2 Part Gas Law Practice!!
Diunggah oleh
ahix123Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2 Part Gas Law Practice!!
Diunggah oleh
ahix123Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chemistry 1B Chapter 10 Worksheet - Daley Name___________________________________
1) The National Weather Service routinely supplies atmospheric pressure data to help pilots set their altimeters. The units the NWS uses for atmospheric pressure are inches of mercury. A barometric pressure of 30.51 inches of mercury corresponds to __________ kPa. A) 103.3 B) 77.50 C) 775 D) 1.020 E) 16.01
4) A balloon originally had a volume of 4.39 L at 44 C and a pressure of 729 torr. The balloon must be cooled to __________C to reduce its volume to 3.78 L (at constant pressure). A) 38 B) 0 C) 546 D) 72.9 E) 273
2) A closed-end manometer was attached to a vessel containing argon. The difference in the mercury levels in the two arms of the manometer was 12.2 cm. Atmospheric pressure was 783 mmHg. The pressure of the argon in the container was __________ mmHg. A) 882 B) 661 C) 122 D) 795 E) 771
5) If 3.21 mol of a gas occupies 56.2 L at 44 C and 793 torr, 5.29 mol of this gas occupies __________ L under these conditions. A) 30.9 B) 14.7 C) 478 D) 92.6 E) 61.7
3) A sample of gas (24.2 g) initially at 4.00 atm was compressed from 8.00 L to 2.00 L at constant temperature. After the compression, the gas pressure was __________ atm. A) 2.00 B) 16.0 C) 1.00 D) 8.00 E) 4.00
6) A gas originally at 27 C and 1.00 atm pressure in a 3.9 L ask is cooled at constant pressure until the temperature is 11 C. The new volume of the gas is __________ L. A) 0.27 B) 0.24 C) 3.9 D) 4.1 E) 3.7
Chemistry 1B Chapter 10 Worksheet - Daley 7) A sample of H2 gas (12.28 g) occupies 100.0 L at 400.0 K and 2.00 atm. A sample weighing 9.49 g occupies __________ L at 353 K and 2.00 atm. A) 54.7 B) 77.3 C) 147 D) 68.2 E) 109 10) The reaction of 50 mL of N2 gas with 150 mL of H2 gas to form ammonia via the equation: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g) will produce __________ mL of ammonia if pressure and temperature are kept constant. A) 50 B) 150 C) 200 D) 250 E) 100
8) If 50.75 g of a gas occupies 10.0 L at STP, 129.3 g of the gas will occupy __________ L at STP. A) 3.92 B) 5.08 C) 50.8 D) 12.9 E) 25.5
11) The density of ammonia gas in a 4.32 L container at 837 torr and 45.0 C is __________ g/L. A) 0.194 B) 0.432 C) 0.717 D) 3.86 E) 4.22 10-2
9) A sample of a gas originally at 25 C and 1.00 atm pressure in a 2.5 L container is allowed to expand until the pressure is 0.85 atm and the temperature is 15 C. The nal volume of the gas is __________ L. A) 2.1 B) 2.8 C) 3.0 D) 0.38 E) 2.6
12) A sample of gas (1.9 mol) is in a ask at 21 C and 697 mmHg. The ask is opened and more gas is added to the ask. The new pressure is 795 mmHg and the temperature is now 26 C. There are now __________ mol of gas in the ask. A) 3.5 B) 1.6 C) 2.9 D) 0.28 E) 2.1
Chemistry 1B Chapter 10 Worksheet - Daley 13) The density of N2O at 1.53 atm and 45.2 C is __________ g/L. A) 1.76 B) 2.58 C) 9.99 D) 18.2 E) 0.388 16) What volume (mL) of sulfur dioxide can be produced by the complete reaction of 3.82 g of calcium sulte with excess HCl (aq), when the nal SO2 pressure is 827 torr at 44.0 C? A) 1.39 10-4 B) 1.00 10-3 C) 761 D) 578 E) 0.106
14) The molecular weight of a gas is __________ g/mol if 3.5 g of the gas occupies 2.1 L at STP. A) 2.7 10-2 B) 41 C) 5.5 103 D) 4.6 102 E) 37
17) Ammonium nitrite undergoes thermal decomposition to produce only gases: NH4NO2 (s) N2 (g) + 2H2O (g) What volume (L) of gas is produced by the decomposition of 35.0 g of NH4NO2 (s) at 525 C and 1.5 atm? A) 160 B) 24 C) 15 D) 47 E) 72
15) The volume of hydrogen gas at 38.0 C and 763 torr that can be produced by the reaction of 4.33 g of zinc with excess sulfuric acid is __________ L. A) 2.71 10-4 B) 0.592 C) 3.69 104 D) 2.84 E) 1.69
18) A sample of He gas (3.0 L) at 5.6 atm and 25 C was combined with 4.5 L of Ne gas at 3.6 atm and 25 C at constant temperature in a 9.0 L ask. The total pressure in the ask was __________ atm. Assume the initial pressure in the ask was 0.00 atm. A) 1.0 B) 3.7 C) 9.2 D) 24 E) 2.6
Chemistry 1B Chapter 10 Worksheet - Daley 19) Since air is a mixture, it does not have a molar mass. However, for calculation purposes, it is possible to speak of its effective molar mass. (An effective molar mass is a weighted average of the molar masses of a mixtures components.) If air at STP has a density of 1.285 g/L, its effective molar mass is __________ g/mol. A) 26.9 B) 31.4 C) 28.8 D) 34.4 E) 30.0 22) Sodium hydride reacts with excess water to produce aqueous sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas: NaH (s) + H2O (l) NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) A sample of NaH weighing __________ g will produce 982 mL of gas at 28.0 C and 765 torr, when the hydrogen is collected over water. The vapor pressure of water at this temperature is 28 torr. A) 0.960 B) 2.93 C) 0.925 D) 925 E) 0.0388
