Advanced Drilling Using A Dual Bit System
Diunggah oleh
tarang_tusharDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Advanced Drilling Using A Dual Bit System
Diunggah oleh
tarang_tusharHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SPE 99478 Advanced Drilling Using a Dual-Bit System
P.M. Gopalsing, Maharashtra Inst. of Technology
Copyright 2006, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was prepared for presentation at the 2006 SPE Western Regional/AAPG Pacific Section/GSA Cordilleran Section Joint Meeting held in Anchorage, Alaska, U.S.A., 810 May 2006. This paper was selected for presentation by an SPE Program Committee following review of information contained in an abstract submitted by the author(s). Contents of the paper, as presented, have not been reviewed by the Society of Petroleum Engineers and are subject to correction by the author(s). The material, as presented, does not necessarily reflect any position of the Society of Petroleum Engineers, its officers, or members. Papers presented at SPE meetings are subject to publication review by Editorial Committees of the Society of Petroleum Engineers. Electronic reproduction, distribution, or storage of any part of this paper for commercial purposes without the written consent of the Society of Petroleum Engineers is prohibited. Permission to reproduce in print is restricted to an abstract of not more than 300 words; illustrations may not be copied. The abstract must contain conspicuous acknowledgment of where and by whom the paper was presented. Write Librarian, SPE, P.O. Box 833836, Richardson, TX 75083-3836, U.S.A., fax 01-972-952-9435.
In petroleum industry rig time plays very vital role. By adopting such innovative method as mentioned above tripping time can be substantially reduced. Introduction: This paper describes all the factors that influence a decision maker while evaluating a project. In any industry economy of time and money is the need of the hour. The major topic under discussion in oil and gas industries is how to decrease the time required for drilling. Because it is associated with money required not only for drilling but it also includes money for rig, various equipments etc. Currently offshore rig costs are about $200,000 per day. Saving such a huge amount will drastically help the economics of the drilling industry. This paper proposes a new drilling mechanism which can help in cutting down the drilling cost drastically. In conventional drilling methods we use a single bit while drilling a particular formation .But if a soft formation is encountered we have to trip out the whole string and replace it with the tricone bit. This process takes a lot of time and hence increases in rig cost. This paper adopts an alternative method to reduce the rig cost by reducing the frequency of tripping operations using a dual bit assembly /system. Description and Application of Equipment and Processes: The different parts of the assembly of the proposed dual bit using dual bit drilling string are as shown in the figure 1. The model contains an expandable PDC bit inside an expandable tricone bit. This arrangement forms the basis of the innovation. The basic parts of this assembly are: BOTTOM HOLE ASSEMBLY: External String: - External string is composed of drill pipe, crossover sub, drill collar, bit sub and bit. External string transmits rotary motion and drilling mud under high pressure to the drill bit .External string is subjected to several types of loading including axial loading due to weight carried and its own weight, radial forces due to well bore pressure, torque due to rotation .The external string must be capable of withstanding all types of imposed loading and must have reasonably long service life.
Abstract: In conventional drilling a majority of drilling problems occur during tripping such as key seating and wall sticking. This leads to increase in rig time hence cost is unnecessarily high, especially in deep sea drilling. Conventional drilling techniques use rotary drill bits which need to be replaced depending on the formations encountered. If the formation is very hard, the bit has to be replaced by a diamond bit. This change of bit requires unnecessary increase in trip time and hence rigs cost. This trip time which can even take a day especially for deep wells and can be eliminated by using a novel method of a drill bit called a Piggy Back Dual Bit system. This paper deals with the design and operation of such a novel Piggy Back Dual Bit system. This new drill bit system has a tricone bit on the outside and a PDC or diamond studded bit inside. Both the tricone bit and PDC bit are expandable. When hard formations are encountered, the tricone bit is expanded by applied pressure to the mud which engages a latching mechanism in the BHA. By this action also the expandable PDC bit is forced out. The entire expansion mechanism is hydraulically actuated, by the pressure from fluid flowing through the bit. The drilling activity is now controlled by the PDC drill bit doing the drilling through the hard formation, while the tricone bit is now piggy back on the PDC drill bit doing no work at all, other than reaming a bigger hole. Thus an entire hole can be drilled conveniently without frequent tripping operation to change the bit. Maximum efficiency can be achieved by this mechanism during drilling.
