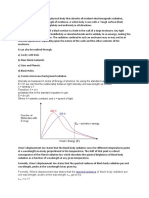
The Speed of Light in Vacuum
Diunggah oleh
Minhatun NafisahDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The Speed of Light in Vacuum
Diunggah oleh
Minhatun NafisahHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics.
Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time
In the special case of electromagnetic waves moving through a vacuum, then v = c, where c is the speed of light in a vacuum, and this expression becomes:
When waves from a monochrome source travel from one medium to another, their frequency remains exactly the same only their wavelength and speed change.
Photons are emitted in many natural processes. For example, when a charge is accelerated it emits synchrotron radiation. During a molecular, atomic or nuclear transition to a lower energy level, photons of various energy will be emitted, from infrared light to gamma rays. A photon can also be emitted when a particle and its corresponding antiparticle are annihilated (for example, electron-positron annihilation). In empty space, the photon moves at c (the speed of light) and its energy and momentum are related by E = pc, where p is the magnitude of the momentum vector p. This derives from the following relativistic relation, with m = 0:[15] E2 = p2c2 + m2c4. The energy and momentum of a photon depend only on its frequency () or inversely, its wavelength ():
where k is the wave vector (where the wave number k = |k| = 2/), = 2 is the angular frequency, and = h/2 is the reduced Planck constant. Since p points in the direction of the photon's propagation, the magnitude of the momentum is
The photon also carries spin angular momentum that does not depend on its frequency.[17] The magnitude of its spin is and the component measured along its direction of motion, its helicity, must be . These two possible helicities, called right-handed and left-handed,
correspond to the two possible circular polarization states of the photon. In applications where frequency is expressed in terms of radians per second ("angular frequency") instead of cycles per second, it is often useful to absorb a factor of 2 into the Planck constant. The resulting constant is called the reduced Planck constant or Dirac constant. It is equal to the Planck constant divided by 2, and is denoted ("h-bar"):
The energy of a photon with angular frequency , where = 2, is given by
The Planck constant has dimensions of physical action; these are the same as those of angular momentum, i.e., energy multiplied by time, or momentum multiplied by distance. In SI units, the Planck constant is expressed in joule seconds (Js) or (Nms). The value of the Planck constant is:[1]
The value of the reduced Planck constant is:
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Dari EverandA New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Belum ada peringkat
- Discussion On Electromagnetic Waves Under The Circumstances of Total Internal Reflection and Optical TunnelingDokumen6 halamanDiscussion On Electromagnetic Waves Under The Circumstances of Total Internal Reflection and Optical TunnelingJulio CaceresBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler Effect and The Law of Conservation of Energy-Momentum.Dokumen8 halamanDoppler Effect and The Law of Conservation of Energy-Momentum.Bezverkhniy VolodymyrBelum ada peringkat
- Physic About LIGHT: Fajrina Qaishum 1007113681 Teknik Kimia ADokumen29 halamanPhysic About LIGHT: Fajrina Qaishum 1007113681 Teknik Kimia AFajrinaQaishumBelum ada peringkat
- Plancks Radiation LawDokumen9 halamanPlancks Radiation Lawna3605220Belum ada peringkat
- A Simplified Approach To Synchrotron RadiationDokumen8 halamanA Simplified Approach To Synchrotron RadiationFaisal AmirBelum ada peringkat
- PhysicsBowl Eqt Sheet AnnotatedDokumen7 halamanPhysicsBowl Eqt Sheet Annotatedhkalloli@gmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- The Apparent Dual Nature of Electromagnetic WavesDokumen5 halamanThe Apparent Dual Nature of Electromagnetic WavesFrederick David TombeBelum ada peringkat
- Formally, Wien's displacement law states that the of black body radiation per unit wavelength, peaks at the wavelength λ given by: λ = b / TDokumen11 halamanFormally, Wien's displacement law states that the of black body radiation per unit wavelength, peaks at the wavelength λ given by: λ = b / TYash TamakuwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Resonance by Floyd A. Sweet. PH. DDokumen4 halamanMagnetic Resonance by Floyd A. Sweet. PH. Dhyiq0% (1)
