Fat, pH, and blood tests reveal stool abnormalities
Diunggah oleh
Sofi AresyDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Fat, pH, and blood tests reveal stool abnormalities
Diunggah oleh
Sofi AresyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
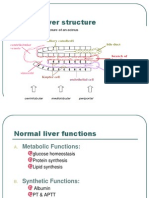
Stool analysis Normal: The stool appears brown, soft, and well-formed in consistency.
The stool does not contain blood, mucus, pus, undigested meat fibers, harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. The stool is shaped like a tube. The pH of the stool is 7.0-7.5. The stool contains less than 0.25 grams per deciliter (g/dL) or less than 13.9 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) of sugars called reducing factors. The stool contains 2-7 grams of fat per 24 hours (g/24h). Abnormal: The stool is black, red, white, yellow, or green. The stool is liquid or very hard. There is too much stool. The stool contains blood, mucus, pus, undigested meat fibers, harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. The stool contains low levels of enzymes, such as trypsin or elastase. The pH of the stool is less than 7.0 or greater than 7.5. The stool contains more than 0.5 g/dL or more than 27.8 mmol/L of sugars called reducing factors; 0.25-0.5 g/dL and 13.9-27.8 mmol/L is considered borderline. The stool contains more than 7 g/24h of fat (if your fat intake is about 100 g a day). Fecal Fat Test << enzim pankreas : cystic fibrosis, insufisiensi pankreas, ca pancreas, g ad gram empedu, -/-> lipase breakdown --> Steatorrhea. stool pale greasy (minyakan) foul smell (tengik) malabsorbtion (bacterial overgrowth, intestinal resection, celiac disease, sprue, lymphoma, chron disease, giardiasis) Fecal Fat test Kualitatif : suddan III, suddan IV identifikasi : TG (netral), asam lemak, kolesterol netral fat normal < 60 / hpf dlm suddan III dlm 95%etanol >> maldigesti kemudian + asam asetat glacial dipanaskan, dilihat lg garam/ asam lemak normal < 100/hpf >> malabsorbsi Kuantitatif : Meat Fiber >> maldigestion (cystic fibrosis, hypermotility) bentuk kotak garis menyilang (muscle fiber), no stria uncounted digested eosin dlm 10%ethanol >> 10/hpf Creatorrhea FOBT guaiac --> g blh knsumsi brokoli, vit c, aspirin tes lain : benzidin, othotolidin, immunoglobin hbA
Suddan IV Small amount of stool sample is mixed with two drops of water, two drops of 95% ethanol, and three to four drops of Sudan IV stain. Increased yellow-orange refractile fat globules (direct Sudan IV stain) identifies neutral fats. Fatty acids and fat soaps are detected after hydrolysis by mixing stool sample with two to three drops each of Sudan IV and glacial acetic acid, followed by heating before microscopic examination.
Fat Stool >> pancreatitis, sprue (celiac disease), cystic fibrosis, or other disorders that affect the absorption of fats. The presence of undigested meat fibers in the stool may be caused by Pancreatitis. << pH << absorption of carbohydrate or fat. Fermentation acid >> pH may mean inflammation in the intestine (colitis), cancer, or antibiotic use. Blood in the stool may be caused by bleeding in the digestive tract. White blood cells ~ inflammation of the intestines, : ulcerative colitis, bacterial infection. >> reducing factors in the stool ~ problem digesting some sugars. << reducing factors may be caused by sprue (celiac disease), cystic fibrosis, or malnutrition. Medicine such as colchicine (for gout) or birth control pills may also cause low levels
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Fatty Liver Cookbook: 87 Effective Fatty Liver Diet Recipes Plus Guide To Reverse And Prevent Fatty LiverDari EverandFatty Liver Cookbook: 87 Effective Fatty Liver Diet Recipes Plus Guide To Reverse And Prevent Fatty LiverBelum ada peringkat
