Company Law Unit - 1
Diunggah oleh
क्षितिज डी एचDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Company Law Unit - 1
Diunggah oleh
क्षितिज डी एचHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
COMPANY LAW
Section3(1) : Company means a company formed and registered under the Companies Act,1956 or an existing company. Section43 : Default in complying with the conditions contained in Section3(1)(iii) constituting a private company.
Section12(2)(b) : Company limited by guarantee i.e. one Section44 : Conversion of private company into public having the liability of its members company - By altering the Articles. limited by the memorandum to such amount as the members may respectively undertake by Section45 : Consequences of membership falling the memorandum to contribute to the assets of the Co. in below legal minimum (7 in case of public the event of its being wound up. and 2 in case of a private company). Section25 : Registration of an association or Non-Profit Making Companies with limited liability. Section3(1)(iii) : Private Company Section560 : Defunct Company Section3(1)(iv) : Public Company Lifting of Corporate Veil & the cases in which Veil of a Company can be lifted Section31(2A) : Where the articles of association are altered in order to convert a public company into a private company, then as per Rule 4B of the Companies (Central Governments) General Rules and Forms, 1956 the co. must have approval of the Central Govt. and after obtaining the approval of the Central Govt., it must file with the Registrar a printed copy of the articles as altered within one month of the date of receipt of the order of approval.
Bowman Vs Secular Society Ltd. : Where the purpose is not lawful, i.e., where any of the objects is illegal, the Registrar may refuse to register and Salomon Vs Salomon & Co. Ltd. : if he register, the certificate of registration is A company is a legal person distinct from its members. It not conclusive for this purpose and the registration itself has its own corporate personality. This principle may be may be cancelled by the Central Government taking referred to as the veil of incorporation. appropriate proceedings. Callaghar Vs Gerrnania Brewing Co. : Section34 : Upon the registration of the documents and A company in reality is an association of persons who are the payment of the necessary fees, the ROC in fact the beneficial owner of all the corporate property. issues a certificate that the company is incorporated and in the case of a limited company that The cases in which the courts have disregard the it is limited. corporate personality of the company are : (1.) Juggilal Vs CIT : For Protection of Revenue Section35 : A certificate of incorporation issued by the Registrar in respect of any association, shall (2.) Jones Vs Lipman : For Prevention of Fraud or be conclusive evidence of the fact that all improper conduct the requirements of the Act have been complied with in respect of registration. (3.) Daimler Co. Ltd. Vs Continental Tyre & Rubber Co. Ltd. Section13 : Contents of Memorandum of Association. Determination of character of a company whether it is enemy. Ultra Vires acts of the Company are void (4.) Cilford Motor Co. Vs Horne : Where the company and inoperative wholly. The cases are :is a sham (not genuine). 1.)Ashbury Railway Carriage and Iron Co. Ltd. Vs Riche 2.) Re German Date Coffee Co. (5.) Workmen of Associated Rubber Industry Ltd. Vs Associated Rubber Industry Ltd. : Avoidance of Section16 : It allows for alteration of memorandum by a welfare legislation. special resolution followed by confirmation (6.) Connors Vs Connors Ltd. : Protection of public thereof by the Company Law Board. policy.
Section20(1) : No Company shall register by a name which in the opinion of the Central Government is undesirable.
Section31 : It vests companies with power to alter or add to its articles.
Section610 : Memorandum and Articles of Association Section20(2) : If the proposed name of the company is of the company are construed as identical with or too nearly resembles the public document. name of another company which is already in existence, the Central Government may refuse to The Royal British Bank Vs Turquand : register it. Doctrine of constructive notice does in no sense mean that the outsiders are deemed to have notice of the Section21 : A Company by Special Resolution and the internal affairs of the company. Doctrine of Indoor approval of the Central Government signed Management also known as Turquand Rule which is in writing, change its name. the only limitation to the doctrine of constructive notice includes that if an act is authorized by the articles or Proviso to Section21 : An approval of Central Govt. memorandum, an outsider is entitled to assume that all would not be necessary where the the detailed formalities for doing the act have been change in name only includes addition or observed. deletion of the words private consequent upon the conversion as per the provisions of the Act of a public Preliminary or Pre - Incorporation Contracts : company into a private company or vice versa. These contracts are entered into by agents or trustees or promoters on behalf of a prospective company before it Section146 : The address of registered office may be has come into