Open Loop and Closed Loop: Description - Modes of Operation
Diunggah oleh
Z_SADeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Open Loop and Closed Loop: Description - Modes of Operation
Diunggah oleh
Z_SAHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
KJ
DATA LINK CONNECTOR (Continued)
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES
8E - 11
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
Fig. 7 DATA LINK CONNECTOR LOCATION
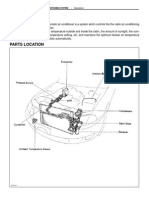
DESCRIPTION - PCM The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is located in the engine compartment (Fig. 8). The PCM is referred to as JTEC.
DESCRIPTION - MODES OF OPERATION As input signals to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) change, the PCM adjusts its response to the output devices. For example, the PCM must calculate different injector pulse width and ignition timing for idle than it does for wide open throttle (WOT). The PCM will operate in two different modes: Open Loop and Closed Loop. During Open Loop modes, the PCM receives input signals and responds only according to preset PCM programming. Input from the oxygen (O2S) sensors is not monitored during Open Loop modes. During Closed Loop modes, the PCM will monitor the oxygen (O2S) sensors input. This input indicates to the PCM whether or not the calculated injector pulse width results in the ideal air-fuel ratio. This ratio is 14.7 parts air-to-1 part fuel. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content through the O2S sensor, the PCM can fine tune the injector pulse width. This is done to achieve optimum fuel economy combined with low emission engine performance. The fuel injection system has the following modes of operation: Ignition switch ON Engine start-up (crank) Engine warm-up Idle Cruise Acceleration Deceleration Wide open throttle (WOT) Ignition switch OFF The ignition switch On, engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up, acceleration, deceleration and wide open throttle modes are Open Loop modes. The idle and cruise modes, (with the engine at operating temperature) are Closed Loop modes.
IGNITION SWITCH (KEY-ON) MODE
Fig. 8 PCM LOCATION
This is an Open Loop mode. When the fuel system is activated by the ignition switch, the following actions occur: The PCM pre-positions the idle air control (IAC) motor. The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure from the MAP sensor input to determine basic fuel strategy. The PCM monitors the engine coolant temperature sensor input. The PCM modifies fuel strategy based on this input. Intake manifold air temperature sensor input is monitored. Throttle position sensor (TPS) is monitored. The auto shutdown (ASD) relay is energized by the PCM for approximately three seconds.
8E - 12
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
The fuel pump is energized through the fuel pump relay by the PCM. The fuel pump will operate for approximately three seconds unless the engine is operating or the starter motor is engaged. The O2S sensor heater element is energized via the ASD or O2S heater relay. The O2S sensor input is not used by the PCM to calibrate air-fuel ratio during this mode of operation.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES
KJ
This is an Open Loop mode. The following actions occur when the starter motor is engaged. The PCM receives inputs from: Battery voltage Engine coolant temperature sensor Crankshaft position sensor Intake manifold air temperature sensor Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor Throttle position sensor (TPS) Camshaft position sensor signal The PCM monitors the crankshaft position sensor. If the PCM does not receive a crankshaft position sensor signal within 3 seconds of cranking the engine, it will shut down the fuel injection system. The fuel pump is activated by the PCM through the fuel pump relay. Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then control the injection sequence and injector pulse width by turning the ground circuit to each individual injector on and off. The PCM determines the proper ignition timing according to input received from the crankshaft position sensor.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the idle air control (IAC) motor and adjusts ignition timing. The PCM operates the A/C compressor clutch through the A/C compressor clutch relay. This is done if A/C has been selected by the vehicle operator and specified pressures are met at the high and lowpressure A/C switches. Refer to Heating and Air Conditioning for additional information. When engine has reached operating temperature, the PCM will begin monitoring O2S sensor input. The system will then leave the warm-up mode and go into closed loop operation.
IDLE MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. During engine warmup, the PCM receives inputs from: Battery voltage Crankshaft position sensor Engine coolant temperature sensor Intake manifold air temperature sensor Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor Throttle position sensor (TPS) Camshaft position sensor signal Park/neutral switch (gear indicator signalauto. trans. only) Air conditioning select signal (if equipped) Air conditioning request signal (if equipped) Based on these inputs the following occurs: Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then control the injection sequence and injector pulse width by turning the ground circuit to each individual injector on and off.
