Dextro-Transposition of The Great Arteries
Diunggah oleh
Luisa BaldiniDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Dextro-Transposition of The Great Arteries
Diunggah oleh
Luisa BaldiniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
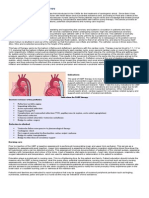
Dextro-Transposition of the Great Arteries
d-TGA
is the most common cyanotic congenital heart lesion in neonates systemic and pulmonary circulations in parallel more frequently in males of normal birth weight
d-TGA
ventriculoarterial discordance aorta arises from the morphologic right ventricle and the pulmonary artery arises from the morphologic left ventricle
Lesiones asociadas
coronary artery anomalies coarctation of the aorta hypoplastic or interrupted arch pulmonic stenosis Interventricular septal defect right ventricular outflow tract obstruction mitral or tricuspid valve abnormalities hypoplasia of the right ventricle left ventricular outflow tract obstruction
Fisiologia Fetal
The low resistance of the umbilicalplacental system receives the right ventricular output left ventricle faces the high pulmonary vascular resistance and placental vascular resistance
Fisiologia Postnatal
oxygenated blood will be ejected into the pulmonary circulation without reaching the systemic circulation. de-oxygenated blood will not reach the pulmonary circulation for oxygenation. hypoxemia incompatible with life unless intracardiac (PFO/ASD or VSD) or extracardiac (patent ductus arteriosusbronchial circulation) communications are patent
Presentacion Clinica
cyanosis, systemic hypoperfusion, cardiogenic shock, metabolic acidosis, oliguria and multiorgan dysfunction symptoms appear after PDA closure or even sooner if the patent foramen ovale is very restrictive prominent cardiac impulse Murmurs are not usually heard pulses are normal until cardiogenic shock appears Sat arterial O2 5070% and arterial PO2
Manejo Inmediato
ABC along with a brief echocardiogram for diagnosis, assessment of ventricular function, and evaluation of patency of DA and FO PGE1 0.01 0.1 mcg/kg/min inotropic support, fluid and bicarbonate If insufficient mixing: emergent ballon atrial septostomy head ultrasound, renal ultrasound, and genetic tests may be done prior to surgical intervention
Tratamiento Quirurgico
arterial switch operation via a median sternotomy with cardiopulmonary bypass and moderate to severe hypothermia transection of both great vessels, translocation of the pulmonary arteries anterior to the aorta and suturing the ascending aorta to the arterial root attached to the left ventricle and the distal main pulmonary artery to the arterial root attached to the right ventricle coronary arteries need to be harvested
ASO
Rastelli
creation of interventricular tunnel funneling the left ventricular blood into the anterior aorta; a conduit is used to established right ventricle to pulmonary artery continuity
R.E.V. (Rparation a lEtage Ventriculaire)
enlargement of the ventricular septal defect to create a more direct communication between the left ventricle and the aorta and a direct anastomosis between the right ventricle and the pulmonary
Aortic Translocation procedure (Nikaidoh procedure)
the aortic root is moved into the pulmonary position, closer to the left ventricle, avoiding the creation of an interventricular tunnel, the right ventricular outflow tract can be repaired with or without a conduit
Complicaciones Postoperatorio
low cardiac output syndrome mitral regurgitation coronary insufficiency and/or ischemia supravalvar aortic stenosis pulmonary stenosis Bleeding arrhythmias
Manejo Cardiovascular
chest open/close TEE immediately available inotropic support: low dose dopamine (3 5g/kg/min), low dose epinephrine (0.05 1 g/kg/min), milrinone (0.75 g/kg/min) and sodium nitroprusside (13 g/kg/min) Avoid high inotropic support: ECMO until the ventricular function recovers!!!! rule out residual lesions, suboptimal myocardial preservation, and/or excessive tissue stretching/damage during the
Manejo Cardiovascular
check: echocardiogram, CVP, left atrial pressure, lactate levels, mixed venous saturations, and NIRS, physical exam ECG Labs Chest Rx
Manejo Respiratorio
extubation when ahemodynamically stable without residual lesions Extubation failure alerts of diaphragmatic paralysis Prior to chest closure endotracheal tube suctioned and a pacemaker must be at the bedside with wires connected chest closed: tidal volumes of 1012 cc/kg, avoid over-distention and collapse, PEEP 56 cm/H2O, and FIO2 to maintain saturations of 98100%
Fluid, Electrolytes and Nutritional Management
Parenteral nutrition is begun 24 hours after repair with Dx 2025%, protein intake 3 g/day, and fat intake 33.5 g/kg/day Enteral nutrition is commenced once the infant reaches hemodynamic stability.
