Worksheet 7.3
Diunggah oleh
Zac YuDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Worksheet 7.3
Diunggah oleh
Zac YuHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHUNG HWA MIDDLE SCHOOL, BSB BIOLOGY YEAR 9 WORKSHEET 7.
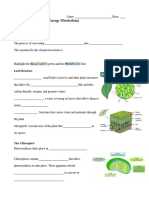
3: The structural adaptation of a leaf supports photosynthesis: STRUCTURE 1) Leaf _________ ADAPTATION Thin and wide / (high TSA/V ratio) to enable (i) Leaf absorb _____________ (ii) Carbon dioxide diffuse into cells easily 2) Leaf veins 3) Epidermis 4) Stomata Mosaic arrangement of leaves to enable _____________ ____________________. has _______ surface to absorb maximum light Has thin __________ to enable carbon dioxide to reach inner cells rapidly sunlight can reach ___________ cells Situated at the centre of the leaf and branched out to the side of the leaf Xylem and __________ are found in the veins. Xylem transports _____and _______from the roots to the leaf Phloem transports ________synthesized in the leaf to all part of the plant Consists of upper epidermis and _________. It serves as a transparent single layer Epidermal cell has no _________and therefore permits light to penetrate into mesophyll tissues. Outer surface of epidermis is covered by _______ which is waterproof. It protects leaf from ________and excessive loss of water . Found abundantly at the _______surface of leaf. Its opening is controlled by _______ . Exchange of ________ and ___________ gas during photosynthesis and respiration takes place through this opening. Elongated cells with many _________inside, near to leaf surface for more and efficient _____________. Irregular shape, loosely arranged beneath the palisade mesophyll with many air sac. It contains many ___________ for photosynthesis. Allow rapid diffusion of ___________________ to mesophyll cells
5) __________ mesophyll 6) __________ mesophyll 7) _____________ system of air spaces in mesophyll
CHUNG HWA MIDDLE SCHOOL, BSB BIOLOGY YEAR 9 WORKSHEET 7.3: Mineral Nutrition in Plants Nutrients Nitrogen Functions Synthesis of _____________, nucleic acids, chlorophyll and enzymes for photosynthesis For rapid stem and __________ growth Increase _______ and fruit yields Synthesis of nucleic acids, ATP As a ______________ in photosynthesis and respiration Effects of deficiency ___________ growth ___________ (synthesis of chlorophyll is inhibited) _____________ leaves
Phosphorus
Poor __________ growth Formation of dull, dark ___________ leaves ________ or ______ spots on old leaves ______________ ___________ regions between veins of mature leaves __________ spots on leaf surfaces Leaves are ______________ Reduce __________ synthesis ____________ leaves
Magnesium
Synthesis of _____________ Activate ______________ Involves in ________________ metabolism
Potassium
_____________ synthesis Involve in ______________ metabolism ___________for enzymes Maintain cell _____________ Build the middle lamella of the ________________ Formation of spindle fibres during _______________
Calcium
_____________ growth Leaves becomes _____________ Areas between leaf veins become ________________
Question: 1. Which element do plants obtain from soil in protein synthesis? A. Carbon B. Hydrogen C. Nitrogen D. Oxygen 2. A plant shows the following symptoms: Red spots on leaf surface Yellowing of regions between the veins of leaves The plants may lack of ______________________.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyDari EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyBelum ada peringkat