When the engine is at operating temperature, this is a Closed Loop mode. At idle speed, the PCM receives inputs from: Air conditioning select signal (if equipped) Air conditioning request signal (if equipped) Battery voltage Crankshaft position sensor Engine coolant temperature sensor Intake manifold air temperature sensor Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor Throttle position sensor (TPS) Camshaft position sensor signal Battery voltage Park/neutral switch (gear indicator signalauto. trans. only) Oxygen sensors Based on these inputs, the following occurs: Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then control injection sequence and injector pulse width by turning the ground circuit to each individual injector on and off. The PCM monitors the O2S sensor input and adjusts air-fuel ratio by varying injector pulse width. It also adjusts engine idle speed through the idle air control (IAC) motor. The PCM adjusts ignition timing by increasing and decreasing spark advance. The PCM operates the A/C compressor clutch through the A/C compressor clutch relay. This is done if A/C has been selected by the vehicle operator and specified pressures are met at the high and lowpressure A/C switches. Refer to Heating and Air Conditioning for additional information.
CRUISE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature, this is a Closed Loop mode. At cruising speed, the PCM receives inputs from: Air conditioning select signal (if equipped) Air conditioning request signal (if equipped)
KJ
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Battery voltage Engine coolant temperature sensor Crankshaft position sensor Intake manifold air temperature sensor Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor Throttle position sensor (TPS) Camshaft position sensor signal Park/neutral switch (gear indicator signalauto. trans. only) Oxygen (O2S) sensors Based on these inputs, the following occurs: Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then adjust the injector pulse width by turning the ground circuit to each individual injector on and off. The PCM monitors the O2S sensor input and adjusts air-fuel ratio. It also adjusts engine idle speed through the idle air control (IAC) motor. The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the ground path to the coil(s) on and off. The PCM operates the A/C compressor clutch through the clutch relay. This happens if A/C has been selected by the vehicle operator and requested by the A/C thermostat.
ACCELERATION MODE
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES
8E - 13
Based on the above inputs, the PCM will adjust engine idle speed through the idle air control (IAC) motor. The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the ground path to the coil on and off.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. The PCM recognizes an abrupt increase in throttle position or MAP pressure as a demand for increased engine output and vehicle acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width in response to increased throttle opening.
DECELERATION MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. During wide open throttle operation, the PCM receives the following inputs. Battery voltage Crankshaft position sensor Engine coolant temperature sensor Intake manifold air temperature sensor Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor Throttle position sensor (TPS) Camshaft position sensor signal During wide open throttle conditions, the following occurs: Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then control the injection sequence and injector pulse width by turning the ground circuit to each individual injector on and off. The PCM ignores the oxygen sensor input signal and provides a predetermined amount of additional fuel. This is done by adjusting injector pulse width. The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the ground path to the coil(s) on and off.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature, this is an Open Loop mode. During hard deceleration, the PCM receives the following inputs. Air conditioning select signal (if equipped) Air conditioning request signal (if equipped) Battery voltage Engine coolant temperature sensor Crankshaft position sensor Intake manifold air temperature sensor Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor Throttle position sensor (TPS) Camshaft position sensor signal Park/neutral switch (gear indicator signalauto. trans. only) Vehicle speed If the vehicle is under hard deceleration with the proper rpm and closed throttle conditions, the PCM will ignore the oxygen sensor input signal. The PCM will enter a fuel cut-off strategy in which it will not supply a ground to the injectors. If a hard deceleration does not exist, the PCM will determine the proper injector pulse width and continue injection.
When ignition switch is turned to OFF position, the PCM stops operating the injectors, ignition coil, ASD relay and fuel pump relay.
