Exp DC-3
Diunggah oleh
Simran Singh MassaunDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Exp DC-3
Diunggah oleh
Simran Singh MassaunHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Experiment-3
Aim :- Introduction to Client-Server Architecture, Peer- to- Peer Networking, Hybrid Networking, Direct Cable Connection.
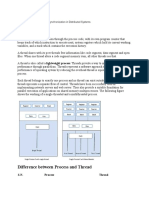
Client-Server Architecture:
The client-server software architecture model distinguishes client systems from server systems, which communicate over a computer network. A client-server application is a distributed system comprising both client and server software. A client software process may initiate a communication session, while the server waits for requests from any client. Client-server describes the relationship between two computer programs in which one program, the client program, makes a service request to another, the server program. Standard networked functions such as email exchange, web access and database access, are based on the client-server model. For example, a web browser is a client program at the user computer that may access information at any web server in the world. The client-server model has become one of the central ideas of network computing. Most business applications being written today use the client-server model. So do the Internet's main application protocols, such as HTTP, SMTP, Telnet, DNS, etc. In marketing, the term has been used to distinguish distributed computing by smaller dispersed computers from the "monolithic" centralized computing of mainframe computers. But this distinction has largely disappeared as mainframes and their applications have also turned to the client-server model and become part of network computing. Each instance of the client software can send data requests to one or more connected servers. In turn, the servers can accept these requests, process them, and return the requested information to the client. Although this concept can be applied for a variety of reasons to many different kinds of applications, the architecture remains fundamentally the same.
The most basic type of client-server architecture employs only two types of hosts: clients and servers. This type of architecture is sometimes referred to as two-tier. It allows devices to share files and resources. The two tier architecture means that the client acts as one tier and application in combination with server acts as another tier. When both the client- and server-software are running on the same computer, this is called a single seat setup. Specific types of clients include web browsers, email clients, and online chat clients. Specific types of servers include web servers, ftp servers, application servers, database servers, mail servers, file servers, print servers, and terminal servers. Most web services are also types of servers.
Peer-to-Peer Networking:
A peer-to-peer (or P2P) computer network uses diverse connectivity between participants in a network and the cumulative band widthof network participants rather than conventional centralized resources where a relatively low number of server provide the core value to a service or application. P2P networks are typically used for connecting nodes via largely ad hoc connections. Such networks are useful for many purposes. Sharing content files containing audio, video, data or anything in digital format is very common, and real time data, such as telephony traffic, is also passed using P2P technology. A type of network architecture is known as peer-to-peer, because each host or instance of the program can simultaneously act as both a client and a server, and because each has equivalent responsibilities and status. Peer-to-peer architectures are often abbreviated using the acronym P2P. Both client-server and P2P architectures are in wide usage today. You can find more details in Comparison of Centralized (Client-Server) and Decentralized (Peer-to-Peer).
A pure P2P network does not have the notion of clients or servers but only equal peer nodes that simultaneously function as both "clients" and "servers" to the other nodes on the network. This model of network arrangement differs from the client-server model where communication is usually to and from a central server. A typical example of a file transfer that is not P2P is an FTP server where the client and server programs are quite distinct: the clients initiate the download/uploads, and the servers react to and satisfy these requests. However, the news server system acted in a clientserver form when individual users accessed a local news server to read and post articles. The same consideration applies to SMTP email in the sense that the core email relaying network of Mail transfer agents follows a P2P model while the periphery of e-mail clients and their direct connections is client-server.
ADVANTAGES:
Peer-to-peer networking has the following advantages over client/server networking: Content and resources can be shared from both the center and the edge of the network. In client/server networking, content and resources are typically shared from only the center of the network. A network of peers is easily scaled and more reliable than a single server. A single server is subject to a single point of failure or can be a bottleneck in times of high network utilization. A network of peers can share its processor, consolidating computing resources for distributed computing tasks, rather than relying on a single computer, such as a supercomputer. Shared resources of peer computers can be directly accessed. Rather than sharing a file stored on a central server, a peer can share the file directly from its local storage. Peer-to-peer networking solves the following problems: Allows the processing resources of edge computers to be utilized for distributed computing tasks.
Allows local resources to be shared directly, without the need for intermediate servers. Allows efficient multipoint communication without having to rely on IP multicast infrastructure.
Hybrid Networking:
A hybrid network is a local area network (LAN) containing a mix of both wired and wireless client devices. In home networks, wired computers and other devices generally connect with Ethernet cables, while wireless devices normally use WiFi technology. It refers to any computer network that contains two or more different communications standards. In this case, the hybrid network uses both Ethernet (802.3) and Wi-Fi (802.11 a/b/g) standards. A hybrid network relies on special hybrid routers, hubs and switches to connect both wired and wireless computers and other network-enabled devices.
