Trapezoidal Rule Notes
Diunggah oleh
Ambreen KhanHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Trapezoidal Rule Notes
Diunggah oleh
Ambreen KhanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Numerical Integration and the Trapezoidal rule Lecture Notes. GC university Faisalabad. By: S.
M Alay-e-Abbas
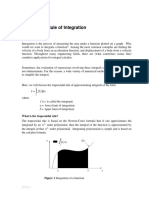
Numerical Integration:
In calculus we come across very complicated and difficult integrals. They are difficult to solve using analytical methods for finding their solutions. This problem can be solved by using numerical integrations e.g. Rectangular rule, limit of Sum definition, Trapezoidal Rule and Simpsons Rule.
Example:
A car accelerates from rest to 50Km/h in 30 seconds find the distance covered by the car using the given data t v 0 0 5 6 10 18 15 27 20 34 25 39 30 50
We know that 30 S =
0
v(t) dt
but we have no knowledge of v as a function of t so it is impossible or even ridiculous to think that given data can be used to solve the value of S by analytical method of integration.
Trapezoid:
A trapezoid is a plan with only two parallel sides as shown in figure
Trapezoidal Rule:
Consider y = f[x] bounded by x=a to x=b. Than by definition integration of the function of x i.e. y w.r.t x is the area under the curve AB shown in figure y A A a h b B B x
Numerical Integration and the Trapezoidal rule Lecture Notes. GC university Faisalabad. By: S.M Alay-e-Abbas i.e. b Area = F[x] = a f[x] dx = a numerical value
now dividing the trapezoid into a Rectangle and an approximate triangle i.e number of rectangles n = 1 we can write F[x] = h f[a] + h {f[b] f [a]} = h {f[a] +1/2f[b] 1/2f[a]} = h/2 {f[a] + f[b]} = h/2 {f[x0] + f[x1]} for n = 2 we have two rectangles and two triangle such that the approximate area under the curve now become F[x] = h/2 {f[a] +f[{a+b}/2]}+ h/2 {f[{a+b}/2] + f[b]} = h/2 {f[a] + 2f[{a+b}/2] + f[b]} = h/2 {f[x0] + 2f[x1] + f[x2]} So generalizing for n divisions of the trapezoid we have F[x] = h/2 {f[x0] + 2f[x1] + 2f[x2] + + 2f[xn-2] + 2f[xn-a] + f[xn]} Is an approximation of of the integral of y = f[x]. Where h=ba n n can be even or odd. And approximation can be improved using large value of n. Q- For each of the following use trapezoidal rule with the specified value of n. Compare your result with the analytically calculated value y = x +1/x, Ix = [2,3], n = 10 y = 1/1+x4, Ix = [1,2], n = 12 y = 1/x, Ix = [1,2], n =10
Note: The Assignment/Report of the solutions of the above given problems should be submitted in hard copy form along with electronic programs used to calculate the approximations.
