Intensive Bio Chapter 3
Diunggah oleh
Chung Heng KongDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Intensive Bio Chapter 3
Diunggah oleh
Chung Heng KongHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Biology Intensive Class
Prepared by: Ms. Lai
Chapter 3: Movement of Substances across the Plasma Membrane
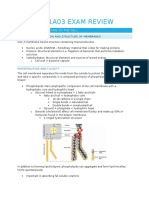
1) It consists of a double layer of phospholipids with proteins of different functions
embedded in it.
2) The model used: Fluid Mosaic Model. 3) Fluid: Plasma membrane not static, the phospholipids moves laterally. 4) Mosaic: Different types of proteins embedded in the double layer of phospholipids.
Why is the plasma membrane selectively permeable (semi permeable)? a) Discriminating barrier of the phospholipids bilayer b) Specific transport proteins built into the membrane The permeability of phospholipid bilayer:
Hydrophobic (nonpolar) molecules and small uncharged molecules can dissolve in the lipid bilayer of the membrane and cross it with ease. (Example: hydrocarbons, CO2 & O2, Vitamin A,D,E,K, fatty acids, glycerol, steroids) Inhibit the direct passage of charged ions and hydrophilic (polar) molecules. (Example: glucose, amino acids, nucleic acids & polysaccharides, H+, Na+, HCO3-, K+)
Movement of substances across the plasma membrane
Biology Intensive Class
Prepared by: Ms. Lai
Passive transport 1) Molecules transported down the concentration gradient. 2) Do NOT need ATP. 3) For facilitated diffusion carrier/pore protein is needed. a) Simple diffusion (fatty acids, glycerol) b) Osmosis (water) c) Facilitated diffusion (glucose, acid amino, H+, Na+).
Active transport 1) Molecules transported against the concentration gradient. 2) Needs ATP and the help of carrier protein. 3) Examples: H+, Na+, HCO3-, K+ Effects of osmosis
Osmosis in Everyday Life Wilting of Plants 1) Occurs when there is excessive use of fertilisers. 2) Fertilisers dissolve in the soil and made the soil water to be more concentrated (hypertonic) than the root cells of the plants. 3) This causes water to diffuse out of the plant cells into the soil by osmosis. 4) Plasmolysis occurs and the plant cells become flaccid causing the plant to wilt. Preservation of Food Food can be preserved by using salt and sugar as the preservatives.
Biology Intensive Class
Prepared by: Ms. Lai
These preservatives dissolve in the solution and make it more concentrated (hypertonic) than the cells of the food. This causes water to diffuse out of the cells into the solution by osmosis. The cells lose water (dehydrated) and become crenate preventing the growth of microorganisms. The microorganisms will eventually die and as the results the food can be preserved longer.
Active Transport in Everyday Life 1) Absorption of mineral salts by root hairs. 2) Uptake of glucose by cells in villi. Notes:
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- KANESS (016-4573342) 10, JLN TPT 10, Taman Puchong Tekali, 47150, Puchong, Selangor Chapter 2: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDokumen6 halamanKANESS (016-4573342) 10, JLN TPT 10, Taman Puchong Tekali, 47150, Puchong, Selangor Chapter 2: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneKaness MathzBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3Dokumen8 halamanBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3MSKBelum ada peringkat
- Wa0000.Dokumen32 halamanWa0000.srijavadlamudi48Belum ada peringkat
- SPM Biology Form 4 NotesDokumen3 halamanSPM Biology Form 4 NotesDelima Adan86% (7)
- 008 - The Cell Surface MembraneDokumen2 halaman008 - The Cell Surface MembraneSanah KhanBelum ada peringkat
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Dokumen6 halamanAP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Omar LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Essay QuestionsDokumen3 halamanEssay QuestionsAytheaBelum ada peringkat
- Cadorna, Chesca L. MicrobiologyDokumen3 halamanCadorna, Chesca L. MicrobiologyCadorna Chesca LoboBelum ada peringkat
- K12 STEM Training on Cell TransportDokumen53 halamanK12 STEM Training on Cell Transportpotato macchiatoBelum ada peringkat
- q1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditDokumen13 halamanq1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditInele Ellia AgReBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 5 Chapter 3Dokumen6 halamanScience Form 5 Chapter 3Roslinda Mohamed OthmanBelum ada peringkat
- The Cell MembraneDokumen23 halamanThe Cell MembraneNaveed AkhterBelum ada peringkat
- Membranes and TransportDokumen7 halamanMembranes and TransportNadeem IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Form 4-Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDokumen7 halamanForm 4-Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membranehuileng_wongBelum ada peringkat