DESCRIPTION - 5 VOLT SUPPLIES Two different Powertrain Control Module (PCM) five volt supply circuits are used; primary and secondary. DESCRIPTION - IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSE This circuit ties the ignition switch to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). DESCRIPTION - POWER GROUNDS The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has 2 main grounds. Both of these grounds are referred to as power grounds. All of the high-current, noisy, electrical devices are connected to these grounds as well as all of the sensor returns. The sensor return comes into the sensor return circuit, passes through noise suppression, and is then connected to the power ground. The power ground is used to control ground circuits for the following PCM loads: Generator field winding
8E - 14
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Fuel injectors Ignition coil(s) Certain relays/solenoids Certain sensors
DESCRIPTION - SENSOR RETURN The Sensor Return circuits are internal to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Sensor Return provides a lownoise ground reference for all engine control system sensors. Refer to Power Grounds for more information.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES
KJ
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM The PCM operates the fuel system. The PCM is a pre-programmed, triple microprocessor digital computer. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio, emission control devices, charging system, certain transmission features, speed control, air conditioning compressor clutch engagement and idle speed. The PCM can adapt its programming to meet changing operating conditions. The PCM receives input signals from various switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operations through different system components. These components are referred to as Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Outputs. The sensors and switches that provide inputs to the PCM are considered Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Inputs. The PCM adjusts ignition timing based upon inputs it receives from sensors that react to: engine rpm, manifold absolute pressure, engine coolant temperature, throttle position, transmission gear selection (automatic transmission), vehicle speed, power steering pump pressure, and the brake switch. The PCM adjusts idle speed based on inputs it receives from sensors that react to: throttle position, vehicle speed, transmission gear selection, engine coolant temperature and from inputs it receives from the air conditioning clutch switch and brake switch. Based on inputs that it receives, the PCM adjusts ignition coil dwell. The PCM also adjusts the generator charge rate through control of the generator field and provides speed control operation.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
J1850 bus (+) circuits J1850 bus (-) circuits Camshaft position sensor signal Crankshaft position sensor Data link connection for DRB scan tool Engine coolant temperature sensor Fuel level (through J1850 circuitry) Generator (battery voltage) output Ignition circuit sense (ignition switch in on/off/ crank/run position) Intake manifold air temperature sensor Knock sensors (2 on 3.7L engine) Leak detection pump (switch) sense (if equipped) Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor Oil pressure Oxygen sensors Park/neutral switch (auto. trans. only) Power ground Power steering pressure switch Sensor return Signal ground Speed control multiplexed single wire input Throttle position sensor Transfer case switch (4WD range position) Vehicle speed sensor
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
A/C request (if equipped with factory A/C) A/C select (if equipped with factory A/C) A/C pressure transducer Auto shutdown (ASD) sense Battery temperature Battery voltage Brake switch
A/C clutch relay Auto shutdown (ASD) relay J1850 bus (+/-) circuits for: speedometer, voltmeter, fuel gauge, oil pressure gauge/lamp, engine temp. gauge and speed control warn. lamp Clutch pedal position switch override relay Data link connection for DRB scan tool EGR valve control solenoid (if equipped) EVAP canister purge solenoid Five volt sensor supply (primary) Five volt sensor supply (secondary) Fuel injectors Fuel pump relay Generator field driver (-) Generator field driver (+) Idle air control (IAC) motor Ignition coil(s) Leak detection pump (if equipped) Malfunction indicator lamp (Check engine lamp). Driven through J1850 circuits. Oxygen sensor heater relays Oxygen sensors (pulse width modulated) Radiator cooling fan relay (pulse width modulated) Speed control vacuum solenoid Speed control vent solenoid Tachometer (if equipped). Driven through J1850 circuits.
8I - 4
IGNITION CONTROL
KJ
AUTO SHUT DOWN RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT The 5pin, 12volt, Automatic Shutdown (ASD) relay is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
OPERATION - ASD SENSE - PCM INPUT A 12 volt signal at this input indicates to the PCM that the ASD has been activated. The relay is used to connect the oxygen sensor heater elements, oxygen sensor heater relay, ignition coil and fuel injectors to 12 volt + power supply. This input is used only to sense that the ASD relay is energized. If the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) does not see 12 volts at this input when the ASD should be activated, it will set a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT The ASD relay supplies battery voltage (12+ volts) to the fuel injectors and ignition coil(s). With certain emissions packages it also supplies 12volts to the oxygen sensor heating elements and the oxygen sensor heater relay. The ground circuit for the coil within the ASD relay is controlled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The PCM operates the ASD relay by switching its ground circuit on and off. The ASD relay will be shutdown, meaning the 12volt power supply to the ASD relay will be de-activated by the PCM if the ignition key is left in the ON position. This is if the engine has not been running for approximately 1.8 seconds.
