Terms
Diunggah oleh
Toni Ann DunnDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Terms
Diunggah oleh
Toni Ann DunnHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Terms
What is capital?
Definitions
Any human-made resource that is used to create other goods or services.
What are factors of production?
Land, labour, and capital; the three groups of resources that are used to make all goods and services.
3. What is the purpose of the production possibilities graph? 4. What makes an economy efficient? What is opportunity cost?
Shows alternative ways to use an economy's productive resources.
Using resources in such a way as to maximize the production or output of goods and services Opportunity cost is the alternative we give up when we choose one option over the other.
6. Why is a production possibilities graph curved?
The axes of the graph can show categories of goods and services, such as farm goods and factory goods or capital goods and consumer goods.
What is a physical capital?
All human-made goods that are used to produce other goods and services; tools and buildings
What is human capital?
The skills and knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience.
9. Why is efficiency so important?
Lesser goods and services will be produced in an inefficient economy.
10. Why is technology important to the economy? What is an entrepreneur?
A countries production possibilities depend on both its technological level and the resources it has available. Ambitious leader who combines land, labor, and capital to create and marked new goods or services
12. What is the purpose of a decision-making grid?
Using a decision making grid can help you determine whether you are willing to accept the opportunity cost of a choice you are about to make.
13. What is land, according to an economist? 14. What is a centrally planned economy? What are the characteristics? 15. What are the key economic
To refer to all natural resources used to produce goods and services.
Economic system in which the central government makes all decisions on the production and consumption of goods and services.
What goods and services should be produced? How should these
questions?
goods and services be produced? Who consumes these goods and services?
16. What are the advantages of the free market? 17. What are the characteristics of a traditional economy?
Individuals and privately owned business own the factors of production, make what they want, and buy what they want. A traditional economy relies on habit, custom, or ritual to decide what to produce, how to produce it, and to whom to distribute it. The traditional economic system revolves around the family.
What is a product market?
The market in which households purchase the goods and services that firms produce.
19. What is the purpose of competition? 20. What is the function of the economic system? 21. What is the role of government in a free enterprise system? 22. What determines whether something is a public good? 23. What is gross domestic product? What is externality?
The struggle among producers for the dollars of consumers. Competition is the regulating force behind the free market. The method used by a society to produce the method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and services. We expect the government to carry out its constitutional responsibilities to protect property rights, contracts, and other business activities in our free enterprise system. Shared good or service for which it would be inefficient or impractical "1" To make consumers pay individually "2" to exclude nonpayers The total value of all final goods and services produced in a particular economy. An economic side effect of a good or service that generates benefits or costs to someone other than the person deciding how much to produce or consume.
25. Why is legal equality important to the free enterprise system? What is a business cycle?
Everyone gets the same equal rights.
A period of macroeconomic expansion followed by a period of contraction.
What is scarcity? What is underutilization? What are services? What are goods?
Limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants. Using fewer resources than an economy is capable of using. Actions or activities one person performs of another Physical objects such as clothes or shoes.
What is labor What is a self-interest group? What are factor payments?
The effort that people devote to a task for which they are paid. Own personal gain. The income people receive for supplying factors of production: land, labor, and capital.
What is a product market?
Market in which households purchase the goods and services that firms produce.
What does it mean to privatize?
To sell to individuals state-run firms, which are then allowed to compete with one another in the marketplace
What is a collective? What is laissez-faire?
Large farm leased from the state to groups of peasant farmers. The doctrine that states the government generally should not intervene in the marketplace.
What is standard of living? What is welfare? What is market failure?
Level of economic prosperity. Government aid to the poor A situation in which the market does not distribute resources efficiently.
What is microeconomics?
The study of the economic behavior and decision making of small units, such as individuals, families and businesses.
What is the poverty threshold?
An income level below which income is insufficient to support families and households
What is an interest group?
A private organization that tries to persuade public officials to act or vote according to group members interests.
