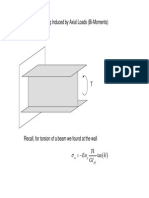
3 Problems Stress Strain Relations 3
Diunggah oleh
Oguzhan TurgutHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
3 Problems Stress Strain Relations 3
Diunggah oleh
Oguzhan TurgutHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 1
Chapter 3
Chapter 3
Stress
Stress
-
-
Strain
Strain
Relations
Relations
Problems
Problems
Linear Behavior
Linear Behavior
Temperature Effects
Temperature Effects
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 2
Problem 3.3
A square plate in the side of a ship with 800mm sides parallel
to the x and y axes has a uniform thickness h=10mm and is
made of an isotropic steel (E=200GPa and v=0.29). The plate is
subjected to a uniform state of stress.
1
2
0 ( ), 500
0 ,
, .
zz zx zy xx
yy yy
If Plane stress MPa and
for the plate determine and the final
dimensions of the plate assuming linearly elastic conditions
o o o o o
c o o
= = = = =
= =
Solution:
0
1
0
0 . 2 9 ( 5 0 0 ) 1 4 5 . 0
z z z x z y x y y y
y y y y x x
y y x x
S i n c e
E E
M P a
o o o o c
u
c o o
o u o
= = = = =
= =
= = =
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 3
1 5 0 0 0 . 2 9 (1 4 5)
0 . 0 0 2 2 9
2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0
0 . 2 9 ( 5 0 0 1 4 5)
( ) 0 . 0 0 0 9 3 5
2 0 0 0 0 0
8 0 0 (1 . 0 0 2 2 9 ) 8 0 1 . 8 3
8 0 0
1 0 (1 0 . 0 0 0 9 3 5) 9 . 9 9
x x x x y y
z z x x y y
x
y
z
E E
E
L
L m m
L m m
u
c o o
u
c o o
= = =
+
= + = =
= =
=
=
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 4
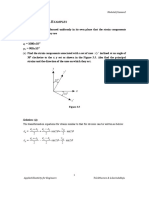
Problem 3.7
An airplane wing is made of an isotropic linearly elastic aluminum
alloy (E=72 GPa and v=0.33). Consider a point in the free surface of
the wing that is tangent to the (x,y) Plane.
250 50 , 150
xx yy xy
If MPa MPa and MPa o o o = = =
2
2( 150)
tan 2 1 0.3927
250 50
xy
xx yy
rad
o
u u
o o
= = = =
+
Determine the directions for strain gages at that point to measure
two of the principal strains. What are the magnitudes of these
principal strains?
Solution:
( )
2
2
2
2
1
2
3
1 1 2
2 2 1
(250 50) 250 50
150 100 212.1 312.1
2 2 2 2
100 212.1 112.1
0
1 312.1 0.33( 112.1)
0.00485
72000 72000
1 112.1 0.33(312.1)
0
72000 72000
xx yy xx yy
xy
MPa
MPa
E E
E E
o o o o
o o
o
o
u
c o o
u
c o o
+
| | +
| |
= + = + + = =
| |
\ .
\ .
= =
=
= = =
= = = .00299
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 5
Problem 3.8
An bearing made of an isotropic bronze (E=82.6 GPa and v=0.35) is
subjected to a state of plane strain . ( 0)
zz zx zy
c c c = = =
, , , 90 , 50 70
zz xx yy xy xx yy xy
Determine and if MPa MPa MPa o c c o o o = = =
:
82600
30590
2(1 ) 2(1 0.35)
0 ( )
0.35(90 50) 14
90 0.35( 50 14)
( ) 0.00124
82600 82600
50 0.35(90 14)
( ) 0.00105
82600 82600
zz
zz xx yy
zz
xx
xx yy zz
yy
yy xx zz
xy
xy
Solution
E
G MPa
E E
MPa
E E
E E
u
o u
c o o
o
o u
c o o
o
u
c o o
o
=
=
= = =
+ +
= = +
= =
+
+ = =
+
+ = =
=
70
0.00229
30590 G
= =
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 6
Problem 3.11
The nonzero stress components at a point in a steel plate
(E=200 GPa and v=0.29) are
( )
( )
2 2
1,2
1 2
:
1 1
(80 0.29(120)) 0.000226
200000
1 1
(80 0.29(120)) 0.000226
200000
1 1.29
(50) 0.000323
200000
1
( )
2 4
0.000355 0.000348
0.000703, 0.
xx xx yy
yy yy xx
xy xy
xx yy
xx yy xy
Solution
E
E
E
c o uo
c o uo
u
c o
c c
c c c c
c c
= = =
= = =
+
= = =
+
= +
=
= =
3
000007
( ) 0.00029
xx yy
E
u
c o o = + =
Determine the principal strains.