20) In a gas mixture of He, Ne, and Ar with a total pressure of 8.40 atm, the mole fraction of Ar is __________ if the partial pressures of He and Ne are 1.50 and 2.00 atm, respectively. A) 0.417 B) 0.238 C) 0.179 D) 0.357 E) 0.583
23) CO (5.00 g) and CO2 (5.00 g) were placed in a 750.0 mL container at 50.0 C. The partial pressure of CO2 in the container was __________ atm. A) 1.60 B) 4.01 C) 6.31 D) 10.3 E) 0.292
21) A gas mixture of Ne and Ar has a total pressure of 4.00 atm and contains 16.0 mol of gas. If the partial pressure of Ne is 2.75 atm, how many moles of Ar are in the mixture? A) 5.00 B) 11.0 C) 6.75 D) 12.0 E) 9.25
24) The root-mean-square speed of CO at 113 C is __________ m/s. A) 58.3 B) 586 C) 31.5 D) 317 E) 993
Chemistry 1B Chapter 10 Worksheet - Daley 25) Which of the following statements about gases is false? A) Distances between molecules of gas are very large compared to bond distances within molecules. B) Non-reacting gas mixtures are homogeneous. C) Gases expand spontaneously to ll the container they are placed in. D) Gases are highly compressible. E) All gases are colorless and odorless at room temperature. 28) Standard temperature and pressure (STP), in the context of gases, refers to __________. A) 273 K and 1 pascal B) 298 K and 1 torr C) 273 K and 1 atm D) 273 K and 1 torr E) 298 K and 1 atm
26) Molecular compounds of low molecular weight tend to be gases at room temperature. Which of the following is most likely not a gas at room temperature? A) LiCl B) CH4 C) H2 D) HCl E) Cl2
29) The molar volume of a gas at STP is __________ L. A) 14.7 B) 0.08206 C) 62.36 D) 1.00 E) 22.4
27) Gaseous mixtures __________. A) are all heterogeneous B) can only contain isolated atoms C) are all homogeneous D) can only contain molecules E) must contain both isolated atoms and molecules
30) Isothermal means __________. A) at constant pressure B) at ideal temperature and pressure conditions C) at constant temperature D) that Hrxn = 0 E) at variable temperature and pressure conditions
Chemistry 1B Chapter 10 Worksheet - Daley 31) The pressure exerted by a column of liquid is equal to the product of the height of the column times the gravitational constant times the density of the liquid, P = ghd. How high a column of water (d = 1.0 g/mL) would be supported by a pressure that supports a 713 mm column of mercury (d = 13.6 g/mL)? A) 9.7 103 mm B) 14 mm C) 713 mm D) 1.2 104 mm E) 52 mm 33) The kinetic-molecular theory predicts that pressure rises as the temperature of a gas increases because __________. A) the gas molecules collide more frequently with the wall B) the gas molecules collide less frequently with the wall C) the gas molecules collide more energetically with the wall D) the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules decreases E) both the gas molecules collide more frequently with the wall and the gas molecules collide more energetically with the wall
32) Which statement about atmospheric pressure is false? A) Atmospheric pressure prevents water in lakes, rivers, and oceans from boiling away. B) With an increase in altitude, atmospheric pressure increases as well. C) The warmer the air, the lower the atmospheric pressure. D) Air actually has weight. E) As air becomes thinner, its density decreases.
34) A 255 mL round-bottom ask is weighed and found to have a mass of 114.85 g. A few milliliters of an easily vaporized liquid are added to the ask and the ask is immersed in a boiling water bath. All of the liquid vaporizes at the boiling temperature of water, lling the ask with vapor. When all of the liquid has vaporized, the ask is removed from the bath, cooled, dried, and reweighed. The new mass of the ask and the condensed vapor is 115.23 g. Which of the following compounds could the liquid be? (Assume the ambient pressure is 1 atm.) A) C2H6 B) C3H7OH C) C4H9OH D) C2H5OH E) C4H10
Chemistry 1B Chapter 10 Worksheet - Daley 35) The average kinetic energy of the particles of a gas is directly proportional to __________. A) the particle mass B) the square of the rms speed C) the square of the particle mass D) the rms speed E) the square root of the rms speed 38) Which one of the following gases would have the highest average molecular speed at 25 C? A) O2 B) SF 6 C) CO2 D) CH4 E) N2
36) According to kinetic-molecular theory, in which of the following gases will the root-mean-square speed of the molecules be the highest at 200 C? A) H2O B) SF 6 C) HCl D) Cl2 E) None. The molecules of all gases have the same root-mean-square speed at any given temperature.