Fig. 2 TYPE 1 RELAY (ISO MICRO RELAY)
Fig. 3 ASD AND FUEL PUMP RELAY TERMINALS TYPE 2
TERMINAL LEGEND NUMBER 30 85 86 87 87A IDENTIFICATION COMMON FEED COIL GROUND COIL BATTERY NORMALLY OPEN NORMALLY CLOSED
bottom of each relay are numbered. Two different types of relays may be used, (Fig. 2) or (Fig. 3). Terminal number 30 is connected to battery voltage. For both the ASD and fuel pump relays, terminal 30 is connected to battery voltage at all times. The PCM grounds the coil side of the relay through terminal number 85. Terminal number 86 supplies voltage to the coil side of the relay. When the PCM de-energizes the ASD and fuel pump relays, terminal number 87A connects to terminal 30. This is the Off position. In the off position,
The following description of operation and tests apply only to the Automatic Shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays. The terminals on the
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ASD AND FUEL PUMP RELAYS
voltage is not supplied to the rest of the circuit. Terminal 87A is the center terminal on the relay. When the PCM energizes the ASD and fuel pump relays, terminal 87 connects to terminal 30. This is the On position. Terminal 87 supplies voltage to the rest of the circuit. The following procedure applies to the ASD and fuel pump relays. (1) Remove relay from connector before testing. (2) With the relay removed from the vehicle, use an ohmmeter to check the resistance between terminals 85 and 86. The resistance should be 75 ohms +/5 ohms. (3) Connect the ohmmeter between terminals 30 and 87A. The ohmmeter should show continuity between terminals 30 and 87A.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Jeep Grand Cherokee PCM Modes of OperationDokumen6 halamanJeep Grand Cherokee PCM Modes of OperationRoyalhawk200290% (10)
- E Theory OperationDokumen7 halamanE Theory Operationdguruge8Belum ada peringkat
- Open Loop and Closed Loop: Description - Modes of OperationDokumen5 halamanOpen Loop and Closed Loop: Description - Modes of OperationLeonardBelum ada peringkat
- E C M InputsDokumen12 halamanE C M InputsMario RaafatBelum ada peringkat
- 10 PP T235 Fuel InjDokumen22 halaman10 PP T235 Fuel InjSivi NallamothuBelum ada peringkat
- 10 PP T235 Fuel InjDokumen22 halaman10 PP T235 Fuel InjSandeep BuntyBelum ada peringkat
- I6 4.0 Part 8 - Induction and ExhaustDokumen10 halamanI6 4.0 Part 8 - Induction and ExhaustHenrique BelliniBelum ada peringkat
- EUI Fuel SystemDokumen27 halamanEUI Fuel SystemMahmoud ElsayedBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Service Information3Dokumen4 halamanTechnical Service Information3JoseBelum ada peringkat
- Toyota Inputs & SensorsDokumen22 halamanToyota Inputs & Sensorsfasdomingo100% (1)
- GDIDokumen7 halamanGDIlinhda561Belum ada peringkat
- Fuel System DiagnosisDokumen34 halamanFuel System DiagnosisAhmed AbazaBelum ada peringkat
- Ignition Timing Inspection: Scan Tool Data Vehicle Condition Normal Condition / Reference ValueDokumen6 halamanIgnition Timing Inspection: Scan Tool Data Vehicle Condition Normal Condition / Reference ValueEric CarterBelum ada peringkat
- 10 PP T235 Fuel InjDokumen22 halaman10 PP T235 Fuel InjShankara SubramanianBelum ada peringkat
- DENSO SystemsDokumen34 halamanDENSO Systemsthailan100% (3)
- Isuzu EngineDokumen53 halamanIsuzu EngineSmaileRun78% (18)
- Sistema de Control de EmisionesDokumen45 halamanSistema de Control de EmisionesDavid ParariBelum ada peringkat
- Motor 4.3L (Blazer 98) - Teoria y FuncionamientoDokumen17 halamanMotor 4.3L (Blazer 98) - Teoria y Funcionamientogdilio50% (2)
- 9913 Ap 34Dokumen108 halaman9913 Ap 34احمدميدوBelum ada peringkat
- Automotive Sensors & ActuatorsDokumen108 halamanAutomotive Sensors & ActuatorsSatyaAditham90% (10)
- Powertrain Control SoftwareDokumen6 halamanPowertrain Control SoftwareJosé AntonioBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 5: Denso-Common Rail System: ObjectivesDokumen27 halamanLesson 5: Denso-Common Rail System: ObjectivesSenghakPhally100% (1)