Numerical Integration and the Trapezoidal rule Lecture Notes. GC university Faisalabad. By: S.M Alay-e-Abbas MS Excel Example for finding the Numerical Values using Trapezoidal Rule
Here
The cells under f[x] are given the values = A#-2 The cells under X are given the values = A2 + 0.1 in the third cell i.e A3 because the first cell contains the initial value X0 = 1 which is at the cell A2 The formula is defined at the cell F21 and has been defined as =(0.1*0.5)*(B2+2*(SUM(B3:B21))+B22)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Trapezoidal RuleDokumen3 halamanTrapezoidal RulesafrasacmBelum ada peringkat
- Trapezoidal RuleDokumen10 halamanTrapezoidal RuleRicardo Wan Aguero0% (1)
- MATRIX ANALYSIS OF STRAIN FROM GPS DATADokumen12 halamanMATRIX ANALYSIS OF STRAIN FROM GPS DATAAmjad Jatoi100% (3)
- Trapezoidal Rule and Simpson's RuleDokumen5 halamanTrapezoidal Rule and Simpson's RuleSai VandanaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 10 Numerical Integration TrapezoidalDokumen27 halamanLecture 10 Numerical Integration Trapezoidalimranakhtar100% (1)
- Greens Theorem ProofDokumen5 halamanGreens Theorem ProofGaurav DharBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Variable Karnaugh Map ExampleDokumen23 halaman5 Variable Karnaugh Map ExampleRobert Lim0% (1)
- Laplace TransformDokumen18 halamanLaplace Transformmim16Belum ada peringkat
- Taylor & Maclaurin Series ExpansionsDokumen8 halamanTaylor & Maclaurin Series ExpansionsKennypherneliaBelum ada peringkat
- Riemann SumsDokumen15 halamanRiemann Sumsapi-310595177Belum ada peringkat
- The Unit Tangent and The Unit Normal VectorsDokumen5 halamanThe Unit Tangent and The Unit Normal VectorsRaj Vardhan PatelBelum ada peringkat
- MTH510 Numerical Analysis: Text: CH 5 & 6Dokumen6 halamanMTH510 Numerical Analysis: Text: CH 5 & 6Winsle AnBelum ada peringkat
- Analytic Geometry FormulasDokumen3 halamanAnalytic Geometry FormulasLinda Fahlberg-StojanovskaBelum ada peringkat
- Complex FunctionsDokumen102 halamanComplex FunctionsRajesh100% (1)
- Three-Dimensional Coordinate SystemsDokumen5 halamanThree-Dimensional Coordinate SystemsYadhuvanth kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential EquationsDokumen31 halamanNumerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equationschandu3072002100% (1)
- NA Curve FittingDokumen31 halamanNA Curve FittingRadwan HammadBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical DifferentiationDokumen17 halamanNumerical DifferentiationamoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Numerical Integration: in This Chapter, You Will LearnDokumen6 halamanChapter 3 Numerical Integration: in This Chapter, You Will LearnArvin 97Belum ada peringkat
- Notes For Abstract AlgebraDokumen2 halamanNotes For Abstract AlgebraSankalp ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Conformal MappingsDokumen22 halamanConformal Mappingsjeff_hammonds351100% (1)
- Karnaugh Maps for Boolean Function SimplificationDokumen30 halamanKarnaugh Maps for Boolean Function SimplificationsrbagavthkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Math 104 - Homework 10 Solutions: Lectures 2 and 4, Fall 2011Dokumen4 halamanMath 104 - Homework 10 Solutions: Lectures 2 and 4, Fall 2011dsmile1Belum ada peringkat
- Optimization Class Notes MTH-9842Dokumen25 halamanOptimization Class Notes MTH-9842felix.apfaltrer7766Belum ada peringkat
- Equation of A PlaneDokumen6 halamanEquation of A PlaneGoh Ai LinBelum ada peringkat
- Solution 2Dokumen5 halamanSolution 2Paulina MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Calc Essay 1 Solids of Revolution AugustDokumen18 halamanCalc Essay 1 Solids of Revolution Augustapi-352669460Belum ada peringkat
- FOURIER SERIESDokumen31 halamanFOURIER SERIESSachi DhanandamBelum ada peringkat
- Complex Integration and Conformal TransformationsDokumen43 halamanComplex Integration and Conformal TransformationsRathnaBelum ada peringkat
- Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesDokumen67 halamanTriple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesJohn Rafael R. CanoosBelum ada peringkat
- Bisection MethodDokumen15 halamanBisection MethodSohar AlkindiBelum ada peringkat
- Linear FunctionalsDokumen7 halamanLinear Functionalshyd arnes100% (1)
