Air Topic 1
Diunggah oleh
Irena MohaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Air Topic 1
Diunggah oleh
Irena MohaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The capsule is a thin layer of dense fibrous connective tissue penetrated by efferent and afferent lymphatic vessels.
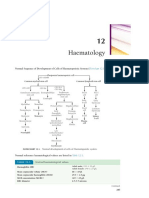
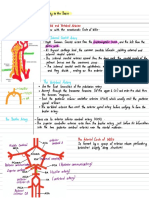
It serves to as a limiting wall preventing flowing of lymph into surrounding tissues, separate surrounding connective tissues from inner lymphoid tissue and as a barrier to the spread of cancers or infections that reach the lymph node. the cortex contains many lymph follicles which are separated by trabeculae. It contains channels which route lymph to the medulla from the afferent lymphatic vessels. Immune reactions are mediated by T and B lymphocytes and antigen-presenting macrophages in the cortex. The medulla contains many macrophages. It also includes medullary cords and lymph sinuses spanned by crisscrossing reticular fibers which act as a filter for the passage of lymph from the cortex to the efferent lymphatic vessels. the follicles has antigen-presenting macrophages and T and B lymphocytes in dendritic cells surrounding germinal centers. They involve in immune reactions to antigens. Germinal center is the light-staining interior of a lymph follicle which holds dendritic cells, antigen-presenting macrophages and many activated proliferating T and B lymphocytes. Afferent vessel is a vascular tube which transports lymph from the tissue spaces into the interior of the cortex of a lymph node. It passes the fluid through a capsule opening. While efferent vessel is a vascular tube which transports lymph from medulla exiting through an opening in the hilus and on through the lymphatic circulation. The sinuses are situated in the cortex and the medulla and are separated by the trabeculae and medullary cords respectively. The hilus of the lymph node is where the efferent lymphatic vessels carry lymph away from the medulla lymph node and on in the lymphatic circulation. Lymph travel to the lymph node through afferent vessels and drains into the subcapsular sinus, trabecular sinuses and finally into medullary sinuses. The sinus is criss-crossed by the macrophages, which trap foreign particles and filter the lymph. The medullary sinuses converge and lymph then leaves the lymph node via the efferent vessel towards either a more central lymph node or for drainage into a central venous subclavian blood vessel. The lymph enters lymph nodes and slowly moves past the cells before leaving so that the lymph can access as many lymphatic cells as possible. There is a dense packaging of immune cells in the lymph node. These are microphages and they engulf and destroy anything dangerous that they can. They also play a role in showing these substances to the T and B cells. There are also areas of the lymph node called 'germinal centres' where all the b cells multiply to fight off infection. In another part of the lymph node, there are mostly T cells. When they need to, the lymphocytes leave the lymph node and enter the circulation to fight infection. The lymph nodes are there as a filter for the lymph before it re-enters the venous system.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Anatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemDokumen34 halamanAnatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemUzma Khan100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Science 6 - Q2 - Test No 3Dokumen2 halamanScience 6 - Q2 - Test No 3MARY JANE PALISPISBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 29 YearsDokumen447 halamanBiology 29 YearsShailuAzad100% (1)
- Permanent MakeupDokumen140 halamanPermanent MakeupNatural Brows AcademyBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Bio 12 Answer Key CH 8-14Dokumen33 halamanBio 12 Answer Key CH 8-14api-2620290510% (1)
- Therapeutic Apheresis Operator Competency Aug06Dokumen43 halamanTherapeutic Apheresis Operator Competency Aug06Jose Gregorio Riobueno BolivarBelum ada peringkat
- NVBSP Form15Dokumen6 halamanNVBSP Form15Rhodz Caballes RefuerzoBelum ada peringkat
- Botulinum Toxin in Painful DiseasesDokumen181 halamanBotulinum Toxin in Painful Diseasesnimitris100% (1)
- Intestinal NematodesDokumen88 halamanIntestinal NematodesVincent Manganaan100% (1)
- Worksheet For Kinder - q1w6Dokumen20 halamanWorksheet For Kinder - q1w6lccyu9Belum ada peringkat
- Cell - The Unit of Life - NCERT Based PYQsDokumen9 halamanCell - The Unit of Life - NCERT Based PYQsAkhil singhBelum ada peringkat
- C40 - RATNA UMI AZIZAH - G41172240 - Prak 2Dokumen3 halamanC40 - RATNA UMI AZIZAH - G41172240 - Prak 2Ratna Umi AzizahBelum ada peringkat
- Urinay SystemDokumen14 halamanUrinay SystemAficionadoBelum ada peringkat
- Amniotic Fluid 2022Dokumen40 halamanAmniotic Fluid 2022Ogbuefi PascalBelum ada peringkat
- Ceva NecropsyDokumen18 halamanCeva NecropsyNanda Ayu Cindy KashiwabaraBelum ada peringkat
- Association Between Battledore Placenta and Perinatal ComplicationDokumen3 halamanAssociation Between Battledore Placenta and Perinatal Complicationtipu42Belum ada peringkat
- Skull, Brain and Orbit (Practical)Dokumen45 halamanSkull, Brain and Orbit (Practical)Chris Jardine LiBelum ada peringkat
- Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease 7Th Edition James F Zachary Full Chapter PDF ScribdDokumen67 halamanPathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease 7Th Edition James F Zachary Full Chapter PDF Scribdtodd.feuer645100% (6)
- Dental Pulp Stem Cells - Function, Isolation and Applications in Regenerative Medicine PDFDokumen12 halamanDental Pulp Stem Cells - Function, Isolation and Applications in Regenerative Medicine PDFmiguelBelum ada peringkat
- Breathing QuestionsDokumen1 halamanBreathing QuestionsAgagwa AgagwaBelum ada peringkat
- Haematology: Normal Sequence of Development of Cells of Haematopoietic SystemDokumen71 halamanHaematology: Normal Sequence of Development of Cells of Haematopoietic SystemMaxamed AadanBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Pressure - QuestionsDokumen5 halamanBlood Pressure - QuestionsErjus HoxhajBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 10Dokumen5 halamanLecture 10bibifamelaganieBelum ada peringkat
- Reproductive Cell, Organ, CycleDokumen56 halamanReproductive Cell, Organ, CycleAjay MeghanathiBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology (2 Course)Dokumen9 halamanPhysiology (2 Course)Divine ElyaBelum ada peringkat
- Module01 AnOverviewofClinicalLaboratoryHemtologyDokumen52 halamanModule01 AnOverviewofClinicalLaboratoryHemtologyKoarie Frae ZuleBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatrics CLINICAL QUESTIONDokumen14 halamanPediatrics CLINICAL QUESTIONAyesha KhatunBelum ada peringkat
- Human Body WorksheetsDokumen20 halamanHuman Body Worksheetsnona wayne dela peñaBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Myeloma: NCCN Guidelines For PatientsDokumen78 halamanMultiple Myeloma: NCCN Guidelines For PatientsAchmad Farodisi AfnaniBelum ada peringkat