- 3grfse 1Dokumen42 halaman3grfse 1Zoli Borbely100% (3)
- Climate Control System Description Ford Fiesta 1.6Dokumen10 halamanClimate Control System Description Ford Fiesta 1.6Ismael LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Descripcion de SensoresDokumen2 halamanDescripcion de SensoresJose FavaBelum ada peringkat
- Bosch Motronic ME7.9.10Dokumen32 halamanBosch Motronic ME7.9.10paulyvon.dicuBelum ada peringkat
- Ob Di I Data InterpretationDokumen8 halamanOb Di I Data InterpretationMohamed WahiebBelum ada peringkat
- Codigos VimsDokumen42 halamanCodigos VimsJuan Ricardo Bolivar PilcoBelum ada peringkat
- Name DDokumen38 halamanName DDarshan GondkarBelum ada peringkat
- Acce Lera To PedalDokumen5 halamanAcce Lera To PedalEKOBelum ada peringkat
- Engine Control System Engine Control System System Diagram: To EsmDokumen40 halamanEngine Control System Engine Control System System Diagram: To EsmAlex RonBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3 Automotive ElectronicsDokumen38 halamanModule 3 Automotive Electronicsdaalidhananjaya2002Belum ada peringkat
- Presentation On Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 92,77,83Dokumen19 halamanPresentation On Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 92,77,83sahil k mehta100% (2)
- Report-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiDokumen19 halamanReport-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiHemant PatraBelum ada peringkat
- Cat c6 6 Troubleshooting Manual PDFDokumen10 halamanCat c6 6 Troubleshooting Manual PDFAlexendra100% (2)
- Siemens MS43 SystemsDokumen26 halamanSiemens MS43 SystemszefrenchBelum ada peringkat
- AC DescriptionDokumen7 halamanAC DescriptionrxhughesBelum ada peringkat
- Engine PADokumen49 halamanEngine PAlartsim115Belum ada peringkat
- Multi Point Fuel InjectionDokumen15 halamanMulti Point Fuel Injectionಶಿವರಾಜ್ ಎನ್Belum ada peringkat
- Tac PDFDokumen3 halamanTac PDFZool Car زول كارBelum ada peringkat
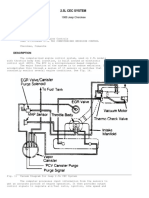
- 4.0L Cec System: 1988 Jeep CherokeeDokumen17 halaman4.0L Cec System: 1988 Jeep CherokeefredericdiBelum ada peringkat
- Acronyms and DefinitionsDokumen8 halamanAcronyms and DefinitionsAlbert BriceñoBelum ada peringkat
- Analog Sensor: SupplyDokumen8 halamanAnalog Sensor: SupplyYUDI WAHYUDI 17249Belum ada peringkat
- 13a Mfi 1.5LDokumen164 halaman13a Mfi 1.5LDian Zahari Zainal AbidinBelum ada peringkat
- Fuel System Specification: Use Only Unleaded Fuel Rated at 89 Octane or HigherDokumen5 halamanFuel System Specification: Use Only Unleaded Fuel Rated at 89 Octane or HigheryermainBelum ada peringkat
- Fuel System Specification: Use Only Unleaded Fuel Rated at 89 Octane or HigherDokumen5 halamanFuel System Specification: Use Only Unleaded Fuel Rated at 89 Octane or HigheryermainBelum ada peringkat
- Torque ShiftDokumen43 halamanTorque ShiftDavid Rosado100% (1)
- Data Stream OBD2Dokumen2 halamanData Stream OBD2kamaleon doradoBelum ada peringkat
- EFI BasicsDokumen168 halamanEFI BasicsBryanMaes100% (1)
- 303-03 Engine Cooling 2.3L EcoBoost - Description and Operation - System OperationDokumen3 halaman303-03 Engine Cooling 2.3L EcoBoost - Description and Operation - System OperationCARLOS LIMADABelum ada peringkat
- Auto Lab ManualDokumen147 halamanAuto Lab ManualjhpandiBelum ada peringkat
- 2.5l Cec SystemDokumen37 halaman2.5l Cec Systemdaniel lacerdaBelum ada peringkat
- ATPL Inst 8.3 PDFDokumen4 halamanATPL Inst 8.3 PDFKoustubh VadalkarBelum ada peringkat
- Phases of Operation - Injection System Magneti Marelli 6LPDokumen16 halamanPhases of Operation - Injection System Magneti Marelli 6LPGrizono MassimoBelum ada peringkat
- On Board DiagnosticsDokumen52 halamanOn Board Diagnosticsjayasundar100% (1)
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SDari EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SBelum ada peringkat
