0625 w04 Ms 3
Diunggah oleh
Komathi LokithasanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
0625 w04 Ms 3
Diunggah oleh
Komathi LokithasanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
MARK SCHEME for the November 2004 question paper
0625 PHYSICS
0625/03 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum mark 80
This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and students, to indicate the requirements of the examination. It shows the basis on which Examiners were initially instructed to award marks. It does not indicate the details of the discussions that took place at an Examiners meeting before marking began. Any substantial changes to the mark scheme that arose from these discussions will be recorded in the published Report on the Examination. All Examiners are instructed that alternative correct answers and unexpected approaches in candidates scripts must be given marks that fairly reflect the relevant knowledge and skills demonstrated. Mark schemes must be read in conjunction with the question papers and the Report on the Examination.
CIE will not enter into discussion or correspondence in connection with these mark schemes.
CIE is publishing the mark schemes for the November 2004 question papers for most IGCSE and GCE Advanced Level syllabuses.
Grade thresholds taken for Syllabus 0625 (Physics) in the November 2004 examination. maximum mark available Component 3 80 minimum mark required for grade: A 57 C 33 E 23 F 14
The threshold (minimum mark) for B is set halfway between those for Grades A and C. The threshold (minimum mark) for D is set halfway between those for Grades C and E. The threshold (minimum mark) for G is set as many marks below the F threshold as the E threshold is above it. Grade A* does not exist at the level of an individual component.
November 2004
INTERNATIONAL GCSE
MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 80
SYLLABUS/COMPONENT: 0625/03 PHYSICS (Extended Theory)
Page 1
Mark Scheme IGCSE November 2004
Syllabus 0625
Paper 3
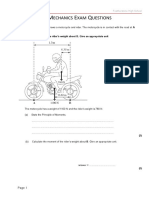
1 (a) (b) (i) (ii) (c)
deceleration/slows down/speed reduces deceleration uniform/comes to rest at 4 s 40 (m/s) 4 (s)
1 1 1 1
speed falls from 0 to 40 m/s in 4 s 1 acceleration = change in speed/time taken or 40(m/s)/4(s) 1 acceleration = 10 m/s2 1 distance = average speed x time or area of triangle under graph = 20 x 4 or 2 x 40 = 80 m pressure = hdg or 20 x 1000 x 10 = 2 x 105 Pa force = pressure x area or 2 x 105 x 0.5 e.c.f. = 1 x 105 N potential energy (at water surface) changed to kinetic energy (at pipe exit) one mark for each labelled diagram both diagrams sensible but no labels newtons/10 is kg or equivalent 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(d)
3 (10) 2 2 2 (6)
2 (a) (b) (c)
3 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
max 1
2 1
2 1 1 1 1 (6)
volume/level/reading of water then volume etc. water + rock 1 difference in the two readings density = mass/volume 1 1
4 (a) (i)
put hot junction in beaker (of hot water) read temperature from galvo. in some way (calibration)
1 1
(ii) high/low temperatures stated or high/low values quoted or temperature varying rapidly or small site/at point or remote place (from meter) or in control systems any 2 2 (b) (i) raises the water temperature 1 1
(ii) provides latent heat or boils/evaporates water
2 (6)
University of Cambridge International Examinations 2005
Page 2
Mark Scheme IGCSE November 2004
Syllabus 0625
Paper 3
5 (a) (i)
any suitable random motion molecules hit walls
1 1
