Circu Nerve 1
Diunggah oleh
Shiva MotianiDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Circu Nerve 1
Diunggah oleh
Shiva MotianiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 12.
The comparative anatomy of the circulatory system
A. General considerations pp.306-314 1. The parts of the circulatory ssytem Systems of branching tubes enclosing circulating fluids Blood-vascular system Lymphatic system Blood-vascular system Closed system Heart Arteries Veins Capillaries Classes of veins: Systemic veins Pulmonary veins Portal veins or portal systems Blood (red) Plasma Corpuscles Red blood cells White blood cells
Lymphatic system Open system Lymph vessels Lymph sinuses Lymph hearts (lower vertebrates) Lymph glands (lymphocytes) Tonsils Thymus Spleen Lymph
Dorsal aorta Caudal artery Anterior cardinal veins Posterior cardinal veins Duct of Cuvier or common cardinal vein Lateral or ventral abdominal veins Umbilical or allantoic veins Subintestinal vein Caudal vein Median visceral or splanchnic branches Lateral visceral branches Parietal or somatic branches
6. The evolution of the heart A straight tube Fishes Assumes an S shape Sinus venosus Atrium Ventricle Conus arteriosus Valves Ventral aorta Venous blood Tetrapod Heart double circulation Right & left atria (auricles) Interauricular septum Aerated blood Systemic veins sinus venosus right auricle ventricle pulmonary arteries lungs pulmonary veins left auricle ventricle conus arteriosus ventral aorta Reptiles Reducing sinus venosus Interauricular septum Interventricular septum Conus arteriorsus three arterial trunks Semilunar valves
Societas Vitae Reviewer - P. Cantiller Hyman, L. (1965). Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy. The University of Chicago Press.
2. The origin of the blood and of the blood vessels Mesoderm (mesenchyme cells) Somatic (somatic vessels) Splanchnic (visceral or splanchnic vessels)
Birds and mammals Interventricular septum Vanished sinus venosus conus arteriosus two arterial trunks (systemic aorta & pulmonary trunk) systemic vein right auricle right ventricle pulmonary artery lungs pulmonary vein left auricle left ventricle systemic aorta Heart beats Sinus venosus Sinoauricular node
F. The circulatory system of mammals Sinus venosus Conus arteriosus 2 auricles 2 ventricles Double circulation Aorta Pulmonary Renal portal system Postcaval vein Hepatic portal system
8. The structure of the heart pp378-379 Systemic veins (right auricle) Pulmonary veins (left auricle) Interauricular septum Auriculoventricular openings Coronary sinus (right auricle) left precaval vein Valve of the coronary sinus Apex of the heart Left ventricle (thickwalled, rounded) Right ventricle (thinwalled, crescentic) Pulmonary artery
3. The origin of the heart Ventral mesentery (anterior part of embryo) Dorsal and ventral mesocardia
5. The origin of the portal systems Portion of the venous system Hepatic portal system (liver) Renal portal system (kidney) a. hepatic portal system Hepatic veins Hepatic portal vein Mesenteric vein b. renal portal system Subcardinal vein Renal portal veins
7. Phylogeny of the vertebrate circulatory system From annelids ? There is @ present no evidence for carrying the circulatory system farther back than Amphioxus
4. The chief embryonic blood vessels Vitelline veins Ventral aorta Aortic arches Dorsal aortae Vitelline artery
1. The chambers of the heart pp.359-360 Pericardial sac Thymus gland Two ventricles (larger left and smaller right) Posterior pointed apex Broad anterior base External groove Coronary artery & vein Auricle (chamber) Auricular appendage (lobe) Pulmonary artery Aorta Conus arteriosus Pulmonary veins Systemic veins Sinus venosus (right auricle) Sinoauricular node
Trabeculae carnae (muscular ridges) Papillary muscles (pointed finger-like muscles) Chordae tendinae (slender fibers) Tricuspid valve (3 thin membraned flaps) right auriculoventricular opening Interventricular septum Pulmonary semilunar valves (3 pocket-shaped) Bicuspid or mitral valve (two flaps) left auriculoventricular opening Aorta Aortic semilunar valves