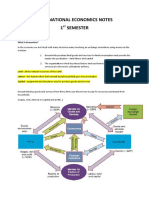
Circular flow diagram
Physical and monetary flow rotate between firms and households
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Scarcity and Efficiency Refers To The Twin Themes of EconomicsDokumen9 halamanScarcity and Efficiency Refers To The Twin Themes of EconomicsYuva Prakash83% (6)
- Jusmiati Kelompok 5Dokumen5 halamanJusmiati Kelompok 5MiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Imperfect CompetitionDokumen28 halamanImperfect Competitionsumitshrivastava82100% (1)
- Sosc 1340Dokumen23 halamanSosc 1340dawBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Introduction To EconomicsDokumen10 halaman1.1 Introduction To Economicsjoel collinsBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2. ActivitiesDokumen3 halamanUnit 2. Activitieswho is sheeeBelum ada peringkat
- Gr12 Basic Ideas Notes NewDokumen11 halamanGr12 Basic Ideas Notes NewAditi JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Toaz - Info CXC Economics Study Guide PRDokumen31 halamanToaz - Info CXC Economics Study Guide PRRickoy Playz100% (1)
- Intro-to-Business Administration - SummaryDokumen14 halamanIntro-to-Business Administration - Summarydaisygetty32Belum ada peringkat
- What Is Economics?Dokumen2 halamanWhat Is Economics?Lupan DumitruBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Market EconomyDokumen17 halamanWhat Is The Market EconomysharifBelum ada peringkat
- Econ Unit Two Study Guide-1Dokumen3 halamanEcon Unit Two Study Guide-1Brayden EvansBelum ada peringkat
- Unit10 Feb2015 PDFDokumen43 halamanUnit10 Feb2015 PDFJared OlivarezBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1Dokumen3 halamanModule 1Chin Keanna BuizonBelum ada peringkat
- Free Market EconomyDokumen3 halamanFree Market EconomyJeanne ClimacoBelum ada peringkat
- The EconomyDokumen25 halamanThe EconomyKim Celestino LingadBelum ada peringkat
- Today's Objectives: - Review Chapter One - QUIZ To Be Uploaded TomorrowDokumen14 halamanToday's Objectives: - Review Chapter One - QUIZ To Be Uploaded Tomorrowwen jing yuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1: Introduction: A. ResourcesDokumen5 halamanChapter 1: Introduction: A. ResourcesGelila TenaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter One and 2 Assessment QuestionsDokumen6 halamanChapter One and 2 Assessment QuestionsSteven Sanderson100% (3)
- Eco 1-1Dokumen6 halamanEco 1-1Binayak MukherjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Abu Naser Mohammad Saif: Assistant ProfessorDokumen29 halamanAbu Naser Mohammad Saif: Assistant ProfessorSH RaihanBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Economic ConceptsDokumen18 halamanBasic Economic ConceptsShakarim AubakirovBelum ada peringkat
- Ch01 - What Is EconomicsDokumen15 halamanCh01 - What Is EconomicsTapasBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Ch1 - 2Dokumen23 halamanMicro Ch1 - 2Awetahegn HagosBelum ada peringkat
- People Make TradeoffsDokumen7 halamanPeople Make TradeoffsgsabiagorBelum ada peringkat
- (Economics) : Managing Within The Dynamic Business Environment: Taking Risks and Making ProfitsDokumen42 halaman(Economics) : Managing Within The Dynamic Business Environment: Taking Risks and Making ProfitsRafayet Omar ShuvoBelum ada peringkat
- Economics NotesDokumen19 halamanEconomics Notesluisemg367Belum ada peringkat
- Role of Government in Market EconomiesDokumen24 halamanRole of Government in Market EconomiesManjunath ShettigarBelum ada peringkat