- Variable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersDari EverandVariable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersBelum ada peringkat
- Automotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 2)Dari EverandAutomotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 2)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Curriculum For Automobile Mechanic: (1 Year)Dokumen34 halamanCurriculum For Automobile Mechanic: (1 Year)Sakib M F KBelum ada peringkat
- BMW CodesDokumen22 halamanBMW CodesOctavio Maciel90% (21)
- Troubleshooting Marine Engine Electrical SystemsDokumen4 halamanTroubleshooting Marine Engine Electrical SystemsSeena Zharaa100% (1)
- Gotech MFIX ManualDokumen24 halamanGotech MFIX ManualJonathan RatcliffBelum ada peringkat
- Scorpio Rev116Dokumen104 halamanScorpio Rev116luisxdBelum ada peringkat
- P2300 Ignition Coil A Primary Control Circuit LowDokumen1 halamanP2300 Ignition Coil A Primary Control Circuit LowSendi IndartoBelum ada peringkat
- Mounting Instructions - 123ignitionDokumen5 halamanMounting Instructions - 123ignitionminimaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Spec 5320 469Dokumen99 halamanSpec 5320 469IvánGarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- MT80 Engine Management SystemDokumen34 halamanMT80 Engine Management SystemHenryMachado100% (1)
- IntroductionDokumen5 halamanIntroductionHarsh GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- CruiserDokumen221 halamanCruisermemorider93% (14)
- SUNBEAM S7 and S8 Tech InfoDokumen74 halamanSUNBEAM S7 and S8 Tech InfoP JBelum ada peringkat
- A Distributor-Based Breaker-Point Ignition System'S Wiring Electronic Ignition System'SDokumen3 halamanA Distributor-Based Breaker-Point Ignition System'S Wiring Electronic Ignition System'SAin Natasya ZulfikreeBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Lab 1st Yr Lab ManualDokumen58 halamanMechanical Lab 1st Yr Lab Manualpiyush138090Belum ada peringkat
- How To Repair Small Engines PDFDokumen4 halamanHow To Repair Small Engines PDFStephane Durel MbidaBelum ada peringkat
- Speeduino ManualDokumen131 halamanSpeeduino ManualMauricio ChirichignoBelum ada peringkat
- SM 25Dokumen17 halamanSM 25ildefonsoBelum ada peringkat
- ST400 Series Tachometers: User ManualDokumen22 halamanST400 Series Tachometers: User ManualEdison100Belum ada peringkat
- Magneto Ignition System Definition Parts Working Principle Advantages Disadvantages Application NotesDokumen6 halamanMagneto Ignition System Definition Parts Working Principle Advantages Disadvantages Application NotesCharan BiradarBelum ada peringkat
- A-I Power Generator Manual (SUA12000E)Dokumen30 halamanA-I Power Generator Manual (SUA12000E)whagen197456% (9)
- RE1102020Dokumen3 halamanRE1102020francis puthuserilBelum ada peringkat
- Ignição VortecDokumen38 halamanIgnição VortecFabricio Félix100% (1)
- Daihatsu Type k3 Engine Service Manual No9737 No9332 No 9237 Ignition SystemDokumen10 halamanDaihatsu Type k3 Engine Service Manual No9737 No9332 No 9237 Ignition SystemJoko Mardiyanto100% (1)
- Distributor Less Ignition SystemsDokumen4 halamanDistributor Less Ignition SystemsxLibelle100% (5)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics - William Ribbens 6edDokumen481 halamanUnderstanding Automotive Electronics - William Ribbens 6edOleksiy OsiychukBelum ada peringkat
- Installation Guide: © 2004 Directed Electronics, Inc. Vista, CA N909610 08-04Dokumen59 halamanInstallation Guide: © 2004 Directed Electronics, Inc. Vista, CA N909610 08-04Robert RooseBelum ada peringkat
- CEE CERT EXAM Sample Paper Set-3Dokumen11 halamanCEE CERT EXAM Sample Paper Set-3Arnaw pandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Enfield Bullet Workshop Manual 2000 2 PDFDokumen53 halamanEnfield Bullet Workshop Manual 2000 2 PDFsivakumar natarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Instrucciones Edelbrock Pro-FlowDokumen32 halamanInstrucciones Edelbrock Pro-FlowWikeon HungBelum ada peringkat
- Om CombustionDokumen121 halamanOm CombustionSergio Recabarren100% (1)