2. The hepatic portal system pp.360-362 Peritoneal cavity Liver lobes Hepatoduodenal ligament Common bile duct Hepatic portal vein (portal vein) large branch to liver right lateral lobe Coronary vein Anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein Right gastroepiploic vein Gastrosplenic vein Middle gastroepiploic veins (1 or more small veins) Pancreatic veins Left and right splenic veins Left gastroepiploic veins Superior mesenteric vein Posterior pancreaticoduodenal vein Inferior mesenteric vein Numerous converging intestinal veins Lymph glands
3. The systemic veins pp.362-369 One precaval vein One postcaval vein
a. The branches of the precaval vein Anterior / superior vena cava or descending vena cava (right auricle) Coronary sinus Coronary veins (heart wall) Azygos vein Intercostal veins Common stem of the internal mammary veins Right and left internal mammary veins Superior epigastric veins Thymus gland Brachiocephalic or innominate veins Vertebral vein Costocervical vein Anterior external jugular vein Lateral subclavian vein Axillary vein (first rib) Brachial plexus nerves (stout white cords) Lymph glands Subscapular vein Posterior circumflex vein Small ventral thoracic vein Long thoracic vein Thoracodorsal vein Brachial vein (w/ nerves & brachial artery)
External jugular vein Small internal jugular vein (w/ carotid artery & vagus nerve) Large transverse scapular vein (shoulder) Cephalic vein Anterior & posterior facial veins Transverse vein Angular vein Anterior & posterior auricular vein
7. The posterior portion of the postcaval vein pp.377-378 2 large common iliac veins sacral or caudal vein Internal and external iliac vein Middle heamorrhoidal vein Gluteal vein Umbilical vein Deep femoral vein External spermatic vein Inferior epigastric vein Femoral vein
Right brachiocephalic or innominate artery Left subclavian artery Right subclavian artery Right and left common carotid artery a. Subclavian artery Internal mammary artery (ventral) Superior epigastric artery Vertebral artery (dorsal) Costocervical axis (artery) divides in 2 @ once Superior intercostal artery Transverse artery of the neck Deep cervical artery Thyrocervical axis (artery) most anterior Transverse scapular artery Axillary artery (first rib) Ventral thoracic artery Long thoracic artery Large subscapular artery Thoracodorsal artery Brachial artery
b. Common carotid artery Superior thyroid artery Occipital artery Internal carotid artery (degenerated cord) External carotid artery Lingual artery External maxillary artery Superior & inferior labial artery Submentalis artery Internal maxillary artery Temporal artery Auricular artery c. The thoracic aorta Arterial ligament or ligament of Botallus Thoracic aorta (mediastinum) Paired intercostal arteries Bronchial arteries Esophageal arteries Thoracic duct (main lymphatic channel) d. The abdominal aorta Dorsal aorta (diaphragm median dorsal line) Unpaired median visceral branches Coeliac artery Superior mesenteric artery Inferior mesenteric artery Coeliac artery
Hepatic artery (most cranial) left side of hepatic portal vein Gastroduodenal branch Pyloric artery Right gastroepiploic artery Anterior pancreaticoduodenal artery Cystic artery Left gastric or coronary artery (lesser curvature) Splenic artery (most caudal & largest) Left and right splenic artery Pancreatic artery Short gastric arteries Left gastroepiploic arteries Superior mesenteric artery Middle colic artery Posterior pancreaticoduodenal artery Ileocolic artery Right colic Intestinal branches Inferior mesenteric artery Left colic artery Superior haemorrhoidal artery
b. The branches of the postcaval vein Posterior / inferior vena cava or ascending vena cava (right auricle) Caval fold Phrenic veins (diaphragm) Postcava (liver right median lobe liver posterior lobule of right lateral lobe) Hepatic veins Right adrenolumbar vein (adrenal galnd) Right renal vein Left adrenolumbar & renal veins (posterior to right) Left internal spermatic or ovarian vein (left renal vein) Right internal spermatic or ovarian vein (postcava) Paired lumbar veins A pair of iliolumbar veins
