Midterm Sample # 2 - GEO1111
Diunggah oleh
mhadd071Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Midterm Sample # 2 - GEO1111
Diunggah oleh
mhadd071Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Midterm 2 - questions 1. During sediment transport in either water or wind medium, detrital grains tend to become: A.
massive, juxtaposed, layered B. agglutinated, dissolved, compacted C. sorted, smaller, rounded C. oxidized, reduced, dissolved 2. A non-conformity is: A. a rock unit that is different than units above or below it B. a gap in the geologic record bounded below by metamorphic rocks and bounded above by sedimentary rocks C. a rock that does not contain fossils D. a sequence of tocks that does not contain any gaps in the geological record 3. Numerical dating refers on a parent elements half life defined as: A. the time required for a daughter isotope to lose half of its radioactive nucleus B. the time required for all the parent to decay to a daughter isotope C. the time required for half of the radioactive nuclei in a sample to decay D. the time required to count half of the fossils in a rock 4. A fault plane north-south is dipping (angled steeply to the east). Geologists observations indicated that most of the fault movement was vertical and that young rocks occur east of the fault and old rocks occur west of the fault. What type of fault is this: A. transform fault B. normal fault C. reverse fault D. none of the above 5. Most coal mining occurs in basins within mountain belts. Which of the following statements about crustal-scale sedimentary basins is true: A. oldest rocks occur in the center and the beds tilt toward the center B. oldest rock occur in the center and the beds tilt away from the center C. youngest rocks occur in the center and the beds tilt toward the center D. youngest rocks occur in the center and the beds tilt away from the center 6. Why does the mid-ocean ridge (along plate spreading centers) have elevated topography relative to the sea floor: A. B. C. D. thicker oceanic sediments thicker oceanic lithosphere thermal buoyancy compressive forces causing uplift
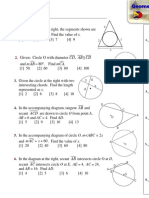
Use the crustal cross-section below for next 7 questions:
7. A. B. C. D. 8. A. B. C. D.
Point A is called the earthquake: hypocenter epicenter seismometer wave front Point B, where the slip initiated during an earthquake, is called: hypocenter epicenter seismometer wave front
9. What type of faulting is illustrated in the diagram above? A. B. C. D. normal fault reverse fault transform fault thrust fault
10. What type of plate boundary commonly displays this fault style? A. divergence B. convergence C. transform D. all of the above 11. What type of tectonic stress is exhibited by this fault: A. B. C. D. extension rotation compression none, conservation of stress
12. List the correct order in which seismic waves will arrive at point A: A. B. C. D. S waves P waves surface waves Suface waves P waves S waves P waves surface waves S waves P waves S waves surface waves
13. How is stress different than strain? Stress is the pressure/area, where as strain measures elongation of a material m/m unitless Geological drawing: unit J is an igneous rock unit, the rest are all sedimentary layers:
14. Which of the following events happened most recently, and WHY A. folding of F, G, H B. tilting of C, D, E C. faulting of C, D, E D. cannot tell from the information given 15. Which of the following events happened most recently and WHY A. B. C. D. intrusion of J erosion along X-X faulting of C, D, E cannot tell from the information given
16. Which of the following units is the oldest and WHY A. B. C. D. unit A unit J unit H cannot tell from the information given
17. Which of the following units is the youngest and WHY A. B. C. D. unit A unit J unit H cannot tell from the information given
18. What type of fault is present and why? A. reverse B. normal C. transform D. cannot tell from the information given
19. Units F, G, H are deformed into which structure, and what type of force forms this structure: A. anticline B. syncline C. headcline D. cannot tell from the information given 20. The wavy, horizontal line labeled X X is a ____ and why nonconformity angular conformity disconformity conformable bed 21. If this section of rock were to be correlated to another section of rock located on another continent, which principle could be applied? A. B. C. D. uniformitarianism fossil succession superposition cross-cutting relationship