Hematologic Management
Bleeding is after ASO, more commonly when the procedure involves a long CPB time and cross clamp time transfusion of platelets, fresh frozen plasma, or cryoprecipitate If bleeding above 710 ml/kg/h: chest reexploration at the bed side blood clots may compress some coronary branches causing ischemia and cardiovascular collapse
Gastrointestinal Management
Liver and pancreatic function should be monitored PO intake after 24 h of extubation, attention to changes in the quality and quantity of the chest and peritoneal drainage after enteral feeds are started (chylothorax and chyloperitoneum)
Renal Management
Furosemide and thiazides are the most commonly used diuretics Furosemide is started within 612 h after repair (dose 0.10.4 mg/kg/h) to achieve negative fluid balance within 2448 h after repair; this will facilitate chest closure and the extubation
Neurologic Management
head ultrasounds may be performed post repair EEG 1224 h post repair to detect seizure activity
Infectious Disease Management
vancomycin and third generation cephalosporins until the chest is closed Following closure first generation cephalosporin is used until the chest tubes are removed Central lines must be discontinued as soon as possible
Long Term Outcome
satisfactory in most patients results are influenced by the surgical learning curve of each institution re-operation free survival rate 82.2% at 10 years and 75.7% at 15 years neurologic abnormalities Late complications:supravalvar aortic stenosis, supravalvar pulmonary stenosis, neoaortic root dilation and neoaortic regurgitation, sinus node dysfunction,
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Care of The Unconscious, Multi-Trauma PatientDokumen37 halamanCare of The Unconscious, Multi-Trauma PatientRomaine BarrettBelum ada peringkat
- Cyanotic Heart DiseaseDokumen66 halamanCyanotic Heart DiseasePrasanth SankarBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Trauma: DR Tarik El Batrawy Specialist General SurgeryDokumen50 halamanLiver Trauma: DR Tarik El Batrawy Specialist General Surgerykata61Belum ada peringkat
- Tamponade KordisDokumen20 halamanTamponade KordisMuhammad Aprianto RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy: Radical NephrectomyDokumen12 halamanAnatomy: Radical Nephrectomyfrozen loombandsBelum ada peringkat
- Open Heart 1Dokumen18 halamanOpen Heart 1mohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Complex Functional Single VentricleDokumen35 halamanComplex Functional Single Ventriclethecount28991Belum ada peringkat
- Total Anomalous Venous ReturnDokumen4 halamanTotal Anomalous Venous ReturnJohn Bernard Ting TizonBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac CatheterizationDokumen6 halamanCardiac Catheterizationgurneet kourBelum ada peringkat
- Wsava - Fecava - Bsava World Congress 2012 - VinDokumen8 halamanWsava - Fecava - Bsava World Congress 2012 - Vinkuriakosejane6Belum ada peringkat
- Cardiac SurgeryDokumen19 halamanCardiac SurgerySimon JosanBelum ada peringkat
- Peri - Operative ManagementDokumen32 halamanPeri - Operative Managementrichamalik99Belum ada peringkat
- Trauma Tumpul AbdomenDokumen30 halamanTrauma Tumpul AbdomendewiswahyuBelum ada peringkat
- Post Op CardiacDokumen7 halamanPost Op CardiacsimplyputmonicBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac General Complications Management Following SurgeryDokumen15 halamanCardiac General Complications Management Following Surgeryummemuhammad4256Belum ada peringkat
- 440 - Med Surg HESI 2Dokumen8 halaman440 - Med Surg HESI 2Chalcey Polson87% (15)
- Post Partum HaemorrhageDokumen6 halamanPost Partum Haemorrhagenancy jeyakumarBelum ada peringkat
- PdaDokumen43 halamanPdaSandy ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Emergency Oral Q.docx26.docx8Dokumen44 halamanMedical Emergency Oral Q.docx26.docx8Simina ÎntunericBelum ada peringkat
- Shock ManagementDokumen26 halamanShock ManagementMuhammad Irfanuddin Bin IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- ABCDE of TraumaDokumen35 halamanABCDE of TraumaIqe ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Post Partum HemorrhageDokumen59 halamanPost Partum HemorrhageMahima SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Catheterization and Coronary AngiographyDokumen5 halamanCardiac Catheterization and Coronary Angiographyedem100% (1)