80 120 50 .
xx yy xy
MPa MPa MPa o o o = = =
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 7
Problem 3.13-14
A steel plate (E=200 GPa and v=0.29) is subjected to a state of plane
stress Determine the
principal stresses and strains. Also calculate the extensional strain in a
direction 20
o
CCW from the x axis.
80 , 100 , 0 50
xx yy zz xy
MPa MPa and MPa o o o o = = = =
2
2
min,max
2
2
1 2 3
:
( , )
2 2
80 100 80 100
50 10 102.96 112.96 92.96
2 2
112.96 , 0, 92.96
xx xy xx xy
xy
Solution
The principal stresses relative to x y axes are given by
MPa
MPa MPa
o o o o
o o
o o o
+
| |
= +
|
\ .
+
| |
= + = =
|
\ .
= = =
1 1 2 3
2 2 1 3
3 3 1 2
1 1
( ) (112.96 0.29(92.96)) 0.0007
200000
1 1
( ) ( 0.29(112.96) 0.29(92.96)) 0.000029
200000
1 1
( ) ( 92.96 0.29(112.96)) 0.0
200000
The corresponding principal strains are
E
E
E
c o uo uo
c o uo uo
c o uo uo
= = + =
= = + =
= = = 006286
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 8
80, 100 50
0
1
( 80 0.29(100)) 0.000545
200000
1
(100 0.29(80)) 0.000616
200000
0.29
( 80 100) 0.000029
200000
1.29
(50) 0.000323
200000
0
xx yy xy
xz yz zz
xx
yy
zz
xy
xz yz
The strain components for
are
o o o
o o o
c
c
c
c
c c
= = =
= = =
= =
= + =
= + =
= =
= =
2 2 2 4
20
20
cos 20 0.9397, sin 20 0.3420, 0
2.016 10
o
o
o o
xx yy zz
For the direction CCW from the x axis
l m n
l m n x c c c c
= = = = =
= + + =
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 9
Problem 3.21
A member Whose material properties remain unchanged (invariant) under
rotations of 90
o
about axes (x, y, z) is called a cubic material relative to axes
(x, y, z) and has three independent elastic coefficients (C
1
, C
2
, C
3
).Its stress-
strain relations relative to axes (x, y, z) are
1 2 2
2 1 2
2 2 1
3
3
3
xx xx yy zz
xx xx yy zz
xx xx yy zz
xx xy
xx xz
xx yz
C C C
C C C
C C C
C
C
C
o c c c
o c c c
o c c c
o
o
o
= + +
= + +
= + +
=
=
=
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 10
1 2 3
( 72 0.33),
103 , 55 27.6 .
0.0003
xx
Although in practice aluminum is often assumed to be an
isotropic material E GPa and v it is actually a
cubic material with C GPa C GPa and C GPa
At a point in an airplane wing the strain components are
c
= =
= = =
= , 0.0002, 0.0001, 0.00005, 0
.
.
.
.
yy zz xy xz yz
a Determine the orientation of the principal axes of strain
b Determine the stress components
c Determine the orientation of the principal axes of stress
d calculate the stress comp
c c c c c = = = = =
.
onents and determine the orientation
of the principal axes of strain and stress under the assumption
that the aluminum is isptropic
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 11
0
) 0, .
( , ) .