- 1.1 Waves and Particles According To Classical PhysicsDokumen8 halaman1.1 Waves and Particles According To Classical PhysicsLUCKY KUSHWAHABelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic RadiationDokumen6 halamanElectromagnetic Radiation09ANKIT MISHRABelum ada peringkat
- Dual, Schizophrenic Nature of Light: Both As A Particle and As A Wave.Dokumen8 halamanDual, Schizophrenic Nature of Light: Both As A Particle and As A Wave.kcvataBelum ada peringkat
- Short Question Bank Physics IIDokumen12 halamanShort Question Bank Physics IIAshish Vimal0% (1)
- Fundamentals of Radiation DosimetryDokumen17 halamanFundamentals of Radiation DosimetryGeoff OwusuBelum ada peringkat
- Polarization and Angular Distribution of The Radiation Emitted in Laser-Assisted RecombinationDokumen5 halamanPolarization and Angular Distribution of The Radiation Emitted in Laser-Assisted RecombinationBayer MitrovicBelum ada peringkat
- Unit II QuantummechanicsDokumen28 halamanUnit II QuantummechanicsKiran ThunuguntlaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Ii - Quantum Mechanics: D e A D EDokumen25 halamanUnit Ii - Quantum Mechanics: D e A D EChiraag ChiruBelum ada peringkat
- Wave MechanicsDokumen18 halamanWave MechanicsVrushanka VaseBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Mechanics NotesDokumen21 halamanQuantum Mechanics NotesPujan MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Question & Answer of Quantum MechanicsDokumen31 halamanQuestion & Answer of Quantum MechanicsSai Printers83% (18)
- Rizwin Notes PDFDokumen133 halamanRizwin Notes PDFHemanta Kumar SaikiaBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Wave Particle DualismDokumen8 halaman1.1 Wave Particle DualismVrushanka VaseBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Case StudyDokumen12 halamanPhysics Case StudyNitkrisBelum ada peringkat
- Radiation Part 1Dokumen24 halamanRadiation Part 1Himanshu JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Sharch 11Dokumen36 halamanSharch 11Uzair WahidBelum ada peringkat
- PolarizationDokumen26 halamanPolarizationArijit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- New OneDokumen7 halamanNew OneDivakar M Divakar MBelum ada peringkat
- From Compton To LarmorDokumen10 halamanFrom Compton To LarmorpaolotrBelum ada peringkat
- Optical Fibers: Structures, Optical Fibers: Structures, Waveguiding & FabricationDokumen99 halamanOptical Fibers: Structures, Optical Fibers: Structures, Waveguiding & FabricationNung NingBelum ada peringkat
- A System To Convert Gravitational Energy Directly Into Electrical EnergyDokumen17 halamanA System To Convert Gravitational Energy Directly Into Electrical EnergyFran De AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- WhatisaphotonDokumen11 halamanWhatisaphotonDiego AlfonsoBelum ada peringkat
- Grouptheory Module3Dokumen34 halamanGrouptheory Module3Mahalakshmi SahasranamanBelum ada peringkat
- Light ScatteringDokumen10 halamanLight ScatteringAndri HanryansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11. Griffiths-Radiation-Dipole Radiation PDFDokumen13 halamanChapter 11. Griffiths-Radiation-Dipole Radiation PDFPranveer Singh Parihar100% (1)
- Kapitza 1933Dokumen5 halamanKapitza 1933Louis DeprezBelum ada peringkat
- EPJSP Biresonance and The Poincaré SphereDokumen22 halamanEPJSP Biresonance and The Poincaré SphererobotomationBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic RadiationDokumen5 halamanElectromagnetic RadiationrendakianBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Mechanics Lecture Note Dr.H. RathDokumen60 halamanQuantum Mechanics Lecture Note Dr.H. RathSoumya Ranjan PandaBelum ada peringkat
- Lectures 1 and 2 Intro and PhotelecDokumen9 halamanLectures 1 and 2 Intro and PhotelecNabil IshamBelum ada peringkat
- New Minimum Requirement Questions For BiophysicsDokumen14 halamanNew Minimum Requirement Questions For BiophysicsAhmed Adnan ShehadahBelum ada peringkat
- 09 (T) - Electromagnetic WavesDokumen6 halaman09 (T) - Electromagnetic WavesEr Rajesh BuraBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Notes Part 1Dokumen59 halamanChemistry Notes Part 1SharleneBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Light Monochromatic Beams Propagation Velocity in Atmospheric Air D.H. Baziev Problem StateDokumen21 halamanNatural Light Monochromatic Beams Propagation Velocity in Atmospheric Air D.H. Baziev Problem StatebraelizaBelum ada peringkat