- Labor Capital Natural Resources Entrepreneur Entrepreneurial AbilityDokumen3 halamanLabor Capital Natural Resources Entrepreneur Entrepreneurial Abilityvivianguo23Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen6 halamanChapter 2Victor Vasquez ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- ITE Chapter 2 SummaryDokumen2 halamanITE Chapter 2 SummaryGregory TurangBelum ada peringkat
- Central Concepts of EconomicsDokumen21 halamanCentral Concepts of EconomicsREHANRAJBelum ada peringkat
- LougdrDokumen44 halamanLougdrjennieBelum ada peringkat
- Total Revenue Is Defined AsDokumen12 halamanTotal Revenue Is Defined AsRia BarisoBelum ada peringkat
- Slide thuyết trình ECODokumen4 halamanSlide thuyết trình ECOTrang Nguyễn thị minhBelum ada peringkat
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDokumen5 halamanTen Principles of Economicshjpa2023-7388-23616Belum ada peringkat
- It Deals With Three Key IssuesDokumen4 halamanIt Deals With Three Key IssuesarunBelum ada peringkat
- Economics Final Study GuideDokumen3 halamanEconomics Final Study Guidemavrik719Belum ada peringkat
- Micro 111 C1 by NayemDokumen10 halamanMicro 111 C1 by NayemHasibul Hasan NayemBelum ada peringkat
- A. A. The Twin Themes of Economics: Scarcity and EfficiencyDokumen19 halamanA. A. The Twin Themes of Economics: Scarcity and EfficiencyIrenej Krayewsky100% (1)
- 001 The Nature and Purpose of Economic ActivityDokumen6 halaman001 The Nature and Purpose of Economic ActivityPratik DahalBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes - Basic Economics 1Dokumen6 halamanLecture Notes - Basic Economics 1lei_sangabrielBelum ada peringkat
- Ch01 - What Is EconomicsDokumen23 halamanCh01 - What Is EconomicsAMINEBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Business Org and MGTDokumen8 halamanChapter 1 Business Org and MGTMargielyn UmbaoBelum ada peringkat
- The Art and Science of EconomicsDokumen27 halamanThe Art and Science of EconomicsIkhwan Al MaidanyBelum ada peringkat
- Kinds of Economic Decision / How Economic Analysis Is Useful in Managerial Decision MakingDokumen5 halamanKinds of Economic Decision / How Economic Analysis Is Useful in Managerial Decision MakingHITESH BANGERABelum ada peringkat
- Abm Lesson 2Dokumen40 halamanAbm Lesson 2Robert BalinoBelum ada peringkat
- Econ 1-Lesson 1 ModuleDokumen9 halamanEcon 1-Lesson 1 ModuleArnie Jovinille Sablay RemullaBelum ada peringkat
- Part I 20101Dokumen6 halamanPart I 20101Lavakesh PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- GR 12 Basic Ideas NotesDokumen21 halamanGR 12 Basic Ideas NotesZayan ChhayaBelum ada peringkat
- Igcse Economics NotesDokumen6 halamanIgcse Economics NotesMunni Chetan0% (1)
- Honors Economics Unit 1 GuideDokumen3 halamanHonors Economics Unit 1 GuideJohn Flair100% (1)
- Notes - EconomicsDokumen69 halamanNotes - EconomicsHaktan OdabasiBelum ada peringkat
- Economics UNIT 1 - Test Review GameDokumen3 halamanEconomics UNIT 1 - Test Review GameMr. PowersBelum ada peringkat
- TOPIC ONE-introdcutionDokumen15 halamanTOPIC ONE-introdcution444 geminiBelum ada peringkat
- International Economic Issues and Challenges Assessment 2Dokumen6 halamanInternational Economic Issues and Challenges Assessment 2Kirschner AmaoBelum ada peringkat
- 001b 10 Principles of EconomicsDokumen7 halaman001b 10 Principles of EconomicsAbigael Esmena100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Economic Issues and ConceptsDokumen87 halamanLecture 1 - Economic Issues and ConceptsB-ton LimbeBelum ada peringkat