39) A 1.44-g sample of an unknown pure gas occupies a volume of 0.335 L at a pressure of 1.00 atm and a temperature of 100.0 C. The unknown gas is __________. A) argon B) helium C) krypton D) xenon E) neon
37) According to kinetic-molecular theory, if the temperature of a gas is raised from 100 C to 200 C, the average kinetic energy of the gas will __________. A) decrease by a factor of 100 B) increase by a factor of 100 C) increase by a factor of 1.27 D) decrease by half E) double
40) Given the equation C2H6 (g) + O2 (g) CO 2 (g) + H2O (g) Determine the number of liters of O2 consumed at STP when 270.0 grams of C2H6 is burned.
Answer Key Testname: CHAPTER 10 WORKSHEET
1) A
Page Ref: Sec. 10.2
24) B
Page Ref: Sec. 10.8
2) C
Page Ref: Sec. 10.2
25) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.1
3) B
Page Ref: Sec. 10.3
26) A
Page Ref: Sec. 10.1
4) B
Page Ref: Sec. 10.3
27) C
Page Ref: Sec. 10.1
5) D
Page Ref: Sec. 10.3
28) C
Page Ref: Sec. 10.4
6) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.3
29) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.4
7) D
Page Ref: Sec. 10.3
30) C
Page Ref: Sec. 10.3
8) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.3
31) A
Page Ref: Sec. 10.2
9) B
Page Ref: Sec. 10.3
32) B
Page Ref: Sec. 10.2, 10.3
10) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.3
33) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.7
11) C
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
34) D
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
12) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.4
35) B
Page Ref: Sec. 10.7
13) B
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
36) A
Page Ref: Sec. 10.7
14) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
37) C
Page Ref: Sec. 10.7
15) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
38) D
Page Ref: Sec. 10.8
16) C
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
39) D
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
17) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
40) 706
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
18) B
Page Ref: Sec. 10.6
19) C
Page Ref: Sec. 10.5
20) E
Page Ref: Sec. 10.6
21) A
Page Ref: Sec. 10.6
22) C
Page Ref: Sec. 10.6
23) B
Page Ref: Sec. 10.6
(PRACTICE TEST CONTINUED)
a) b) c) d) e)
H2 He O2 N2 CO2
40. At a given temperature, this has the highest rate of diffusion. 41. This gas is the most plentiful in the earths atmosphere. 42. 1 mole of this occupying 1 liter would have the largest density.
43. Nitrogen gas was collected over water at a temperature of 40 C, and the pressure of the sample was measured at 796 mm Hg. If the vapor pressure of water at 40 C is 55 mm Hg, what is the partial pressure of the nitrogen gas? a) b) c) d) e) 756 mm Hg 796 mm Hg 851 mm Hg 741 mm Hg 55 mm Hg
44. An experiment to determine the molecular mass of a gas begins by heating a solid to produce a gaseous product. The gas passes through a tube and displaces water in an inverted, water-filled bottle. Which of the following necessary items may be determined after the experiment is completed? a) b) c) d) e) mass of the solid used vapor pressure of water temperature of the displaced water volume of the displaced water barometric pressure in the room
45. Determine the formula for a gaseous silane (SinH2n+2) if it has a density of 5.47 g per L at 0 C and 1.00 atm. a) b) c) d) e) Si5H12 SiH4 Si4H10 Si3H8 Si2H6
46. A sample of methane gas was collected over water at 35 C. The sample was found to have a total pressure of 756 mm Hg. Determine the partial pressure of the methane gas in the sample (vapor pressure of water at 35 C is 41 mm Hg). a) b) c) d) e) 797 mm Hg 760 mm Hg 41 mm Hg 756 mm Hg 715 mm Hg
47. A sample of argon gas is sealed in a container. The volume of the container is doubled. If the pressure remains constant, what happens to the absolute temperature? a) b) c) d) e) It is doubled. It is squared. No change. It is halved. It cannot be predicted.
48. A gas sample is confined in a 5-liter container. Which of the following will occur if the temperature of the container is increased? I. The kinetic energy of the gas will increase. II. The pressure of the gas will increase. III. The density of the gas will increase. a) b) c) d) e) I only I and II only II only I and III only I, II and III
49. Increasing the temperature of an ideal gas from 50 C to 75 C at constant volume will cause which of the following to increase for the gas? I. the average distance between the molecules II. the average speed of the molecules III. the average molecular mass of the gas. a) b) c) d) e) I and II II only II and III I only III only
50. A 22.0 gram sample of an unknown gas occupies 11.2 liters at standard temperature and pressure. Which of the following could be the identity of the gas? a) b) c) d) e) carbon dioxide gas helium gas sulfur trioxide gas oxygen gas nitrogen gas
51. The true volume of a particular real gas is larger than that calculated from the ideal gas equation. This occurs because the ideal gas equation is NOT correct for: a) b) c) d) e) the shape of the molecules the speed the molecules are moving the mass of the molecules the attraction between the molecules the volume of the molecules
52. Two balloons are at the same temperature and pressure. One contains 14 g of nitrogen and the other contains 20.0 g of argon. All of the following statements are true EXCEPT a) b) c) d) e) The density of the nitrogen sample is less than the density of the argon sample. The average kinetic energy of the nitrogen molecules is the same as the average kinetic energy of the argon molecules. The volume of the nitrogen container is the same as the volume of the argon container. The average speed of the nitrogen molecules is the same as the average speed of the argon molecules. The number of molecules in the nitrogen container is the same as the number of atoms in the argon container.