- Laplace 2Dokumen32 halamanLaplace 2Rian RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes On Differential EquationsDokumen51 halamanLecture Notes On Differential EquationsSachin AryanBelum ada peringkat
- Probability Distributions.Dokumen47 halamanProbability Distributions.Sarose ThapaBelum ada peringkat
- Newton's Divided Difference Interpolation FormulaDokumen31 halamanNewton's Divided Difference Interpolation FormulaAnuraj N VBelum ada peringkat
- An Application of Vector Space Theory in Data TransmissionDokumen4 halamanAn Application of Vector Space Theory in Data TransmissionHash zeeBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 & 2 Fourier SeriesDokumen25 halamanUnit 1 & 2 Fourier SeriesAakashAkronosBelum ada peringkat
- Charging and Discharging A Capacitor (LAB 3) IrnaDokumen7 halamanCharging and Discharging A Capacitor (LAB 3) IrnaIrna FarhanaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 15 Trigonomeertric FunctionsDokumen32 halamanModule 15 Trigonomeertric Functionsbakaraz7523027Belum ada peringkat
- C1.Vector AnalysisDokumen27 halamanC1.Vector AnalysisRudy ObrienBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab Methods For OdeDokumen16 halamanMatlab Methods For OdeGrassrehLeBelum ada peringkat
- Curve FittingDokumen31 halamanCurve FittingNoel DaefBelum ada peringkat
- The Newton Raphson MethodDokumen39 halamanThe Newton Raphson MethodElisa LaseBelum ada peringkat
- Functions Relations and Graphsv2Dokumen9 halamanFunctions Relations and Graphsv2IsuruBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Mass Spring SystemDokumen11 halamanSimple Mass Spring SystemArindam MondalBelum ada peringkat
- MATLAB Basics in 40 CharactersDokumen50 halamanMATLAB Basics in 40 CharactersOleg ZenderBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Linear Signal ModelsDokumen40 halamanChapter 2 Linear Signal ModelsSisayBelum ada peringkat
- The Handshaking LemmaDokumen14 halamanThe Handshaking LemmaYusuf AmirudinBelum ada peringkat
- Coordinate systems in physics guideDokumen7 halamanCoordinate systems in physics guideObert MutavaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 14Dokumen33 halamanUnit 14varshiBelum ada peringkat
- Solution of Fredholm Integral Equations by CollocationDokumen4 halamanSolution of Fredholm Integral Equations by Collocationrodwellhead100% (1)
- M55 Lec15 The Fundamental Theorem of Line Integrals and Greens Theorem PDFDokumen19 halamanM55 Lec15 The Fundamental Theorem of Line Integrals and Greens Theorem PDFalyssaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Gauss SeidelDokumen20 halaman1 Gauss SeidelYanes Kristianus HediBelum ada peringkat
- GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONSDokumen47 halamanGRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONSSatheesh Kumar MBelum ada peringkat
- Regression and CorrelationDokumen4 halamanRegression and CorrelationClark ConstantinoBelum ada peringkat
- Newton Gauss MethodDokumen37 halamanNewton Gauss MethodLucas WeaverBelum ada peringkat
- SMP 16-19 Mathematics - Revision Notes Unit 5 - Calculus MethodsDokumen2 halamanSMP 16-19 Mathematics - Revision Notes Unit 5 - Calculus MethodsPrincess KimBelum ada peringkat
- Visual Techniques for Integrating Calculus ConceptsDokumen21 halamanVisual Techniques for Integrating Calculus Conceptskaushik247Belum ada peringkat
- BITSAT-2023-Paper-Memory-BasedDokumen19 halamanBITSAT-2023-Paper-Memory-Basedkrishbhatia1503Belum ada peringkat
- csc201 Assignment3Dokumen1 halamancsc201 Assignment3Ambreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Merit List PhysicsDokumen1 halaman3rd Merit List PhysicsAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic Physics FundamentalsDokumen254 halamanAtomic Physics FundamentalsAli AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Solid State Chapter 2Dokumen75 halamanSolid State Chapter 2Ambreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- BS Math Mechanics CourseDokumen3 halamanBS Math Mechanics CourseAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- csc201 Assignment1Dokumen1 halamancsc201 Assignment1Ambreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- ND Mathematical Methods Lecture NotesDokumen502 halamanND Mathematical Methods Lecture Notesucaptd3Belum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Classical MechanicsDokumen3 halamanFinal Exam Classical MechanicsAmbreen Khan100% (1)