SPE 99478
Expandable tricone drill bit: - This is a totally new concept, which is a modification to a normal tricone bit into one which can be expanded to facilitate the downward movement of the PDC bit. It is connected to the external string. The external string provides rotary motion to the expandable tricone bit. It is used for drilling soft formations. ARRANGEMENT:
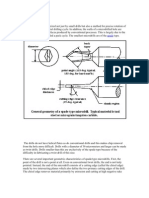
Figure: - 1 Different parts of the proposed system. Figure: - 2 Sectional view of the proposed system. Internal string: -Internal string also comprises of a drill pipe, crossover sub, drill collar, bit sub and bit similar to the external string the only difference being the diameter which is comparatively less. Internal string is used to transmit drilling mud under high pressure to the expandable PDC bit. Down hole motor: - The down hole motor provides rotary motion to the internal expandable PDC bit, thereby eliminating the need to rotate the drill string from the surface. The down hole motor is normally placed above the drill bit. The main advantage of downhole motor is that they give better control of dogleg severity and better hole conditions .The downhole motor used in the assembly is Turbine type motor. Reamers: - Reamers are attached to the external string. They are provided with tungsten carbide teeth in order to ream or expand bore hole diameter. The reamer is used to ream out space for fitting the external expandable tricone drill bit when it is retratced.The reamers are driven by torque provided by the external sting. Drive shaft: - The rotor blades of the down hole motor are attached to the drive shaft, which, in turn, is attached to the expandable PDC bit. It is used to carry power from the downhole motor and transmit it to the internal expandable PDC bit. Expandable PDC drill bit: - The expandable drill bit has tungsten carbide teeth. The expandable PDC bit is connected to the internal string, which is concentrically inside the expandable tricone bit. The torque is provided to the PDC bit by the downhole motor. It is used for drilling hard formations. The proposed arrangement of the dual bit is as shown in the fig.1 and section view as shown in fig. 2. Working mechanism: In conventional drilling, the bit is attached to a long drill pipe. Its job is to break up the rock or to allow the drilling to progress deeper into the earths crust. There are many different varieties of drilling bits, each with a different specialty. Some major varieties are Steel Tooth Rotary Bits, Insert Bits, Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Bits, and Diamond Bits. In addition there are hybrid bits that combine features from different variations. When drilling deep wells through different layers of rock, several different bits might be used on a single well. The decision to change bits is not made easily, however, because it takes time and extra equipment to remove the entire drill pipe and bit, and then to reassemble it using a different bit. Sometimes, changing a bit could involve, removing close to a mile of drill pipe. The external strings working is similar to that of the conventional drilling method. The external string uses an expandable tricone bit. The torque to the bit is provided by the rotary motion of the external string. The external string is rotated with the help of a rotary table and master bushing arrangement. While drilling the hole cutting particles have to be constantly pushed out to the surface. The cutting particles are pushed out by mud flowing in from the nozzles provided in the external tricone and the internal PDC bit. The mud reaches the nozzles through the external and internal strings. The flow of mud is controlled by the valves provided in both the strings.