- Reviewer 418Dokumen15 halamanReviewer 418Denese JocsonBelum ada peringkat
- Portal HypertensionDokumen60 halamanPortal HypertensionParul VarshneyBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Vascular Disease (TBL) : AcuteDokumen3 halamanPulmonary Vascular Disease (TBL) : AcutetangledprincessBelum ada peringkat
- Care of Patients With Acute Biologic CrisisDokumen72 halamanCare of Patients With Acute Biologic CrisisJames QuilingBelum ada peringkat
- 8 - DR. Khaled - Cardiac SurgeryDokumen26 halaman8 - DR. Khaled - Cardiac SurgeryMuhand.Belum ada peringkat
- Decreased Pulmonary Blood Flow (CYANOTIC HEART DEFECTS)Dokumen88 halamanDecreased Pulmonary Blood Flow (CYANOTIC HEART DEFECTS)leenaBelum ada peringkat
- Damage Control SurgeryDokumen71 halamanDamage Control SurgeryAshish SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Transurethral Resection of The Prostate Anesthetic Considerations Dr. Frank TitzeDokumen25 halamanTransurethral Resection of The Prostate Anesthetic Considerations Dr. Frank TitzeFityan Aulia RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Valvular Heart Disease To TW FinalDokumen13 halamanValvular Heart Disease To TW FinalMohammed ElSayedBelum ada peringkat
- CME UGIB, Hypovolemic Shock 31.12.21 - FINALDokumen58 halamanCME UGIB, Hypovolemic Shock 31.12.21 - FINALThayalan RaviBelum ada peringkat
- Tetralogy of FallotDokumen41 halamanTetralogy of Fallotthecount28991Belum ada peringkat
- 19 Anesthetic Emergencies 2006Dokumen8 halaman19 Anesthetic Emergencies 2006clikgoBelum ada peringkat
- Aortic Aneurysms and Their Anaesthetic ManagementDokumen68 halamanAortic Aneurysms and Their Anaesthetic ManagementMonika Dabgotra100% (1)
- Approach To PolytraumaDokumen46 halamanApproach To PolytraumaAyush ChaliseBelum ada peringkat
- Venous Thromboembolism STDokumen40 halamanVenous Thromboembolism STThe ProfessorBelum ada peringkat
- Universal Algorithm (According To The European Conference 2000)Dokumen11 halamanUniversal Algorithm (According To The European Conference 2000)Pawan MishraBelum ada peringkat
- DialysisDokumen19 halamanDialysisSachin Singh100% (2)
- Intra Aortic Balloon PumpDokumen3 halamanIntra Aortic Balloon PumpNkk Aqnd MgdnglBelum ada peringkat
- PDA Case StudyDokumen5 halamanPDA Case StudyDiana Andrea AyongaoBelum ada peringkat
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesDokumen25 halamanCyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesAlvin OmondiBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Artery Catheterization and MonitoringDokumen31 halamanPulmonary Artery Catheterization and MonitoringVhince Norben PiscoBelum ada peringkat
- Care of Patient With Pulmonary EmbolismDokumen19 halamanCare of Patient With Pulmonary Embolismtankmp100% (1)
- Anaesthetic Management in Obstetric Haemorrhage: DR B.Srikanth Iindyrpg Dept. of AnaesthesiaDokumen34 halamanAnaesthetic Management in Obstetric Haemorrhage: DR B.Srikanth Iindyrpg Dept. of AnaesthesiaEDI CBelum ada peringkat
- CompressedDokumen73 halamanCompressedapi-667225436Belum ada peringkat
- Written Report On MS - Valvular Heart DisordersDokumen8 halamanWritten Report On MS - Valvular Heart DisordersJan SaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Gi Bleeding 6th Year Seminar GRP BB PDFDokumen32 halamanGi Bleeding 6th Year Seminar GRP BB PDFmohamedeen hamzaBelum ada peringkat
- Anaesthetic Management of PheochromocytomaDokumen22 halamanAnaesthetic Management of PheochromocytomaZoelBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Care and Small Bowel ObstructionDokumen16 halamanCritical Care and Small Bowel Obstructionsofea zamriBelum ada peringkat
- CABGDokumen29 halamanCABGDeepika PatelBelum ada peringkat
- TURPDokumen7 halamanTURPRiley EscobarBelum ada peringkat
- Antenatal and Intrapartum CareDokumen22 halamanAntenatal and Intrapartum Caresanjay vigneshBelum ada peringkat