53. Nitrogen gas was collected over water at 25C. If the vapor pressure of water at 25C is 23 mm Hg, and the total pressure in the container is measured at 781 mm Hg, what is the partial pressure of the nitrogen gas? a) b) c) d) e) 758 mm Hg 46 mm Hg 735 mm Hg 551 mm Hg 23 mm Hg
54. Which of the following expressions is equal to the density of helium gas at standard temperature and pressure? a) b) c) d) e) 55. Which of the following conditions would be most likely to cause the ideal gas laws to fail? I. High pressure II. High temperature III. Large volume a) b) c) d) e) I only II only I and III only I and II only II and III only
56. Aluminum metal reacts with HCl to produce aluminum chloride and hydrogen gas. How many grams of aluminum metal must be added to an excess of HCl to produce 33.6 L of hydrogen gas, if the gas is at STP? a) b) c) d) e) 18.0 g 4.50 g 27.0 g 9.00 g 35.0 g
57. A glass container is filled, at room temperature, with equal numbers of moles of H 2(g), O2(g), and NO2(g). The gases slowly leak out through a pinhole. After some of the gas has effused, which of the following is true of the relative values for the partial pressures of the gases remaining in the container? a) b) c) d) e) O2 < NO2 < H2 H2 = NO2 = O2 H2 < O2 < NO2 NO2 < H2 < O2 H2 < NO2 < O2
58. Ideal gases vary from real gases at conditions of a) b) c) d) e) high temperature and low pressure. low temperature and low pressure. low temperature and high pressure. high temperature and high pressure. both high density and low pressure.
59. The average kinetic energy of nitrogen molecules changes by what factor when the temperature is increased from 30C to 60C? a) b) c) d) e) square root of (333 - 303) 2 0.5 (333 303) 28
60. Which of the following gases probably deviates most considerably from ideal gas behavior? a) b) c) d) e) O2 SF4 SiH4 He Ar
61. A 14.0-L cylinder contains 5.60 g N 2, 79.9 g Ar and 6.40 g 0 2. What is the total pressure in atm at 27C? (R =the ideal gas constant.) a) b) c) d) e) 120 R 26 R 30 R 20 R 60 R
62. Which of the following assumptions is/are valid based on kinetic molecular theory? a) b) c) d) e) Gas molecules have negligible volume. Gas molecules exert no attractive forces on one another The temperature of a gas in celcius is directly proportional to its kinetic energy. All of the above Only a and b
63. Which of the following best explains why a hotair balloon rises? a) b) c) d) e) The heating of the air causes the pressure inside the balloon to increase. The temperature difference between the inside and outside air causes convection currents. Hot air has a lower density than cold air. Cooler air diffuses more slowly than the warmer air. The cool outside air pushes the balloon higher.
64. In an experiment H2(g) and O2(g) were completely reacted, above the boiling point of water. If the initial pressure in the container before the reaction is denoted as x , which of the following expressions gives the final pressure, assuming ideal gas behavior? a) b) c) d) e) 1.5x 2x x (0.6666666666.....)x 0.5x
65. An ideal gas of volume 189. mL is collected over water at 30C and 777 torr. The vapor pressure of water is 32 torr@ 30C. What pressure is exerted by the dry gas under these conditions? a) b) c) d) e) 777 torr 32 x 777 torr 745 torr 32/77 torr 320 torr
66. An ideal gas sample weighing 1.28 grams at 127C and 1.00 atm has a volume of 0.250 L. Determine the molar mass of the gas. a) b) c) d) e) 80.5 g/mol 0.00621 g/mol 322 g/mol 168 g/mol 49.4 g/mol
67. When 4.0 moles of oxygen are confined in a 24-liter vessel at 176C, the pressure is 6.0 atm. If the oxygen is allowed to expand isothermally until it occupies 36 liters, what will be the new pressure? a) b) c) d) e) 2 atm 4 atm 3 atm 9 atm 8 atm
68. A sealed container containing 8.0 grams of oxygen gas and 7.0 of nitrogen gas is kept at a constant temperature and pressure. Which of the following is true? a) b) c) d) e) The density of nitrogen is greater than the density of oxygen. The volume occupied by nitrogen is greater than the volume occupied by oxygen. The volume occupied by oxygen is greater than the volume occupied by nitrogen. The average molecular speeds of the two gases are the same. The volume occupied by oxygen is equal to the volume occupied by nitrogen
69. An ideal gas is contained in a 5.0 liter chamber at a temperature of 37C. If the gas exerts a pressure of 2.0 atm on the walls of the chamber, which of the following expressions is equal to the number of moles of the gas? The gas constant, R, is 0.08 (L-atm)/(mol-K).