existence. changed within the local limits of any city, town or village where such office is situated Provisional Contracts : These contracts are entered by a by just giving a notice to the concerned Registrar within company after its incorporation 30 days after the date of the change. But a special and before it is entitled to resolution may be required if the change of the registered commence business. office is from one village, town etc. to another village, town etc. in the same State. Section17(1) : It lists the purposes for which alteration of objects is permitted. Section18(1) : A company shall file with the Registrar a copy of special resolution passed by the company in relation to the clauses of section17(1) within one month from the date of such resolution with a printed copy of memorandum as altered. Section19 : If documents required to be filed with the Registrar under Section18 are not filed within the prescribed time, the alteration shall at the expiry of such period, become void and inoperative. Section38 : No member of a company shall be bound by an alteration made in the memorandum or articles after the date on which he became a member, if such an alteration requires him to take or subscribe for more shares then the number held by him as at the date of alteration or in any way increase his liability, unless he agrees to it in writing. Proviso to Section38 : Where the company is a club or any other association and the alteration requires the member to pay recurring or periodical subscription at a higher rate, although he does not agree in writing to be bound, it will bind him.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Request For Dismissal Form Civ 110Dokumen2 halamanRequest For Dismissal Form Civ 110soyjairoBelum ada peringkat
- Property Plant and EquipmentDokumen32 halamanProperty Plant and EquipmentKyllie CamantigueBelum ada peringkat
- Suspects Script Edited FinalDokumen8 halamanSuspects Script Edited Finalapi-592508137Belum ada peringkat
- Unfolding The Ethical Issues of Lawyers Practicing Dual Professions A Case StudyDokumen120 halamanUnfolding The Ethical Issues of Lawyers Practicing Dual Professions A Case StudyReynald LumambaBelum ada peringkat
- Jones v. Superior CourtDokumen4 halamanJones v. Superior CourtKerriganJamesRoiMaulitBelum ada peringkat
- Observations On Poverty and Poor in Plato and Aristotle, Cicero and SenecaDokumen26 halamanObservations On Poverty and Poor in Plato and Aristotle, Cicero and SenecaJuanBelum ada peringkat
- State vs. Johnny Church (Drew Blahnik)Dokumen15 halamanState vs. Johnny Church (Drew Blahnik)Michael Howell100% (1)
- Tutorial III Agreement of Sale: Submitted byDokumen6 halamanTutorial III Agreement of Sale: Submitted byManasi DicholkarBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Supreme Court Jurisprudence: Home Law Firm Law Library Laws JurisprudenceDokumen29 halamanPhilippine Supreme Court Jurisprudence: Home Law Firm Law Library Laws JurisprudenceBowthen BoocBelum ada peringkat
- Acctg ProbDokumen7 halamanAcctg ProbFrancisco MarvinBelum ada peringkat
- Ict349 Ict649 Topic 04Dokumen116 halamanIct349 Ict649 Topic 04jacklee1918Belum ada peringkat
- The Revolt in BarbadosDokumen3 halamanThe Revolt in BarbadosConrad SawyersBelum ada peringkat
- Lift Plan v2Dokumen3 halamanLift Plan v2Hussain YahyaBelum ada peringkat
- Bailment and BankruptcyDokumen14 halamanBailment and BankruptcyEdith NtitiBelum ada peringkat
- Auditing Theory: All of TheseDokumen7 halamanAuditing Theory: All of TheseKIM RAGABelum ada peringkat
- ACD10403 Group Assignment 2019Dokumen3 halamanACD10403 Group Assignment 2019Atqh ShamsuriBelum ada peringkat
- 4ATDokumen3 halaman4ATPaula Mae DacanayBelum ada peringkat
- Blends and Digraphs PassagesDokumen27 halamanBlends and Digraphs PassagesAnu Gupta100% (3)
- Electromagnetic Induction - Revision Notes 1Dokumen5 halamanElectromagnetic Induction - Revision Notes 1Suyash GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Governor-General of IndiaDokumen15 halamanGovernor-General of IndiaveersainikBelum ada peringkat
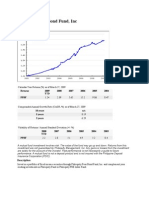
- Phil Equity Peso Bond FundDokumen2 halamanPhil Equity Peso Bond Funderic aunzoBelum ada peringkat
- American Rubber V CIR, 1975Dokumen12 halamanAmerican Rubber V CIR, 1975Rald RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises of Analytical Exposition TextDokumen2 halamanExercises of Analytical Exposition TextSovie UnyilBelum ada peringkat
- Synd UPI TCDokumen9 halamanSynd UPI TCneel bhangureBelum ada peringkat
- SFA HANDBOOK 201-280 Registration ProceduresDokumen80 halamanSFA HANDBOOK 201-280 Registration ProceduresGraeme NichollsBelum ada peringkat
- Problem 11 - 6 Multiple Choice (AICPA Adapted)Dokumen3 halamanProblem 11 - 6 Multiple Choice (AICPA Adapted)Mobi Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- God'S Judgement: A Neo-Testamentarian PerspectiveDokumen5 halamanGod'S Judgement: A Neo-Testamentarian PerspectiveEdward KanuBelum ada peringkat
- Bates Dittus TBL 37 Users Manual 2014 PDFDokumen13 halamanBates Dittus TBL 37 Users Manual 2014 PDFErikBelum ada peringkat
- #25 Magno V CADokumen2 halaman#25 Magno V CAGladys CubiasBelum ada peringkat
- Minutes of The Meeting GadDokumen10 halamanMinutes of The Meeting GadERIC PASIONBelum ada peringkat