A. B. C. D.
22. Because of gravitational instability, old, dense, oceanic lithosphere is consumed at: A. B. C. D. convergent plate boundaries divergent plate boundaries transform plate boundaries all of the above 23. Which of the following statements about the asthenosphere is false: A. it lies beneath the lithosphere B. it is stronger than the lithosphere C. it rises close to the surface beneath mid-ocean ridges
D. it is partially molten
24. Which of the following statements is not an assumption of numerical dating: A. B. C. D. rock has remained a closed system when the rock formed it contained only parent isotope rate of radioactive decay has decreased through time daughter products are trapped in the rock after decay 25. Why do tectonic plates move: A. B. C. D. random drifting of continental crust on molten magma drag of the plates by push-pull forces electromagnetic pulses radiating from core solar winds
26. Directed pressure during high temperature metamorphism results in a rock containing: A. mineral cleavage B. minerals aligned as foliation C. randomly oriented minerals D. equant, interlocking minerals 26. A sample of basalt has deformed brittely during a laboratory experiment. If we wish our next sample of basalt to deform plastically rather than brittely, we should conduct our next experiment at: A. higher temperatures and lower confining pressures B. higher temperatures and higher confining pressures C. lower temperatures and lower confining pressures D. lower temperatures and higher confining pressures
2. The travel time difference between the arrival of the P and S waves can be used to determine: A. B. C. D. distance to the earthquake location of the earthquake magnitude of the earthquake type of faulting that occurred during the earthquake
3. What is the minimum number of seismographs needed to locate the epicenter of an earthquake:
A. B. C. D.
1 2 3 4
4. In C-14 geochronology, Carbon-14 is produced by: A. B. C. D. radioactive decay of Uranium 235 in the mineral cosmic ray bombardment of Nitrogen-14 in the atmosphere transpiration of lichen sunspots
5. In plate tectonics, slab-pull is defined as: A. movement of thermal convection cells producing drag on overlying plates B. movement of crust into mantle imparted by down-going slab during subduction C. movement of astenosphere due to convection in the mantle D. movement of crust resulting from elevated position of oceanic ridge system causing crust to gravitationally slide down flanks of ridge 6. The study of faunal succession allows: A. B. C. D. matching of similarly-aged rocks from different outcrops absolute dating of fossil-bearing strata correlation of fossils with mammals of today the study of habitats of extinct mammals
7. How do rock particles move during passage of a P wave through the rock? A. back and forth parallel to the direction of wave travel B. back and forth at right angles to the direction of wave travel C. in a rolling elliptical motion D. in a rolling circular motion 34. Metamorphism occurs: A. B. C. D. adjacent to igneous intrusions during burial at subductions zones all of the above 35. The 3 factors which control sand dune formation: A. wind direction, wind supply, dry climate B. wind strength, sand supply, vegetation C. wind direction, sand supply, soil depth
D. wind strength , sand supply, dry climate
36. Define the main characteristics of plate tectonics. Main characteristics of plate tectonics: - brittle litosphereic plates - ductile aestnosphere - collision of plates convergent event - moving apart divergence event - slip past each other transform boundary 37. What are arguably the 2 largest geodynamic forces that cause tectonic plates to move? E. Slap push and slab pull F. Mantle convection. Rising and sinking action of mantle generates currents which put plats in motion. They float on a ductile astenosphere 34. What are the 4 factors, which control the breakdown of rock? G. Parent rock, climate + precipitation, wheter rock is covered by soil, time 34. Why is there usually a calcite (limestone) build-up problem on water heaters? H. Calcite solubility decreases as water temperature increases. Solubility of CO2 is inversely proportionally with temperature but directly proportionally to calcite solubility. Thus when solubility of CO2 decreases, it causes the solubility of calcite to decrease as well and thus calcite precipitates out.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- ERSC 1P01 Midterm 2016Dokumen8 halamanERSC 1P01 Midterm 2016Gurleen DhaliwalBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Sample # 3 - GEO1111Dokumen7 halamanMidterm Sample # 3 - GEO1111mhadd071100% (1)