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Organismal BiologyDari EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Organismal BiologyBelum ada peringkat
- WORKSHEET 6.7 Photosynthesis - Leaf Structure (New)Dokumen4 halamanWORKSHEET 6.7 Photosynthesis - Leaf Structure (New)netiiyah netiiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Cells: 3.1 The MicroscopeDokumen9 halamanChapter 3 Cells: 3.1 The MicroscopeFoh Lian HuaiBelum ada peringkat
- Plant NutritionDokumen9 halamanPlant NutritionZain ul abedin AliBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 5 Feeding RelationshipsDokumen22 halamanUNIT 5 Feeding RelationshipsKelly ChamBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedDokumen7 halamanWorksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedKaung Myat SanBelum ada peringkat
- SOL Review Answer SheetDokumen15 halamanSOL Review Answer Sheetbrandonaniah7Belum ada peringkat
- Cells: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDokumen8 halamanCells: Cells: The Building Blocks of Lifems_m_tan100% (8)
- Biology WS1Dokumen2 halamanBiology WS1Fiery RoseBelum ada peringkat
- Food Production and Utilization of PlantsDokumen33 halamanFood Production and Utilization of PlantsSamKris Guerrero MalasagaBelum ada peringkat
- SCIENCE9 Q1 WEEK6 (LESSONS 17-18) - Photosynthesis (22 Pages)Dokumen22 halamanSCIENCE9 Q1 WEEK6 (LESSONS 17-18) - Photosynthesis (22 Pages)Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Laboratory Manual Series General Zoology Laboratory ManualDokumen18 halamanBiology Laboratory Manual Series General Zoology Laboratory ManualAnnaBelum ada peringkat
- WORKSHEET 6.7 Photosynthesis - Leaf StructureDokumen4 halamanWORKSHEET 6.7 Photosynthesis - Leaf StructureLim Wai Wai SmktpBelum ada peringkat
- Question Chapter 2Dokumen3 halamanQuestion Chapter 2Kenneth JamesBelum ada peringkat
- Name:: Score: Quiz 1: The Microscope and The Study of The CellDokumen2 halamanName:: Score: Quiz 1: The Microscope and The Study of The CellRyan BersaminBelum ada peringkat
- Module in Science 7: Department of Education Schools Division of Pasay CityDokumen20 halamanModule in Science 7: Department of Education Schools Division of Pasay CityTorres Jhon Chriz GabrielBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and Function HWDokumen2 halamanCell Structure and Function HWareej salimBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 - TissuesDokumen11 halamanModule 4 - TissuesArianne Mae VillajuanBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 2.1-2.2Dokumen5 halamanWorksheet 2.1-2.2Polka SalsaBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Respiration ReadingDokumen5 halamanCellular Respiration ReadingJ15Belum ada peringkat
- SCIENCE 7 2nd PeriodicalDokumen4 halamanSCIENCE 7 2nd PeriodicalKa KlasmeytBelum ada peringkat
- Cells Objectives For Exam #1Dokumen6 halamanCells Objectives For Exam #1Nelsi Antonius Kala100% (1)
- A View of The Cell Review PacketDokumen7 halamanA View of The Cell Review Packetapi-259727482Belum ada peringkat
- Photosynthesis Lessons Student NotesDokumen12 halamanPhotosynthesis Lessons Student NoteslinaBelum ada peringkat
- Composition of The Cell Membrane and Functions ActivityDokumen2 halamanComposition of The Cell Membrane and Functions ActivityHannah KaurBelum ada peringkat
- A. Label The Diagrams Below: WORKSHEET 7.3 Respiration in PlantsDokumen5 halamanA. Label The Diagrams Below: WORKSHEET 7.3 Respiration in PlantsGhanapathi RamanathanBelum ada peringkat
- GB - 1st Quarter - wk5 - PDFDokumen10 halamanGB - 1st Quarter - wk5 - PDFHeaven Leigh100% (1)