- Cell PhysiologyDokumen15 halamanCell PhysiologyHENRY MURIGIBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Membrane FunctionsDokumen60 halamanCell Membrane FunctionsKate Clancy NugaoBelum ada peringkat
- Membrane Properties and Transport ProcessesDokumen7 halamanMembrane Properties and Transport ProcessesStudent Alejandro Zhou WeiBelum ada peringkat
- Phospholipid MoleculeDokumen3 halamanPhospholipid MoleculeHock OoiBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Form Two Marking SchemeDokumen2 halamanBiology Form Two Marking Schemeideal writersBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 110 - Chapter 5Dokumen32 halamanBio 110 - Chapter 5moayadBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3-Biology Form 4-Part 1Dokumen23 halamanChapter 3-Biology Form 4-Part 1Purnima KadarasenBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Biology Form 4 – Movement of Substances Across the Plasma MembraneDokumen12 halamanSPM Biology Form 4 – Movement of Substances Across the Plasma MembraneAidah Amir100% (1)
- The Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesDokumen11 halamanThe Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesSyeda Kaneez Mohammadi MohammadiBelum ada peringkat
- Mader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and FunctionDokumen4 halamanMader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and Functionapi-455371000Belum ada peringkat
- Test Essays January 4Dokumen7 halamanTest Essays January 4Stephanie JenkinsBelum ada peringkat
- AO1 Quiz Transport Across MembranesDokumen3 halamanAO1 Quiz Transport Across MembranesFaiza HamidBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and Functions in Amoeba and ParameciumDokumen11 halamanCell Structure and Functions in Amoeba and ParameciumFaheymBelum ada peringkat
- IB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsDokumen5 halamanIB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsTiffani Choy100% (1)
- Answers To Model Exam PaperDokumen4 halamanAnswers To Model Exam PaperAlex TanBelum ada peringkat
- Cell StandardsDokumen5 halamanCell Standardsapi-300752528Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Membrane & HomeostasisDokumen50 halamanCell Membrane & Homeostasisapi-233187566Belum ada peringkat
- Biology 1A03 Exam ReviewDokumen69 halamanBiology 1A03 Exam Review0xVi3tfireBelum ada peringkat
- Endocytosis vs exocytosis: how cells transport moleculesDokumen11 halamanEndocytosis vs exocytosis: how cells transport moleculesJGHUNGERBelum ada peringkat
- O-Level Biology NotesDokumen119 halamanO-Level Biology Notesjia wenBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology Lec 2Dokumen45 halamanMicrobiology Lec 2Mushtaq HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology and Biotechnology ScriptDokumen18 halamanMicrobiology and Biotechnology ScriptDavid RăscuţoiBelum ada peringkat
- Movement Across the Plasma MembraneDokumen18 halamanMovement Across the Plasma MembraneSivam DhanabalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Cell Membranes and TransportDokumen33 halamanChapter 4 Cell Membranes and TransportChia Hon LamBelum ada peringkat
- CEE 6492 RevisionDokumen7 halamanCEE 6492 RevisionGabriel TambweBelum ada peringkat
- Question and Answers Membrane Transport Extended Response QuestionDokumen4 halamanQuestion and Answers Membrane Transport Extended Response QuestionJohn OsborneBelum ada peringkat
- Transport Across Cell Membrane.: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfDokumen67 halamanTransport Across Cell Membrane.: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfAspireBelum ada peringkat
- Cells: A. Ultrastructure & Function of The CellDokumen9 halamanCells: A. Ultrastructure & Function of The CellRhea Lyn LamosteBelum ada peringkat
- مذكرة بيولوجي للصف الثاني الاعدادي الترم الاولDokumen116 halamanمذكرة بيولوجي للصف الثاني الاعدادي الترم الاولLolaBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Nutrisi Dan Pertumbuhan Mikroba 2Dokumen9 halaman04 Nutrisi Dan Pertumbuhan Mikroba 2Irvan YudhistiraBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 2 Cell Membrane and Lesson 3 HomeostasisDokumen14 halamanLesson 2 Cell Membrane and Lesson 3 HomeostasisAj MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell MembraneDokumen3 halamanCell MembraneQaran PrintingBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 CellDokumen94 halamanChapter 3 Cellmohamedshilleh7Belum ada peringkat
- (284704265) 1.2 Fluid Mosaic ModelDokumen16 halaman(284704265) 1.2 Fluid Mosaic ModelNurul Hana OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Oxfordaqa International Gcse Biology SpecificationDokumen21 halamanOxfordaqa International Gcse Biology Specificationjameelah santillanBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology - DissertationDokumen7 halamanCell Biology - Dissertationprerana chakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- LESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Dokumen4 halamanLESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Jhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesBelum ada peringkat