- Earthquake QuizDokumen4 halamanEarthquake QuizMary Ann DimacaliBelum ada peringkat
- Eesa06 Lecture Notes Lec1 Lec7 EESA06 2018Dokumen15 halamanEesa06 Lecture Notes Lec1 Lec7 EESA06 2018RAYYAN ADEELBelum ada peringkat
- Solar System KEY PDFDokumen32 halamanSolar System KEY PDFAchmad FahrizaBelum ada peringkat
- Esct 01Dokumen6 halamanEsct 01Nina Livefive BurneyBelum ada peringkat
- Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen12 halamanStatic Equilibrium and Elasticity Multiple Choice QuestionsChristelle DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Sample # 1 - GEO1111Dokumen7 halamanMidterm Sample # 1 - GEO1111mhadd071Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and The Other Terrestrial WorldsDokumen27 halamanChapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and The Other Terrestrial WorldsEdwin ChuenBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ of Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Subject: Module 1: Properties of FluidsDokumen55 halamanMCQ of Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Subject: Module 1: Properties of FluidsBala MetturBelum ada peringkat
- Rotation of Rigid Bodies MCQ TestDokumen7 halamanRotation of Rigid Bodies MCQ Testeka123Belum ada peringkat
- Name - Earth Science Wind/Pressure/Weather Webquest Part 1. Air MassesDokumen4 halamanName - Earth Science Wind/Pressure/Weather Webquest Part 1. Air Massesapi-330185541Belum ada peringkat
- Shearing Forces and Bending MomentsDokumen12 halamanShearing Forces and Bending Momentsjacob ellyBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Study Guide Sedimentary and Stratigraphy SequenceDokumen25 halamanFinal Exam Study Guide Sedimentary and Stratigraphy SequenceTHỊNH NGUYỄN HÁNBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 14 Our Star: The Cosmic Perspective, 7e (Bennett Et Al.)Dokumen22 halamanChapter 14 Our Star: The Cosmic Perspective, 7e (Bennett Et Al.)Edwin ChuenBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - Folds, Faults & UnconformityDokumen30 halaman5 - Folds, Faults & Unconformitymoorpvr100% (1)
- 8 WeatheringDokumen21 halaman8 Weatheringnayvalente11Belum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresDokumen17 halamanTest Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresaimeeBelum ada peringkat
- IsostasyDokumen2 halamanIsostasyarqianBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Earth's Layers Cuarto BásicoDokumen23 halamanUnit 2 Earth's Layers Cuarto BásicoConstanza FillaBelum ada peringkat
- Addis Ababa University Physics Worksheet IIDokumen3 halamanAddis Ababa University Physics Worksheet IIDanielBelum ada peringkat
- Eesa06 MC Test Ch1-4Dokumen9 halamanEesa06 MC Test Ch1-4Minyan ZhuBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes For Week 2 - General Geology PDFDokumen35 halamanLecture Notes For Week 2 - General Geology PDFRuby LenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3: Marine ProvincesDokumen30 halamanChapter 3: Marine ProvincesCarol GirottoBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Motion and GraphDokumen1 halamanLinear Motion and GraphmydadawalfnBelum ada peringkat
- EOSC 114 - Practice Midterm 2Dokumen6 halamanEOSC 114 - Practice Midterm 2Corrie BrodyBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquake science and effects quiz answersDokumen52 halamanEarthquake science and effects quiz answersmgupta72Belum ada peringkat
- Report On Geology About Malekhu AreaDokumen65 halamanReport On Geology About Malekhu Areabimal0% (1)
- Motion in Two Dimensions (Physics)Dokumen11 halamanMotion in Two Dimensions (Physics)GiovannaPacheco100% (1)
- Rock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsDokumen4 halamanRock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsJACKSON SANDERS-PUGHBelum ada peringkat