(ii) 1. rebound/bounce back or many hits per unit area or per unit time or collisions create force 1 2. (av) k.e./speed of molecules increases 1 more hits(/sec) or harder hits 1 (b) p 1 v 1 = p 2 v 2 quoted or any recognisable substitution 2 x 105 x 0 . 3 5 = 5 x 1 0 5 x v volume = 0.14 (m3) expect two internal reflections at sensible angles angle of incidence at Y greater than critical angle total internal reflection occurs frequency = velocity/wavelength or 1.9 x 108/3.2 x 10-7 = 5.9 x 1014Hz 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
6 (a) (b) (c) (i)
3 (8) 1 2
(ii) refractive index = 3/1.9 or 1.9/3 = 1.58 (no e.c.f.) 7 (a) I = V/R or 12/8 = 1.5 A 10()
4 (7) 2
(b) (i)
(ii) 2() (c) power = VI or I2R or V2/R = 72W
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 2
(d) (i) 12(V) (ii) 6(V) (e) (i) (resistance) less
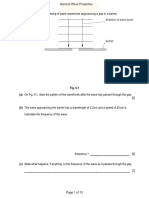
(ii) (resistance) less 8 (a) (b) diffraction plane waves in front of gap
2 (10) 1
curved end effect shown, reasonable curves 1 wavelength constant throughout and approximately same as in Fig. 8.1 1 good quality i.e. end effect starts at correct points 1 (c) particles/water oscillate/vibrate/move up and down at right angles to wave direction 1 1
4 2 (7)
University of Cambridge International Examinations 2005
Page 3
Mark Scheme IGCSE November 2004
Syllabus 0625
Paper 3
(a) (i)
two coils on continuous core (not allow coils joined) primary coil to 240 V, secondary coil to 6 V iron core, primary/input and secondary/output labelled
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 2 2 (8)
(ii) any values with correct 40:1 ratio, accept here or on diagram (b) power in = power out or 240 x I = 12 current = 0.05 A must be a changing magnetic field, only from a.c. so that induction can take place switch, relay or amplifier
(c)
10 (a) (i)
(ii) any one of the three versions below, each 2 marks 1. vary base current transistor switches on for Vbe >0.6 V 2. small change in base current produces a large change in collector/emitter current 3. vary potential divider connected to transistor base transistor switches on for Vbe > 0.6 V (b) (i) standard symbol with 2 inputs and an output labelled 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 (6) 3 (6) 2 3
(ii) one or both inputs 1, output 1 (accept on, high for 1) both inputs 0, output 0 (accept off, low for 0) 11 (a) (b) (i) correct equation i.e. Ra gives Rn + alpha particle or He all numbers correct on Rn and He radiation from surroundings/background radiation
(ii) 532 to 552 counts/min (iii) 5/6 cm (iv) beyond 5/6 cm no alpha, only background radiation
University of Cambridge International Examinations 2005
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Mat Kpsea 2023 PredictionsDokumen34 halamanMat Kpsea 2023 PredictionsAbdallah100% (1)
- Edexcel IAS Physics Unit 2 Physics at Work Topic 2 The Sound of Music Test With Mark Scheme 16 - 17Dokumen32 halamanEdexcel IAS Physics Unit 2 Physics at Work Topic 2 The Sound of Music Test With Mark Scheme 16 - 17Paul BurgessBelum ada peringkat
- II Puc Physics Revised Mannual 2018Dokumen76 halamanII Puc Physics Revised Mannual 2018rajannaBelum ada peringkat
- Don Bosco Park Circus Class 10 Physics Preboards Paper Icse 2024Dokumen7 halamanDon Bosco Park Circus Class 10 Physics Preboards Paper Icse 2024utsavdutta7d11dpsmBelum ada peringkat
- 9th Eng Chapter-WiseDokumen17 halaman9th Eng Chapter-WiseIsha NisarBelum ada peringkat
- Ionic EquilibriaDokumen15 halamanIonic EquilibriaAtharva ShirdhankarBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Equation WorksheetsDokumen15 halamanWave Equation WorksheetsOmar ShamaylehBelum ada peringkat
- Cbse Class XI Physics Chapter 1 Class TestDokumen3 halamanCbse Class XI Physics Chapter 1 Class TestroythomascBelum ada peringkat