4. The pulmonary veins p.369 Pulmonary veins (roots of the lungs) left auricle
5. The pulmonary artery p.369 Pulmonary artery (right ventricle) Right & left pulmonary arteries Trachea
6. The aorta and its branches pp.369-377 Aorta (left ventricle) Right & left coronary arteries Arch of the aorta
Paired lateral visceral branches Adrenolumbar arteries Phrenic arteries Renal arteries Internal spermatic or ovarian arteries Paired somatic branches Paired lumbar arteries Dorsal aorta Iliolumbar arteries External iliac arteries Deep femoral artery External spermatic artery Inferior epigastric artery Femoral artery Internal iliac arteries Median sacral or caudal artery Umbilical arteries Middle haemorrhoidal arteries Uterine arteries
Chapter 14. The comparative anatomy of the nervous system and the sense organs A. General considerations pp.428-456 1. The parts of the nervous system Nerve cell or neuron (ganglion cell) Cell body Neurites/nerve fibers Neurosensory cell Sensory receptor and conductor Unpolarized nerve cell Several neurites Polarized nerve cell Afferent processes or dendrites Efferent process or axon Ganglion (PNS) Nucleus or center (CNS) Nerve Bundle of neurites Nerve fibers Medullary or myelin sheath Medullated or myelinated or white fibers Nonmedullated or unmyelinated or gray fibers
Vertebrate nervous system 3 parts: Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Gray matter (nerve-cell bodies) White matter (nerve fibers) Peripheral nervous system Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Autonomic (also called sympathetic & vegetative) nervous system Ganglionated cord
3. Gross features of the adult central nervous system Spinal cord Cervical and lumbar enlargements Terminal filament Central canal Ependyma Gray matter H or butterfly like shape Dorsal columns (posterior horns) Ventral columns (anterior horns) Lateral column Dorsal and ventral commissures White matter Dorsal, lateral, and ventral funiculi Median ventral fissure Vertebrate brain Cranial cavity Myelencephalon or medulla oblongata Spinal cord Foramen magnum Central canal Large rhomboidal or triangular cavity (fourth ventricle) Ependymal epithelium Pia mater Tela choroidea Choroid plexi Fifth to twelfth cranial nerves
Metencephalon Cerebellum Body or corpus Lateral lobes (auricular lobes / floccular lobes) auricular recesses Transverse fissures Cerebellar hemispheres Cerebellar cortex Arbor vitae Valvula Cerebellar ventricle Pons Functions of cerebellum ? Proprioceptive impulses Mesencephalon or midbrain Optic tectum Optic lobes or corpora bigemina Corpora quadrugemina Superior and inferior colliculi Cerebral peduncles Cerebral aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius Optic ventricles Diencephalon or thalamencephalon Third ventricle Ependyma & pia mater tela choroidea Choroid plexi Choroidal sacs Parencephalon Lamina terminalis Transverse velum
Epithalamus Epiphyseal apparatus Habenulae Parapineal or parietal body Pineal body or epiphysis Pineal eye or parietal eye Thalamus (lateral walls) Intermediate mass Hypothalamus Optic chiasma Tuber cinereum Infundibulum Hypophysis Oral epithelium of Rathkes pouch (adenohypophysis) Neurohypophysis Saccus vasculosus or vascular sac Mammillary region Mammillary bodies Telencephalon Paired olfactory bulbs Olfactory stalk or peduncle Cerebral hemispheres Preoptic recess Neuroporic recess Lamina terminalis anterior commissure Velum transversum Tela choroidea Choroid plexi Paraphysis Lateral ventricles Interventricular foramen (faramen of Munro)
Cerebral hemispheres Roof or pallium Subpallium Primordium of the hippocampus Primordium of the pyriform lobe Neopallium Cerebral cortex Medial septum Corpus striatum or striatal region Corpus callosum Fornix (from the hippocampus to the mammillary body on each side) Septum pellucidum Brain stem Bulb
2. The development of the nervous system Ectoderm layer Neuroglia Transverse ventral fold primitive fore and hind brain Infundibulum Telencephalon Cerebral hemispheres Diencephalon or thalamencephalon Pineal apparatus Mesencephalon Optic lobes Metencephalon Cerebellum Myelencephalon or medulla oblongata Spinal cord