- Physics Course ContentsDokumen84 halamanPhysics Course ContentsAmbreen Khan100% (1)
- Eddy CurrentsDokumen13 halamanEddy CurrentsAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Radiotherapy Dose CalculationsDokumen25 halamanRadiotherapy Dose CalculationsAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- E-Governance in India: Case Studies and Best PracticesDokumen23 halamanE-Governance in India: Case Studies and Best PracticesNeeraj DaswaniBelum ada peringkat
- Cover Letter As SAMPLEDokumen1 halamanCover Letter As SAMPLEAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- NTU Faisalabad 3rd Quiz Spring 2015 Physics-IIDokumen1 halamanNTU Faisalabad 3rd Quiz Spring 2015 Physics-IIAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Circle The Right OptionDokumen2 halamanCircle The Right OptionAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam July-22-2015 Section D Ph-1002Dokumen5 halamanFinal Exam July-22-2015 Section D Ph-1002Ambreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 1Dokumen1 halamanQuiz 1Ambreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- A Solid Water Phantom Material For Radiotherapy X-Rays and Gamma Ray Beam CalibrationDokumen6 halamanA Solid Water Phantom Material For Radiotherapy X-Rays and Gamma Ray Beam CalibrationAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1 (Ph-1002) Lectures by Ambreen AslamDokumen26 halamanWeek 1 (Ph-1002) Lectures by Ambreen AslamAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Week 4 (Ph-1002) Lectures by Ambreen AslamDokumen33 halamanWeek 4 (Ph-1002) Lectures by Ambreen AslamAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus PDFDokumen150 halamanSyllabus PDFAsma SethiBelum ada peringkat
- Chronological Order of Events PDFDokumen7 halamanChronological Order of Events PDFSadam GillalBelum ada peringkat
- 1000 Cuvinte EnglezaDokumen10 halaman1000 Cuvinte EnglezaNotar SorinBelum ada peringkat
- Week 2 (Ph-1002) Lectures by Ambreen AslamDokumen40 halamanWeek 2 (Ph-1002) Lectures by Ambreen AslamAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- An Overview of Monte CarlAN OVERVIEW OF MONTE CARLO TREATMENTo TreatmentDokumen7 halamanAn Overview of Monte CarlAN OVERVIEW OF MONTE CARLO TREATMENTo TreatmentAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- A Monte Carlo Study of IMRT Beamlets in Inhomogeneous MediaDokumen5 halamanA Monte Carlo Study of IMRT Beamlets in Inhomogeneous MediaAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- DareechayDokumen92 halamanDareechayAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Black Holes: Ambreen Aslam M.Phil. Physics University of Agriculture, FSD, PakistanDokumen20 halamanBlack Holes: Ambreen Aslam M.Phil. Physics University of Agriculture, FSD, PakistanAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Use Your HeadDokumen157 halamanUse Your HeadPraveen95% (39)
- Catphan500 600manualDokumen40 halamanCatphan500 600manualAmbreen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry Glossary: M ABCDokumen19 halamanGeometry Glossary: M ABCfree_progBelum ada peringkat
- Republic of the Philippines Math TestDokumen4 halamanRepublic of the Philippines Math TestJimmy T. CarmelotesBelum ada peringkat
- Math ReviewerDokumen4 halamanMath ReviewerMikaela UyBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Grading ExaminationDokumen9 halaman2nd Grading ExaminationUrbiztondo TrishaBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 3: Triangles and QuadrilateralsDokumen36 halamanMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 3: Triangles and QuadrilateralsLeny LaurenteBelum ada peringkat
- Mensuration QuestionsDokumen4 halamanMensuration Questionsajaykumar ballipalliBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry ShapesDokumen1 halamanGeometry Shapesapi-556601115Belum ada peringkat
- Year 7 Angles and Shapes WorkbookDokumen37 halamanYear 7 Angles and Shapes Workbookapi-291565828Belum ada peringkat
- Four-Side Plane FiguresDokumen26 halamanFour-Side Plane FiguresFajrin Maulana Kingwijati100% (1)
- 114 Handy Formulae For Quantitative Aptitude ProblemsDokumen12 halaman114 Handy Formulae For Quantitative Aptitude ProblemsRaju.Konduru91% (69)
- Weights and Coloring - Joshua Nichols-Barrer - MOP (Black) 2011Dokumen3 halamanWeights and Coloring - Joshua Nichols-Barrer - MOP (Black) 2011ahoaseoBelum ada peringkat
