Blood Infections
Diunggah oleh
Sarah PlunkettDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Blood Infections
Diunggah oleh
Sarah PlunkettHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
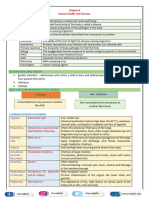
Transmission Infectious Endocarditis Bacteria or virus in the blood infects interior heart muscle, causing damage and resulting
clot
Pathogenesis Bacteria stick to the clot, may increase it Emboli clot breaks off, flows to a smaller blood vessels and blocks blood flow petechial hemorrhages, stroke, coronary embolism Abs bind the emboli and recruit complement, increasing cell damage
Incidence Common causes: oralstreptococci enter via bleeding gums Skin or fecal bacteria enter via wounds
Symptoms
Other
Diseases
Vaccine?
Bacteremia Same as endocarditis bugs and Group B Strep (GBS) Beta hemolytic streptococcus S.agalactiae normal vaginal flora, but not present in all women. Testing in last 3 weeks before giving birth Epstein Barr Virus (EBV; herpes 4)
Most common cause of neonatal death in US
Puerperal fever, sepsis in mother, post birth. Major cause of death due to childbirth if no access to clean water, Abx. Neonatal bacteremia, meningitis, pneumonia depending on where infant infected
Droplet-hard to get: requires high ID50
Kills pharyngeal cells, causing inflammation. Causes some B cells to divide, encouraging viral replication. Makes B cells look like Monocytes (atypical lymphocytes_ Tissue tropism: lytic in pharyngeal epithelia, latent in B cells
-Asymptomatic in most healthy people, just feel tired -fetuses if mothers primary infection is in pregnancy, fetus may be born jaundiced -hearing loss and learning disabilities may develop later. Immunocompromised pneumonia if respiratory, flu like symptoms and pneumonia if via transfusion/transplant -Rash sometimes bullseye shape with fever, pain for months. Lack of neutrophil response, chronic inflammation. -Arthritis later inflammation to joints, very painful
Lyme Disease Borellia borgdorferi: fastidious spiral bacterium with reservoir in mice, problem especially in E. US
Deer tick
Difficult to study! Hypothesis: unusual cell wall LPS triggers confused chronic immune reaction wherever pathogen is (first skin, later joints/brain)
Chagas Disease Trypanosoma cruzi Protozoan flagellate
Transmission Vector, vertical kissing bug so called because it is attracted to CO2 exhaled while victim sleeps. Bites near mouth, but actual transmission is from its poop, which may enter through eye or wound. Lives in thatched roofs Food esp. unpasteurized milk. Goats/sheep, swine, cattle Multiple usually would infected while butchering small mammals. Ex: rabbits, squirrels for meat. Improbable but ID 50 is low! Vector: flea bite
Pathogenesis May stay at bite site inflammation. If disseminates, forms a pseudocyst inside cardiac or autonomic nervous system cells
Incidence Distribution: LatinAmericaUS issue with immigrants, blood banks
Brucellosis Brucella spp.
Tularemia (Rabbit fever) Francisella tularensis fastidious bacterium
Symptoms Acute: flu-like symptoms. If poop was in eye, get droopy eye for a few weeks, like the kid. Some develop chronic infection and may immediately or years later suffer organ failure, especially of heart or GI, due to pseudocyts Flu-like symptoms. May develop into chronic nocturnal fever -Causes spontaneous abortion in humans too Ulcerated would Granulomas in skin Buboes -if disseminated, high fever, organ failure, high mortality
Other
Diseases
Vaccine?
Bioterrorism: has been explored as possible bioterror agent
Bioterror: can also be inhaled, so proposed bioterror agent (but so tough to grow this is really unlikely)
Plague Black plague name for buboes Yersinia pestis Gram negative bacteria
Lives in macrophages, spreads to lymph nodes and rapidly multiplies. -Massive immune recruitment there, and dying bacteria release LPS into lymph, then blood septic/toxic shock
Bubonic Plague: buboes are purple, swollen lymph nodes. High fever, death in days
Rickettsial infections Obligate intracellular bacteria. Very small and simple, kind of like viruses, and also intracellular. Rickettsial infections Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever R. rickettsia Rickettsial infections Typhus flu-like symptoms
Arthropods. All are transmitted by insect/arachnid bites
Vector: tick
Infects and kills endothelial cells, causing blood vessel collapse.