Direct Cable Connection:
A direct cable connection is a link between the input/output (I/O) ports of two computers by using a single cable rather than a modem or other interfacing device. Direct Cable Connection (DCC), is a feature that allows a computer to transfer and share files (or connected printers) with another computer, via a connection using either the serial port, parallel port or the infrared port of each computer.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Client Server ModelDokumen8 halamanClient Server ModelShreya DubeyBelum ada peringkat
- Client server and peer to peer architecture project reportDokumen64 halamanClient server and peer to peer architecture project reportPooja HemnaniBelum ada peringkat
- Client-Server Network: Local Area Networks (Lans) FTP DnsDokumen8 halamanClient-Server Network: Local Area Networks (Lans) FTP DnsPopa AlinBelum ada peringkat
- Unit IIDokumen14 halamanUnit IIP. Nivedha Shree B. Com CA shift2Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 3Dokumen23 halamanUnit 3Pravakar GhimireBelum ada peringkat
- Operating System Workstation Personal Computer Terminal Lan Netware Windows NT OpenvmsDokumen4 halamanOperating System Workstation Personal Computer Terminal Lan Netware Windows NT OpenvmsRicha BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Client Server Architecture in 40 CharactersDokumen7 halamanClient Server Architecture in 40 CharactersMohit Kumar GahlayanBelum ada peringkat
- Client Server SystemsDokumen13 halamanClient Server SystemsGheethu Maria JoyBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Computer NetworkingDokumen17 halamanIntroduction to Computer Networkingস্বপ্নবালক100% (1)
- Client-Server Computing: Unit I - Introduction ObjectiveDokumen30 halamanClient-Server Computing: Unit I - Introduction ObjectiveRishabh DewanganBelum ada peringkat
- Client Server Technology: Ansu Elizabeth PhilipDokumen10 halamanClient Server Technology: Ansu Elizabeth PhilipAnnonymous963258Belum ada peringkat
- Csa-Unit1 3Dokumen13 halamanCsa-Unit1 3Chhavi GaggarBelum ada peringkat
- Client Server Technical DocumentationDokumen6 halamanClient Server Technical DocumentationjimBelum ada peringkat
- A2 PDFDokumen12 halamanA2 PDFMuhammad Usman SajadBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental Computer Networks ConceptsDokumen10 halamanFundamental Computer Networks ConceptsMaestro Cabado100% (2)
- Client ServerDokumen38 halamanClient Serverannamyem100% (1)
- NetworkingDokumen86 halamanNetworkingKanishka Siriwardana100% (6)
- Almas BajiDokumen21 halamanAlmas BajiiamnomandungeBelum ada peringkat
- CSA 2 Marks MvitDokumen13 halamanCSA 2 Marks MvitPrema RajuBelum ada peringkat
- AnnexureDokumen7 halamanAnnexureVrushabh HuleBelum ada peringkat
- Im ReportDokumen45 halamanIm ReportRamu DasBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing hardware and software resource sharing in distributed systemsDokumen5 halamanAssessing hardware and software resource sharing in distributed systemsJunvy AbordoBelum ada peringkat
- Extended Essay - IBDokumen14 halamanExtended Essay - IBKhalil AlamehBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper On Client Server ArchitectureDokumen8 halamanResearch Paper On Client Server Architecturenekynek1buw3100% (1)
- Network Service Paradigm - 584Dokumen6 halamanNetwork Service Paradigm - 584Entertainment's worldBelum ada peringkat
- Client and Server RoleDokumen2 halamanClient and Server RoleMaureen KiamcoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5 (Application Layer)Dokumen24 halamanLecture 5 (Application Layer)Abdullah AnwaarBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Client Servertechnology BasicDokumen42 halaman04 Client Servertechnology BasicS M Shamim শামীমBelum ada peringkat
- ClientDokumen5 halamanClientraghusysengBelum ada peringkat
- Computer NetworksDokumen8 halamanComputer NetworksFarai Willias MasochaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 E-Commerce ArchitectureDokumen28 halamanChapter 3 E-Commerce ArchitecturepriyankaBelum ada peringkat
- Distributed System NotesDokumen23 halamanDistributed System NotesaryanBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA New2Dokumen102 halamanCCNA New2niravsoni001Belum ada peringkat