- LE Bare Essentials Word BankDokumen51 halamanLE Bare Essentials Word BankhiBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem: Life Energy: PhotosynthesisDokumen8 halamanEcosystem: Life Energy: PhotosynthesisHelma Jabello AriolaBelum ada peringkat
- SCIENCE 7 2nd Periodical TestDokumen2 halamanSCIENCE 7 2nd Periodical TestAngelica BacolodBelum ada peringkat
- I. Lab Safety - (Pg. 669 - 671, Lab Safety Contract)Dokumen13 halamanI. Lab Safety - (Pg. 669 - 671, Lab Safety Contract)Diya PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Sheet: Name - DateDokumen2 halamanRevision Sheet: Name - Datevqtr630Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2B Guided Notes 2022Dokumen6 halamanUnit 2B Guided Notes 2022Victoria WarrenBelum ada peringkat
- Edenton Mission College, Inc.: PhotosynthesisDokumen1 halamanEdenton Mission College, Inc.: PhotosynthesisLae DeeBelum ada peringkat
- Fusion Book Unit 3 Lesson 1-What Are Some Plant Structures?Dokumen6 halamanFusion Book Unit 3 Lesson 1-What Are Some Plant Structures?missrawan225Belum ada peringkat
- Bio Leaf Structure Lab F21Dokumen4 halamanBio Leaf Structure Lab F21Victoria WarrenBelum ada peringkat
- Sciebce Cell GrowthDokumen3 halamanSciebce Cell GrowthMr Ling Tuition CentreBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Test 2 - 1SDokumen2 halamanBiology Test 2 - 1SRomel AtallahBelum ada peringkat
- Science7 2nd M.E R. CatamponganDokumen3 halamanScience7 2nd M.E R. CatamponganRoy CatamponganBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Chap 7 f4Dokumen3 halamanLatihan Chap 7 f4Faizal PejerBelum ada peringkat
- LAB 09 Cell DivisionDokumen9 halamanLAB 09 Cell DivisionGlaiza Nicole CuarteronBelum ada peringkat
- Science7 Q2 WeeK4 LAS1Dokumen2 halamanScience7 Q2 WeeK4 LAS1maeshengBelum ada peringkat
- SMA - Unit 2 Guided NotesDokumen7 halamanSMA - Unit 2 Guided NotesFORKMANIABelum ada peringkat
- Grade 5 Science Weeks 9-12 Worksheets - Term 1Dokumen25 halamanGrade 5 Science Weeks 9-12 Worksheets - Term 1Latchmini DyalBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Worksheet 2Dokumen2 halamanCell Worksheet 2diehlscienceBelum ada peringkat
- Content Review PacketDokumen9 halamanContent Review Packetapi-342334216Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Adaptations Video QuizDokumen2 halamanPlant Adaptations Video Quiz27keenkBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Act 1Dokumen8 halamanLab Act 1KarenBelum ada peringkat
- Exam LeakDokumen7 halamanExam LeakVenz Lei Collyn Atis EsinBelum ada peringkat
- ds74 Sol Review CellsDokumen6 halamands74 Sol Review Cellsapi-110789702Belum ada peringkat
- 2.2.4 Photosynthesis WorksheetDokumen4 halaman2.2.4 Photosynthesis WorksheetHo Thi Phuong Oanh0% (1)
- Biology Final Exam 2024Dokumen2 halamanBiology Final Exam 2024Rollie Boy EsguerraBelum ada peringkat
- NS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 3Dokumen4 halamanNS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 3Anabel Sánchez RubiaBelum ada peringkat
- A Scientific Paper On The - Cell Model: Group - MembersDokumen9 halamanA Scientific Paper On The - Cell Model: Group - MembersJaderick BucaoBelum ada peringkat
- Plants Target Sheet KS3 AVGDokumen1 halamanPlants Target Sheet KS3 AVGArisa PatthawaroBelum ada peringkat
- GB1 LS2Dokumen3 halamanGB1 LS2Luz AguineaBelum ada peringkat
- BiogeochemicalCyclesFoldable1 PDFDokumen16 halamanBiogeochemicalCyclesFoldable1 PDFRaheem Don Breedz Phillips67% (3)
- Quiz About Cell & Cell OrganellesDokumen6 halamanQuiz About Cell & Cell OrganellesJune Emerson ManalangBelum ada peringkat