( , )
2
1
arctan 22.5
2
)
xz yz
xy
strain strain
xx yy
a Since the z axis is a principal strain axis
The other principal axes lie in the x y plane The CCW
rotation from x y axes to principal axes is given by
b By the stress strain
c c
c
u u
c c
= =
= =
103(0.0003) 55(0.0002 0.0001) 47.4
55(0.0003 0.0001) 103(0.0002) 42.6
55(0.0003 0.0002) 103(0.0001) 37.8
2(27.6)(0.00005) 2.76
) 0,
xx
yy
zz
xy
xz yz
relations
MPa
MPa
MPa
MPa
c Since the z axis is a principal st
o
o
o
o
o o
= + + =
= + + =
= + + =
= =
= =
0
, ( , )
1 2(2.76)
arctan 24.5
2 47.4 42.6
stress
ress axis
Thus in the x y plane
u = =
11/11/2005 Chapter 3 12
0
) 22.5
,
51.61
(1 )(1 2 )
0.0006. 25.88
2(1 )
(51.61)(0.0006) 2(25.88)(0.0003) 46.49
(51.61)(0.0006) 2(25.88)(0.0002
strain
xx yy zz
xx
yy
d
To compute the stresses compute and e as follows
E
GPa
E
e G GPa
MPa
u
u u
c c c
u
o
o
=
= =
+
= + + = = =
+
= + =
= +
0
0
) 41.32
2(25.88)(0.00005) 2.588
1 2(2.588)
arctan 22.5
2 46.49 41.32
22.5
xy
stress
strain stress
MPa
MPa o
u
u u
=
= =
= =
= =
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Numerical Examples PDFDokumen20 halamanNumerical Examples PDFHamid MasoodBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 3 1Dokumen16 halamanTutorial 3 1abinBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment (1) Vibrations: Submitted ToDokumen11 halamanAssignment (1) Vibrations: Submitted ToMahmoud KassabBelum ada peringkat
- Deriving Shape Functions For 10 Noded Cubic Triangular Element in Natural Coordinate System and VerifiedDokumen11 halamanDeriving Shape Functions For 10 Noded Cubic Triangular Element in Natural Coordinate System and VerifiedsunnywhizBelum ada peringkat
- Bending Stresses & Direct Stresses CombinedDokumen12 halamanBending Stresses & Direct Stresses Combinedvsathees2350% (2)
- Advanced Structural Analysis Prof. Devdas Menon Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDokumen33 halamanAdvanced Structural Analysis Prof. Devdas Menon Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasSonuBelum ada peringkat
- Cumulative Effect of TolereanceDokumen7 halamanCumulative Effect of Tolereancecoolcrab89Belum ada peringkat
- Rolled Steel JoistsDokumen20 halamanRolled Steel Joistsmanish dhariwalBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual Shigleys Mechanical Engineering Design 10th Edition by Budynas PDFDokumen23 halamanSolution Manual Shigleys Mechanical Engineering Design 10th Edition by Budynas PDFAbhinash KumarBelum ada peringkat
- The Stress TensorDokumen18 halamanThe Stress Tensorhiimruju50% (2)
- CIV3506 2022 Assign2 Exemplary2Dokumen33 halamanCIV3506 2022 Assign2 Exemplary2Neil WayneBelum ada peringkat
- Assgn No.4 CE OD 86 CED 87Dokumen2 halamanAssgn No.4 CE OD 86 CED 87xoham57089100% (1)
- HW1Dokumen3 halamanHW1Naveen RajBelum ada peringkat
- DomeDokumen8 halamanDomes.skumar1Belum ada peringkat
- Design of CarportDokumen3 halamanDesign of CarportNadir Khattak Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Q.15. Derive Expression For Ratio of Tension On Tight Side and Slack SideDokumen8 halamanQ.15. Derive Expression For Ratio of Tension On Tight Side and Slack SideVishal RajBelum ada peringkat
- Finite Difference Buckling Analysis of Non Uniform ColumnsDokumen8 halamanFinite Difference Buckling Analysis of Non Uniform ColumnsumeshapkBelum ada peringkat
- c0 and c1 ContinuityDokumen7 halamanc0 and c1 ContinuityGamini SureshBelum ada peringkat
- 112 116Dokumen10 halaman112 116Monica Jones100% (1)
- Example For CH-2Dokumen25 halamanExample For CH-2antenehBelum ada peringkat
- U4 - L21 Shape Factors PDFDokumen9 halamanU4 - L21 Shape Factors PDFDevesh SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- ESO 208A: Computational Methods in Engineering: Tutorial 4Dokumen3 halamanESO 208A: Computational Methods in Engineering: Tutorial 4jana.elmasry.9277Belum ada peringkat
- 02 03ChapGereDokumen16 halaman02 03ChapGereXavier Pacheco PaulinoBelum ada peringkat
- 008x TF-compressed PDFDokumen66 halaman008x TF-compressed PDFJosé Francisco Blanco VillalbaBelum ada peringkat