- Portal HypertensionDokumen22 halamanPortal Hypertensionsara.sherif099Belum ada peringkat
- Cardiac SurgeryDokumen27 halamanCardiac SurgeryReeti Singh100% (1)
- Intraabdominal PressureDokumen15 halamanIntraabdominal Pressurearditia dwiBelum ada peringkat
- Transurethral Resection of The Prostate Anesthetic ConsiderationsDokumen25 halamanTransurethral Resection of The Prostate Anesthetic ConsiderationsSeaoon IdianBelum ada peringkat
- A Patient With Uncontrolled Hypertension: Case DiscussionDokumen2 halamanA Patient With Uncontrolled Hypertension: Case DiscussionkeboooooBelum ada peringkat
- Group 7 Case Study: Pre-InternshipDokumen6 halamanGroup 7 Case Study: Pre-InternshipTrish ShangBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Marrow: Diseases, Transplants and Cost - MeddcoDokumen11 halamanBone Marrow: Diseases, Transplants and Cost - MeddcoMeddco HealthcareBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Patients With Structural Infections and Inflammatory Cardiac Disorders Hinkle PPT CH 28Dokumen50 halamanManagement of Patients With Structural Infections and Inflammatory Cardiac Disorders Hinkle PPT CH 28DelindaEvans100% (4)
- Case Presentation Final2Dokumen36 halamanCase Presentation Final2zerpthederpBelum ada peringkat
- Premalignant LesionsDokumen76 halamanPremalignant LesionsPrima D Andri100% (1)
- Acupuncture InformationDokumen5 halamanAcupuncture Informationsamlee65Belum ada peringkat
- B. Within 24 Hours After DischargeDokumen15 halamanB. Within 24 Hours After DischargeRichard SonsingBelum ada peringkat
- PERFORMING STERILE DRESSING CHANGE IN PATIENT WHO UNDERGO EYE and EAR SURGERYDokumen4 halamanPERFORMING STERILE DRESSING CHANGE IN PATIENT WHO UNDERGO EYE and EAR SURGERYPolo Gabriel MendiolaBelum ada peringkat
- 5z23. ED Crowding Overview and Toolkit (Dec 2015)Dokumen33 halaman5z23. ED Crowding Overview and Toolkit (Dec 2015)Peter 'Pierre' RobsonBelum ada peringkat
- TriosDokumen4 halamanTriosTej PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Englishwritten Released 2018 PDFDokumen401 halamanEnglishwritten Released 2018 PDFbobobo96Belum ada peringkat
- Stroke: What Is A Stroke?Dokumen12 halamanStroke: What Is A Stroke?asyafujisakiBelum ada peringkat
- Compusoft, 2 (3), 65-72Dokumen8 halamanCompusoft, 2 (3), 65-72Ravi Tyagi TyagiBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To Spontaneous PneumothoraxDokumen25 halamanApproach To Spontaneous PneumothoraxMohdGhazaliAcoyBelum ada peringkat
- Main Tendencies of Nls DevelopmentDokumen3 halamanMain Tendencies of Nls Developmentapi-186101394Belum ada peringkat
- Peer Support Workers Theory and PracticeDokumen16 halamanPeer Support Workers Theory and PracticeSimple FaceBelum ada peringkat
- Welling 2019Dokumen9 halamanWelling 2019riskiBelum ada peringkat
- MuscleDokumen29 halamanMuscleAvdi ShtukaBelum ada peringkat
- MRCP EthicsDokumen33 halamanMRCP EthicstaherBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System DisordersDokumen46 halamanNervous System DisordersJobelle AcenaBelum ada peringkat
- DR Anuj Raj BijukchheDokumen95 halamanDR Anuj Raj BijukchheMUHAMMAD JAWAD HASSANBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanisms Case StudyDokumen13 halamanMechanisms Case Studyshane_tin143Belum ada peringkat
- Retinoblastoma - EyeWikiDokumen11 halamanRetinoblastoma - EyeWikimay171989Belum ada peringkat
- Living With PainDokumen84 halamanLiving With PainGanesh Babu100% (11)
- 3638 Scut SheetDokumen2 halaman3638 Scut Sheetjesse_szymanski3978Belum ada peringkat
- The 8 D's of Stroke CareDokumen3 halamanThe 8 D's of Stroke Caremuhammad fahrizaBelum ada peringkat
- 13 Otoscope UseDokumen61 halaman13 Otoscope UseJayakumar D Swamy0% (1)
- Electrolytes & FluidimbalancesDokumen80 halamanElectrolytes & FluidimbalancesDennis Nyambane MomanyiBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDokumen69 halamanAcute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisJirran CabatinganBelum ada peringkat
- Best Practices For Prospect Research in Healthcare Philanthropy - 2nd EditionDokumen66 halamanBest Practices For Prospect Research in Healthcare Philanthropy - 2nd EditionPaul Jacob RobertsBelum ada peringkat