Pain Care Plan
Diunggah oleh
jordanw0613Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pain Care Plan
Diunggah oleh
jordanw0613Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
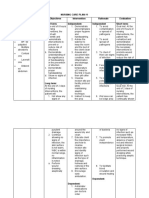
Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationales Evaluations
S- Age 56 y/o S- Admitting Dx: perforated appendicitis S- Hx: Pancreatitis S- Drainage of ABD abscess on 9/26/2011 S- S/P Exploratory Laparotomy on 9/29/2011 S- S/P appendectomy on 9/29/2011 S- Patient states pain level of 7 on a scale of 0-10 S- Patient statesYeah, that hurts upon palpation
Acute pain R/T abdominal surgical incisions AEB subjective reports of pain of a 7 on a scale of 0-10.
1.Assess patient every 2 hrs. for pain
This was successful. I was unable to enter the patients room for a consistent every two hours, however. To modify this I assessed the patients pain every time I entered or left the patients room. A.A rating scale is the most reliable method for assessing pain severity (Williams, Hopper, p. 158, 2011).
A. Assess pain level in the patient by using a self-report pain tool such as 0-10 pain rating tool.
This tool was effective to successfully identify the patients pain level. No modifications were needed.
Care Plan near surgical incision O- LOC: AAO x 3; patient accurately states name, DOB, and knows that he is in the hospital. O: JP tube x 2; L and R O: Surgical incision wound on lower abdomen midline O: Peripheral IV # 77 in LFA Piperacil/Tazobac 50 Ml begin 0545 09/29/2011 O: Peripheral IV # 114 in LFA KCl 1000 mL begin 1815 09/30/2011 O: Other meds administered: enoxaparin, famotidine, and 2. Use pain control measures as needed before activities that will entice pain in the patient B. Observe for grimacing irritability, reluctance to move or inability to lie quietly
B. Non-verbal cues are helpful in recognizing the presence of pain (Doenges, Moorhouse, & Murr, 2010, p. 577)
I watched for non-verbal cues as I was in contact with the patient to be sure that he was not masking his pain. His grimaces and pain rating of 7s were helpful in identifying his pain and subsequently providing treatment. This was successful and did not need modifications.
Effective pain management maximizes the patients ability to tolerate or participate in procedures such as bathing and ambulation (Williams & Hopper, 2011, p. 579).
This intervention was successful and useful in preventing worsened pain in the patient. After pain control measures he was more
Care Plan hydromorphone O: Patient exhibits full gross and fine motor control willing to bath and ambulate because he was not in much pain. It did not require any modifications except me informing his RNs of his need of medication before activity before I left the floor.
Short Term Objective 1: Patient will report a pain level of 2 or 3 within 30 minutes of their pain report Short Term Objective 2: Patient will express the need for pain control measures every time prior to receiving wound care, ambulation, or before performing ADLs A. Administer analgesics to the maximum dose before pain becomes severe as ordered by the physician A. The administration of analgesics before a pain producing event helps to minimized the pain that will Be experienced. They are more effective if given before pain becomes severe because mild to moderate pain is controlled more quickly and effectively than severe pain (Williams & Hopper, 2011, p. 53). And The type of medicine ordered depends on the severity of the pain. Acetometophin and NSAIDs are commonly used to treat mild to moderate pain,
I did not administer his pain medication because it was prn and was given IV by the nurse. I modified this by watching the nurse give the patient his medication. The medication was given in a timely manner within 5-10
Care Plan Long Term Objective: Upon discharge the patient will be able to perform activities of recovery or ADLs easily with a pain level of 2. while opiates (morphine, oxycodone, and fentanyl) are used to treat moderate to severe pain (Williams & Hopper, 2011, p. 579). minutes of his request so this was a successful intervention
i. i. Hydromorphone by IV. 1 mg for pain scale 1-4
Hydromorphone reduces moderate pain by binding to opiate receptors in the CNS and altering the perception of painful stimuli while producing CNS depression.
This medication was not given because the patients reported pain was always over a 6 on a 010 scale. Distraction techniques were used for pain on the level of 1-4.
i. ii. Hydromorphone by IV. 2mg for pain scale 5-10
Hydromorphone reduces severe pain by binding to opiate receptors in the CNS and altering the perception of painful stimuli while producing CNS depression.