- Moments Exam QuestionsDokumen11 halamanMoments Exam QuestionsboobooBelum ada peringkat
- Prose Fiction - Sample ResponseDokumen7 halamanProse Fiction - Sample ResponseKelly ShengBelum ada peringkat
- Radar SystemsDokumen91 halamanRadar SystemsVijaya SimhaBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel GCE A2 Physics Unit 4 Oscillations Test 14 - 15 With Marks SchemeDokumen27 halamanEdexcel GCE A2 Physics Unit 4 Oscillations Test 14 - 15 With Marks SchemePaul Burgess100% (1)
- Class Xii Physics SQPDokumen125 halamanClass Xii Physics SQPbrutalrx3310Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 8Dokumen9 halamanAssignment 8vidhya dsBelum ada peringkat
- AITS 1819 OT JEEA PAPER 2 SolDokumen12 halamanAITS 1819 OT JEEA PAPER 2 SolAryan Gupta67% (3)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Dokumen24 halamanCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Công Phạm BáBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage ReferenceDokumen22 halamanVoltage Referencesatyam100% (1)
- S4 MathsDokumen5 halamanS4 Mathsbulemuibrahim6746Belum ada peringkat
- AITS 03 - Test Paper - Arjuna NEET 2024Dokumen22 halamanAITS 03 - Test Paper - Arjuna NEET 2024drh.air12345678Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse/O Level Physics: Properties of Waves ExerciseDokumen21 halamanIgcse/O Level Physics: Properties of Waves ExerciseNasser AlsowyanBelum ada peringkat
- Model Question Solution Made By: Krishna Shah Group 'A': Answer ExplanationDokumen22 halamanModel Question Solution Made By: Krishna Shah Group 'A': Answer ExplanationKrishna ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Simple PendulumDokumen5 halamanSimple PendulumReshan ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- If The Ledge of 3 MTR Is Maintained On Galhar Side, The Ledge Available On Dul Side Is ZeroDokumen75 halamanIf The Ledge of 3 MTR Is Maintained On Galhar Side, The Ledge Available On Dul Side Is ZeroAaron WilsonBelum ada peringkat
- 1704425949Dokumen14 halaman1704425949Joydeep DuttaBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 4 - Absorption by Roots - Biology - Class X - ICSE (2019-20) - Unlocked PDFDokumen11 halamanCh. 4 - Absorption by Roots - Biology - Class X - ICSE (2019-20) - Unlocked PDFthe lillyBelum ada peringkat
- FM ReceiverDokumen3 halamanFM ReceiverAshok Ekanath KalangeBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Sample PaperDokumen6 halamanMaths Sample PaperPonharish kumar.JBelum ada peringkat
- ANALYSIS OF PUPIL PERFORMANCE 2013 PART II - Science and MathsDokumen170 halamanANALYSIS OF PUPIL PERFORMANCE 2013 PART II - Science and Mathssanath50% (2)
- Units and Measurement NcertDokumen23 halamanUnits and Measurement NcertAnurag ShivranBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter14 Electric CurrentDokumen11 halamanChapter14 Electric CurrenteltytanBelum ada peringkat
- Neet Model All Unit p+c+B-24!06!21Dokumen43 halamanNeet Model All Unit p+c+B-24!06!21Akshay S MBelum ada peringkat
- SC Sample Paper 1 Unsolved-MergedDokumen343 halamanSC Sample Paper 1 Unsolved-MergedMANARSHBelum ada peringkat
- Maths 10 Objective - IndbDokumen9 halamanMaths 10 Objective - IndbPiyush ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Board's Question Papers 2021Dokumen19 halamanBoard's Question Papers 2021subtractnewBelum ada peringkat
- 03-IIT Screening-2006 (Chemistry)Dokumen11 halaman03-IIT Screening-2006 (Chemistry)api-3721555Belum ada peringkat
- 9702 Electric Field All Completed Upto May June 2011Dokumen17 halaman9702 Electric Field All Completed Upto May June 2011Kumail Mustafa0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Mark Scheme Foundation: Number Answer Marks Level/ Band Guidance 1 2 3Dokumen3 halamanChapter 1 Mark Scheme Foundation: Number Answer Marks Level/ Band Guidance 1 2 3Adam Steven GuzyBelum ada peringkat