- ASMO 2019 Maths Grade 7Dokumen10 halamanASMO 2019 Maths Grade 7anthonyBelum ada peringkat
- School: Grade Level: Grade 8 Teacher: Learning Area: QuadrilateralsDokumen22 halamanSchool: Grade Level: Grade 8 Teacher: Learning Area: QuadrilateralsAdonis FabillaranBelum ada peringkat
- Euclid's Book On Divisions of Figures - Eunclidean GeometryDokumen111 halamanEuclid's Book On Divisions of Figures - Eunclidean GeometryvincepayBelum ada peringkat
- Sorabh 1Dokumen17 halamanSorabh 1koushalBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 11-2 Areas of Parallelograms, Trapezoids, Rhombuses and Kites Find The Area of Each FigureDokumen1 halamanWorksheet 11-2 Areas of Parallelograms, Trapezoids, Rhombuses and Kites Find The Area of Each FigureMelvinRuiz-Reyes100% (2)
- Geoquizquadrilaterals 2021Dokumen5 halamanGeoquizquadrilaterals 2021Akeem Winston JrBelum ada peringkat
- Corrected - Mathematics-9-Quarter-3-Module-3Dokumen22 halamanCorrected - Mathematics-9-Quarter-3-Module-3Emmanuel Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Icteam - Lesson Plans2 PDFDokumen118 halamanIcteam - Lesson Plans2 PDFAdriana VatavuBelum ada peringkat
- Session Guide For GeometryDokumen11 halamanSession Guide For Geometryabulug nrvhsBelum ada peringkat
- Machine DesignDokumen376 halamanMachine Designssierro100% (5)
- Describing QuadrilateralsDokumen1 halamanDescribing QuadrilateralsbrunerteachBelum ada peringkat
- 14th Pui Ching Invitational Mathematics Competition (2015)Dokumen12 halaman14th Pui Ching Invitational Mathematics Competition (2015)Jake WongBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 4: Daily Lesson LogDokumen42 halamanGrade 4: Daily Lesson LogAerom GenobebeBelum ada peringkat
- Level 2: New Century Mathematics (Second Edition) S3 Question Bank 3B Chapter 7 QuadrilateralsDokumen33 halamanLevel 2: New Century Mathematics (Second Edition) S3 Question Bank 3B Chapter 7 QuadrilateralsYuenHei KwokBelum ada peringkat
- Solid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IDokumen21 halamanSolid Mensuration: Mr. Mark Jave C. Gualberto, RME Lecturer IAzha Clarice Villanueva100% (1)
- Math 9 ModuleDokumen25 halamanMath 9 Modulewetlog lolololimBelum ada peringkat
- Holiday Homework Class IxDokumen3 halamanHoliday Homework Class IxpkBelum ada peringkat
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDokumen3 halamanGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRamil Galido0% (1)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorDari EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsDari EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingDari EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormDari EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra For DummiesDari EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra For DummiesPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (6)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenDari EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenBelum ada peringkat
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Dari EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusDari EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeDari EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Pre-Calculus Workbook For DummiesDari EverandPre-Calculus Workbook For DummiesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceDari EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceBelum ada peringkat
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Dari EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Belum ada peringkat
- Psychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideDari EverandPsychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideBelum ada peringkat
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDari EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (8)
- Math Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsDari EverandMath Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (15)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersDari EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormDari EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (20)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsDari EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (9)