a)
b)
c) d)
e) 70. A 2 L evacuated flask has a 0.2 mol sample of NO5(s) sealed inside it. The flask is heated to decompose the solid and cooled to 300 K. What is the nearest value to the final total pressure of the gases in the flask? (The value of the gas constant, R, is 0.082 L atm mol-1K-1.) a) b) c) d) e) 0.6 atm 3 atm 0.05 atm 1.2 atm 6 atm
71. A gas sample contains 0.1 mole of oxygen and 0.4 moles of nitrogen. If the sample is at standard temperature and pressure, what is the partial pressure due to nitrogen? a) b) c) d) e) 0.2 atm 0.1 atm 0.8 atm 0.5 atm 1.0 atm
72. If a sample of CH4 effuses at a rate of 9.0 mol per hour at 35C, which of the gases below will effuse at approximately twice the rate under the same conditions? a) b) c) d) e) CO F2 SiH4 O2 He
73. A mixture of gases contains 1.5 moles of oxygen, 3.0 moles of nitrogen, and 0.5 moles of water vapor. If the total pressure is 700 mm Hg, what is the partial pressure of the nitrogen gas? a) b) c) d) e) 210 mm Hg 350 mm Hg 70 mm Hg 280 mm Hg 420 mm Hg
74. A balloon occupies a volume of 1.0 liter when it contains 0.16 grams of helium at 37 C and 1 atm pressure. If helium is added to the balloon until it contains 0.80 grams while pressure and temperature are kept constant, what will be the new volume of the balloon? a) b) c) d) e) 0.50 liters 1.0 liters 4.0 liters 2.0 liters 5.0 liters
75. A reaction produces a gaseous mixture of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and water vapor. After one reaction, the mixture was analyzed and found to contain 0.60 mol of carbon dioxide, 0.30 mol of carbon monoxide, and 0.10 mol of water vapor. If the total pressure of the mixture was 0.80 atm, what was the partial pressure of the carbon monoxide? a) b) c) d) e) 0.080 atm 0.48 atm 0.34 atm 0.24 atm 0.13 atm
76. Which of the following gases would be expected to have a rate of effusion that is one-third as large as that of H 2? a) b) c) d) e) O2 CO2 He N2 H2O
77. A gaseous mixture at a constant temperature contains O2, CO2, and He. Which of the following lists the three gases in order of increasing average molecular speeds? a) b) c) d) e) He, CO2, O2 He, O2, CO2 O2, CO2, He O2, He, CO2 CO2, O2, He
78. A sealed, rigid container is filled with three ideal gases: A, B, and C. The partial pressure of each gas is known. The temperature and volume of the system are known. What additional information is needed to determine the masses of the gases in the container? a) b) c) d) e) the molar masses of the gases the total pressure the volume of the gas molecules the intermolecular forces the average distance traveled between molecular collisions
79. What is the volume of n moles of gas@ STP? a) b) c) d) e) 22.4 L n X 22.4 L n X 22.4 L X 760 n X 22.4 LL X 273 X 760 Cannot be determined.
80. A mixture of helium and neon gases has a total pressure of 1.2 atm. If the mixture contains twice as many moles of helium as neon, what is the partial pressure due to neon? a) b) c) d) e) 0.2 atm 0.8 atm 0.3 atm 0.9 atm 0.4 atm
81. A steel tank containing argon gas has additional argon gas pumped into it at constant temperature. Which of the following is true for the gas in the tank? a) b) c) d) e) There is an increase in the volume of the gas. The gas atoms travel with the same average speed. The gas atoms are separated by a greater average distance. There is no change in the number of gas atoms. There is a decrease in the pressure exerted by the gas.
82. An ideal gas fills a balloon at a temperature of 27C and 1 atm pressure. By what factor will the volume of the balloon change if the gas in the balloon is heated to 127C at constant pressure? a) b) c) d) e) 4/3 4.703703703703..... 2 0.75 27/127
83. A gas sample with a mass of 10 grams occupies 6.0 liters and exerts a pressure of 2.0 atm at a temperature of 26C. Which of the following expressions is equal to the molecular mass of the gas? The gas constant, R, is 0.08 (L-atm)/(mol-K).
a)
b)
c)
d)
e) 84. The temperature of a sample of an ideal gas confined in a 2.0 L container was raised from 27C to 77C. If the initial pressure of the gas was 1,200 mm Hg, what was the final pressure of the gas? a) b) c) d) e) 1,400 mm Hg 600 mm Hg 3,600 mm Hg 2,400 mm Hg 300 mm Hg
85. In a closed inflexible system, 7.0 mol CO 2, 7.0 mol Ar, 7.0 mol N2, and 4.0 mol Ne are trapped, with a total pressure of 10.0 atm. What is the partial pressure exerted by the neon gas? a) b) c) d) e) 1.6 atm 29.0 atm 4.0 atm 10.0 atm 21.0 atm
10
Short Answer 86. A hydrogen gas sample is collected over water. The volume of the sample was 190.0 mL at 26 C, and the pressure in the room was 754 mm Hg. The vapor pressure of water at 26 C is 25.2 mm Hg. (a) Calculate the number of moles of hydrogen in the sample. (b) Calculate how many molecules of water vapor are present in the sample. (c) Determine the density (in g/L) of the gas mixture. (d) determine the mole fraction of water. 87. A sample containing 2/3 mole of potassium chlorate, KClO3, is heated until it decomposes to potassium chloride and oxygen gas. The oxygen is collected in an inverted bottle through the displacement of water. Answer the following questions using this information. (a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. (b) How many moles of oxygen gas are produced? (c) The temperature and pressure of the sample are adjusted to STP. The volume of the sample is found to be slightly greater than 22.4 liters. Explain. (d) An excess of sulfur is burned in the oxygen. Write a balanced chemical equation and calculate the number of moles of gas formed. (e) After the sulfur had completely reacted, a sample of the residual water was removed from the bottle and found to be acidic. Explain.