SPE 99478
Figure: - 4 Figure: - 3 We know that two types of tricone bit are available. Tricone bit with milled teeth and tricone bit tungsten carbide inserts where milled teeth bit is suitable for soft formations while insert type bits can drill medium to hard formations. While drilling we can only use one bit at a time i.e. either milled teeth or tungsten carbide. Now suppose a parallel well is being drilled, we have an idea about the approximate thickness of the formation to be drilled. If the thickness is negligible say of the order of 10m we use the same bit other wise if a hard formation of thickness about 100m or more is present we need to trip out the bit in use and trip in the appropriate bit. Instead if we use the Advanced Drill Using a Dual Bit the Internal PDC is pushed out to perform the drilling. For the PDC bit to be pushed out the expandable tricone bit is to be pulled up .The reamers facilitate this operation. We know the exact distance between the reamers and the expandable tricone bit. Reamers driven by the external string ream out the borehole wall to accommodate the expandable tricone bit as shown in fig. 3. The drill pipe is tripped out accordingly so that the expandable tricone bit reaches the reamed out borehole and can expand as shown in fig. 4. The tricone bit is expanded similar to the expansion of the PDC bit described later. The expansion of tricone bit is necessary so that it provides enough space for the PDC bit to be pushed and perform the drilling operation. Here a question arises that how do we push out the internal PDC bit? This is done by using a piston. As shown in fig. 5 that the central valve is closed keeping the other valves open. As a result the pressure applied by the fluid (mud) is applied on the central inner string. This makes the string to move downwards. The pressure can be maintained as stated above by changing the density of the mud. The PDC bit is driven by the down hole motor present in the internal string through a connecting shaft. The down hole motor consists of multistage blade type motor and stator sections, a thrust bearing section and a drive shaft. The no. of rotor sections can vary from 25 to 250. The stator retains stationary and its main function is to deflect the mud to the rotor blades. The rotor blades are attached to the drive shaft, which is inturn, attached to the bit. Mud under high pressure is pumped down the drill string to the motor section where it is deflected by the stator blades to the rotor blades. This then imparts rotor and inturn to drive shaft and drill bit. To maintain the borehole diameter we have to expand the PDC bit. The original operating mechanism concept of four blades, pivoting about their rearmost end, in a housing retained, but now attached to an outer hydraulic cylinder, not carrying any axial drilling forces. Rearward movement of the cylinder under the influence of pressure differential draws the blades over a profiled surface, causing them to open outwards, to the expanded position. The blades are now retained in slots machined into the head of the bit, as a means of transmitting the drilling torque. Retaining pins, mounted on the head, act on grooves machined into the blades to actively retract blades as the bit closes. The entire drilling weight is applied directly to the head of the bit and on to the PDC cutting structure mounted on the blades. The blades are not directly loaded with any compressive forces applied to the pivoting end. The pivot is only a means of locating the rear end of the blades. Pulling out of hole imparts a down thrust onto the blades, promoting a closing action, in addition to that imparted by the return spring. This results in an Expansion ratio of twenty percent. The cutting pieces are delivered at the surface by the mud flowing through the nozzle provided in the PDC bit. We have to keep in mind that the internal string has some limitations regarding its length. In such a case the PDC bit has to pull up and the whole arrangement tripped in further. A new hole is to ream out to fit the tricone bit so that the PDC bit can reach further down. If we again encounter a soft formation the internal PDC bit is to be pulled up. As shown in the fig. 8 the valves 1, 2 are all in closed position. As a result the drilling mud passes through valves 3 which are returning valves. This increases the liquid in the space between the internal and external string. This will result in tripping up of the internal string. Now the expandable tricone bit retracts and the drill pipe is tripped in to the original position.
SPE 99478
Explanation for flow of mud and nozzle positions: Fig 5 shows the valve positions and the resulting mud flow when the tricone bit is used for drilling, where 1 shows central non return valve, 2 shows bypass non return valves and 3 shows bottom return valves. All the valves are in open position and mud flows through both the internal and external strings. Fig. 6 shows the valve positions and resulting mud flow when hard formation are encountered and the PDC bit is to be pushed out. The central valve is closed and all the valves mounted on the piston are closed. The resulting mud flow helps in pushing the PDC bit out. Fig. 7 shows the valve positions and mud flow when PDC bit is used for drilling. The central valve is closed and bypass valve is open. Mud flows from bypass to valves mounted on internal string; As a result the mud passes through the downhole motor and produces torque. Also the mud flows only through the nozzle of the PDC bit. Fig. 8 shows the valve positions and mud flow for retracting the PDC bit. The central valve and bypass valves are closed. The valves mounted on the internal string (return valves) are open. As a result the internal string is pulled up to normal position.