- Album ForamDokumen45 halamanAlbum ForamlukmanBelum ada peringkat
- 45CDokumen8 halaman45Cjhacademyhyd100% (4)
- ASSMENT1Dokumen2 halamanASSMENT1satoruheineBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Geography and History SB 1 Sample UnitDokumen8 halamanEssential Geography and History SB 1 Sample Unitmagrotas100% (1)
- Astro Baba 4 U: (Vashikaran Specialist)Dokumen14 halamanAstro Baba 4 U: (Vashikaran Specialist)VeronicaWelchBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Conservation: The Gravity of Wildlife TradeDokumen9 halamanBiological Conservation: The Gravity of Wildlife TradeSeha JumayyilBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 3100 Biochemistry Palomino Exams BlankDokumen14 halamanBio 3100 Biochemistry Palomino Exams Blankteamaqua360100% (1)
- 2over Population Not The ProblemDokumen3 halaman2over Population Not The ProblemMaríaPazSotoVergaraBelum ada peringkat
- Contribution of Indian ScientistsDokumen3 halamanContribution of Indian ScientistsAkash JainBelum ada peringkat
- Can God Become ManDokumen6 halamanCan God Become ManSharief SkBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Bellwork - Earth in The UniverseDokumen15 halaman1 Bellwork - Earth in The Universeapi-250250006Belum ada peringkat
- 33 Estrategias de La GuerraDokumen15 halaman33 Estrategias de La GuerraLuz MaBelum ada peringkat
- ECG 345 CHAPTER 1 - Introduction To Land - New (Compatibility Mode)Dokumen37 halamanECG 345 CHAPTER 1 - Introduction To Land - New (Compatibility Mode)annnnnaaaaaaBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen344 halamanUntitledPaochain LayBelum ada peringkat
- Paine Rocky ShoresDokumen175 halamanPaine Rocky ShoresictioceronteBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Janma KundaliDokumen2 halamanAnalysis of Janma Kundalirahul106Belum ada peringkat
- 4413 - 8993 - Grain Size Distribution & Depositional Process - Visher 1969Dokumen35 halaman4413 - 8993 - Grain Size Distribution & Depositional Process - Visher 1969Ulfah NastiBelum ada peringkat
- Depotional EnvironmentDokumen30 halamanDepotional EnvironmentAziz Fathiry RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Leica NA700 Auto LevelDokumen2 halamanLeica NA700 Auto Levelbbutros_317684077Belum ada peringkat
- Gravity Analysis of The Tendaho Graben, Afar Depression - EthiopiaDokumen90 halamanGravity Analysis of The Tendaho Graben, Afar Depression - EthiopiaAnyak2014Belum ada peringkat
- Core - Earth and Life Science Learning GuideDokumen3 halamanCore - Earth and Life Science Learning GuideJerico Karlos Logarta CortesBelum ada peringkat
- Hanson 2017Dokumen17 halamanHanson 2017FherpoolBelum ada peringkat
- A Horse With No Name - AmericaDokumen1 halamanA Horse With No Name - AmericapickquackBelum ada peringkat
- Zafranal 43 101 Technical Report PDFDokumen173 halamanZafranal 43 101 Technical Report PDFVictor ValdiviaBelum ada peringkat
- TestDokumen10 halamanTestAndi AlamsyahBelum ada peringkat
- Meet Our Solar SystemDokumen9 halamanMeet Our Solar SystemJeannette McphersonBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 ClassificationDokumen18 halamanUnit 2 ClassificationLeonita Swandjaja100% (1)
- Galaxy Morphology and Clasification Van Der Bergh PDFDokumen124 halamanGalaxy Morphology and Clasification Van Der Bergh PDFlover.foreverBelum ada peringkat
- Leaves Quiz-Raw MaterialDokumen50 halamanLeaves Quiz-Raw Materialtyas mouriBelum ada peringkat
- EclipsesDokumen45 halamanEclipsesKATRINA MARIE AmayBelum ada peringkat