Worksheet - Economics - Supply and Demand
Diunggah oleh
Awais UR RehmanDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Worksheet - Economics - Supply and Demand
Diunggah oleh
Awais UR RehmanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
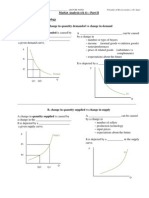
Economics Supply and Demand
Supply _____ Supply _____ Demand _____ Demand _____ Quantity _____ Quantity _____ Price _____ Price _____
Demand
Definition:
Supply
Definition:
Non-Price Factors that Change Demand 1. Substitutional Effect
Non-Price Factors that Change Supply 1. Government Policies
2. Complimentary Good
2. Cost of Production
3. Income Effect
3. Change in Technology
4. Change in the Number of Consumers
4. Natural Disasters
5. Change in Consumer Expectations
5. Other (Strikes, Imports)
6. Change in Consumer Tastes Types of Demand 1. Example: 2. Example:
Law of Diminishing Returns -
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility -
Supply and Demand Practice
1. Create a demand curve based on the following schedule for 2 liter Pepsi-Cola: Price (P) $.90 $1.00 $1.10 $1.20 $1.30 Demand (D) 6 5 4 3 3
2. Demonstrate the effect on the demand curve if the price of Coca-Cola rises. 3. Demonstrate the effect on demand if the news report describes the negative health risks when too many soft drinks are consumed. 4. Identify the non-price factors that changed demand in #2 and #3. 5. Create a supply curve based on the following schedule for 2 liter Pepsi-Cola: Price (P) $.90 $1.00 $1.10 $1.20 $1.30 Supply (S) 2 3 4 5 6
6. Demonstrate the effect on the supply curve if Pepsi-Cola employees go on strike. 7. Demonstrate the effect on the supply curve if the price of sugar rises. 8. Identify the non-price factors that changed supply in #6 and #7. 9. Combine the original demand and supply curves onto one graph. 10. What is the market price? 11. Add the curves from #2 and #6 to the same graph use in #9. 12. What is the new market price? 13. What economic condition exists above the market price? 14. What economic condition exists below the market price? 15. How do businesses deal with each of those conditions?
Reasons For Changes in Demand
A B C D E
Price (P)
Beef consumption in May
Read the following eight newspaper headlines. In each case decide if the event will cause a change in the demand for beef. If so, determine if it is an increase or a decrease, and write the correct answer. Begin at curve C. If you think headline 1 means there will be a decrease in demand, write decrease in the first blank and B in the second blank: move to curve B to do headline 2. If you think demand will increase, write increase and D in the blanks for headline 1; move to curve D to do headline 2. Move only one curve at a time. Do not skip from say A to C even if you think the headline means there will be a large change in demand. Do not go beyond the five curves. If you are at A and the next headline implies a decrease in demand, you goofed somewhere. There is one headline which implies that the demand for beef does not change.
5. MIGRATORY BIRDS HEAD NORTH, SUMMER AWAITS Demand _______________ Curve ________
6. REAL INCOME FOR AMERICANS DROPS 3RD
MONTH IN ROW Demand _______________ Curve ________
7. CHARCOAL SHORTAGE THREATENS MEMORIAL DAY COOKOUTS Demand _______________ Curve ________ 8. NATIONWIDE FAD: THE DISCO-BURGER Demand _______________ Curve ________ Optional Bonus: Categorize each change in demand in the exercise above according to the reason that demand changed. Write the number of the headline(s) next to the reason for the change in demand. One category will have two headlines numbers. _____ A change in consumer expectations.