4. The meninges Meninges (meninx) Primitive meninx Outer dura mater Inner secondary meninx Outer dura mater Arachnoid Subarachnoid space Pia mater Cerebrospinal fluid
5. The functional divisions of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system Somatic Visceral Afferent or sensory Efferent or motor Somatic sensory component Somatic motor component Visceral sensory component Visceral motor component Peripheral nervous system Spinal nerves (intervertebral foramina) Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Caudal Cauda equina or horses tail Root Dorsal or sensory root Somatic sensory fibers Visceral sensory fibers Nerve-cell bodies outside CNS (dorsal or spinal ganglia) Ventral or motor root Somatic motor fibers Visceral motor fibers Nerve-cell bodies in CNS
Spinal nerve Intervertebral foramina 3 branches: Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus Communicating ramus Plexus (network) Brachial plexus Lumbar or lumbosacral plexus Cervical plexus Cervicobrachial plexus Phrenic nerves Medulla spinal cord Spino-occipital nerves Occipital nerves Occipito-spinal nerves Hypobranchial nerve Cranial nerves a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. nervus terminalis olfactory nerve optic nerve oculomotor nerve trochlear nerve trigeminus nerve abducens nerve facial nerve auditory or vestibulocochlear or acoustic nerve j. glossopharyngeal nerve k. vagus nerve l. spinal accessory nerve m. hypoglossal nerve
6. Concept of neurobiotaxis Nuclei tend to migrate in the direction from which they receive their most frequent or most important stimulation 7. The autonomic nervous system Ganglia Nerves Plexi Visceral motor division Preganglionic fibers autonomic ganglia postganglionic fibers Division: Cranial outflow Cervical sympathetic Thoracolumbar chain of ganglia Sacral outflow Collateral ganglia Peripheral ganglionated plexi
11. The segmentation of the head Head is composed of a series of mesodermal segments w/c, thru cephalization, have become almost indistinguishably fused together
F. The nervous system and sense organs of mammals 1. The spinal nerves, the autonomic system, and the vagus pp.490-494 a. Cervical portion of the sympathetic and the vagus Carotid artery Vagus nerve Descending branch of the hypoglossal nerve Sympathetic trunk Vagosympathetic trunk (lateral to carotid artery bound by a common sheath) Middle cervical ganglion Subclavian artery Ansa subclavia Inferior cervical ganglion Cardiac branches Phrenic nerve Right vagus Recurrent or posterior laryngeal nerve
b. The anterior cervical spinal nerves Spinal nerves Intervertebral foramina Cervical nerves (8 pairs) Cervical plexus (first 4) Brachial plexus (last 4 & first thoracic) *pull muscles inserted anterior end of sternum (sternomastoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid) laterally or cut across them to expose cervical nerves (ventral rami) Phrenic nerve (fifth & sixth cervical nerve) Sympathetic ganglia Diaphragm
Chief nerves from the brachial plexus: 1. The phrenic nerve Form fifth and sixth cervical nerves The suprascapular nerve Most anterior from the sixth cervical nerve 2 ventral thoracic nerves (pectorals) Most ventral first from the seventh cervical, second from the eighth cervical & first thoracic 3 subscapular nerves Dorsally situated first from sixth cervical, second from seventh cervical, third (latissimus) from seventh & eighth cervicals 5. The axillary nerve Chiefly from the seventh cervical The dorsal or long thoracic nerve From the seventh cervical (serratus ventralis) 6. 4. 3. 2.
The musculocutaneous nerve Ventral surface of sixth & seventh cervicals 8. The radial nerve Largest nerve from seventh & eighth cervicals & first thoracic 9. The median nerve Last 3 nerves, w/ brachial artery 10. The ulnar nerve Chiefly from the first thoracic nerve 11. The medial cutaneous Chiefly from the first thoracic, in contact w/ the preceding nerve
7.