This medication was given every time the patient complained of pain in my care. He responded well to it, without any nausea or vomiting. His pain was
Care Plan reduced from a 7 to a 3 every time so the medication was successful B.Non-pharmacologic relaxation skills and techniques have no detrimental side effects (Doenges, Moorhouse, & Murr, 2010, p. 580) Nonpharmacologic techniques were used successfully by the patient. He used techniques such as breathing and distraction by watching TV and movies on his personal DVD player to reduce his pain. He used this technique when his pain level was between a 1 and 4. This did not need to be modified.
B. Encourage nonpharmacologic therapeutic techniques to help relieve pain i. ii. iii. Back rub Visualization Guided imagery
3. Evaluate adverse
3. Intolerable adverse symptoms require a change of
The patient did not appear to
Care Plan medication effects such as decreased mental activity, change in thought process, confusion, urine retention, nausea, vomiting, or puritis medications for the patient (Williams & Hopper, 2011, p. 580). have any adverse effects after medication administration in my care. He did not appear to have any decreased mental activity or confusion. He stated that he was not nauseous and did not vomit or itch. He seemed more relaxed after his pain medication was given.
4. Position patient in a semi-Fowlers position to promote comfort
4. A semi-fowlers position will decrease the tension on the abdomen and will reduce stress on the suture line (Williams & Hopper, 2011, p. 763)
The patient remained in a semi-Fowlers position while he was in the bed even as he rested. He stated that the position was most comfortable for him. This was successful and
Care Plan did not require modification. 5. Ambulation promotes an active role in preventing further pain due to muscle spasms or contractures and enhances sense of control (Williams & Hopper, 2011, p. 580).
5. Encourage performance of individual physical therapy or exercise programs such as ambulation
Patient enjoyed ambulation and even looked forward to it. He stated that he understood the importance of ambulation. He always requested pain medication before ambulation so that it would remain enjoyable to him. He was completely active in ADLs and only needed assistance to wash his legs and feet. This was successful and did not require modification.
Care Plan 6. Splinting will stabilize the site and reduce pain, this will increase the likelihood of deep breathing and coughing (Williams & Hopper, 2011, p. 676) The patient was well informed the importance of splinting and deep breathing exercises. He did not require a pillow to splint as he did his deep breathing exercises but did use a pillow to splint when I bathed his back. This was successful. He had been informed of this by all of his prior and current nurses
6. Teach patient the importance of splinting his abdomen when performing necessary deep breathing exercises and coughing
A. Inform the patient and his family why it is necessary to deep breath despite pain
A. Deep breathing and coughing after surgical procedures helps prevent atelectasis and respiratory tract infections (Williams & Hopper, 2011, p. 763).
The patient and his sister understood that although deep breathing may be painful it was necessary expand his lungs. His sister said that she
Care Plan would continue to encourage her brother to deep breath. This was successful and did not require any modification because the patient and his sister had been informed of this many times
B. Show the patient how to splint the abdominal incision by using his hands or a pillow
B. Using a pillow to splint will ease the discomfort of coughing and taking deep breaths (Gulanick & Myers, 2011, p. 553).
The patient was informed by his RNs how to use a pillow to splint after he was admitted on the floor. He was well aware how to use it and said it was useful when he was being bathed but not for deep breathing. This was successful and did not require
Care Plan modification. C. Incentive spirometry encourages deep breathing, and allows for full expansion of the alveoli (Gulanick & Myers, 2011, p. 553).
C. Encourage the patient to use his incentive spirometer 10 times every hour
The patient was informed on the benefits of the incentive spirometer by all of his RNs and me. He was able to show me how to use it and express to me why it is useful. I do not think my patient used it as much as he should. Every time I came into his room while he was watching TV I would ask him if he had been using it and he said he hadnt since the last time I asked. He would then do it in front of me. To modify this I asked his RNs
Care Plan to remind him to use his spirometer because he would forget.
Short Term Objective 1: Patient will report a pain level of 2 - 3 within 30 minutes of their pain report
STO 1 This short term objective was met. He was administered his pain medication by his RN within ten minutes after he requested pain medication. He rated his pain a 7 before analgesic administration and a 3 thirty minutes after administration. I believe that this objective was appropriate for my patients
Care Plan situation. I knew that it would be unrealistic to expect his abdominal pain to be reduced to less than a pain scale of two. So I believe that a target goal of a 3 on the pain scale was realistic and appropriate for my patients post- surgical abdominal pain. I did not need any modifications. I did everything that I was capable of doing in this situation by reporting his pain to his attending RN immediately and watching her administer the analgesic.