1. PRICE OF BEEF TO RISE IN JUNE Demand _______________ Curve ________
2. MILLIONS OF ALIENS SWELL U.S. POPULATION Demand _______________ Curve ________
_____ A change in consumer tastes. _____ A change in number of consumers in the market. _____ A change in income.
3. PORK PRICES DROP Demand _______________
Curve ________
_____ A change in price of a substitute good. _____ A change in the price of a complementary good.
4. SURGEON GENERAL WARNS THAT EATING BEEF CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO HEALTH Demand _______________ Curve ________
Reasons For Change in Supply
A B C D E
Price (P)
Supply of foreign and domestically produced cars in the U. S. (Q) Read the following seven newspaper headlines. In each case, decide if the event will cause any change in the supply of cars. If so, determine if it is an increase or decrease, and write the correct answer. Begin at curve C. If you think headline 1 means there will be a decrease in supply, write decrease in the first blank and B in the second blank; move to curve B to do headline 2. If you think supply will increase, write increase and D in the blanks for headline 2; move to curve D to do headline 3. Move only one curve at a time. Do not skip from say A to C even if you think the headline means there will be a large change in supply. Do not go beyond the five curves. If you are at A and the next headline implies a decrease in supply, you goofed somewhere. There is one headline which implies that the supply of cars does not change. 4. NEW AUTO IMPORT QUOTAS REDUCE FLOW OF FOREIGN CARS Supply _______________ Curve ________ 5. COST OF STEEL RISES Supply _______________
Curve ________
6. AUTO PRODUCER GOES BANKRUPT, CLOSES OPERATION Supply _______________ Curve ________ 7. BUYERS REJECT NEW MODELS Supply _______________ Curve ________
1. AUTO WORKERS UNION AGREES TO WAGE AND FRINGE CUTS Supply _______________ Curve ________ 2. NEW ROBOT TECHNOLOGY INCREASES EFFIEIENCY Supply _______________ Curve ________ 3. NATIONWIDE AUTO STRIKE BEGAN AT MIDNIGHT Supply _______________ Curve ________
Optional Bonus: Categorize each change in supply according to the reason that affected supply. Write the number of the headline next to the reason for the change in supply. In some cases, more than one headline could be matched to a reason.
_____ A change in the cost of production. _____ A change in technology. _____ Natural disaster/other event that causes decrease in production. _____ Government policies.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Book Value Per Share: RequiredDokumen19 halamanBook Value Per Share: RequiredLouise73% (11)
- Simple Economics For O.LevelsDokumen86 halamanSimple Economics For O.LevelsthugnatureBelum ada peringkat
- Furry Tales FinalDokumen46 halamanFurry Tales FinalRitu Makkar100% (1)
- Worksheet #3 - Supply and DemandDokumen2 halamanWorksheet #3 - Supply and Demandhuhu4545Belum ada peringkat
- Small Farm Decision-Making & Enterprise Planning Workbook: Cooperative ExtensionDokumen18 halamanSmall Farm Decision-Making & Enterprise Planning Workbook: Cooperative ExtensionTrisha BakerBelum ada peringkat
- Demand WorksheetDokumen4 halamanDemand Worksheetsusheel kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Business Management Course of IB-DP 2024Dokumen20 halamanBusiness Management Course of IB-DP 2024Tata MarchyquitaBelum ada peringkat
- IB Workshop Summary For The New SyllabusDokumen54 halamanIB Workshop Summary For The New SyllabusousoulegrandBelum ada peringkat
- Economics Unit 1 Revision NotesDokumen32 halamanEconomics Unit 1 Revision NotesJohn EdwardBelum ada peringkat
- Mergers and Acquisitions 314 v1 PDFDokumen434 halamanMergers and Acquisitions 314 v1 PDFKavita KumawatBelum ada peringkat
- Economics Notes Chapter 3 - Supply and DemandDokumen4 halamanEconomics Notes Chapter 3 - Supply and Demandruchia17100% (2)
- IGCSE Economics Chapter 30 Key Concept - Macroeconomic ObjectivesDokumen2 halamanIGCSE Economics Chapter 30 Key Concept - Macroeconomic ObjectivesemilyBelum ada peringkat
- A Level Essay Questions by TopicsDokumen11 halamanA Level Essay Questions by TopicsDD97Belum ada peringkat