Figure: - 6
Figure: - 5 Figure: - 7
SPE 99478
the trip in and trip out time which inturn cuts down the well cost. DISADVANTGES: 1) It is not wise to use Tricone Bit on Inner string. As string is not rotating, when inner bit is working. So the chances of differential sticking are highest, if Tricone bit is on the Inner string .So it is mandatory to have PDC Bit on Inner String, with somewhat compromise on its efficiency. 2) The design of the system is quiet complex. Presentation and data of results:
Figure:-8 Figure: - 9 Comparison of two different bits. APPLICATIONS: 1) It can be used for two different formations without tripping out. 2) It can be used in directional drilling. 3) It can be used in pilot hole drilling. ADVANTAGES: 1) While drilling we have to frequently trip in and trip out the drill string depending on various factors. The most important being the type of formation encountered .Here the advanced drill using a dual bit can be highly advantageous. 2) In drilling operations theres is always a risk of well blow out or kick when we trip in or trip out the string. Using a dual bit less number of trip in and trip out takes place. Hence reducing the risk of blow outs. 3) We can vary the diameter of the PDC bit and hence it is useful in pilot hole drilling without using a different assembly. This is done to find out the hydrocarbon content. 4) Applicable successfully in all type of drilling operations. (Horizontal / Vertical / Directional). 5) Avoid damage to soft Formations, which might result in heavy loss to the Company, during Production Phase. 6) Economics is a major factor while drilling a well. The advanced drill using a dual bit helps in cutting down Though we have pending field study for the proposed arrangement, we have data regarding individual bits. The data provided compares the 17 1/2 expandable tricone bit and 17 expandable PDC bit on the basis of ROP, WOB and Torque. From this data we can say expandable PDC bit have enough efficiency to drill hard formation like any non-expandable PDC bit or tricone bit. If we use a dual bit system, which uses expandable tricone bit and expandable PDC bit. We will get much better results. Conclusion: All the aspects of mechanical feasibility have been carefully looked into and as far as this paper is concerned there are no loopholes theoretically in the proper functioning of the advanced drill using a dual bit. Acknowledgements: I would like to thank 1) Dr. L. K. Kshirsagar Head, Department of Petroleum Engineering 2) Mr. S. J. Naik Assistant Professor DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM 3) MR. Chaitanya V. Kachare DEPARMENT OF MECHANICAL from MIT Pune, INDIA, and for the support and help on this paper.
SPE 99478
References: 1) Martin, M. D. and Gledhill, A. D. et al.: Expandable Dill Bit provides new method of drilling increased diameter hole paper SPE/IADC 79793 presented at the 2003 SPE/IADC drilling conference, Amsterdam, 19-21 February 2003. 2) RABIA, H.: OILWELL DRILLING ENGINEERING: principles and practice
SPE 99478
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- SPE 36827 Drilling Liner Technology For Depleted ReservoirDokumen6 halamanSPE 36827 Drilling Liner Technology For Depleted Reservoirmsm.ele2009Belum ada peringkat
- Downhole Motors PDFDokumen15 halamanDownhole Motors PDFarasquare100% (1)
- CoringDokumen14 halamanCoringfaisal muhamamdBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of DrillingDokumen8 halamanDetermination of DrillingDanna DeaBelum ada peringkat
- Coring AssignmentDokumen5 halamanCoring AssignmentheroocruseBelum ada peringkat
- Design of PistonDokumen8 halamanDesign of PistonBharath TrichyBelum ada peringkat
- Drilling With Casing Promises Major BenefitsDokumen12 halamanDrilling With Casing Promises Major BenefitsRaul Alberto Miranda LoayzaBelum ada peringkat
- K.v.ramana, Deilling and BlastingDokumen53 halamanK.v.ramana, Deilling and BlastingVenkata RamanaBelum ada peringkat