Care Plan Short Term Objective 2: Patient will express the need for pain control measures, everytime, 30 minutes prior to receiving wound care, ambulation, or before performing ADLs STO 2 This goal was met. The patient was consistent in requesting pain medication before activities that caused him pain. He requested medication before activities such as walking to the bathroom to defecate because he said the strain of sitting caused him pain in his abdomen. He also requested pain medication before ambulating, sitting up in his chair, and bathing. He said that bending over while his nurses washed his back or bending to wash or put socks on
Care Plan his feet caused his pain to intensify. I offered to wash his back and his feet for him as well as put on his socks. I believe that this outcome is appropriate because requesting pain medication before activity will benefit him by reducing his pain. I also believe this Outcome is realistic for my patient. To modify my outcome I informed his RNs before I left the unit, that he would be ambulating soon and that he would be needing pain medication
Care Plan before he started. LTO This outcome was not yet because I was not there for his discharge. I believe, however, that this long term goal will be met. The patient has been progressing very well. By my second shift my patient had reduced signs of pain. He requested pain medication less frequently as the first day, only requesting it before ambulation. I believe that if he is consistent in telling his attending RNs about his pain
Long Term Objective: Upon discharge the patient will be able to perform activities of recovery or ADLs easily with a pain level of 2.
Care Plan before it reaches a severe level he will be able to keep his pain at low level of 2. Because of the previous statement, I believe that the goal is realistic and appropriate for my patients specific pain. This goal was modified by informing his RNs of my long term goal for him. They also agreed that it is an appropriate and realistic goal. The patient may also be prescribed a pain medication at discharge for use at home to keep his pain controlled.
Care Plan
Care Plan
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Focus ChartingDokumen6 halamanFocus ChartingChie Suarez100% (3)
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Nurs 125 Clinical ProjectDokumen20 halamanNurs 125 Clinical ProjectMelissa100% (1)
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseDari EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseBelum ada peringkat
- Focus ChartingDokumen5 halamanFocus ChartingJeselo Ouano GormeBelum ada peringkat
- Community Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandCommunity Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilBelum ada peringkat
- Narratives Case NotesDokumen4 halamanNarratives Case NotesKnigh RiderBelum ada peringkat
- Records and Reports DocumentationDokumen18 halamanRecords and Reports DocumentationJomarBelum ada peringkat
- Charting ExamDokumen2 halamanCharting Examleanne_567100% (1)
- Marquez - Case Study 4Dokumen4 halamanMarquez - Case Study 4Caren MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Focus Charting Example PDFDokumen1 halamanFocus Charting Example PDFRegine Lorenzana Mey-AngBelum ada peringkat
- Nurses Notes: Pre-Op and Post-Op CareDokumen3 halamanNurses Notes: Pre-Op and Post-Op CareLouie ParillaBelum ada peringkat
- LIM NursesNotesDokumen2 halamanLIM NursesNotesSophia limBelum ada peringkat
- OB Care Plan: Assessment DataDokumen12 halamanOB Care Plan: Assessment Dataapi-520985654Belum ada peringkat
- Clinical Concept MapDokumen5 halamanClinical Concept MapMj FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- NCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Dokumen3 halamanNCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Anne DyBelum ada peringkat
- Peds Nursing Care PlanDokumen9 halamanPeds Nursing Care Planapi-327793284100% (1)
- NCP Bed SoresDokumen3 halamanNCP Bed SoresShe CalliBelum ada peringkat
- University of Makati student clinical exposure reportDokumen4 halamanUniversity of Makati student clinical exposure reportdhianne_garcia2001Belum ada peringkat