8. The sense organs 9. The nervous system and sense organs of Amphioxus 10. The nervous system and main sense organs of cyclostomes
c. The brachial plexus Ansae Brachial plexus Broad connection - sixth & seventh cervical nerves Stout trunks intricately connected seventh & eighth cervicals & first thoracic nerves
5. The structure of the brain pp.511-517
a. The membranes or meninges of the brain Dura mater (periosteum) Subdural space Pia mater (brain) Arachnoid (in-between) Subarachnoid space Cerebrospinal fluid
b. The dorsal aspect of the brain Two olfactory bulbs Cerebral hemispheres (telencephalon) Gyri Sulci/fissures Longitudinal cerebral fissure Corpus callosum (thick, white mass) Diencephalon (concealed in dorsal view) Choroid plexus (of the roof of diencephalon) Mesencephalon (midbrain) concealed in dorsal view Corpora quadrugemina or colliculi (4 rounded lobes or hillocks) Superior colliculi Inferior colliculi
Cerebellum (metencephalon) Vermis or worm (median lobe) Cerebellar hemispheres (a pair of lateral lobes) Flocculus (lobes) Myelencephalon (medulla oblongata) Fourth ventricle (cavity) Medullary velum membrane (w/ choroid plexus) Clava Tuberculum cuneatum Somatic sensory column Restiform body or posterior peduncle (of the cerebellum) Area acustica or primary auditory center (elevation)
Tuber cinereum (rounded elevation) w/ slitlike aperture Pituitary body or hypophysis (stalk) Mammillary body Posterior perforated substance (depressed area) oculomotor nerve Cerebral peduncles (midbrain) Trochlear nerves (between cerebellum & inferior colliculi) Hindbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Brachium pontis or middle peduncle (white cord) metencephalon Trigeminus nerve (thick root) large dorsal sensory root (portio major) and small ventral motor root (portio minor) Trapezoid body (facial nerve) Area acustica or auditory center (auditory nerve) Median ventral fissure Pyramids or somatic motor tracts (two) abducens nerves Glossopharyngeal nerve Vagus nerve Spinal accessory nerve Hypoglossal nerve
d. The median sagittal section Longitudinal cerebral fissure Corpus callosum (white band) Genu (anterior) Splenium (posterior) Fornix (curves ventrally) Septum pellucidum Lateral ventricles (cavities) Column of the fornix Anterior commissure Lamina terminalis Optic chiasma Third ventricle (fornix, anterior commissure, & lamina terminalis anterior boundary) Tuber cinereum & hypophysis Diencephalon (between fornix, lamina terminalis, & midbrain) Dorsal epithalamus (roof) Tela choroidea Pineal body Habenula Posterior commissure
Central & lateral thalamus Intermediate mass or middle commissure 3 low elevations: Dorsal, medial pulvinar Lateral, whiter lateral geniculate body Optic tract (white band) Posterior, ventral medial geniculate body Ventral hypothalamus Optic chiasma Tuber cinereum Mammillary body Hypophysis Midbrain Corpora quadrugemina Aqueduct of the brain Fourth ventricle Medulla oblongata Tegmentum Arbor vitae or tree of life Gray matter (nerve cells) White matter (nerve fibers) Medullary velum (membrane)
Corpus callosum (narrow band of fibers) Lateral ventricles Corpus striatum Hippocampus (fimbria) Pyriform lobe Thalamus Corona radiata
Thalamus Cerebral cortex Clava Tuberculum cuneatum Diencephalon Corona radiata Cerebral cortex Cerebral cortex Motor cortex Corona radiata Cerebral peduncles Medulla Pyramidal tracts or pyramids Spinal cord Ventral columns of the cord (motor cells) Cerebral peduncles Pyramidal tracts Large tracts from cortex to pons Cerebellum Cerebellum Restiform bodies or posterior peduncles Medulla & spinal cord Brachium pontis or middle peduncle cerebral cortex Anterior peduncles (cerebellum and midbrain and thalamus) Area acustica Ampullae of semicircular ducts
c. The ventral aspect of the brain Basilar artery Circle of Willis Internal carotid artery Two olfactory bulbs Olfactory tract (white) Pyriform lobe (posteroventral) Rhinal fissure/sulcus Diencephalon or thalamencephalon Optic chiasma (optic nerves) Anterior perforated substance