Epidemic Typhus R. prowazeckii Vector: lice Endemic Typhus R. typhi Vector: rat flea
-rash due to blood leaking into tissues, possible clot development and subsequent embolism. -rash (same rash as RMSF), very high fever, high mortality if untreated
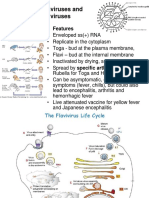
Arboviruses Insect born viruses
Transmission Aedes mosquitoesstriped mosquito invasive to Americas
Pathogenesis
Incidence Distribution Dengue Fever: tropics (can only be spread by Aedes) US Emergence? Mosquito recently seen in SW US Distribution of Yellow fever: Equatorial Africa and Latin America
Symptoms
Other West Nile born by other species of Aedes mosquito genus, found father north, including here. Serious human infections rare.
Diseases Dengue Fever: Quebrante huesos breakbone fever. Terrible muscle and joint pain, high fever. Dengue Hemorrhagic fever: may develop, depending on strains. Hemmorhage internal and external Yellow fever virus: diseases similar to dengue fever but pain is less and liver problems more. Jaundice, swollen abdomen, Hemorrhagic fever may develop.
Vaccine? Vaccine for Yellow Fever: most effect vaccine ever developed. You get a yellow card (photo) to prove you have it.
Ebola and Marburg viruses
Blood reservoir unknown; bats suspected. Possibly begins with bat bite and spreads to victims caretakers
Break down cell: cell boundaries between epi/endothelial cells
Lymphatic filiariasis Sometimes called elephantiasis Wuchereria bancrofi, Brugia malayi roundworms Malaria: review from unit 1 HIV: review from unit 5
Mosquito
Baby worms in blood; adult worms live in lymph vessels. Have bacteria inside them that, when released on worm death, cause inflammation, scarring.
Outbreaks: small, every few year in Central/East Africa. Only large outbreaks (numbering in hundreds) associated with iatrogenic transmission: non sterile practices in hospital care Distribution: tropics
Fever Sever hemorrhaging Inside and out
Early: parasitemia (baby worms in blood), fever, fatigue. People born in endemic areas may not have symptoms. Later, if untreated: painful swollen limbs. scrotum from repeated scarring.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Microbial Diseases of the Nervous System: An OverviewDokumen30 halamanMicrobial Diseases of the Nervous System: An OverviewBangtan SonyeondanBelum ada peringkat
- Microbial Diseases of The CardiovascularDokumen5 halamanMicrobial Diseases of The CardiovascularToby MapaBelum ada peringkat
- ExplanationDokumen6 halamanExplanationLerma PagcaliwanganBelum ada peringkat
- Typhoid Fever: Life-Threatening Illness Caused by Salmonella Typhi BacteriaDokumen48 halamanTyphoid Fever: Life-Threatening Illness Caused by Salmonella Typhi BacteriaJoyce_Hao_4373Belum ada peringkat
- Microbial Mechanisms of PathogenicityDokumen48 halamanMicrobial Mechanisms of PathogenicitywfBelum ada peringkat
- Penyebab Virus - Flaviridae (Dengue)Dokumen32 halamanPenyebab Virus - Flaviridae (Dengue)Bendy Dwi IrawanBelum ada peringkat
- Gram Staining and Classifications of BacteriaDokumen33 halamanGram Staining and Classifications of BacteriaSchola De san joseBelum ada peringkat
- Micropara 1Dokumen30 halamanMicropara 1Myla OrlandaBelum ada peringkat
- Transmission Pathogenesis Incidence Symptoms Other Diseases Vaccine? Acute MeningitisDokumen4 halamanTransmission Pathogenesis Incidence Symptoms Other Diseases Vaccine? Acute MeningitisSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Infections and SeizuresDokumen16 halamanInfections and SeizuresJoseph Toledo LoboBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8 ProjectDokumen10 halamanGrade 8 ProjectJollebee Ampis GeronaBelum ada peringkat
- Bot 111 Module 1Dokumen16 halamanBot 111 Module 1Jericho whiteBelum ada peringkat
- Babesiosis: A Protozoan Infection Caused by Tick BitesDokumen38 halamanBabesiosis: A Protozoan Infection Caused by Tick Bitesturinawe haggaiBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori-A: Transmission Pathogenesis Incidence Symptoms Other Diseases Vaccine? Stomach UlcersDokumen4 halamanHelicobacter Pylori-A: Transmission Pathogenesis Incidence Symptoms Other Diseases Vaccine? Stomach UlcersSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Despite All The Research Every One of Us Catches Cold and Most of Us Catch It FrequentlyDokumen1 halamanDespite All The Research Every One of Us Catches Cold and Most of Us Catch It FrequentlyKM GamingBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Emerging and ReDokumen15 halamanUnderstanding Emerging and ReGWeezyBelum ada peringkat
