OSI Layer
Diunggah oleh
Anand_Boudh_2811Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
OSI Layer
Diunggah oleh
Anand_Boudh_2811Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
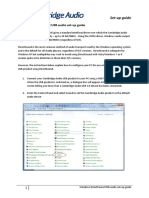
Layer
Application
User Interface
Function
used for applications specifically written to run over the network allows access to network services that support applications; directly represents the services that directly support user applications handles network access, flow control and error recovery Example apps are file transfer,e-mail, NetBIOSbased applications Translates from application to network format and vice-versa all different formats from all sources are made into a common uniform format that the rest of the OSI model can understand responsible for protocol conversion, character conversion,data encryption / decryption, expanding graphics commands, data compression sets standards for different systems to provide seamless communication from multiple protocol stacks not always implemented in a network protocol establishes, maintains and ends sessions across the network responsible for name recognition (identification) so only the designated parties can participate in the session provides synchronization services by planning check points in the data stream => if session fails, only data after the most recent checkpoint need be transmitted
Protocols
DNS; FTP; TFTP; BOOTP; SNMP;RLOGIN; SMTP; MIME; NFS; FINGER; TELNET; NCP; APPC; AFP; SMB
Network Components
Gateway
Presentation
Translation
Gateway Redirector
Session
"syncs and sessions"
NetBIOS Names Pipes Mail Slots RPC
Gateway
manages who can transmit data at a certain time and for how long Examples are interactive login and file transfer connections, the session would connect and reconnect if there was an interruption; recognize names in sessions and register names in history additional connection below the session layer TCP, ARP, RARP; manages the flow control of data between parties across the network SPX divides streams of data into chunks or packets; the transport layer of the receiving computer reassembles NWLink the message from packets "train" is a good analogy => the data is divided into identical units NetBIOS / NetBEUI provides error-checking to guarantee error-free data delivery, with on losses or duplications ATP provides acknowledgment of successful transmissions; requests retransmission if some packets dont arrive error-free provides flow control and error-handling translates logical network address and names to their physical address (e.g. computername ==> MAC address) responsible for o addressing o determining routes for sending o managing network problems such as packet switching, data congestion and routing if router cant send data frame as large as the source computer sends, the network layer compensates by breaking the data into smaller units. At the receiving end, the network layer reassembles the data think of this layer stamping the addresses on each train car
Transport
packets; flow control & error-handling
Gateway Advanced Cable Tester Brouter
Network
addressing; routing
IP; ARP; RARP, ICMP; RIP; OSFP; IGMP;
Brouter Router Frame Relay Device
IPX ATM Switch NWLink Advanced Cable Tester NetBEUI OSI
DDP DECnet Logical Link Control Bridge Switch ISDN Router Intelligent Hub NIC Advanced Cable Tester
Data Link
data frames to bits
turns packets into raw bits 100101 and at the receiving end turns bits into packets. handles data frames between the Network and error correction Physical layers and flow control the receiving end packages raw data from the manages link Physical layer into data frames for delivery to the control and Network layer defines SAPs responsible for error-free transfer of frames to other computer via the Physical Layer 802.1 OSI Model this layer defines the methods used to transmit and receive data on the network. It consists of the wiring, the devices use to connect the NIC to the wiring, the 802.2 Logical Link Control signaling involved to transmit / receive data and the Media Access ability to detect signaling errors on the network Control media communicates with the adapter card controls the type of media being used:
802.3 CSMA/CD (Ethernet) 802.4 Token Bus (ARCnet) 802.5 Token Ring 802.12 Demand Priority IEEE 802