- PDC Bit Running Procedures DDIDokumen39 halamanPDC Bit Running Procedures DDImaicrv100% (1)
- Proto Copy Finale DraeteDokumen60 halamanProto Copy Finale DraeteAjinkya MoreBelum ada peringkat
- IADC/SPE 115283 Casing Drilling Technology As The Alternative of Drilling EfficiencyDokumen10 halamanIADC/SPE 115283 Casing Drilling Technology As The Alternative of Drilling EfficiencyMicaela Flores Lanza100% (1)
- Multiple Angle Pipe Bending MachineDokumen99 halamanMultiple Angle Pipe Bending MachineselvarajBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Fabrication of Multi-Purpose MachineDokumen48 halamanDesign and Fabrication of Multi-Purpose MachineglisoBelum ada peringkat
- SPE /IADC 85333 Cantilever Drilling - Ushering A New Genre of DrillingDokumen6 halamanSPE /IADC 85333 Cantilever Drilling - Ushering A New Genre of DrillingJohnSmithBelum ada peringkat
- Bits & Core HeadsDokumen74 halamanBits & Core HeadsdaveBelum ada peringkat
- MULTI-PURPOSE MACHINE ReportDokumen48 halamanMULTI-PURPOSE MACHINE Reportganesh86% (7)
- The International Society For Trenchless Technology: GlossaryDokumen15 halamanThe International Society For Trenchless Technology: GlossaryswhuntBelum ada peringkat
- Drilling Bit SelectionDokumen8 halamanDrilling Bit SelectionanateghpourBelum ada peringkat
- Spe Iadc Bi Cetre BitDokumen9 halamanSpe Iadc Bi Cetre Bitthought001Belum ada peringkat
- Bicenter Running ParametersDokumen4 halamanBicenter Running ParametersJonathanBelum ada peringkat
- Part 2 - Directional DrillingDokumen18 halamanPart 2 - Directional DrillingEugene TanBelum ada peringkat
- Rotary SystemDokumen9 halamanRotary SystemHomam MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Coiled Tubing & SnubbingDokumen4 halamanCoiled Tubing & SnubbingMichael LunaBelum ada peringkat
- December 2006: Coiled Tubing Drilling Goes DeeperDokumen5 halamanDecember 2006: Coiled Tubing Drilling Goes Deeper1mmahoneyBelum ada peringkat
- IADC Directional DrillingDokumen10 halamanIADC Directional DrillingomnoyBelum ada peringkat
- Question Homework of DrillingDokumen3 halamanQuestion Homework of DrillingNazeer AlyasBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 08 DrillingDokumen184 halamanChapter 08 DrillingWeatherford75267% (3)
- Day 2Dokumen15 halamanDay 2shanujanuuu000Belum ada peringkat
- SPE 95162 New Horizons in Wide-Bore Drilling and Completion TechnologyDokumen7 halamanSPE 95162 New Horizons in Wide-Bore Drilling and Completion TechnologydagingoBelum ada peringkat
- 6.intro To Photo of Multi Drill HolderDokumen35 halaman6.intro To Photo of Multi Drill Holdervijay vijayBelum ada peringkat
- Well InterventionDokumen21 halamanWell InterventionCito Ali100% (1)
- Chapter 2Dokumen44 halamanChapter 2Yash GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Expandable Drill BitDokumen6 halamanExpandable Drill BitJohnSmithBelum ada peringkat
- Mud Motor - WikipediaDokumen3 halamanMud Motor - WikipediaKamp RichardBelum ada peringkat
- Micro DrillingDokumen9 halamanMicro DrillingsubavlBelum ada peringkat
- Coiled TubingDokumen4 halamanCoiled TubingMihir PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Gk23a Umb Manual eDokumen16 halamanGk23a Umb Manual ejultur4oBelum ada peringkat
- COIL TubingDokumen2 halamanCOIL TubingHamid RazaBelum ada peringkat
- New Rock-Fracturing Excavation Method For Hard Rock Tunneling by FON Drill and FASE MethodDokumen8 halamanNew Rock-Fracturing Excavation Method For Hard Rock Tunneling by FON Drill and FASE Methodafzal taiBelum ada peringkat
- Casingdisegn 2Dokumen11 halamanCasingdisegn 2wissam hashimiBelum ada peringkat
- L7 - Wellbore Deflection & BHA SelectionDokumen32 halamanL7 - Wellbore Deflection & BHA SelectionLaxmi Kant Prasad100% (1)
- Down Hole MotorDokumen29 halamanDown Hole MotorBalasai SabarinathBelum ada peringkat