f. Functions of the parts of the brain Olfactory apparatus Olfactory bulbs Olfactory tracts Pyriform lobes Tuber cinereum Fornix Habenulae Mammillary body Hippocampus Fimbria Telencephalon Diencephalon Lateral geniculate body Optic tracts Corona radiata Cerebral hemispheres Pulvinar Superior colliculi Area acustica Trapezoid body Inferior colliculi Medial geniculate body Corona radiata Cerebral cortex
e. Further structure of the cerebral hemispheres Cortex (gray outer coat) nerve cell bodies Interior white matter (nerve fibers) Convoluted cortex Central white matter core covered by thick gray matter coat
Societas Vitae Reviewer - P. Cantiller Hyman, L. (1965). Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy. The University of Chicago Press.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cranial Nerves FlowchartDokumen6 halamanCranial Nerves FlowchartGhe CuaresmaBelum ada peringkat
- Rare Watches (Christie's) 16. 05. 2016.Dokumen236 halamanRare Watches (Christie's) 16. 05. 2016.Simon LászlóBelum ada peringkat
- Off Grid Solar Hybrid Inverter Operate Without Battery: HY VMII SeriesDokumen1 halamanOff Grid Solar Hybrid Inverter Operate Without Battery: HY VMII SeriesFadi Ramadan100% (1)
- Of Time and The MindDokumen18 halamanOf Time and The MindAntonio LanotBelum ada peringkat
- New Study - Reproduction and Electromagnetic Field ExposureDokumen9 halamanNew Study - Reproduction and Electromagnetic Field ExposureEMFsafetyBelum ada peringkat
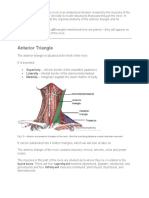
- The Anterior and Posterior Triangles of The NeckDokumen10 halamanThe Anterior and Posterior Triangles of The NeckClair TomBelum ada peringkat
- Su Poder en El Espiritu Santo Your Power in The Holy Spirit Spanish Edition by John G Lake PDFDokumen4 halamanSu Poder en El Espiritu Santo Your Power in The Holy Spirit Spanish Edition by John G Lake PDFRodrigo MendezBelum ada peringkat
- فسلجة الحيوان PDFDokumen9 halamanفسلجة الحيوان PDFelhamBelum ada peringkat
- Posterior MediastinumDokumen31 halamanPosterior MediastinumHfm 4Belum ada peringkat
- UE Review (Color!)Dokumen2 halamanUE Review (Color!)Research4OTBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 7 - Nervous, Endocrine, Reproductive, Urinary SystemDokumen37 halamanLesson 7 - Nervous, Endocrine, Reproductive, Urinary SystemAlejandro GuerreroBelum ada peringkat
- CNS RosettesDokumen5 halamanCNS RosettesSick DuckBelum ada peringkat
- Pineal Region Tumors PDFDokumen15 halamanPineal Region Tumors PDFhimadriBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy (2023 Reviewer) Musculoskeletal Brachial Plexus Injuries - 3 Cords Terminal Branches MotorDokumen11 halamanAnatomy (2023 Reviewer) Musculoskeletal Brachial Plexus Injuries - 3 Cords Terminal Branches MotorStephen MontoyaBelum ada peringkat
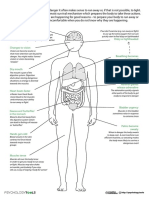
- Major OrgansDokumen8 halamanMajor Organsapi-251588588Belum ada peringkat
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDokumen24 halamanAutonomic Nervous Systemardywilliams01Belum ada peringkat
- I 2x Get Laid On FridaysDokumen3 halamanI 2x Get Laid On FridaysRoma Fe MabanagBelum ada peringkat
- Principia DiscordiaDokumen85 halamanPrincipia DiscordiaAbraham OgdenBelum ada peringkat
- S07-08-Lab Manual Sheep BrainDokumen40 halamanS07-08-Lab Manual Sheep BrainRobert MartinBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal PDFDokumen14 halamanJurnal PDFIcha IchaBelum ada peringkat
- Tentorial IncisuraDokumen23 halamanTentorial Incisurabodeadumitru9261100% (1)
- Neurology - Saif.wesmosis.2013 104907Dokumen68 halamanNeurology - Saif.wesmosis.2013 104907Helene AlawamiBelum ada peringkat
- Elbow AnatomyDokumen2 halamanElbow Anatomyapi-195986134Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDokumen10 halamanAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerMae Christelle FigueroaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology MnemonicsDokumen7 halamanAnatomy and Physiology MnemonicsLalajimBelum ada peringkat
- Neuroscience: Parts of The BrainDokumen5 halamanNeuroscience: Parts of The BrainAthena BorjaBelum ada peringkat