Physical
hardware; raw bit stream
transmits raw bit stream over physical cable defines cables, cards, and physical aspects defines NIC attachments to hardware, how cable is attached to NIC
Repeater
defines techniques to transfer bit stream to cable IEEE 802.2 ISO 2110 ISDN
Multiplexer Hubs
Passive Active
TDR Oscilloscope Amplifier
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Automatic Road Safety Reflector Lightning System: Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDokumen2 halamanAutomatic Road Safety Reflector Lightning System: Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringSrujan ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- User Guide: NCR Realpos Value Touch Display (5966 15-Inch)Dokumen54 halamanUser Guide: NCR Realpos Value Touch Display (5966 15-Inch)Akrom77khasaniBelum ada peringkat
- Latitude 3580: Owner's ManualDokumen53 halamanLatitude 3580: Owner's ManualSuresh Babu BonthuBelum ada peringkat
- Windows Direct Sound Set Up PDFDokumen2 halamanWindows Direct Sound Set Up PDFFrancescoBelum ada peringkat
- H61h2i5 Manual PDFDokumen84 halamanH61h2i5 Manual PDFArijit BhattacharyaBelum ada peringkat
- LEC-7230M Manual v0.1Dokumen23 halamanLEC-7230M Manual v0.1B0gdanBelum ada peringkat
- Software Testing Unit-3 (IMP)Dokumen6 halamanSoftware Testing Unit-3 (IMP)Aditya vtBelum ada peringkat
- 10th July 2013Dokumen102 halaman10th July 2013Adam Richardson100% (1)
- VLSI Signal ProcessingDokumen1 halamanVLSI Signal ProcessingNaveenBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Hardware Concept MCQ SetsDokumen5 halamanComputer Hardware Concept MCQ SetssanaullahBelum ada peringkat
- Triaxis® Position Sensor: Product Code Temperature Code Package Code Option Code Packing Form CodeDokumen48 halamanTriaxis® Position Sensor: Product Code Temperature Code Package Code Option Code Packing Form CodeGoran MiljkovicBelum ada peringkat
- FM Transmitter Circuit DiagramDokumen7 halamanFM Transmitter Circuit DiagramJose Garcia50% (2)
- Mackie PPM608 Power Amp SchematicsDokumen4 halamanMackie PPM608 Power Amp SchematicsGilbert MarinezBelum ada peringkat
- Fujitsu F56 Multi Cassette Media/Currency Dispenser: Data SheetDokumen3 halamanFujitsu F56 Multi Cassette Media/Currency Dispenser: Data SheetTu Tran DanhBelum ada peringkat
- Enterprise Cloud Strategy PDFDokumen109 halamanEnterprise Cloud Strategy PDFNenad Stamenović100% (2)
- ETP4860 B1A201074817 001 Embedded Power System Datasheet 01 20200...Dokumen2 halamanETP4860 B1A201074817 001 Embedded Power System Datasheet 01 20200...Charmer JiaBelum ada peringkat
- Row-Column Major AddressDokumen4 halamanRow-Column Major AddressVinod SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- LM494 Spice ModelDokumen3 halamanLM494 Spice ModelRobertBelum ada peringkat
- Ramaiah Chinna SwamyDokumen5 halamanRamaiah Chinna SwamySyed AbrarBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 10 14T21 01 57 - R3dlogDokumen6 halaman2020 10 14T21 01 57 - R3dlogAndrei VrlanBelum ada peringkat
- Kartik Takyar 101803618 Jatin Kapoor 101803619 Himanshu Mahajan 101803620 Gaurish Garg 101803621 Aditi Pandey 101803622Dokumen23 halamanKartik Takyar 101803618 Jatin Kapoor 101803619 Himanshu Mahajan 101803620 Gaurish Garg 101803621 Aditi Pandey 101803622GAURISH GARGBelum ada peringkat
- Bugreport Dandelion - Eea QP1A.190711.020 2022 02 15 07 45 54Dokumen9.715 halamanBugreport Dandelion - Eea QP1A.190711.020 2022 02 15 07 45 54João Carlos Pereira ChoinasBelum ada peringkat
- LVC14ADokumen19 halamanLVC14Atolin430Belum ada peringkat
- Training Document For InTouchDokumen27 halamanTraining Document For InTouchthakur941264191950% (2)
- Java - InterfacesDokumen7 halamanJava - Interfaces@jazBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Operating Systems - GeeksforGeeksDokumen1 halamanTypes of Operating Systems - GeeksforGeeksBefkadubirhanu7Belum ada peringkat
- 2080 Rn001a en PDokumen4 halaman2080 Rn001a en PeriktorricoBelum ada peringkat
- Rectificadores No ControladosDokumen25 halamanRectificadores No ControladosPablo AcuñaBelum ada peringkat
- CAYC Bank Preli Digest For 2020 Based SO ExamsDokumen96 halamanCAYC Bank Preli Digest For 2020 Based SO ExamsDuffer Media DMBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4Dokumen12 halamanUnit 4Cameron FernandesBelum ada peringkat