- Weatherford School: Alexandria University Student Chapter of The AapgDokumen15 halamanWeatherford School: Alexandria University Student Chapter of The Aapgmoussa mrzgBelum ada peringkat
- Machining ToolsDokumen4 halamanMachining Toolshirocode zeroBelum ada peringkat
- Coiled Tubing Skid-Mount UnitDokumen5 halamanCoiled Tubing Skid-Mount Unitnoel chris Jindjou100% (1)
- Deepreach Coiled Tubing Service: Extends Reach Up To 30% Compared To Conventional Tapered CT StringsDokumen2 halamanDeepreach Coiled Tubing Service: Extends Reach Up To 30% Compared To Conventional Tapered CT StringsMohamad QandeelBelum ada peringkat
- Technology UpdateDokumen6 halamanTechnology UpdateDaniel MeloBelum ada peringkat
- Proposal of Stinger BitsDokumen22 halamanProposal of Stinger BitsAbhinav SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- 13 - Tools Used To Deflect A WellboreDokumen19 halaman13 - Tools Used To Deflect A WellboreFarouq EngBelum ada peringkat
- 316 - Recent Advances in Overburden and Down-The-Hole Drilling TechniquesDokumen10 halaman316 - Recent Advances in Overburden and Down-The-Hole Drilling Techniquessoja2009Belum ada peringkat
- Casing While Drilling-SlideDokumen29 halamanCasing While Drilling-SlideNur Rizal100% (1)
- Conversão de Granalha para Uma Shot PeeningDokumen9 halamanConversão de Granalha para Uma Shot PeeningRodrigo HenkeBelum ada peringkat
- Spe 48856 PDFDokumen6 halamanSpe 48856 PDFkahutzed666Belum ada peringkat
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Dari EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Steam Turbines A Book of Instruction for the Adjustment and Operation of the Principal Types of this Class of Prime MoversDari EverandSteam Turbines A Book of Instruction for the Adjustment and Operation of the Principal Types of this Class of Prime MoversPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Automotive Machining: A Guide to Boring, Decking, Honing & MoreDari EverandAutomotive Machining: A Guide to Boring, Decking, Honing & MorePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (11)
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesDari EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)
- Performance Exhaust Systems: How to Design, Fabricate, and Install: How to Design, Fabricate, and InstallDari EverandPerformance Exhaust Systems: How to Design, Fabricate, and Install: How to Design, Fabricate, and InstallPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (8)
- Vedic Maths Quick LearnDokumen9 halamanVedic Maths Quick LearnBobby MandaBelum ada peringkat
- ONGC - Drilling Operation Practices Manual.-2007Dokumen368 halamanONGC - Drilling Operation Practices Manual.-2007tarang_tushar96% (49)
- Speed MathematicsDokumen18 halamanSpeed MathematicsBookMaggotBelum ada peringkat
- Underbalanced Coiled Tubing Drilled Horizontal Well in The North SeaDokumen6 halamanUnderbalanced Coiled Tubing Drilled Horizontal Well in The North Seatarang_tusharBelum ada peringkat
- ENI - Completion Design ManualDokumen295 halamanENI - Completion Design ManualKingsley Okenyi100% (1)
- Drilling FormulasDokumen211 halamanDrilling FormulastarangtusharBelum ada peringkat
- Mitchell-Advanced Oil Well Drilling EngineeringDokumen626 halamanMitchell-Advanced Oil Well Drilling EngineeringYASSER_MABelum ada peringkat
- Drilling Design ManualDokumen230 halamanDrilling Design Manualtarang_tushar100% (1)
- Amco Drilling ManualDokumen149 halamanAmco Drilling Manualtarang_tusharBelum ada peringkat
- Drilling Design ManualDokumen230 halamanDrilling Design Manualtarang_tushar100% (1)
- Amco Drilling ManualDokumen149 halamanAmco Drilling Manualtarang_tusharBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Drilling Using A Dual Bit SystemDokumen7 halamanAdvanced Drilling Using A Dual Bit Systemtarang_tusharBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To The PETROLEUM IndustryDokumen106 halamanAn Introduction To The PETROLEUM IndustryMmohsenN1984100% (1)