- General Wave Properties 1 QPDokumen13 halamanGeneral Wave Properties 1 QPLoguBelum ada peringkat
- Cbieenss 10Dokumen5 halamanCbieenss 10Ayusman100% (1)
- 9 Maths Chapter 10 Assignments 2Dokumen1 halaman9 Maths Chapter 10 Assignments 2SandyaBelum ada peringkat
- Y12 Oscilloscope QuestionsDokumen25 halamanY12 Oscilloscope QuestionsHarry StuarttitchenerBelum ada peringkat
- F4 Phy Pre-Necta I (2023)Dokumen6 halamanF4 Phy Pre-Necta I (2023)Abdallah Kunamba100% (1)
- Practice Questions Linear Equations in Two Variables Class XDokumen2 halamanPractice Questions Linear Equations in Two Variables Class XAnonymous La3xzbvxyWBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report Phase-1 PDFDokumen41 halamanProject Report Phase-1 PDFGayathri kBelum ada peringkat
- CDS (Combined Defence Service) : Eligibility Criteria & Exam PatternDokumen21 halamanCDS (Combined Defence Service) : Eligibility Criteria & Exam Patternkshitij vaidyaBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 Nov 2006Dokumen6 halamanPaper 2 Nov 2006MSHBelum ada peringkat
- High Definition TelevisionDokumen40 halamanHigh Definition TelevisionMousum Dutta100% (1)
- Problems of Chapter 1: Construction DepartmentDokumen2 halamanProblems of Chapter 1: Construction DepartmentAbdulaziz Mohamed100% (1)
- Physics: End of Year Exam RevisionDokumen18 halamanPhysics: End of Year Exam Revisionapi-354037574Belum ada peringkat
- English Set 2 (Answer Key)Dokumen7 halamanEnglish Set 2 (Answer Key)wirax41247Belum ada peringkat
- Paper 4 Nov 2001 PhysicsDokumen2 halamanPaper 4 Nov 2001 Physicssolarixe100% (1)
- Phy SamplePaper Paper1 2 eDokumen48 halamanPhy SamplePaper Paper1 2 e2233haBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of PhysicsDokumen3 halamanPrinciples of Physicsclinton koechBelum ada peringkat
- MSC Mechanical BUET-All QuestionsDokumen13 halamanMSC Mechanical BUET-All QuestionsTahsin IbtidaBelum ada peringkat
- 47 Test Bank 11Dokumen14 halaman47 Test Bank 11Pamela HancockBelum ada peringkat
- Treasure Trove Workbook Answers Daffodils: Passage-1Dokumen4 halamanTreasure Trove Workbook Answers Daffodils: Passage-1Rohan CharlesBelum ada peringkat
- T2-1 MS PDFDokumen27 halamanT2-1 MS PDFManav NairBelum ada peringkat
- Co-Ordinate GeometryDokumen66 halamanCo-Ordinate GeometryCA Deepak EhnBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Paper 3 October-November 2004Dokumen6 halamanPhysics Paper 3 October-November 2004Samar AlfadilBelum ada peringkat
- Marking SchemeDokumen6 halamanMarking SchemeIuthisam HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Summary-DasDokumen6 halamanAssessment Summary-Dasapi-283942000Belum ada peringkat
- Assessing Vocabulary in The Language ClassroonDokumen14 halamanAssessing Vocabulary in The Language Classroonrm53Belum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 1 Lesson 2cDokumen3 halamanCHAPTER 1 Lesson 2cHeheBelum ada peringkat
- Crshs Application Form For AdmissionDokumen2 halamanCrshs Application Form For AdmissionJmlo6675100% (1)
- Tle - Ictan912Ci-Iiia-J-2 Tle - Ictan912Ci-Iiia-J - 2 Tle - Ictan912Ci - Iiia-J-2 Tle - Ictan912Ci - Iiia-J-2Dokumen5 halamanTle - Ictan912Ci-Iiia-J-2 Tle - Ictan912Ci-Iiia-J - 2 Tle - Ictan912Ci - Iiia-J-2 Tle - Ictan912Ci - Iiia-J-2Nockie Hipolito RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Differentiated Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanDifferentiated Lesson Planbobtyler100% (1)