- Lorma Colleges Con Template Nursing Care Plan With Fdar Related Learning ExperienceDokumen4 halamanLorma Colleges Con Template Nursing Care Plan With Fdar Related Learning ExperienceMark Jason GalangBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan EportfolioDokumen14 halamanNursing Care Plan Eportfolioapi-279212367Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan #1: Preventing InfectionDokumen5 halamanNursing Care Plan #1: Preventing InfectionAlmer OstreaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan for Seizure PatientDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan for Seizure PatientAngelica CorpuzBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing InterventionsDokumen18 halamanNursing InterventionsMark BellBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan ForDokumen7 halamanNursing Care Plan ForVanessaMUellerBelum ada peringkat
- HIV Case Study: Priority Nursing Diagnoses and CareDokumen3 halamanHIV Case Study: Priority Nursing Diagnoses and CarechoobiBelum ada peringkat
- Care Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleDokumen3 halamanCare Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleVette Angelikka Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Manage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanDokumen5 halamanManage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusBelum ada peringkat
- Wound Care Case Study: Managing Risks for Diabetic ClientDokumen5 halamanWound Care Case Study: Managing Risks for Diabetic ClientJulia KennedyBelum ada peringkat
- Post Test 30 Items OBDokumen5 halamanPost Test 30 Items OBJohnasse Sebastian NavalBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Map 360Dokumen6 halamanConcept Map 360api-273469220Belum ada peringkat
- Sbar Simulation ReflectionDokumen3 halamanSbar Simulation Reflectionapi-314635911100% (2)
- Small Bowel Obstruction Concept MapDokumen1 halamanSmall Bowel Obstruction Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiBelum ada peringkat
- Study On Pressure UlcerDokumen219 halamanStudy On Pressure UlcerThein Ko Oo100% (1)
- Clinical Portrait Pertinent DataDokumen9 halamanClinical Portrait Pertinent DataGermin CesaBelum ada peringkat
- Valdez Reflective-Questions PDFDokumen3 halamanValdez Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- L&D C-Section Care PlanDokumen12 halamanL&D C-Section Care PlanGina Giammalvo100% (2)
- SBAR ReportDokumen1 halamanSBAR ReportvanessambaileyBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen5 halamanNCPSheana TmplBelum ada peringkat
- Content: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderDokumen4 halamanContent: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderRaffy Sebastian Seballos100% (1)
- Narrative ChartDokumen5 halamanNarrative Charthady920100% (1)
- Concept Map RSV 4Dokumen10 halamanConcept Map RSV 4api-546577761Belum ada peringkat
- NANDA Nursing DiagnosesDokumen8 halamanNANDA Nursing DiagnosesShreejana PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- OB Session 1 Student Simulation Preparation Worksheet ObjectivesDokumen3 halamanOB Session 1 Student Simulation Preparation Worksheet ObjectivesI Koffi100% (1)
- Ampicillin Med InfoDokumen1 halamanAmpicillin Med InfoJan McgovernBelum ada peringkat
- Final Course in The WardDokumen4 halamanFinal Course in The WardMichael Boado100% (1)
- Carla Hernandez Clinical WorksheetDokumen2 halamanCarla Hernandez Clinical WorksheetJasmyn RoseBelum ada peringkat
- Ob Ward Timeline of ActivitiesDokumen2 halamanOb Ward Timeline of Activitiesjohncarlo ramosBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Implementation Objective DataDokumen8 halamanNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Implementation Objective DataMoonBelum ada peringkat
- SBAR Report To Physician About A Critical SitutionDokumen3 halamanSBAR Report To Physician About A Critical SitutionRandolph DjanieBelum ada peringkat
- Sepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultDokumen11 halamanSepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultShrests SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Health Assessment 51-100 QuestionnaireDokumen27 halamanHealth Assessment 51-100 QuestionnairetflorenzBelum ada peringkat
- GUIDELINES AND PROTOCOLS IN DOCUMENTATION - HceDokumen5 halamanGUIDELINES AND PROTOCOLS IN DOCUMENTATION - HceRoshin TejeroBelum ada peringkat
- Name: Nornisah H. Pangandaman Section: BSN 2A Fdar Date & Time Focus Data Action ResponseDokumen2 halamanName: Nornisah H. Pangandaman Section: BSN 2A Fdar Date & Time Focus Data Action ResponseNornisah H. PangandamanBelum ada peringkat