- Reporting MicrobioDokumen2 halamanReporting MicrobioTeresa Mae Dimen BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- CURA Mono, Rheu, HyperDokumen89 halamanCURA Mono, Rheu, Hyperwiwi_13Belum ada peringkat
- Patho Unit 5Dokumen37 halamanPatho Unit 5Shafiya ShaikBelum ada peringkat
- Tuberculosis (T.B) : What Is TB?Dokumen16 halamanTuberculosis (T.B) : What Is TB?Usman MirzaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-8 Human Health and DiseasesDokumen10 halamanChapter-8 Human Health and DiseasesbpmbhamoraBelum ada peringkat
- Diseases and VaccinesDokumen37 halamanDiseases and Vaccinesraghu ramBelum ada peringkat
- Bovine BabesiosisDokumen6 halamanBovine BabesiosisPawan PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- GI Infections2Dokumen8 halamanGI Infections2OM JHABelum ada peringkat
- Botany AssignmentDokumen21 halamanBotany Assignmentabdul hadiBelum ada peringkat
- Microbial Diseases of the Circulatory SystemDokumen3 halamanMicrobial Diseases of the Circulatory SystemmoigomezBelum ada peringkat
- Infectious DiseasesDokumen65 halamanInfectious DiseasesFathimah UswahBelum ada peringkat
- Diseases Spread by Pigeons and Prevention MethodsDokumen6 halamanDiseases Spread by Pigeons and Prevention MethodsVidya DufareBelum ada peringkat
- What Is LeptospirosisDokumen18 halamanWhat Is LeptospirosisLuphly TaluvtaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio VascularDokumen86 halamanCardio VascularNic KorapatBelum ada peringkat
- Bovine Ephemeral Fever: A Short-Lived Arbovirus DiseaseDokumen2 halamanBovine Ephemeral Fever: A Short-Lived Arbovirus Diseasebilal ahmadBelum ada peringkat
- PNVL Biological Science Lecture on VirusesDokumen3 halamanPNVL Biological Science Lecture on VirusesJenny MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Canine BabesiosisDokumen10 halamanCanine BabesiosisIonuț Gabriel ȚoleaBelum ada peringkat
- Lec8 Infectious DiseasesDokumen32 halamanLec8 Infectious DiseasesmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Necrotising Fasciitis and Myositis Impetigo Pharyngitis Pneumonia Lymphangitis Erysipelas and Cellulitis Scarlet Fever/ Streptococcal TSDokumen20 halamanNecrotising Fasciitis and Myositis Impetigo Pharyngitis Pneumonia Lymphangitis Erysipelas and Cellulitis Scarlet Fever/ Streptococcal TSPadmavathy Naidu ChokkapuBelum ada peringkat
- Ebola Virus Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokumen15 halamanEbola Virus Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAlvin AlmazanBelum ada peringkat
- Outdoor Pursuits LeafletDokumen2 halamanOutdoor Pursuits LeafletJon Oates100% (1)
- CLASICAL HOG FEVER UnfinishDokumen19 halamanCLASICAL HOG FEVER UnfinishZeus CuiBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDokumen1 halamanUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionsSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Diseases and Pathogens ExplainedDokumen4 halamanTypes of Diseases and Pathogens ExplainedCarlos WebsterBelum ada peringkat
- What Is InfectionDokumen20 halamanWhat Is InfectionsakunBelum ada peringkat
- Herpesvirida E& Adenoviridae: By: MJ Briones Bsn-IiDokumen93 halamanHerpesvirida E& Adenoviridae: By: MJ Briones Bsn-IiMj BrionesBelum ada peringkat
- Pyrexia of Unknown OriginDokumen55 halamanPyrexia of Unknown OriginsanjeevBelum ada peringkat
- Bloodlymphatic DiseaseDokumen127 halamanBloodlymphatic Diseaseone_nd_onlyuBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Bacterial Fungal Infections of Blood PDFDokumen54 halaman1 Bacterial Fungal Infections of Blood PDFahmad mohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Infectious Diseases of the Central Nervous System: Bacteria and VirusesDokumen71 halamanInfectious Diseases of the Central Nervous System: Bacteria and VirusesCarmela EgaminoBelum ada peringkat