11
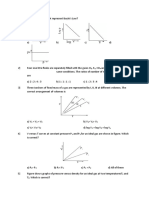
88.
The graph above shows the changes in pressure with changing temperature of gas samples of helium and argon confined in a closed 2-liter vessel. (a) What is the total pressure of the two gases in the container at a temperature of 200 K? (b) How many moles of helium are contained in the vessel? (c) How many molecules of helium are contained in the vessel? (d) What is the ratio of the average speeds of the helium atoms to the average speeds of the argon atoms? (e) If the volume of the container were reduced to 1 liter at a constant temperature of 300 K, what would be the new pressure of the helium gas?
89. Equal molar quantities of two gases, O2 and H2O, are confined in a closed vessel at constant temperature. (a)Which gas, if any, has the greater partial pressure? (b)Which gas, if any, has the greater density (c) Which gas, if any, has the greater concentration? (d) Which gas, if any, has the greater average kinetic energy? (e) Which gas, if any, will show the greater deviation from ideal behavior? (f) Which gas, if any, has the greater average molecular speed?
12
90. SF6, H2O, and CO2 are all greenhouse gases because they absorb infrared radiation in the atmosphere. As such they are of interest to many researchers. (a) Of the three gases, which deviates the most from ideal gas behavior? (b) If all three ideal gases are held at constant temperature, which gas would have the highest average molecular speed? (c) A container was with equal amounts H2O and CO2 and the pressure was measured. Assuming ideal behavior, if SF6 was then added such that the final pressure was four times that before its addition, the final number of moles of SF6 is how many times that of H2O? (d) If a container held equal molar amounts of all three greenhouse gases, but was then compressed decreasing the volume within, which of the gases has the highest, final partial pressure assuming ideal behavior. (e) Gas molecules exert pressure through collisions with the walls of the containers they are in. If a container is filled with equal amounts of each of the greenhouse gases, which gas undergoes the fewest collisions with the wall of the container per unit time?
13
ID: A
(PRACTICE TEST CONTINUED) Answer Section
MATCHING 40. A 41. D 42. E MULTIPLE CHOICE 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. D B C E A B B A E D A D A C C C D B C E C D C D B E E E C E E E D 1
ID: A 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. E E A B E B A C A A
ID: A SHORT ANSWER
86.
ID: A
87.
ID: A
88.
ID: A
89.
ID: A
90.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 1000 Most Common Words (SAT)Dokumen70 halaman1000 Most Common Words (SAT)grellian95% (20)
- Con Men ScamsDokumen14 halamanCon Men ScamsTee R TaylorBelum ada peringkat
- AP Chem Ch 5 Practice Quiz and KeyDokumen5 halamanAP Chem Ch 5 Practice Quiz and KeyhydrocrackermanBelum ada peringkat
- THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND KINETIC THEORYDokumen13 halamanTHE IDEAL GAS LAW AND KINETIC THEORYLuis AndersonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 WorkbookDokumen12 halamanChapter 5 Workbookahix123Belum ada peringkat
- Perspective in PharmacyDokumen3 halamanPerspective in PharmacyAgniez Hannah Permites100% (4)
- Chem Questions and Answers 151 FinalDokumen12 halamanChem Questions and Answers 151 FinalTom TeslaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry-Gas Laws Multiple ChoiceDokumen5 halamanChemistry-Gas Laws Multiple ChoiceGeorge Isaac McQuilesBelum ada peringkat
- SPONSORSHIP GUIDE FOR FIJI'S NATIONAL SPORTS FEDERATIONSDokumen17 halamanSPONSORSHIP GUIDE FOR FIJI'S NATIONAL SPORTS FEDERATIONSvaidwara100% (1)
- Recovering Mind and Body (Mental Health)Dokumen24 halamanRecovering Mind and Body (Mental Health)Shivamani143100% (1)
- Fitch CLOs and Corporate CDOsRating Criteria PDFDokumen57 halamanFitch CLOs and Corporate CDOsRating Criteria PDFantonyBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Question CHM 101Dokumen26 halamanMultiple Question CHM 101Emmanuella OffiongBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise GasesDokumen4 halamanExercise GasesAri AdiantariBelum ada peringkat
- Gases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryDokumen20 halamanGases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryAshley Marie ChildersBelum ada peringkat
- CH 5 Practice ProblemsDokumen16 halamanCH 5 Practice Problemsjaskaran singhBelum ada peringkat
- COVID 19 ReportDokumen21 halamanCOVID 19 ReportDatu Nor Balindong82% (11)
