada peringkat
- Brainwave Entrainment To Improve Problem-Solving Skills in People With The Neurodevelopmental Disorder ADHDDokumen8 halamanBrainwave Entrainment To Improve Problem-Solving Skills in People With The Neurodevelopmental Disorder ADHDRaul Morales VillegasBelum ada peringkat
- European Journal of Pain PDFDokumen2 halamanEuropean Journal of Pain PDFAprilBelum ada peringkat
- Volkmann 1986Dokumen16 halamanVolkmann 1986Agustin AlberdiBelum ada peringkat