- Fatty Liver Diet: Guide and healthy recipes to help lose weight and reverse fatty liverDari EverandFatty Liver Diet: Guide and healthy recipes to help lose weight and reverse fatty liverBelum ada peringkat
- Stool ExaminationDokumen30 halamanStool ExaminationSonam JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Stool ExaminationDokumen82 halamanStool Examinationambadepravin100% (2)
- clinical pathology ( urin and feces) 4semesterDokumen6 halamanclinical pathology ( urin and feces) 4semesterSiddhi KaulBelum ada peringkat
- Urine AND Feces: Prepared By: Group 5Dokumen37 halamanUrine AND Feces: Prepared By: Group 5Chantal RaymondsBelum ada peringkat
- Stool Exam and Lab HepatitisDokumen10 halamanStool Exam and Lab HepatitisGabriella TjondroBelum ada peringkat
- Urine Examination New-1Dokumen81 halamanUrine Examination New-1H GondaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Enzymes Liver Pancreas FCDokumen10 halamanEnzymes Liver Pancreas FCLois Lipanovich100% (1)
- Stool AnalysisDokumen8 halamanStool AnalysisLuciaGomez100% (1)
- Investigation PDFDokumen26 halamanInvestigation PDFsonia87100% (1)
- Urinalysis: Clin. Immunol. / Lab. Work/ Renal Disorders/ Urine Analysis/ Dr. Batool Al-HaidaryDokumen11 halamanUrinalysis: Clin. Immunol. / Lab. Work/ Renal Disorders/ Urine Analysis/ Dr. Batool Al-HaidaryIM CTBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Function TestDokumen17 halamanLiver Function TestKarthiyayini .S.JBelum ada peringkat
- Your Liver-It Is Amazing and EssentialDokumen5 halamanYour Liver-It Is Amazing and Essentialsudha_karBelum ada peringkat
- Urine and Feces ExaminationsDokumen36 halamanUrine and Feces Examinationsshubhamthakurst1108Belum ada peringkat
- Normal ValuesDokumen1 halamanNormal ValuesJohnmark DubdubanBelum ada peringkat
- Faeces: Juan Marcos Martínez ZevallosDokumen18 halamanFaeces: Juan Marcos Martínez ZevallosJuan Marcos Martinez ZevallosBelum ada peringkat
- 3,4Biochemestry 2021 بسجDokumen38 halaman3,4Biochemestry 2021 بسجغالب الموسويBelum ada peringkat
- Routine Stool Analysis GuideDokumen2 halamanRoutine Stool Analysis GuideNicole Tan90% (10)
- UrinalysisDokumen9 halamanUrinalysisSukma EffendyBelum ada peringkat
- LipidsDokumen13 halamanLipidsalianaBelum ada peringkat
- Urine AnalysisDokumen69 halamanUrine Analysisvinay0717100% (3)
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer with MRSA InfectionDokumen49 halamanDiabetic Foot Ulcer with MRSA InfectionMaulana IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Function Test InterpretationDokumen89 halamanLiver Function Test InterpretationprashanthshamBelum ada peringkat
- Urine AnalysisDokumen53 halamanUrine AnalysisMaath KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- UrinalysisDokumen43 halamanUrinalysisJames Knowell75% (4)
- UrinalysisDokumen6 halamanUrinalysisAsmadayana HasimBelum ada peringkat
- GoutyDokumen27 halamanGoutyroshanleung11Belum ada peringkat
- Acid Alkaline Food ChartDokumen3 halamanAcid Alkaline Food Charta1n2d3i4v5Belum ada peringkat
- NILAI NORMAL FUNGSI LABORAT NoviDokumen14 halamanNILAI NORMAL FUNGSI LABORAT NoviLans ProductionBelum ada peringkat
- Ayurvedic Tips For Lowering Cholesterol NaturallyDokumen13 halamanAyurvedic Tips For Lowering Cholesterol Naturallykuldip1951Belum ada peringkat
- Stool Analysis (D/R) TestDokumen8 halamanStool Analysis (D/R) TestAbed AbusalemBelum ada peringkat
- The Anatomy of The Liver: Sub To: DR Suguna Rao Professor Dept of Vet PathDokumen13 halamanThe Anatomy of The Liver: Sub To: DR Suguna Rao Professor Dept of Vet PathAdarshBijapurBelum ada peringkat
- Grading edema levels and vital signs chartDokumen3 halamanGrading edema levels and vital signs chartKristina EitelBelum ada peringkat
- Dealing With Fatty Liver: Healthy Lifestyle Healthy LiverDari EverandDealing With Fatty Liver: Healthy Lifestyle Healthy LiverBelum ada peringkat