- Chang's Test Bank (Chapters 5, 7, 8, 9)Dokumen27 halamanChang's Test Bank (Chapters 5, 7, 8, 9)asfaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Questions For Ch. 5: Name: - Class: - Date: - Id: ADokumen23 halamanPractice Questions For Ch. 5: Name: - Class: - Date: - Id: APrem MehrotraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 Multiple Choice Gas LawsDokumen12 halamanChapter 10 Multiple Choice Gas LawsNoranisza MahmudBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Quarter Review Honors ChemDokumen27 halaman3rd Quarter Review Honors Chemjkomtil7Belum ada peringkat
- AP CHEM Unit 03 Exam Part 1Dokumen8 halamanAP CHEM Unit 03 Exam Part 1andersondmchsBelum ada peringkat
- Students - Sheet 2Dokumen6 halamanStudents - Sheet 2basemhazemBelum ada peringkat
- Phy Chem Topics Set 2Dokumen8 halamanPhy Chem Topics Set 2Anonymous RbmGbYvBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 WorksheetDokumen6 halamanChapter 5 WorksheetJules BrunoBelum ada peringkat
- Gases Self Check ProblemsDokumen5 halamanGases Self Check ProblemsLissa HannahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Homework 2Dokumen4 halamanChapter 5 Homework 2Mary JewelBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 Answered QuestionsDokumen4 halamanChapter 10 Answered Questionssameera abedBelum ada peringkat
- IIT Jee Mayank Test-2Dokumen5 halamanIIT Jee Mayank Test-2kamalkantmbbsBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank Chapter 5Dokumen7 halamanTest Bank Chapter 5Ahmed ZakiBelum ada peringkat
- CHE 160 Semester Review Zumdahl CH 5-7Dokumen20 halamanCHE 160 Semester Review Zumdahl CH 5-7Kinal PatelBelum ada peringkat
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDokumen11 halamanMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionVenus Abigail GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank Chapter 5Dokumen9 halamanTest Bank Chapter 5geenah111Belum ada peringkat
- Honors Chemistry Gas Laws ReviewDokumen2 halamanHonors Chemistry Gas Laws ReviewRocket FireBelum ada peringkat
- Gases (AP MC)Dokumen5 halamanGases (AP MC)Mohamed RafatBelum ada peringkat
- CH 222 Exam 2 Practice CombinedDokumen23 halamanCH 222 Exam 2 Practice CombinedSick JaysBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 GasesDokumen37 halamanChapter 5 GasesNeally WeallyBelum ada peringkat
- Gases (AP MC)Dokumen11 halamanGases (AP MC)rejymolBelum ada peringkat
- Taller de GasesDokumen20 halamanTaller de GasesAle Cruz DBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 - GasesDokumen22 halamanChapter 5 - GasesTony Ansah100% (1)
- Ebook Chemistry The Central Science 11Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokumen67 halamanEbook Chemistry The Central Science 11Th Edition Brown Test Bank Full Chapter PDFformatbalanoidyxl100% (11)
- Chemistry Gaseous StateDokumen6 halamanChemistry Gaseous Stateraghavendra jBelum ada peringkat
- Test for Gases答案Dokumen5 halamanTest for Gases答案Mary JewelBelum ada peringkat
- Topic C PDFDokumen8 halamanTopic C PDFBrian Zachariah DuBelum ada peringkat
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5Dokumen8 halamanChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5haha_le12Belum ada peringkat
- MCQsDokumen6 halamanMCQsKashan NoorBelum ada peringkat
- AP Chemistry Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen7 halamanAP Chemistry Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsJohn RammBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Questions - Chapter 12Dokumen7 halamanSample Questions - Chapter 12Rasel IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry SheetsDokumen10 halamanChemistry Sheetshebaneyar74Belum ada peringkat
- Class15 Chemistry G11 Homework Dec 11-15Dokumen4 halamanClass15 Chemistry G11 Homework Dec 11-15ErinBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Laws Prac Test and Answers1Dokumen9 halamanGas Laws Prac Test and Answers1Debayanbasu.juBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Laws and Stoichiometry Practice ProblemsDokumen6 halamanGas Laws and Stoichiometry Practice ProblemsJames DellavaBelum ada peringkat
- Ch12 GasesDokumen12 halamanCh12 GasesCeleste SchepersBelum ada peringkat
- CHM 1102 Worksheet 5 2022Dokumen2 halamanCHM 1102 Worksheet 5 2022kevin persaudBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank Chapter 5Dokumen8 halamanTest Bank Chapter 5teafBelum ada peringkat
- CHE 110 E3 S13 v1 DR GibianDokumen6 halamanCHE 110 E3 S13 v1 DR GibianMicahBelum ada peringkat
- POPDokumen16 halamanPOPzaneBelum ada peringkat
- Gases Sample Questions PDFDokumen25 halamanGases Sample Questions PDFKhay Nochefranca100% (1)
- Gas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry REVIEW (Mass-Volume) : Name: - Date: - PerDokumen4 halamanGas Laws and Gas Stoichiometry REVIEW (Mass-Volume) : Name: - Date: - PerAxl AlfonsoBelum ada peringkat
- HW2 Gas LawsDokumen2 halamanHW2 Gas LawsSALAMANCA, AZELEI B.Belum ada peringkat
- AP Chemistry Fr3 Test BankDokumen9 halamanAP Chemistry Fr3 Test BankzeustamBelum ada peringkat