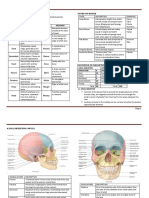
- Anatomy Lecture 02 - Anatomic Topograhic Regions - HeadDokumen94 halamanAnatomy Lecture 02 - Anatomic Topograhic Regions - HeadNikita Prasad100% (1)
- Meninges, Ventricles - CSF - Study GuideDokumen3 halamanMeninges, Ventricles - CSF - Study Guideshivani patelBelum ada peringkat
- Neck Triangles (Regional Anatomy) Anterior Triangle Borders Arteries Veins Nerves MiscDokumen6 halamanNeck Triangles (Regional Anatomy) Anterior Triangle Borders Arteries Veins Nerves Misczara_emmeBelum ada peringkat
- An Analysis of Canine Hair Re-Growth After Clipping For A Surgical Procedure (Pages 25-30)Dokumen6 halamanAn Analysis of Canine Hair Re-Growth After Clipping For A Surgical Procedure (Pages 25-30)jenBelum ada peringkat
- Ascending Tracts Neuro AnatomyDokumen2 halamanAscending Tracts Neuro AnatomyrachellesliedeleonBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Endocrine SystemDokumen32 halamanReview of Endocrine SystemJames FBelum ada peringkat
- Aaron Driver Doctor of PhysiotherapyDokumen12 halamanAaron Driver Doctor of Physiotherapyaaronjdriver2248Belum ada peringkat
- The Peripheral Nervous SystemDokumen80 halamanThe Peripheral Nervous SystemDanitra B AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Gastro ExamDokumen2 halamanGastro ExamJessica Brittain-GeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- Fight or Flight Response En-UsDokumen1 halamanFight or Flight Response En-Ussusie cabrillanaBelum ada peringkat
- I. Walls: Walls Muscles/Comp. Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Actions DiseaseDokumen8 halamanI. Walls: Walls Muscles/Comp. Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Actions DiseaseAustin CabreraBelum ada peringkat
- Neuro Practical I TablesDokumen9 halamanNeuro Practical I TablesSolomon Seth Sallfors100% (1)
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsDokumen10 halamanAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsIssac LauBelum ada peringkat
- Region Function Damage Cognitive Disease Brain StemDokumen2 halamanRegion Function Damage Cognitive Disease Brain StemVivek PatelBelum ada peringkat
- 1.5 DermatomesDokumen2 halaman1.5 DermatomesAngela CaguitlaBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal System: Term Meaning Term Meaning Body NeckDokumen7 halamanSkeletal System: Term Meaning Term Meaning Body NeckLaurel Vida Mentiza OrayleBelum ada peringkat
- Scrotum Anatomy and Scanning TechniqueDokumen7 halamanScrotum Anatomy and Scanning TechniqueAnonymous wyF4yQZwZBelum ada peringkat
- WWW Kenhub Com en Library Anatomy Endocrine SystemDokumen20 halamanWWW Kenhub Com en Library Anatomy Endocrine SystemIvana Odelia NainggolanBelum ada peringkat
- Diaphragm Gross AnatomyDokumen3 halamanDiaphragm Gross AnatomyCoy NuñezBelum ada peringkat
- CH 11 Heart NotesDokumen2 halamanCH 11 Heart Notesummnicole0% (1)
- Nonvisual Photoreceptors of The PinealDokumen36 halamanNonvisual Photoreceptors of The Pinealrambo_style19Belum ada peringkat
- 5.10.09-Anatomy of MediastinumDokumen23 halaman5.10.09-Anatomy of MediastinumHadi TryadiBelum ada peringkat
- OMS Central Nervous SystemDokumen312 halamanOMS Central Nervous SystemDenisa Gherman100% (1)
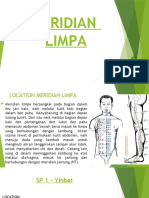
- Meridian LimpaDokumen23 halamanMeridian LimpaHilyatul ilmi Al mufidahBelum ada peringkat
- SCIT 1408 Applied Human Anatomy and Physiology II - Heart Chapter 18 ADokumen28 halamanSCIT 1408 Applied Human Anatomy and Physiology II - Heart Chapter 18 AChuongBelum ada peringkat
- Neuro AnatomyDokumen23 halamanNeuro AnatomysachinylibBelum ada peringkat
- Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas Final PresentationDokumen60 halamanLiver, Gallbladder and Pancreas Final PresentationqueenuagBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SYSTESTDokumen19 halamanNervous SYSTESTedwalk1250% (2)
- Renal PathologyDokumen5 halamanRenal PathologyEmmanuel De LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Cranial NerveDokumen39 halamanCranial NerveСуджива Гунасинха100% (2)