- Impact Markers in The Stratigraphic Record PDFDokumen360 halamanImpact Markers in The Stratigraphic Record PDFSantiago RodríguezBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Statics MomentsDokumen15 halamanIntroduction to Statics MomentsHussein HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Kepler Laws Review AnswersDokumen2 halamanKepler Laws Review Answersgabriel UYBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11-Angular Momentum: Multiple ChoiceDokumen16 halamanChapter 11-Angular Momentum: Multiple ChoiceMarcial Aguilar BarahonaBelum ada peringkat
- Encyclopedia of Astrobiology - ADokumen136 halamanEncyclopedia of Astrobiology - ALogan NorrellBelum ada peringkat
- CirclesDokumen3 halamanCirclesericmilamattimBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 22 The Birth of The Universe: The Cosmic Perspective, 7e (Bennett Et Al.)Dokumen20 halamanChapter 22 The Birth of The Universe: The Cosmic Perspective, 7e (Bennett Et Al.)mark100% (1)
- 3.1 WeatheringDokumen25 halaman3.1 WeatheringSipu GiriBelum ada peringkat
- FM&HM Objective TypeDokumen113 halamanFM&HM Objective TypePradeep JuvvadiBelum ada peringkat
- PMC Practice Test Questions of Heat & ThermodynamicsDokumen25 halamanPMC Practice Test Questions of Heat & ThermodynamicsAb Hadi100% (1)
- BPKIHS Questions 2069-11-19Dokumen18 halamanBPKIHS Questions 2069-11-19siddhantaBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz #2: Seismic Waves and Layers of the EarthDokumen1 halamanQuiz #2: Seismic Waves and Layers of the EarthJamayka Jessa Jebulan Evaristo100% (1)
- Testbank Chapter15Dokumen11 halamanTestbank Chapter15AnaMendezBelum ada peringkat
- EOSC 114 Module 2 - Earthquakes Practice Quiz 1Dokumen2 halamanEOSC 114 Module 2 - Earthquakes Practice Quiz 1Corrie BrodyBelum ada peringkat
- Plot Subsurface Geology from MapsDokumen11 halamanPlot Subsurface Geology from MapsKaizoku-OBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 07 G278 2007 Optical IndicatrixDokumen27 halamanLecture 07 G278 2007 Optical IndicatrixAaqib AliBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Discovering The Universe 10th Edition by CominsDokumen42 halamanTest Bank For Discovering The Universe 10th Edition by Cominsa558645663Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 13Dokumen15 halamanChapter 13Michelle Hsieh100% (2)
- Mapping Earths Interior ExtractDokumen4 halamanMapping Earths Interior ExtractJoanna CerreliBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics Case StudyDokumen6 halamanElectrostatics Case StudyAbsar AlamBelum ada peringkat
- Plate Tectonics Review WorksheetDokumen3 halamanPlate Tectonics Review WorksheetJayson Tafalla Lopez100% (1)
- KIPS COLLEGE NOTES ON MOTION AND FORCEDokumen7 halamanKIPS COLLEGE NOTES ON MOTION AND FORCEFaisal IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- GEOPHYSICS TWO MARKSDokumen9 halamanGEOPHYSICS TWO MARKSArunodhaya NBelum ada peringkat
- Geology Final Exam NotesDokumen14 halamanGeology Final Exam NotesKuhoo UBelum ada peringkat
- Part - I (MCQ) (Compulsory)Dokumen2 halamanPart - I (MCQ) (Compulsory)Fatima BabarBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of A Subduction ZoneDokumen1 halamanAnatomy of A Subduction ZonecvytasekBelum ada peringkat
- Plate Tectonics Quiz Explains Continental DriftDokumen3 halamanPlate Tectonics Quiz Explains Continental DriftElizerBelum ada peringkat
- Gravity MethodDokumen9 halamanGravity MethodHarshBelum ada peringkat
- Summative Assessment Module 3 & Module 4 Science 10Dokumen6 halamanSummative Assessment Module 3 & Module 4 Science 10MYLYN JULIOBelum ada peringkat
- 1ST Quarter Exam - in Science 10Dokumen5 halaman1ST Quarter Exam - in Science 10Allen Marohombsar100% (2)
- Lesson 2 - Plate BoundariesDokumen24 halamanLesson 2 - Plate BoundariesArnel Jeffrey OñateBelum ada peringkat
- Seafloor Spreading Guided Notes: Slide 1: A Hypothesis For The Building of New Seafloor, Proposed by Harry HessDokumen4 halamanSeafloor Spreading Guided Notes: Slide 1: A Hypothesis For The Building of New Seafloor, Proposed by Harry HessMarilyn Castro LaquindanumBelum ada peringkat