- Auc Curriculum Overview Explanation August 2021Dokumen2 halamanAuc Curriculum Overview Explanation August 2021Amelija SokolovskajaBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching English To Young Learners and Factors To Consider in Designing The MaterialsDokumen17 halamanTeaching English To Young Learners and Factors To Consider in Designing The MaterialsJack ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Director VP Program Manager in Raleigh NC Resume Mary Paige ForresterDokumen6 halamanDirector VP Program Manager in Raleigh NC Resume Mary Paige ForresterMaryPaigeForresterBelum ada peringkat
- FS4 FinalDokumen36 halamanFS4 FinalNoreen OnorBelum ada peringkat
- Edited MATH1 Quarter1 Module3 Week3Dokumen25 halamanEdited MATH1 Quarter1 Module3 Week3Junaliza Mansalay DaquioBelum ada peringkat
- E-Article: Are You Wasting Time?Dokumen1 halamanE-Article: Are You Wasting Time?api-224713068Belum ada peringkat
- FCE Formal Letter - EmailDokumen7 halamanFCE Formal Letter - EmailFrancisco Javier Navas GonzálezBelum ada peringkat
- Men in Early Childhood Education: Fathers &teachers: Mid-America AEYC Curriculum Institute 2012Dokumen11 halamanMen in Early Childhood Education: Fathers &teachers: Mid-America AEYC Curriculum Institute 2012StevebalboniBelum ada peringkat
- Aircrew Standards Manual FY2015 V1Dokumen211 halamanAircrew Standards Manual FY2015 V1Anonymous Pb39klJ100% (1)
- Syllabus ManagerialEconomics IUDokumen3 halamanSyllabus ManagerialEconomics IUmanhducBelum ada peringkat
- English Language Learning Materials - Brian TomlinsonDokumen344 halamanEnglish Language Learning Materials - Brian TomlinsonLe Do Ngoc Hang97% (35)
- Week 5 Rational FunctionsDokumen3 halamanWeek 5 Rational FunctionsAngelicaHermoParasBelum ada peringkat
- UCLA Guide To AdmissionDokumen4 halamanUCLA Guide To AdmissionNhiên SuBelum ada peringkat
- MBA Coaching and Institutes IndiaDokumen2 halamanMBA Coaching and Institutes IndiamakemycareerBelum ada peringkat
- Nwanosike, Oba F. & Onije, Liverpool Eboh 2011 'Colonialism and Education' Proceedings of The International Conference On Teaching, Learning and Change, IATEL (Pp. 624 - 631)Dokumen8 halamanNwanosike, Oba F. & Onije, Liverpool Eboh 2011 'Colonialism and Education' Proceedings of The International Conference On Teaching, Learning and Change, IATEL (Pp. 624 - 631)voxpop88Belum ada peringkat
- Weekly Evaluation Week 10Dokumen3 halamanWeekly Evaluation Week 10api-105224564Belum ada peringkat
- How To Create Professional Course Content People Will Love - TeachableDokumen49 halamanHow To Create Professional Course Content People Will Love - TeachableLiiza Diani Manzil KinantiBelum ada peringkat
- Holistic Teaching Competence Aspects: Study Analysis in State Senior High School of Makassar City IndonesiaDokumen7 halamanHolistic Teaching Competence Aspects: Study Analysis in State Senior High School of Makassar City IndonesiaRonaldBelum ada peringkat
- 6506 2nd AssignmentDokumen28 halaman6506 2nd Assignmentbillsoop135Belum ada peringkat
- I.Objectives: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Should Be Able ToDokumen2 halamanI.Objectives: at The End of The Lesson, The Students Should Be Able ToCherie Faye Ignacio Acompañado100% (4)
- PST ModuleDokumen1 halamanPST ModulerexazarconBelum ada peringkat
- Number.. The Language of Science (Dantzig T., Mazur J. Pearson 2005 0131856278) PDFDokumen414 halamanNumber.. The Language of Science (Dantzig T., Mazur J. Pearson 2005 0131856278) PDFdnoufal100% (2)
- Timetable For NUS ECE Gradute ModulesDokumen2 halamanTimetable For NUS ECE Gradute ModuleswebvenkyBelum ada peringkat
- Moh ExamsDokumen12 halamanMoh ExamsYusuf SiddiquiBelum ada peringkat