- Three Types of Economic Systems: Spirit MembersDokumen25 halamanThree Types of Economic Systems: Spirit MembersAbdelrahman YasserBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Economics and Bangladesh EconomyDokumen6 halamanPrinciples of Economics and Bangladesh EconomyZonal office ChapainawbagnajBelum ada peringkat
- Government and the Economy: Enriching Language and Literacy Through ContentDari EverandGovernment and the Economy: Enriching Language and Literacy Through ContentBelum ada peringkat
- Competition and EfficiencyDokumen26 halamanCompetition and EfficiencyBharathi KamathBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of ProductionDokumen30 halamanTheory of ProductionMerzi BadoyBelum ada peringkat
- Nechyba 2e CH 16ABDokumen47 halamanNechyba 2e CH 16ABsnazrulBelum ada peringkat
- Model Examination 2016-17: Ii) All Questions Carry One MarkDokumen3 halamanModel Examination 2016-17: Ii) All Questions Carry One Markm.arunBelum ada peringkat
- Public GoodDokumen48 halamanPublic GoodPutri IndahSariBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Price Determination in Different Markets Part 2Dokumen46 halamanChapter 4 Price Determination in Different Markets Part 2siva883100% (2)
- EconomicsDokumen31 halamanEconomicsLakshmi KruthigaBelum ada peringkat
- Rotten Kid TheoremDokumen4 halamanRotten Kid TheoremKashi KafleBelum ada peringkat
- Cost ConceptsDokumen19 halamanCost ConceptsPrabha Karan100% (1)
- Lab 4 1 Econ203 b06Dokumen20 halamanLab 4 1 Econ203 b06api-235832666Belum ada peringkat
- KeynesDokumen29 halamanKeynesCatarina DuarteBelum ada peringkat
- Isocost Line: © 2008 Prentice Hall Business Publishing - Microeconomics - Pindyck/Rubinfeld, 7eDokumen12 halamanIsocost Line: © 2008 Prentice Hall Business Publishing - Microeconomics - Pindyck/Rubinfeld, 7eMaple OcenaBelum ada peringkat
- Mgea02 TT1 2011F ADokumen9 halamanMgea02 TT1 2011F AexamkillerBelum ada peringkat
- The Determinants of Market StructureDokumen15 halamanThe Determinants of Market StructureBharathi KamathBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2: The Demand For Money: Learning ObjectivesDokumen12 halamanChapter 2: The Demand For Money: Learning Objectiveskaps2385Belum ada peringkat
- National Income: Three and Four Sector ModelDokumen13 halamanNational Income: Three and Four Sector ModelKratika PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 10-Externality and Public GoodsDokumen4 halamanExercise 10-Externality and Public GoodsJirayusBelum ada peringkat
- The Law of Diminishing Marginal ReturnsDokumen17 halamanThe Law of Diminishing Marginal ReturnsrazishadabBelum ada peringkat
- MicroEconomics 2012 Midterms at IIM KozhikodeDokumen5 halamanMicroEconomics 2012 Midterms at IIM KozhikodeShri DharBelum ada peringkat
- IB Eco Paper SLDokumen9 halamanIB Eco Paper SLSatyamBairoliyaBelum ada peringkat
- List of BooksDokumen92 halamanList of BooksKaran SuriBelum ada peringkat
- HET New+Classical+and+New+KeynesianDokumen55 halamanHET New+Classical+and+New+Keynesiansyedur92Belum ada peringkat
- Attfield Et Al. - Rational Expectations in Macroeconomics NOTESDokumen6 halamanAttfield Et Al. - Rational Expectations in Macroeconomics NOTESShay Rahman100% (1)
- Marginal Utility and Consumer Choice: Chapter in A NutshellDokumen36 halamanMarginal Utility and Consumer Choice: Chapter in A Nutshelleinsteinspy67% (3)
- Econ 4351 - Practice Exam - Midterm IDokumen7 halamanEcon 4351 - Practice Exam - Midterm IAdam RenfroBelum ada peringkat
- Economic OptimizationDokumen28 halamanEconomic OptimizationharlloveBelum ada peringkat
- Econ Chapter 15 QuizwaDokumen6 halamanEcon Chapter 15 Quizwaalex324usBelum ada peringkat
- PQ4Dokumen11 halamanPQ4Swastik MohapatraBelum ada peringkat