- GASES Free Response WorksheetDokumen4 halamanGASES Free Response WorksheetJJBelum ada peringkat
- Bcfnl08ans Space 3Dokumen26 halamanBcfnl08ans Space 3Martin LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test on Gas LawsDokumen2 halamanPractice Test on Gas LawsAthena AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- States of Matter - Entrance Exam Model Question Paper 2012Dokumen3 halamanStates of Matter - Entrance Exam Model Question Paper 2012Vinod BhaskarBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry Gas Workshop ProblemsDokumen2 halamanGeneral Chemistry Gas Workshop ProblemsPSCBelum ada peringkat
- Gaseous State PDFDokumen4 halamanGaseous State PDFramanji1021Belum ada peringkat
- CHP 10Dokumen4 halamanCHP 10aysekrzm07Belum ada peringkat
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsDari EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Mq9a PDFDokumen1 halamanMq9a PDFahix123Belum ada peringkat
- Res Sweep500 SecDokumen1 halamanRes Sweep500 Secahix123Belum ada peringkat
- InductorDokumen37 halamanInductorBorad AlpeshBelum ada peringkat
- MIT8 01SC Problems21Dokumen8 halamanMIT8 01SC Problems21ahix123Belum ada peringkat
- MQ 9 ADokumen1 halamanMQ 9 Aahix123Belum ada peringkat
- EssayDokumen5 halamanEssayahix123Belum ada peringkat
- MIT8 01SC Problems21Dokumen8 halamanMIT8 01SC Problems21ahix123Belum ada peringkat
- History 2Dokumen6 halamanHistory 2ahix123Belum ada peringkat
- HistoryDokumen6 halamanHistoryahix123Belum ada peringkat
- Psychology Test 5 Review: Motor, Emotional, Cognitive DevelopmentDokumen2 halamanPsychology Test 5 Review: Motor, Emotional, Cognitive Developmentahix123Belum ada peringkat
- Review 2Dokumen2 halamanReview 2ahix123Belum ada peringkat
- Mythical Origins of The Hungarian Medieval LegislationDokumen8 halamanMythical Origins of The Hungarian Medieval LegislationLucas LixaBelum ada peringkat
- CHN ReviewerDokumen9 halamanCHN ReviewerAnonymousTargetBelum ada peringkat
- Eq 1Dokumen4 halamanEq 1jppblckmnBelum ada peringkat
- Automation and Artificial Intelligence in Hospitality and TourismDokumen19 halamanAutomation and Artificial Intelligence in Hospitality and TourismShawn WangBelum ada peringkat
- Vaclav Havel - From 'Mistake'. SAGEDokumen9 halamanVaclav Havel - From 'Mistake'. SAGEADIELruleBelum ada peringkat
- Criminal Law Notes SummaryDokumen12 halamanCriminal Law Notes SummaryPurplaawBelum ada peringkat
- IEEE COMMUNICATIONS LETTERS, VOL. 10, NO. 6, JUNE 2006Dokumen3 halamanIEEE COMMUNICATIONS LETTERS, VOL. 10, NO. 6, JUNE 2006Regina PittsBelum ada peringkat
- FortiEDR Product Overview TrainingDokumen16 halamanFortiEDR Product Overview TrainingRafael Steven Soto del CampoBelum ada peringkat
- 2 10 1 PBDokumen4 halaman2 10 1 PBHeesung KimBelum ada peringkat
- A History Analysis and Performance Guide To Samuel Barber?Dokumen117 halamanA History Analysis and Performance Guide To Samuel Barber?giorgio planesioBelum ada peringkat
- Differential and Integral Calculus FormulasDokumen33 halamanDifferential and Integral Calculus FormulasKim Howard CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Present Tense Review for Motorcycle RepairDokumen2 halamanPresent Tense Review for Motorcycle RepairFaheemuddin Veterans50% (2)
- Week 3 21ST Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDokumen13 halamanWeek 3 21ST Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldConrado AreolaBelum ada peringkat
- Sanjay Chandra Vs Cbi On 23 November, 2011Dokumen21 halamanSanjay Chandra Vs Cbi On 23 November, 2011SaiBharathBelum ada peringkat
- Adler Individual-PsychologyDokumen3 halamanAdler Individual-PsychologyPORRAS, REJEAN ANN D.Belum ada peringkat
- ELC650-Movie Critique Yusri, YassinDokumen14 halamanELC650-Movie Critique Yusri, YassinYusri MalekBelum ada peringkat
- Personal Assistant With Telegram & ArduinoDokumen8 halamanPersonal Assistant With Telegram & ArduinoAbhijit PattnaikBelum ada peringkat
- Memorial On Behalf of PetitionerDokumen35 halamanMemorial On Behalf of PetitionerAjitabhGoel67% (3)
- GUINNESS F13 Full Year BriefingDokumen27 halamanGUINNESS F13 Full Year BriefingImoUstino ImoBelum ada peringkat
- Case StudyDokumen9 halamanCase StudySidharth A.murabatteBelum ada peringkat
- HIST 124 - Course Outline KARRARDokumen3 halamanHIST 124 - Course Outline KARRARtahmeemBelum ada peringkat
- 211 - Organizational Behaviour-Pearson Education Limited (2020)Dokumen5 halaman211 - Organizational Behaviour-Pearson Education Limited (2020)mozam haqBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan For KSSR Year 4 (SK)Dokumen4 halamanLesson Plan For KSSR Year 4 (SK)Mohamad Firdaus100% (3)
- Africa S Top 15 Cities in 2030Dokumen10 halamanAfrica S Top 15 Cities in 2030loca018Belum ada peringkat