- Photon - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen22 halamanPhoton - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMaxim ŠporkiBelum ada peringkat
- Franck-Condon Principle - WikipediaDokumen14 halamanFranck-Condon Principle - WikipediaSufiya BanoBelum ada peringkat
- Wave OpticsDokumen12 halamanWave Opticsrishi kaushikBelum ada peringkat
- Burgot G., Burgot J.-L. - General Analytical Chemistry - SeparationDokumen60 halamanBurgot G., Burgot J.-L. - General Analytical Chemistry - SeparationAytekin GaribliBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction Quantum MechDokumen18 halamanIntroduction Quantum MechVivek Ranjan MaitreyBelum ada peringkat
- Light Polarization and Brewster LawDokumen12 halamanLight Polarization and Brewster LawAnatoly PylaevBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Light: Chapter 1, Light Propagation in MediaDokumen58 halamanIntroduction To Light: Chapter 1, Light Propagation in MediaLee Kar HuoBelum ada peringkat
- OrbitalDokumen2 halamanOrbitaladam millerBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT I Lecture Notes PDFDokumen9 halamanUNIT I Lecture Notes PDFAyush SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Rad PhysicsDokumen109 halamanRad PhysicsRicardo EdanoBelum ada peringkat
- Wave OpticsDokumen15 halamanWave OpticsroceniBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Optics Notes For Class 12Dokumen15 halamanWave Optics Notes For Class 12Rick Harrison100% (1)
- Balmer Series Lab ReportDokumen11 halamanBalmer Series Lab Reportsohaila gaberBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Optics Notes For Class 12Dokumen15 halamanWave Optics Notes For Class 12roceniBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 2 - Principles of SpectrosDokumen59 halamanChap 2 - Principles of SpectrosRezaul Karim100% (3)
- Year 11 Prelim Exams PhysicsDokumen22 halamanYear 11 Prelim Exams PhysicsTimothy KurbyBelum ada peringkat
- 9702 s14 QP 12Dokumen32 halaman9702 s14 QP 12Jing WangBelum ada peringkat
- Dodl Past Exam Questions - 240417 - 095612Dokumen22 halamanDodl Past Exam Questions - 240417 - 095612omtyson72Belum ada peringkat
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper Solutions 9 January MorningDokumen45 halamanJEE Main 2020 Question Paper Solutions 9 January MorningDishant ShahBelum ada peringkat
- (SPIE Press Monograph Vol. PM152) Larry C. Andrews, Ronald L. Phillips-Laser Beam Propagation Through Random Media, Second Edition-SPIE Publications (2005) PDFDokumen808 halaman(SPIE Press Monograph Vol. PM152) Larry C. Andrews, Ronald L. Phillips-Laser Beam Propagation Through Random Media, Second Edition-SPIE Publications (2005) PDFСтефан ПанићBelum ada peringkat
- Airspeed NistDokumen15 halamanAirspeed NistPAULOBelum ada peringkat
- Oscillation NotesDokumen53 halamanOscillation NotesrahmaBelum ada peringkat
- C1 ErroriDokumen164 halamanC1 ErroriVitalie LunguBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Principles of X-RayDokumen10 halamanBasic Principles of X-RayJasmina CabukovskaBelum ada peringkat
- wph12-01-rms-20230817 2Dokumen14 halamanwph12-01-rms-20230817 2Mehmet Derin Ozser100% (1)
- Test 12H Review AnswersDokumen7 halamanTest 12H Review Answerstedien252Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Waves WorksheetDokumen3 halamanPhysics Waves WorksheetRizky HermawanBelum ada peringkat
- June 2017 MS - Paper 2 OCR (A) Physics AS-levelDokumen15 halamanJune 2017 MS - Paper 2 OCR (A) Physics AS-levelCharles Lin 林彥承Belum ada peringkat
- Rutherford and Bohr's Atomic ModelDokumen101 halamanRutherford and Bohr's Atomic Modelthrivikram100% (1)
- Dual Nature of LightDokumen15 halamanDual Nature of LightUriahs Victor75% (4)
- Refractor Telescope ReportDokumen57 halamanRefractor Telescope ReportBammBelum ada peringkat
- B. Tech. HA - 06-01-2023Dokumen2 halamanB. Tech. HA - 06-01-2023Sheikh SaifBelum ada peringkat
- Optek Brochure PI C4000 C8000 US 2011 03 24Dokumen24 halamanOptek Brochure PI C4000 C8000 US 2011 03 24nhasrounBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Surveying: 3 Assignment PresentationDokumen12 halamanAdvanced Surveying: 3 Assignment PresentationPoojaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 9 Diffraction Gratings: 1. How A Diffraction Grating Works?Dokumen5 halamanExperiment 9 Diffraction Gratings: 1. How A Diffraction Grating Works?MNA tounsa sharifBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Optical PropertiesDokumen17 halamanElectrical Optical Propertieschen18111004 KFUEITBelum ada peringkat