- SASI Lab 4 DATA COMMDokumen10 halamanSASI Lab 4 DATA COMMSasi TharenBelum ada peringkat
- Topic-2 - Networks ICT A LEVELDokumen116 halamanTopic-2 - Networks ICT A LEVELD S A DHAKA SPACE AGENCYBelum ada peringkat
- Dcc-Microproject Jay-1Dokumen8 halamanDcc-Microproject Jay-12235 Jaydeep KonkarBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-2 (Client Server Architecture) - 1Dokumen6 halamanUnit-2 (Client Server Architecture) - 1Jatin NandalBelum ada peringkat
- Cloud Computing Unit-2 (A)Dokumen23 halamanCloud Computing Unit-2 (A)nabeelBelum ada peringkat
- Client/Server Networks: Peer-To-Peer NetworksDokumen2 halamanClient/Server Networks: Peer-To-Peer NetworksAnthony LunaBelum ada peringkat
- Local Area NetworkDokumen7 halamanLocal Area Networkkerusacba_2011Belum ada peringkat
- Selective CourseDokumen51 halamanSelective CoursewilliamBelum ada peringkat
- Client Server and Multimedia NotesDokumen71 halamanClient Server and Multimedia NotesJesse KamauBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 17 Description of Network DesignDokumen3 halamanLesson 17 Description of Network DesignWinny Shiru MachiraBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Network Tutorial by VipulDokumen21 halamanComputer Network Tutorial by VipulVipul Sharma100% (1)
- Topic Notes - Building A Simple NetworkDokumen4 halamanTopic Notes - Building A Simple NetworkSarsij MishraBelum ada peringkat
- TEXT BOOK:"Client/Server Survival Guide" Wiley INDIA Publication, 3 Edition, 2011. Prepared By: B.LoganathanDokumen41 halamanTEXT BOOK:"Client/Server Survival Guide" Wiley INDIA Publication, 3 Edition, 2011. Prepared By: B.LoganathanrenumathavBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Contents Computer-NetworksDokumen57 halamanDigital Contents Computer-Networksnk1982632Belum ada peringkat
- The Application Layer Includes The Following FunctionsDokumen15 halamanThe Application Layer Includes The Following FunctionsCaptain AmericaBelum ada peringkat
- Client Server Architecture (Class Presentation Assignment)Dokumen20 halamanClient Server Architecture (Class Presentation Assignment)kisakye diana michelleBelum ada peringkat
- BBA Unit 2Dokumen13 halamanBBA Unit 2Somnath DasBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Computer Network?: Networking in GeneralDokumen19 halamanWhat Is A Computer Network?: Networking in GeneralMahesh KarreiahgariBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Computer NetworkDokumen21 halamanWhat Is A Computer NetworkPradeep PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Data Comm LabDokumen14 halamanData Comm LabSasi TharenBelum ada peringkat
- Data, Voice, and Network InfrastructureDokumen9 halamanData, Voice, and Network InfrastructureCharla SuanBelum ada peringkat
- Client-Server Architecture Explained in 40 CharactersDokumen3 halamanClient-Server Architecture Explained in 40 CharactersSubramonia Muthu Perumal PillaiBelum ada peringkat
- Middleware Technologies IMPDokumen19 halamanMiddleware Technologies IMPYadavilli VinayBelum ada peringkat
- Middleware Technologies 2marksDokumen16 halamanMiddleware Technologies 2marksappsectesting3Belum ada peringkat
- Qu.1. What Is Distributed Operating System and Role of Middleware in A Distributed System ?Dokumen23 halamanQu.1. What Is Distributed Operating System and Role of Middleware in A Distributed System ?Kishore SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LineDari EverandComputer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LineBelum ada peringkat
- Critical TheoryDokumen23 halamanCritical TheorySimran Singh MassaunBelum ada peringkat
- Build dynamic websites with PHP and MySQLDokumen56 halamanBuild dynamic websites with PHP and MySQLSimran Singh MassaunBelum ada peringkat
- Build dynamic websites with PHP and MySQLDokumen56 halamanBuild dynamic websites with PHP and MySQLSimran Singh MassaunBelum ada peringkat
- Automobile IndustryDokumen101 halamanAutomobile IndustryDenzil HebronBelum ada peringkat
- DaaDokumen17 halamanDaaSimran Singh MassaunBelum ada peringkat
- Female FoeticideDokumen16 halamanFemale FoeticideSimran Singh MassaunBelum ada peringkat
- DISTRIBUTED COMPUTING CONCEPTSDokumen4 halamanDISTRIBUTED COMPUTING CONCEPTSSimran Singh MassaunBelum ada peringkat