- Stool Analysis: What Is The Stool or Feces?Dokumen28 halamanStool Analysis: What Is The Stool or Feces?Annisa SafiraBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Function Tests and EnzymesDokumen90 halamanLiver Function Tests and EnzymesNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (1)
- Liver Function TestDokumen27 halamanLiver Function Testom pal singh lodhiBelum ada peringkat
- Benefits of cow urine highlighted in Ayurvedic text and researchDokumen15 halamanBenefits of cow urine highlighted in Ayurvedic text and researchsillymindsBelum ada peringkat
- BLD, Stool, Urine Analysis & MCSDokumen73 halamanBLD, Stool, Urine Analysis & MCSnoblefxBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Pathology Fecalysis and UrnalysisDokumen16 halamanClinical Pathology Fecalysis and UrnalysisRem Alfelor100% (3)
- Interpretasi Urine RutinDokumen118 halamanInterpretasi Urine Rutinboy jendri huluBelum ada peringkat
- Determine Serum Cholesterol LevelDokumen8 halamanDetermine Serum Cholesterol Levelpuhranee nathanBelum ada peringkat
- Decena, Cyrille Justine A. BSN-4A: Competency AppraisalDokumen4 halamanDecena, Cyrille Justine A. BSN-4A: Competency AppraisalJohn Glenn Balacano100% (2)
- Session 4 Phase 2Dokumen65 halamanSession 4 Phase 2ayoub shams mohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Nutritional Value of Lime and Lemon in Hypercholesterolaemic Induced RatsDokumen4 halamanNutritional Value of Lime and Lemon in Hypercholesterolaemic Induced RatszainabBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem FecalysisDokumen5 halamanBiochem FecalysisDonna DominnoBelum ada peringkat
- Nutri Lec ReviewerDokumen182 halamanNutri Lec ReviewerRaquel MonsalveBelum ada peringkat
- UrinalysisDokumen3 halamanUrinalysisKim MoranoBelum ada peringkat
- Organ Function TestDokumen49 halamanOrgan Function TestmekuriawBelum ada peringkat
- Secretion of Bile and The Role of Bile Acids in DigestionDokumen8 halamanSecretion of Bile and The Role of Bile Acids in DigestionMarianne Kristelle NonanBelum ada peringkat
- Acidity: Cure YourselfDokumen17 halamanAcidity: Cure Yourselfआदित्य मोदीBelum ada peringkat
- Complete guide to stool examination: what it tests and how it's performedDokumen2 halamanComplete guide to stool examination: what it tests and how it's performedLILY MAINBelum ada peringkat
- Urine JSJ EoDokumen9 halamanUrine JSJ EokeiBelum ada peringkat
- Fecal Fat Test-2020Dokumen4 halamanFecal Fat Test-2020Djdjjd SiisusBelum ada peringkat
- Biological MoleculesDokumen4 halamanBiological MoleculesLet's hit 100k sub without any videosBelum ada peringkat
- UrineDokumen17 halamanUrinealynne_pascua8530Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing I - Workshop 5 Sem B 2020Dokumen10 halamanNursing I - Workshop 5 Sem B 2020Santiago AlejandroBelum ada peringkat
- Fatty Liver Diet: 85 Step-by-Step Recipes and Guide To Reverse Fatty Liver Disease And Live LongerDari EverandFatty Liver Diet: 85 Step-by-Step Recipes and Guide To Reverse Fatty Liver Disease And Live LongerBelum ada peringkat
- Fatty Liver: Recipes and Guide to Prevent, Cure and Reverse Fatty Liver Disease, Lose Weight and Promote Good HealthDari EverandFatty Liver: Recipes and Guide to Prevent, Cure and Reverse Fatty Liver Disease, Lose Weight and Promote Good HealthBelum ada peringkat
- Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder: Florian Daniel Zepf, Caroline Sarah Biskup, Martin Holtmann, & Kevin RunionsDokumen17 halamanDisruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder: Florian Daniel Zepf, Caroline Sarah Biskup, Martin Holtmann, & Kevin RunionsPtrc Lbr LpBelum ada peringkat
- Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmDokumen1 halamanLocal Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmSydney JenningsBelum ada peringkat