- Diseases Caused by VirusDokumen6 halamanDiseases Caused by VirusJannet De Lara VergeldeDiosBelum ada peringkat
- Communicable Diseases: in The PhilippinesDokumen3 halamanCommunicable Diseases: in The PhilippinesMitchie CallosBelum ada peringkat
- CEGE2008 – Environmental Pollution and Pathogen Risk AssessmentDokumen43 halamanCEGE2008 – Environmental Pollution and Pathogen Risk AssessmentmiBelum ada peringkat
- MB Virology 5 & 6 – Overview of HerpesvirusesDokumen7 halamanMB Virology 5 & 6 – Overview of HerpesvirusesUsman Ali AkbarBelum ada peringkat
- Infex para SupplementDokumen27 halamanInfex para SupplementShubh ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Diseases and VaccinesDokumen22 halamanDiseases and VaccineslakshBelum ada peringkat
- Microbes and DiseaseDokumen2 halamanMicrobes and Diseasearma nengsihBelum ada peringkat
- An Insight Into Bovine Babesiosis - Epashupalan Mar 2021Dokumen6 halamanAn Insight Into Bovine Babesiosis - Epashupalan Mar 2021Deepak CBelum ada peringkat
- Disha Publication Chapter With Exercises BiologyDokumen32 halamanDisha Publication Chapter With Exercises BiologyAnuj TripathiBelum ada peringkat
- Herpesviruses S MunsakaDokumen20 halamanHerpesviruses S Munsakamulengamordecai92Belum ada peringkat
- (16b) Togaviridae, FlaviviridaeDokumen44 halaman(16b) Togaviridae, FlaviviridaeFarrah BenoitBelum ada peringkat
- ARTHROPOD-BORNE RICKETTSIAL DISEASESDokumen14 halamanARTHROPOD-BORNE RICKETTSIAL DISEASESFatima AbasovaBelum ada peringkat
- Micro I ReviewDokumen15 halamanMicro I ReviewEmilee Tu100% (1)
- Rhythm Strips AnalysisDokumen107 halamanRhythm Strips AnalysisSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Student Clinical Report SheetDokumen2 halamanStudent Clinical Report SheetSarah Plunkett100% (1)
- MRN: - Weight: - KG Age: - : Risk/RestraintDokumen2 halamanMRN: - Weight: - KG Age: - : Risk/Restraintrustiejade100% (3)
- SPA Team Volunteer ApplicationDokumen7 halamanSPA Team Volunteer ApplicationSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Map of Nursing SchoolDokumen1 halamanConcept Map of Nursing SchoolSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- NCLEX Cram SheetDokumen2 halamanNCLEX Cram SheetSarah Plunkett100% (1)
- Backup NclexDokumen61 halamanBackup NclexSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Med-SurgTest 3Dokumen6 halamanDrugs Med-SurgTest 3Sarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Patho FinalDokumen25 halamanPatho FinalSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- MedSurg Drug List Test 1Dokumen2 halamanMedSurg Drug List Test 1Sarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- MedSurg Medications & TablesDokumen71 halamanMedSurg Medications & TablesSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDokumen1 halamanUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionsSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- SAMs Pre TestDokumen5 halamanSAMs Pre TestSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- MedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Dokumen12 halamanMedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Sarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Final NotesDokumen24 halamanMicro Final NotesSarah Plunkett100% (1)
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDokumen3 halamanLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic Infections Affecting Skin All ViralDokumen2 halamanSystemic Infections Affecting Skin All ViralSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Surface InfectionsDokumen1 halamanSurface InfectionsSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Eye InfectionsDokumen1 halamanEye InfectionsSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDokumen1 halamanSoft Tissue InfectionsSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Reproductive InfectionsDokumen2 halamanReproductive InfectionsSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Transmission Pathogenesis Incidence Symptoms Other Diseases Vaccine? Acute MeningitisDokumen4 halamanTransmission Pathogenesis Incidence Symptoms Other Diseases Vaccine? Acute MeningitisSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori-A: Transmission Pathogenesis Incidence Symptoms Other Diseases Vaccine? Stomach UlcersDokumen4 halamanHelicobacter Pylori-A: Transmission Pathogenesis Incidence Symptoms Other Diseases Vaccine? Stomach UlcersSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- GI Infections HepatitisDokumen4 halamanGI Infections HepatitisSarah PlunkettBelum ada peringkat