- Plate Boundaries: Earth's Surface Is Dramatically Reshaping Itself in An Endless, Slow-Motion Movement Called PlateDokumen3 halamanPlate Boundaries: Earth's Surface Is Dramatically Reshaping Itself in An Endless, Slow-Motion Movement Called Platedaisy sorianoBelum ada peringkat
- Ocean BasinDokumen13 halamanOcean BasinhomeylinBelum ada peringkat
- Baguio Mining DistrictDokumen4 halamanBaguio Mining DistrictCarmina CaringalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10Dokumen4 halamanChapter 10seraphinehundredBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Geography Notes 04 Distribution of Oceans and ContinentsDokumen6 halaman11 Geography Notes 04 Distribution of Oceans and ContinentsAkashBelum ada peringkat
- Plate Tectonics Lab Assignment GuideDokumen4 halamanPlate Tectonics Lab Assignment GuideTonni TonishBelum ada peringkat
- An Isotopic Survey of Pacific Oceanic Plateaus - Implications For Their Nature and OriginDokumen14 halamanAn Isotopic Survey of Pacific Oceanic Plateaus - Implications For Their Nature and OriginMonica UrbietaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Exercise 1 - Plate Tectonics - Answer Sheet QuestionsDokumen3 halamanLab Exercise 1 - Plate Tectonics - Answer Sheet QuestionsCandiceBelum ada peringkat
- Plate Tectonics Theory Revolutionized Earth SciencesDokumen44 halamanPlate Tectonics Theory Revolutionized Earth SciencesTran Dang SangBelum ada peringkat
- Tectonics and BasinsDokumen43 halamanTectonics and Basinsalbert mwairwaBelum ada peringkat
- Plate Tectonics Lecture NotesDokumen72 halamanPlate Tectonics Lecture Notesapi-27996976767% (3)
- Learning Activity 1: The Magma Flows Out of The Crack Cools Down and It Becomes The New SeafloorDokumen6 halamanLearning Activity 1: The Magma Flows Out of The Crack Cools Down and It Becomes The New SeafloorGinger BreadBelum ada peringkat
- EbooksHouse Super Earth Encyclopedia - DKDokumen210 halamanEbooksHouse Super Earth Encyclopedia - DKRaj100% (6)
- Diverging Plates: Rifts, Ridges and Separating ContinentsDokumen2 halamanDiverging Plates: Rifts, Ridges and Separating ContinentsFernadez Rodison100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To GeologyDokumen37 halamanChapter 1 - Introduction To GeologynnsBelum ada peringkat
- ES Study Guide - Lesson10 - Plate TectonicsDokumen14 halamanES Study Guide - Lesson10 - Plate TectonicsFranzel GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Continental Drift and Seafloor Spreading: Sci-BoxDokumen26 halamanContinental Drift and Seafloor Spreading: Sci-BoxNhet Ytienza100% (1)
- Ebook Earth An Introduction To Physical Geology Canadian 3Rd Edition Tarbuck Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokumen56 halamanEbook Earth An Introduction To Physical Geology Canadian 3Rd Edition Tarbuck Test Bank Full Chapter PDFaddlingsottawask07u100% (12)
- Mysteries of The Pacific PDFDokumen41 halamanMysteries of The Pacific PDFGonzalo Palazuelos100% (1)
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Volcano and Its Relation To Plate TectonicsDokumen41 halamanScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Volcano and Its Relation To Plate TectonicsLani Bernardo Cuadra100% (8)
- OphioliteDokumen7 halamanOphiolitemimiwBelum ada peringkat
- Sea floor spreading processDokumen20 halamanSea floor spreading processNeil De Guzman100% (1)
- July-15 Science10 Q1 M2 Plate-Boundaries-FINALDokumen31 halamanJuly-15 Science10 Q1 M2 Plate-Boundaries-FINALAglanot IS83% (6)
- Plate Tectonics A Scientific Reolution UnfoldsDokumen32 halamanPlate Tectonics A Scientific Reolution UnfoldsJuan Esteban BernalBelum ada peringkat
- Science10 - q1 - Mod3 - Processes and Landforms Along Plate Boundaries - FINAL08082020Dokumen20 halamanScience10 - q1 - Mod3 - Processes and Landforms Along Plate Boundaries - FINAL08082020ravioli kim100% (2)
- Structure of The EarthDokumen47 halamanStructure of The Earthapi-270383743100% (1)
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 3 Plate TectonicsDokumen32 halamanScience: Quarter 1 - Module 3 Plate TectonicsRUTH PIANG100% (3)
- Lantawan Integrated School tests Earth Science conceptsDokumen14 halamanLantawan Integrated School tests Earth Science conceptsNoreza CabigonBelum ada peringkat