- Solving Following Problem by Holzer Method in MATLABDokumen2 halamanSolving Following Problem by Holzer Method in MATLABswapnil100% (2)
- Rayleigh Damping PDFDokumen9 halamanRayleigh Damping PDFmattilandBelum ada peringkat
- Load-Deflection Response of A Prestressed Concrete T-Beam (By Abaqus) PDFDokumen39 halamanLoad-Deflection Response of A Prestressed Concrete T-Beam (By Abaqus) PDFRizki Nuursirullah Mahib100% (1)
- Unit II: Analysis of Bars of Varying Cross SectionsDokumen15 halamanUnit II: Analysis of Bars of Varying Cross Sectionsermias0% (1)
- ME7360 Assignment 1 PDFDokumen3 halamanME7360 Assignment 1 PDFVivek V ShetBelum ada peringkat
- Compound Stress - ProblemDokumen1 halamanCompound Stress - ProblemPalash RoyChoudhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Lapox Epoxy Resin l12 With Hardener K 6 1 1 KG PackingDokumen2 halamanLapox Epoxy Resin l12 With Hardener K 6 1 1 KG PackingKarthick MuruganBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of Solid 2 Lab ManualDokumen63 halamanMechanics of Solid 2 Lab ManualMazharYasin100% (1)
- Excel Fatigue AnalysisDokumen11 halamanExcel Fatigue AnalysisAli GhBelum ada peringkat
- SampleqsDokumen8 halamanSampleqstommtommBelum ada peringkat
- Undamped Vibration Absorber - v3Dokumen14 halamanUndamped Vibration Absorber - v3prem_chaurasiyaaBelum ada peringkat
- C 2Dokumen4 halamanC 2Vinay GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Matrix Analysis - Alternative Formulation of The Stiffness Method - Summary and ExamplesDokumen7 halamanMatrix Analysis - Alternative Formulation of The Stiffness Method - Summary and ExamplesRobin D. Ramirez MolinaBelum ada peringkat
- Problems CH-10 Thick Cylinders (Blank)Dokumen20 halamanProblems CH-10 Thick Cylinders (Blank)محمد خريبط100% (1)
- Solutions To Chapter 9 Problems 2014 Structural and Stress Analysis Third EditionDokumen22 halamanSolutions To Chapter 9 Problems 2014 Structural and Stress Analysis Third EditionAlainBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1Dokumen7 halamanTutorial 1Shuvam Pyakurel33% (3)
- Comp BeamDokumen9 halamanComp BeamYen CeynasBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Elasticity and PlasticityDokumen2 halamanApplied Elasticity and PlasticityManu Sharma Viswanadha50% (2)
- Microplane Snippets For Ansys 18Dokumen3 halamanMicroplane Snippets For Ansys 18Flavia GelattiBelum ada peringkat
- Inverse Square & Cosine LawDokumen12 halamanInverse Square & Cosine LawAdisu0% (1)
- Influence Lines For Moving Loads On MathcadDokumen13 halamanInfluence Lines For Moving Loads On MathcadBarnaby NgBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Processes (ME 361) Lecture-17: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDokumen21 halamanManufacturing Processes (ME 361) Lecture-17: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaBelum ada peringkat
- C9789810694364SM PDFDokumen34 halamanC9789810694364SM PDFJohnrey FlandezBelum ada peringkat
- Elastic Mechanics AssignmentsDokumen8 halamanElastic Mechanics AssignmentsEng Bagaragaza Romuald100% (2)
- CFD Lab Manual PK Final PDFDokumen55 halamanCFD Lab Manual PK Final PDFYBSV PRASADBelum ada peringkat
- Alciatore Mechatronics Solution Manual 5th EditionDokumen16 halamanAlciatore Mechatronics Solution Manual 5th Editionsajal agarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 1 - Buckling of Columns - SolutionsDokumen1 halamanExercise 1 - Buckling of Columns - SolutionsTumelo InnocentBelum ada peringkat
- Twisting by Axial LoadsDokumen15 halamanTwisting by Axial LoadsVignesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #5: (5×5 25 POINTS)Dokumen9 halamanAE 321 - Solution of Homework #5: (5×5 25 POINTS)Arthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- Teknik Kekuatan BahanDokumen29 halamanTeknik Kekuatan BahanfayuangBelum ada peringkat
- G e G G G e E: Now, The Strain Tensor Is Given byDokumen1 halamanG e G G G e E: Now, The Strain Tensor Is Given byAshutosh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 08 Plasticity 02 Stress AnalysisDokumen7 halaman08 Plasticity 02 Stress AnalysisAvijit DeyBelum ada peringkat
