IHRM Final Notes
Diunggah oleh
haughtonfDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IHRM Final Notes
Diunggah oleh
haughtonfHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Repatriation
Questions about repatriation should be addressed before assignment begins Issues of: Professional readjustment Psychological/social re adjustment Concepts Lecture Three Role of international assignees Agent of control expatriates can be a bureaucratic control mechanism for ensuring compliance through direct supervision Agent of socialization There is an expectation that expatriates will assist in the transfer shared values and beliefs. Knowledge sharing and competence transfer. Network builder - assignments are a way of developing social capital. Making interpersonal relationships can be useful for informal control and communication purposes. Boundary spanner expatriates are spanners because they can collect hostcountry information, act as representatives of their firms in the host country and can influence agents Overcome skills shortages. Develop global leadership. Diffusion of Knowledge
Cultural/Institutional adjustment - Social Cultural Environment (communication, relations to locals, norms etc) - General Environment (Directions, transportation, climate, living standards etc) - Work Environment (relates directly to job performance) Honeymoon ->Culture Shock->Pulling Up ->Adjustment
Lecture Four Types of Adjustment Assimilation - Go Native Integration - Dual Citizen Marginalize - Free Agent Separation - Hearts at Home
Modes of Adjustment Replication assignee attempts not to change or to change the environment. Absorption assignee attempts to change only themselves. Determination assignee attempts to change environment. Exploration- combines absorption and determination. Withdrawal avoids engagement at any level.
Lecture Five Return on Investment A calculation in which the financial and non-financial benefits to the firm are compared with the financial and non-financial costs of the international assignment, as is relevant and appropriate to the assignments purpose Continuous Assignment Review R.O.I mobility Champion a specific manager who is in charge of expatriate success on assignment. They track the progress of assignment and assignee. Lecture Seven Repatriation Phases - Preparation tidying up. - Physical relocation the physical act of removal. Of importance here is the need to reduce the uncertainty, stress and disruption experienced by the expatriate and family. - Transition Re-settling. - Readjustment dealing with reverse culture shock etc
Readjustment Factors Job-related factors 1) Career Anxiety: out of sight/out of mind, demotion upon return/guaranteed re-entry position, restructuring, retrenchment 2) The Value of International Experience Traditionally undervalued but this has changed in recent years Returnees may face less challenging work and global talent requires challenge to be retained.. Career development Plan
3) Coping with Re-entry role Re-adjustment will depend partly on the type of adjustment they made overseas. In the case Mark Chan & co. integrated well into the new setting. Role clarity, role conflict and role discretion appear to be linked to positive re-adjustment.
4) Loss of status and Pay - The big fish and the small pond. - Pay and benefits.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Data Collection Methods and Tools For ResearchDokumen29 halamanData Collection Methods and Tools For ResearchHamed TaherdoostBelum ada peringkat
- Enhancing reliability of CRA piping welds with PAUTDokumen10 halamanEnhancing reliability of CRA piping welds with PAUTMohsin IamBelum ada peringkat
- Business Advantage Pers Study Book Intermediate PDFDokumen98 halamanBusiness Advantage Pers Study Book Intermediate PDFCool Nigga100% (1)
- MSDS Metafuron 20 WPDokumen10 halamanMSDS Metafuron 20 WPAndi DarmawanBelum ada peringkat
- ADC Driver Reference Design Optimizing THD, Noise, and SNR For High Dynamic Range InstrumentationDokumen22 halamanADC Driver Reference Design Optimizing THD, Noise, and SNR For High Dynamic Range InstrumentationAdrian SuBelum ada peringkat
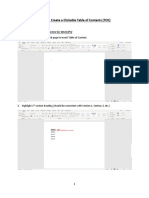
- How To: Create A Clickable Table of Contents (TOC)Dokumen10 halamanHow To: Create A Clickable Table of Contents (TOC)Xuan Mai Nguyen ThiBelum ada peringkat
- Specialized Government BanksDokumen5 halamanSpecialized Government BanksCarazelli AysonBelum ada peringkat
- Nuxeo Platform 5.6 UserGuideDokumen255 halamanNuxeo Platform 5.6 UserGuidePatrick McCourtBelum ada peringkat
- Bajaj 100bDokumen3 halamanBajaj 100brmlstoreBelum ada peringkat
- Best Homeopathic Doctor in SydneyDokumen8 halamanBest Homeopathic Doctor in SydneyRC homeopathyBelum ada peringkat
- Market Participants in Securities MarketDokumen11 halamanMarket Participants in Securities MarketSandra PhilipBelum ada peringkat
- Savable Data Page - Its Configuration, Usage & ExecutionDokumen20 halamanSavable Data Page - Its Configuration, Usage & ExecutionsurmanpaBelum ada peringkat
- Perbandingan Sistem Pemerintahan Dalam Hal Pemilihan Kepala Negara Di Indonesia Dan SingapuraDokumen9 halamanPerbandingan Sistem Pemerintahan Dalam Hal Pemilihan Kepala Negara Di Indonesia Dan SingapuraRendy SuryaBelum ada peringkat
- (Lesson 10-1) - Quality Assurance, Hemocytometry, Thoma PipetsDokumen22 halaman(Lesson 10-1) - Quality Assurance, Hemocytometry, Thoma PipetselleBelum ada peringkat
- PDS-1st PageDokumen1 halamanPDS-1st PageElmer LucreciaBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Consulting Frameworks To Learn For Case Interview - MConsultingPrepDokumen25 halaman10 Consulting Frameworks To Learn For Case Interview - MConsultingPrepTushar KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Skills:: Surabhi SrivastavaDokumen3 halamanTechnical Skills:: Surabhi SrivastavaPrasad JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitDokumen3 halamanUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- KL Wellness City LIvewell 360 2023Dokumen32 halamanKL Wellness City LIvewell 360 2023tan sietingBelum ada peringkat
- Reynold's Number Flow ExperimentDokumen8 halamanReynold's Number Flow ExperimentPatrick GatelaBelum ada peringkat
- Exp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsDokumen1 halamanExp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsMuhammad ArslanBelum ada peringkat
- Chi Square LessonDokumen11 halamanChi Square LessonKaia HamadaBelum ada peringkat
- Amos Code SystemDokumen17 halamanAmos Code SystemViktor KarlashevychBelum ada peringkat
- CONFLICT ManagementDokumen56 halamanCONFLICT ManagementAhmer KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Alexander Lee ResumeDokumen2 halamanAlexander Lee Resumeapi-352375940Belum ada peringkat
- Password CrackingDokumen13 halamanPassword CrackingBlue MagicBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Venue For Monday Sep 25, 2023 - 12-00 To 01-00Dokumen7 halamanExam Venue For Monday Sep 25, 2023 - 12-00 To 01-00naveed hassanBelum ada peringkat
- Managing operations service problemsDokumen2 halamanManaging operations service problemsJoel Christian Mascariña0% (1)
- 59 - 1006 - CTP-Final - 20200718 PDFDokumen11 halaman59 - 1006 - CTP-Final - 20200718 PDFshubh.icai0090Belum ada peringkat
- BIU and EU functions in 8086 microprocessorDokumen12 halamanBIU and EU functions in 8086 microprocessorDaksh ShahBelum ada peringkat