- MInTFM Programme Brochure 2019Dokumen12 halamanMInTFM Programme Brochure 2019Shoban RajBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrients: Obesity and Dyslipidemia in South AsiansDokumen26 halamanNutrients: Obesity and Dyslipidemia in South AsiansFitriBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - MidazolamDokumen2 halamanDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- Low Back Pain in Elderly AgeingDokumen29 halamanLow Back Pain in Elderly AgeingJane ChaterineBelum ada peringkat
- Tabel Obat ObatanDokumen7 halamanTabel Obat ObatanMega Suciati100% (1)
- 3401 Review On Goat Milk Composition and Its Nutritive ValueDokumen10 halaman3401 Review On Goat Milk Composition and Its Nutritive ValueRed DiggerBelum ada peringkat
- A Client With A Brain Tumor: Nursing Care PlanDokumen1 halamanA Client With A Brain Tumor: Nursing Care Planshabatat2002Belum ada peringkat
- Garfinkel Case at The University of MinnesotaDokumen9 halamanGarfinkel Case at The University of MinnesotaMarkingsonCaseBelum ada peringkat
- Reliability of Anatomic Reference Planes in Establishing The Occlusal Plane in Different Jaw Relationships: A Cephalometric StudyDokumen8 halamanReliability of Anatomic Reference Planes in Establishing The Occlusal Plane in Different Jaw Relationships: A Cephalometric Studyedy harahapBelum ada peringkat
- MYMAN Chanchinbu Issue No. 5Dokumen6 halamanMYMAN Chanchinbu Issue No. 5Langa1971Belum ada peringkat
- Ozone Therapy in DentistryDokumen16 halamanOzone Therapy in Dentistryshreya das100% (1)
- Mental RetardationDokumen11 halamanMental RetardationTherese Tee-DizonBelum ada peringkat
- Group 9 - Dental FluorosisDokumen37 halamanGroup 9 - Dental Fluorosis2050586Belum ada peringkat
- VP ShuntDokumen5 halamanVP ShuntPradeep SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Study ReportDokumen5 halamanClinical Study ReportAlexandraCirlanBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual For Dosage Calculations A Multi Method Approach 0132158620Dokumen13 halamanSolution Manual For Dosage Calculations A Multi Method Approach 0132158620RandallValdezypfqw100% (86)
- 4926-02 L2 Certificate Qualification Handbook v1 PDFDokumen116 halaman4926-02 L2 Certificate Qualification Handbook v1 PDFforumuse3bBelum ada peringkat
- The New ILAE Seizure Classification, 63 Seizure TypesDokumen3 halamanThe New ILAE Seizure Classification, 63 Seizure TypesAndreea AtănăsoaeiBelum ada peringkat
- Organsymbol KartenDokumen24 halamanOrgansymbol KartenMacaio100% (2)
- Daftar Regulasi Bidang KeperawatanDokumen128 halamanDaftar Regulasi Bidang KeperawatanSanti AndrianiBelum ada peringkat
- Free Gingival Graft Procedure OverviewDokumen1 halamanFree Gingival Graft Procedure OverviewTenzin WangyalBelum ada peringkat
- Formulation Development of Garlic Powder (Allium Sativum) For Anti-Diabetic Activity Along With Pharmaceutical EvaluationDokumen5 halamanFormulation Development of Garlic Powder (Allium Sativum) For Anti-Diabetic Activity Along With Pharmaceutical EvaluationIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- A New Drug-Shelf Arrangement For Reducing MedicatiDokumen9 halamanA New Drug-Shelf Arrangement For Reducing MedicatiEmmanuel LawerBelum ada peringkat
- Angels Bridging Angels Bridging Angels Bridging Angels Bridging Gaps Gaps Gaps GapsDokumen13 halamanAngels Bridging Angels Bridging Angels Bridging Angels Bridging Gaps Gaps Gaps Gapsapi-251664135Belum ada peringkat
- Practitioner Agreement PCP/SpecialistDokumen20 halamanPractitioner Agreement PCP/SpecialistCommunityBridgesBelum ada peringkat
- Consultant Physician Gastroenterology Posts Clyde SectorDokumen27 halamanConsultant Physician Gastroenterology Posts Clyde SectorShelley CochraneBelum ada peringkat
- ActivatorDokumen69 halamanActivatorParijat Chakraborty PJBelum ada peringkat
- About Critical Care NursingDokumen7 halamanAbout Critical Care NursingaivynBelum ada peringkat