- Uncracked Section Example: QuestionsDokumen8 halamanUncracked Section Example: QuestionsRaju SkBelum ada peringkat
- New Numerical-Examples ElasticityDokumen19 halamanNew Numerical-Examples ElasticityEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- F - A-18 External Configuration Effects On High Angle of Attack DepDokumen93 halamanF - A-18 External Configuration Effects On High Angle of Attack DepBlaze123x100% (1)
- Https WWW - Viewtrip.com ETR - Aspx CRS &RecLoc M907LO&LName GARCDokumen2 halamanHttps WWW - Viewtrip.com ETR - Aspx CRS &RecLoc M907LO&LName GARCLuis Fernando GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Aptis Exercice 12.11Dokumen1 halamanAptis Exercice 12.11Eduardo RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Leonardo Da Vinci and The PropellerDokumen27 halamanLeonardo Da Vinci and The PropellerMarina0% (1)
- MIG 29 Aircraft Design Project Part 2Dokumen44 halamanMIG 29 Aircraft Design Project Part 2Sakthi Nsk100% (1)
- Encoder Total 7thDokumen51 halamanEncoder Total 7thNguyen Hoang HaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Aircraft Morphing An Industry Visi - 2018 - Morphing Wing TechnologiDokumen17 halamanChapter 2 - Aircraft Morphing An Industry Visi - 2018 - Morphing Wing TechnologiRichardBelum ada peringkat
- Navy Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) Program: Background and Issues For CongressDokumen72 halamanNavy Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) Program: Background and Issues For CongresssamlagroneBelum ada peringkat
- RAF BanffDokumen12 halamanRAF BanffTrev Baker100% (1)
- FSII in Fet FuelDokumen10 halamanFSII in Fet FuelVu HungBelum ada peringkat
- Positioning & Navigation SystemsDokumen42 halamanPositioning & Navigation SystemsNguyen Anh0% (1)
- Authorised Release Certificate: Casa Form 1Dokumen18 halamanAuthorised Release Certificate: Casa Form 1Adalberto Sánchez SolórzanoBelum ada peringkat
- ECAM Wheel Page IndicationsDokumen2 halamanECAM Wheel Page IndicationsIsmael GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Aircraft Performance - Atmosphere 2010Dokumen4 halamanAircraft Performance - Atmosphere 2010Bali KhanBelum ada peringkat
- SB Open LJRDokumen10 halamanSB Open LJRrockmansatuBelum ada peringkat
- Rocket PropulsionDokumen33 halamanRocket PropulsionAnonymous TedqS0h6ZkBelum ada peringkat
- Astronaut Kin JeDokumen7 halamanAstronaut Kin JekvrgepilimBelum ada peringkat
- FraunhoferIISB - Brochure - Compact & Lightweight Aviation Power ElectronicsDokumen2 halamanFraunhoferIISB - Brochure - Compact & Lightweight Aviation Power ElectronicsSanjo ChackoBelum ada peringkat
- Richter-Trummer2016 Article FatigueCrackGrowthBehaviourInFDokumen15 halamanRichter-Trummer2016 Article FatigueCrackGrowthBehaviourInFTrimakisBelum ada peringkat
- Jingbo Lin: First Officer/Airline PilotDokumen1 halamanJingbo Lin: First Officer/Airline PilotAssignment GuruBelum ada peringkat
- Gyroscope: Presented By: Akshay Agrawal Bits Edu CampusDokumen52 halamanGyroscope: Presented By: Akshay Agrawal Bits Edu CampusNirmal KushwahaBelum ada peringkat
- Referencelist 2014-03 ENDokumen18 halamanReferencelist 2014-03 ENbalabhaviniBelum ada peringkat
- Abstract FastenersDokumen2 halamanAbstract FastenersJay VoraBelum ada peringkat
- Ijes Project FileDokumen17 halamanIjes Project FilebhargavBelum ada peringkat
- WL V333 Pro 2Dokumen2 halamanWL V333 Pro 2Amir Ma'rufBelum ada peringkat
- Caab Atpl Requirement PamphletDokumen5 halamanCaab Atpl Requirement PamphletblessedbuddhaBelum ada peringkat
- Boeing - Exemption RulemakingDokumen3 halamanBoeing - Exemption RulemakingM DBelum ada peringkat
- Route Check Report: (Jet Transport Aircraft Below 5700Kgs & Turbo Prop)Dokumen1 halamanRoute Check Report: (Jet Transport Aircraft Below 5700Kgs & Turbo Prop)Nitesh PalBelum ada peringkat
- MA-8 TranscriptDokumen184 halamanMA-8 TranscriptBob AndrepontBelum ada peringkat
- 기계적 사출 방식을 이용한 2단 로켓 설계Dokumen8 halaman기계적 사출 방식을 이용한 2단 로켓 설계이준Belum ada peringkat