- Ayurvedic Dosha TheoryDokumen72 halamanAyurvedic Dosha Theoryyogiraj mishraBelum ada peringkat
- Sanctification of The Heart 4th Edition by DR Michelle StrydomDokumen771 halamanSanctification of The Heart 4th Edition by DR Michelle StrydomDios Estrella67% (3)
- Case Study 5 Year Boy With CoughDokumen3 halamanCase Study 5 Year Boy With CoughAryl Eduarte100% (1)
- Anterior Segment OctDokumen53 halamanAnterior Segment OctA.c. RaghuBelum ada peringkat
- Litrature & Case StudyDokumen74 halamanLitrature & Case Studynaol buloBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of Fetal HeartDokumen59 halamanEvaluation of Fetal Heartاد ريما البدر100% (3)
- Urinary System Disorders Practice Quiz #1 (50 Questions)Dokumen26 halamanUrinary System Disorders Practice Quiz #1 (50 Questions)Emy TandinganBelum ada peringkat
- How To Maintain Throat HygieneDokumen9 halamanHow To Maintain Throat Hygieneankita singhBelum ada peringkat
- Amavatha & VathasonithaDokumen125 halamanAmavatha & VathasonithaCicil AbrahamBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan Respiratory SystemDokumen7 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan Respiratory Systemjane89% (9)
- Comparison Between DOAC To Enoxaparin For Risk of Intracranial BleedingDokumen2 halamanComparison Between DOAC To Enoxaparin For Risk of Intracranial BleedingFathima Sheik KatherBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Literature on Rabies Prevention and ControlDokumen24 halamanReview of Literature on Rabies Prevention and ControlBeah Claudette AbundoBelum ada peringkat
- Ir Medical 2017 A3 PDFDokumen25 halamanIr Medical 2017 A3 PDFHeidi BlueBelum ada peringkat
- Obstetrics and GynacologyDokumen14 halamanObstetrics and GynacologykalkidanBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 Book AntimicrobialResistanceDokumen606 halaman2022 Book AntimicrobialResistanceFety Andriani100% (1)
- 2012 Karshaniya YavaguDokumen4 halaman2012 Karshaniya YavaguRANJEET SAWANTBelum ada peringkat
- PrimaquineDokumen3 halamanPrimaquineVijayakumar NsBelum ada peringkat
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDokumen4 halamanPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsNovanza RayhanBelum ada peringkat
- HCCC ComplaintDokumen23 halamanHCCC ComplaintPaul GallagherBelum ada peringkat
- US Elsevier Health Bookshop - Mosby, Saunders, Netter & MoreDokumen4 halamanUS Elsevier Health Bookshop - Mosby, Saunders, Netter & MoreWilmer Zambrano GuerreroBelum ada peringkat
- Dental CatalogueDokumen28 halamanDental CataloguePaulus LagadanBelum ada peringkat
- Final Written Lab Exam Form ADokumen4 halamanFinal Written Lab Exam Form AErvin T MileBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal Polyps and PolyposisDokumen244 halamanIntestinal Polyps and PolyposisVladislav KotovBelum ada peringkat
- IV Drug ReactionsDokumen19 halamanIV Drug Reactionsphp_czarina04421Belum ada peringkat
- UAS Genap Semester II Kebidanan STIKES HafshawatyDokumen3 halamanUAS Genap Semester II Kebidanan STIKES HafshawatyHanna HannaBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Cases For MRCPCH PART 2 Applied Knowledge in PracticeDokumen218 halamanClinical Cases For MRCPCH PART 2 Applied Knowledge in Practiceaeyousef88% (16)
- Corneal Dystrophies: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentDokumen2 halamanCorneal Dystrophies: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentBadgal BazingaBelum ada peringkat
- ICU Accomplishment Report and Improvement PlanDokumen5 halamanICU Accomplishment Report and Improvement PlanMikhaelEarlSantosTacordaBelum ada peringkat
- Type2 Diabetes HandoutDokumen1 halamanType2 Diabetes Handouthendra_darmawan_4Belum ada peringkat
- Myocardial InfarctionDokumen18 halamanMyocardial InfarctionMarc Lorenz DucusinBelum ada peringkat