- OMT Sacral PelvisDokumen3 halamanOMT Sacral PelvisMedShare100% (1)
- 9 Anterior Triangle of The Neck E-LearningDokumen22 halaman9 Anterior Triangle of The Neck E-LearningHashim GhazoBelum ada peringkat
- LECTURE Nervous SystemDokumen4 halamanLECTURE Nervous SystemanonymousBelum ada peringkat
- Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyDokumen5 halamanNeuroembryology and NeurohistologyCZARINA TUAZONBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy & Physiology Terms DECODED! Vol.3A: Muscular System: Gross AnatomyDari EverandAnatomy & Physiology Terms DECODED! Vol.3A: Muscular System: Gross AnatomyBelum ada peringkat
- Arteries Arteries of The Upper Limb: Subclavian ArteryDokumen6 halamanArteries Arteries of The Upper Limb: Subclavian Arterydrusmansaleem100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System and Disorders (Original)Dokumen36 halamanCardiovascular System and Disorders (Original)Wirya PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Cornish BoilerDokumen3 halamanCornish BoilerDeepak KV ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- DOT RequirementsDokumen372 halamanDOT RequirementsMuhammadShabbirBelum ada peringkat
- Level I 2018 2019 Program Changes PDFDokumen2 halamanLevel I 2018 2019 Program Changes PDFMuhammad BurairBelum ada peringkat
- Request For Proposals/quotationsDokumen24 halamanRequest For Proposals/quotationsKarl Anthony Rigoroso MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDokumen2 halamanDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesISMAEL KRIS DELA CRUZBelum ada peringkat
- Writing About Graphs, Tables and DiagramsDokumen68 halamanWriting About Graphs, Tables and DiagramsLangers BastasaBelum ada peringkat
- Sustainable Strategic Management BarbosaDokumen11 halamanSustainable Strategic Management BarbosapurwawardhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Masking Conventional Metallic Cast Post For Enhancing EstheticsDokumen5 halamanMasking Conventional Metallic Cast Post For Enhancing EstheticsleilyanisariBelum ada peringkat
- NA ReadingStrategies U5M11L03Dokumen1 halamanNA ReadingStrategies U5M11L03Lila AlwaerBelum ada peringkat
- Half Yearly Examination, 2017-18: MathematicsDokumen7 halamanHalf Yearly Examination, 2017-18: MathematicsSusanket DuttaBelum ada peringkat
- DatuinMA (Activity #5 - NSTP 10)Dokumen2 halamanDatuinMA (Activity #5 - NSTP 10)Marc Alen Porlaje DatuinBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Communication in ContextDokumen19 halamanOral Communication in ContextAzory ZelleBelum ada peringkat
- Lahore Waste Management CompanyDokumen45 halamanLahore Waste Management CompanyHadia NasirBelum ada peringkat
- 835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 GuideDokumen306 halaman835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 Guideअरूण शर्माBelum ada peringkat
- LAB REPORT - MGCLDokumen5 halamanLAB REPORT - MGCLKali stringsBelum ada peringkat
- Democracy or Aristocracy?: Yasir MasoodDokumen4 halamanDemocracy or Aristocracy?: Yasir MasoodAjmal KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Data Mining in IoTDokumen29 halamanData Mining in IoTRohit Mukherjee100% (1)
- Cella Di Carico Sartorius MP77 eDokumen3 halamanCella Di Carico Sartorius MP77 eNCBelum ada peringkat
- Ass AsDokumen23 halamanAss AsMukesh BishtBelum ada peringkat
- Ishrana Studenata I Nastavnika Visoke Škole U Subotici Tokom Pandemije COVID-19Dokumen4 halamanIshrana Studenata I Nastavnika Visoke Škole U Subotici Tokom Pandemije COVID-19DejanBelum ada peringkat
- Swiss Army Triplet 1Dokumen2 halamanSwiss Army Triplet 1johnpwayBelum ada peringkat
- Speaking RubricDokumen1 halamanSpeaking RubricxespejoBelum ada peringkat
- (Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesDokumen196 halaman(Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesAmbrose66Belum ada peringkat
- Present Perfect Simp ContDokumen14 halamanPresent Perfect Simp ContLauGalindo100% (1)
- NauseaDokumen12 halamanNauseakazakom100% (2)
- Mossbauer SpectrosDokumen7 halamanMossbauer SpectroscyrimathewBelum ada peringkat