- Tifr Paper 2019Dokumen16 halamanTifr Paper 2019prakash ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- (3924) DPPDokumen157 halaman(3924) DPPBeyond ur imaginationBelum ada peringkat
- SAR Remote SensingDokumen58 halamanSAR Remote SensingMr.Mohammed Zakir B ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATIONBelum ada peringkat
- Ch13 Sound WavesDokumen18 halamanCh13 Sound WavesJamal RamadanBelum ada peringkat
- (Applications of Communications Theory) Stewart D. Personick (Auth.) - Fiber Optics - Technology and Applications (1985, Springer US)Dokumen265 halaman(Applications of Communications Theory) Stewart D. Personick (Auth.) - Fiber Optics - Technology and Applications (1985, Springer US)Irfan Ahmad100% (1)
- Worksheet #1Dokumen17 halamanWorksheet #1jal bayaniBelum ada peringkat
- Optics Unit: Kps ParmarDokumen48 halamanOptics Unit: Kps ParmarSabya SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Ge6163 Set 1Dokumen2 halamanGe6163 Set 1heavendewBelum ada peringkat
- Diffracction - Grating PDFDokumen5 halamanDiffracction - Grating PDFKamila MartinBelum ada peringkat
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDari EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyBelum ada peringkat
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDari EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2193)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDari EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniversePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDari EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (64)
- Higgs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpaceDari EverandHiggs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpacePenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (30)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDari EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDari EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeBelum ada peringkat
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDari EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and SciencePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (51)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDari EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (410)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDari EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDari EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (125)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Dari EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (157)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDari EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in SciencePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessDari EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (57)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDari EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (54)
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishDari EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (4)
- Quantum Physcis for Beginners: An Easy Guide for Discovering the Hidden Side of Reality One Speck at a TimeDari EverandQuantum Physcis for Beginners: An Easy Guide for Discovering the Hidden Side of Reality One Speck at a TimeBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeDari EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (13)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDari EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (60)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDari EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (49)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itDari EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (13)
- Beyond Weird: Why Everything You Thought You Knew about Quantum Physics Is DifferentDari EverandBeyond Weird: Why Everything You Thought You Knew about Quantum Physics Is DifferentPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (25)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionDari EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDari EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (78)