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation: Date/Time F Focus D Date A Action R ResponseDokumen11 halamanDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation: Date/Time F Focus D Date A Action R ResponseMJ LomuntadBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan2Dokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan2gaeLtorvzBelum ada peringkat
- ER Simulation Game Self-DebriefingDokumen2 halamanER Simulation Game Self-DebriefingRyrey Abraham PacamanaBelum ada peringkat
- Cesarean Section PDFDokumen9 halamanCesarean Section PDFIeien MuthmainnahBelum ada peringkat
- Department of SurgeryDokumen8 halamanDepartment of SurgeryDeusah EzrahBelum ada peringkat
- Practice TestDokumen11 halamanPractice TestOhTenThickeBelum ada peringkat
- Foreign and Local Literature Fatigue Among NursesDokumen5 halamanForeign and Local Literature Fatigue Among NursesMay Therese B. BoriborBelum ada peringkat
- Diaz 2009Dokumen1 halamanDiaz 2009Nasrudin EfendiBelum ada peringkat
- Elective 1 Course Outline (Read)Dokumen5 halamanElective 1 Course Outline (Read)Anel CapaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation (AEORIEDokumen3 halamanAssessment Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation (AEORIEMjhay Montemayor100% (1)
- TB Screening in Pregnancy 1Dokumen32 halamanTB Screening in Pregnancy 1nurfitriwidiBelum ada peringkat
- Study of The Disease AchondraplasiaDokumen5 halamanStudy of The Disease AchondraplasiaEries Lacanlale LumbaBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To Hypoglycemia in Infants and Children - UpToDateDokumen19 halamanApproach To Hypoglycemia in Infants and Children - UpToDateOmar Nayef TaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Neuroanesthesia ProposalDokumen2 halamanNeuroanesthesia ProposalPatricio CaballeroBelum ada peringkat
- CASE REPORT-Devyana Enggar TaslimDokumen24 halamanCASE REPORT-Devyana Enggar TaslimvivitaslimBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacokinetics Compartment ModelingDokumen94 halamanPharmacokinetics Compartment ModelingPinkishBlue100% (1)
- Kuhn Et Al-2017-Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and VenereologyDokumen16 halamanKuhn Et Al-2017-Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and VenereologyShree ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Reasons Youre Tired All The Time PreventionDokumen16 halaman7 Reasons Youre Tired All The Time Preventionsharkz fujiwaraBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Map PEDokumen3 halamanConcept Map PERobert MariasiBelum ada peringkat
- IHITool Visual Management BoardDokumen5 halamanIHITool Visual Management Boardslimane AmBelum ada peringkat
- MCQs on skin flaps, burns, trauma and thyroid disordersDokumen9 halamanMCQs on skin flaps, burns, trauma and thyroid disordersFarrukh Ali Khan0% (1)
- DKADokumen64 halamanDKAAravindhan Gunasekaran PaediatricianBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Seminar Q SIPDokumen2 halamanDaftar Seminar Q SIPririn widyaBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid CytologyDokumen36 halamanThyroid CytologyNaglaa RamadanBelum ada peringkat
- Managing corticosteroids and their side effectsDokumen6 halamanManaging corticosteroids and their side effectsKrista Madranca CastroBelum ada peringkat
- AP Psych Midterm Study Guide 09-10 ObjDokumen4 halamanAP Psych Midterm Study Guide 09-10 Objmrsaborges0% (1)
- Eob2 Drug PDFDokumen2 halamanEob2 Drug PDFBayu PrabowoBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of The Management of Acute Kidney Injury in Adults - UpToDateDokumen13 halamanOverview of The Management of Acute Kidney Injury in Adults - UpToDateDaniely FreitasBelum ada peringkat
- Update On Stemi Management: Dr. Adi Purnawarman, SP - JP (K) - Fiha.,FasccDokumen39 halamanUpdate On Stemi Management: Dr. Adi Purnawarman, SP - JP (K) - Fiha.,FasccArfiska Ridha Fausa 'ucha'Belum ada peringkat
- Dental Rest Seats GuideDokumen42 halamanDental Rest Seats GuideAhmad Khalid HumidatBelum ada peringkat
- 1556188104-Workshop Overview On Stoma CareDokumen31 halaman1556188104-Workshop Overview On Stoma CareZuldi ErdiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- TrakCare Overview 09012015Dokumen5 halamanTrakCare Overview 09012015keziajessBelum ada peringkat
- Latissimus Dorsi Flap To BreastDokumen13 halamanLatissimus Dorsi Flap To Breastokida192100% (1)
- Echs EmpanelmentDokumen316 halamanEchs EmpanelmentYudhvir SawhneyBelum ada peringkat