- Bacterial Cell StructureDokumen41 halamanBacterial Cell Structuremuhammad attiqueBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Notes For O LevelDokumen36 halamanBiology Notes For O LevelemmaBelum ada peringkat
- CHP 1,2Dokumen4 halamanCHP 1,2MD MotinBelum ada peringkat
- Cell PhysiologyDokumen12 halamanCell PhysiologyJaseme OtoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Bio ReportDokumen15 halamanBio ReportNur ShuhadaBelum ada peringkat
- STD Ix Bio 1Dokumen4 halamanSTD Ix Bio 1Sourav DasBelum ada peringkat
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDari EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Rigid Risers For Tanker FPSOsDokumen10 halamanRigid Risers For Tanker FPSOsHariprasad RajannaBelum ada peringkat
- Rigid Risers For Tanker FPSOsDokumen10 halamanRigid Risers For Tanker FPSOsHariprasad RajannaBelum ada peringkat
- Intensif Chapter 2 and 3Dokumen8 halamanIntensif Chapter 2 and 3Chung Heng KongBelum ada peringkat
- Progression FormulaDokumen2 halamanProgression FormulaChung Heng KongBelum ada peringkat
- Progression FormulaDokumen2 halamanProgression FormulaChung Heng KongBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Animal Science For Plant ScienceDokumen63 halamanIntroduction To Animal Science For Plant ScienceJack OlanoBelum ada peringkat
- Funds Flow Statement ExplainedDokumen76 halamanFunds Flow Statement Explainedthella deva prasad0% (1)
- C. Drug Action 1Dokumen28 halamanC. Drug Action 1Jay Eamon Reyes MendrosBelum ada peringkat
- Đề cương ôn tập tiếng anh 9Dokumen28 halamanĐề cương ôn tập tiếng anh 9Nguyễn HoaBelum ada peringkat
- of Types of Nuclear ReactorDokumen33 halamanof Types of Nuclear Reactormandhir67% (3)
- Theories of Motivation and Child Moral DevelopmentDokumen5 halamanTheories of Motivation and Child Moral DevelopmentPamela mirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz EmbryologyDokumen41 halamanQuiz EmbryologyMedShare90% (67)
- Owners Manual Water Mist PDFDokumen6 halamanOwners Manual Water Mist PDFZeeBelum ada peringkat
- Abstract - Tropen Tag 2011 PDFDokumen634 halamanAbstract - Tropen Tag 2011 PDFzmoghesBelum ada peringkat
- MEDICO-LEGAL ASPECTS OF ASPHYXIADokumen76 halamanMEDICO-LEGAL ASPECTS OF ASPHYXIAAl Giorgio SyBelum ada peringkat
- TS4-F - Fire SafetyDokumen2 halamanTS4-F - Fire SafetyDominic SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Wastewater Treatment Plant Design PDFDokumen68 halamanWastewater Treatment Plant Design PDFmostafa1alaahobaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Fast SwimmingDokumen9 halamanFundamentals of Fast SwimmingTorcay Ulucay100% (1)
- Sub Erna RekhaDokumen2 halamanSub Erna Rekhasurabhi mandalBelum ada peringkat
- GSIS vs. de LeonDokumen9 halamanGSIS vs. de Leonalwayskeepthefaith8Belum ada peringkat
- EEDMATH1 - Teaching Mathematics in The Primary Grades Beed 2E Learning Activity PlanDokumen3 halamanEEDMATH1 - Teaching Mathematics in The Primary Grades Beed 2E Learning Activity PlanBELJUNE MARK GALANANBelum ada peringkat
- Gebauer 2012Dokumen26 halamanGebauer 2012Seán GallagherBelum ada peringkat
- Pack Alimentacion Clin in Perin 14Dokumen194 halamanPack Alimentacion Clin in Perin 14Paz BustosBelum ada peringkat
- QRF HD785-7Dokumen2 halamanQRF HD785-7Ralf MaurerBelum ada peringkat
- RA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Dokumen2 halamanRA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Jazreth Gaile100% (1)
- Hinduism Today April May June 2015Dokumen43 halamanHinduism Today April May June 2015jpmahadevBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources in PakistanDokumen5 halamanNatural Resources in PakistanSohaib EBelum ada peringkat
- Parasitology Lecture Hosts, Symbiosis & TransmissionDokumen10 halamanParasitology Lecture Hosts, Symbiosis & TransmissionPatricia Ann JoseBelum ada peringkat
- Cap 716 PDFDokumen150 halamanCap 716 PDFjanhaviBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 7 Tabata TrainingDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan 7 Tabata Trainingapi-392909015100% (1)
- Válvulas Flomatic USADokumen40 halamanVálvulas Flomatic USAEfrain DuarteBelum ada peringkat
- Iso 28000Dokumen11 halamanIso 28000Aida FatmawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Cot 1 Vital SignsDokumen22 halamanCot 1 Vital Signscristine g. magatBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension Protocol Mukta VatiDokumen18 halamanHypertension Protocol Mukta VatiDr. Avnish UpadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- Comm Part For A320Dokumen1 halamanComm Part For A320ODOSBelum ada peringkat