- 802.11ac 2×2 Wireless Ap With Bakpak Lite: Description Feature and Benefit HighlightsDokumen5 halaman802.11ac 2×2 Wireless Ap With Bakpak Lite: Description Feature and Benefit HighlightsSoluciones En EnergiaBelum ada peringkat
- Apple TalkDokumen8 halamanApple TalkSaroj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Latest Cisco 100-105 Exam Questions and Answers Free UpdateDokumen6 halamanLatest Cisco 100-105 Exam Questions and Answers Free UpdatePattersonsBelum ada peringkat
- Vyatta BasicSystem R6.3 v01Dokumen360 halamanVyatta BasicSystem R6.3 v01rygetzBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco UCS Adapter TroubleshootingDokumen90 halamanCisco UCS Adapter TroubleshootingShahulBelum ada peringkat
- Brkarc 3445Dokumen117 halamanBrkarc 3445aarnulfoBelum ada peringkat
- Adva Multi-Layer Control Plane Technologies For Hybrid NetworksDokumen15 halamanAdva Multi-Layer Control Plane Technologies For Hybrid Networkssrotenstein3114Belum ada peringkat
- IPv6 and Internet Technology For The Aeronautical Telecommunication NetworkDokumen10 halamanIPv6 and Internet Technology For The Aeronautical Telecommunication NetworkpoketupiBelum ada peringkat
- BCC Basic Troubleshooting GuideDokumen21 halamanBCC Basic Troubleshooting GuideafrozBelum ada peringkat
- IXIA Black Book - Voice Over IP Edition 10Dokumen266 halamanIXIA Black Book - Voice Over IP Edition 10SDBelum ada peringkat
- Deciso About OPNsense Latest PDFDokumen18 halamanDeciso About OPNsense Latest PDFMohd Syamsuri Che MudBelum ada peringkat
- Configure and Manage a RADWIN JET DUO Wireless SystemDokumen72 halamanConfigure and Manage a RADWIN JET DUO Wireless SystemAndres Pipe Casallas100% (2)
- Kit GE-IPDokumen9 halamanKit GE-IPZouhair IguerhzifenBelum ada peringkat
- 4.4.3.2 Packet Tracer - Examine NAT On A Wireless RouterDokumen2 halaman4.4.3.2 Packet Tracer - Examine NAT On A Wireless RouterDennis Ray G DumaguinBelum ada peringkat
- 8.1.2.8 Lab - Converting IPv4 Addresses To BinaryDokumen4 halaman8.1.2.8 Lab - Converting IPv4 Addresses To Binarynexus22387% (39)
- Interim ReportDokumen3 halamanInterim ReportkomalkasatBelum ada peringkat
- Suricata User Guide: Release 4.1.0-DevDokumen272 halamanSuricata User Guide: Release 4.1.0-DevDavid Simon Hoyos GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- HTTP Status MessagesDokumen2 halamanHTTP Status MessagesLEO_2020Belum ada peringkat
- Accesssync™ - Osa 5401 Syncplug™: Sfp-Based PTP Grandmaster, NTP Server, Boundary/Slave Clock, Gnss ReceiverDokumen4 halamanAccesssync™ - Osa 5401 Syncplug™: Sfp-Based PTP Grandmaster, NTP Server, Boundary/Slave Clock, Gnss ReceiverYoucef KHELIFABelum ada peringkat
- Network ProjectDokumen8 halamanNetwork Projectmohammed naifBelum ada peringkat
- MC0087 MQPDokumen13 halamanMC0087 MQPManjeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 4MP Vari-Focal Network Dome Camera With 30m IR RangeDokumen3 halaman4MP Vari-Focal Network Dome Camera With 30m IR RangepjaguilarBelum ada peringkat
- 6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkDokumen8 halaman6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkParthPatel100% (8)
- CCNA 4 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 4 Exam Answers FullDokumen16 halamanCCNA 4 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 4 Exam Answers Fullabdel6qui6onez6jaimeBelum ada peringkat
- Evo Controller 8200 IP Configuration KODokumen56 halamanEvo Controller 8200 IP Configuration KORogerioBelum ada peringkat
- HUAWEI AR150&160&200&1200&2200&3200 Series Enterprise Routers Product DescriptionDokumen86 halamanHUAWEI AR150&160&200&1200&2200&3200 Series Enterprise Routers Product DescriptionJuan Pablo100% (1)
- Niemeyer, P (2000) - Learning Java PDFDokumen2 halamanNiemeyer, P (2000) - Learning Java PDFJadra FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) 802.3ad and VLACP For ES and ERS Technical Configuration GuideDokumen67 halamanLink Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) 802.3ad and VLACP For ES and ERS Technical Configuration Guidevvacthy99Belum ada peringkat
- IP ServicesDokumen156 halamanIP ServicesNguyen HoangBelum ada peringkat
- Network and Ip TechnologyDokumen77 halamanNetwork and Ip Technologylayyah2013Belum ada peringkat