- 1.understand The Case Study IbGeniusDokumen13 halaman1.understand The Case Study IbGeniusVinodBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Economic Ideas: Opportunity Cost.Dokumen37 halamanBasic Economic Ideas: Opportunity Cost.huzaifathe007100% (2)
- IGCSE Economics IntroDokumen16 halamanIGCSE Economics IntrosilBelum ada peringkat
- Paper - 1 - MARK SCHEME and EXAMINER COMMENTS - SLDokumen44 halamanPaper - 1 - MARK SCHEME and EXAMINER COMMENTS - SLlarry wangBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank for Introductory Economics: And Introductory Macroeconomics and Introductory MicroeconomicsDari EverandTest Bank for Introductory Economics: And Introductory Macroeconomics and Introductory MicroeconomicsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Jamba Juice Company AnalysisDokumen24 halamanJamba Juice Company AnalysisMary Kim100% (6)
- MICROECONOMICS - Revison Notes 2013 S1 Ques Set 2Dokumen6 halamanMICROECONOMICS - Revison Notes 2013 S1 Ques Set 2Imelda WongBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel As Unit 1Dokumen202 halamanEdexcel As Unit 1rishamsaif100% (1)
- Economics Paper 2 SL PDFDokumen9 halamanEconomics Paper 2 SL PDFsansBelum ada peringkat
- CIE IGCSE Unit 3.3 - Workers - Occupations, Earnings and The Labour Market - Miss PatelDokumen19 halamanCIE IGCSE Unit 3.3 - Workers - Occupations, Earnings and The Labour Market - Miss PatelJingyao HanBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study 1 Demand and Supply of Wii Console Questions and DiscussionsDokumen29 halamanCase Study 1 Demand and Supply of Wii Console Questions and DiscussionsVisitacion Sunshine Baradi100% (1)
- Demand WorksheetDokumen4 halamanDemand WorksheetbkjanetBelum ada peringkat
- Determinan at of DemandDokumen4 halamanDeterminan at of Demandgeraldine andalBelum ada peringkat
- A Level Economics ProtectionismDokumen8 halamanA Level Economics Protectionismchinsw1996Belum ada peringkat
- IB Economics DefinitionsDokumen21 halamanIB Economics DefinitionsYokesh ProBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 3-Indifference CurveDokumen1 halamanWorksheet 3-Indifference CurvearushiBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study GlobeDokumen13 halamanCase Study GlobeAnn Camaya100% (1)
- Ib Economics Study Guide MacroDokumen43 halamanIb Economics Study Guide Macroapi-196719233Belum ada peringkat
- Marketing PlanDokumen51 halamanMarketing PlanSukh RajputBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Economics Exam QuestionsDokumen1 halamanIGCSE Economics Exam QuestionsEllie HousenBelum ada peringkat
- Macro Tutor2u BDokumen20 halamanMacro Tutor2u BdBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Fixed AssetsDokumen45 halamanSAP Fixed Assetsrohitmandhania80% (5)
- Action Aid International Staff ManualDokumen138 halamanAction Aid International Staff Manualejazahmad5100% (1)
- Economics IA MACRODokumen7 halamanEconomics IA MACROAayush KapriBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Dokumen4 halamanPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine SauerBelum ada peringkat
- Examiners' Report Principal Examiner Feedback January 2020Dokumen6 halamanExaminers' Report Principal Examiner Feedback January 2020DURAIMURUGAN MIS 17-18 MYP ACCOUNTS STAFF100% (1)
- IAS Economics - Student Book Answers - Unit2Dokumen88 halamanIAS Economics - Student Book Answers - Unit2temwaniBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Economics - Monetary Policy - Handout PDFDokumen7 halamanIGCSE Economics - Monetary Policy - Handout PDFdenny_sitorusBelum ada peringkat
- Elasticity Exam Paper Model AnswersDokumen5 halamanElasticity Exam Paper Model AnswersNicole BostanBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 1Dokumen2 halamanProblem Set 1Cooper Greenfield0% (1)
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Business 9609/13 May/June 2019Dokumen12 halamanCambridge Assessment International Education: Business 9609/13 May/June 2019AbdulBasitBilalSheikhBelum ada peringkat
- Busi 1083: Microeconomics Assessments: WWW - Yorkvilleu.CaDokumen11 halamanBusi 1083: Microeconomics Assessments: WWW - Yorkvilleu.CaKomal khubbad50% (2)
- Page 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandDokumen4 halamanPage 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandRumana AliBelum ada peringkat
- Production Possibility CurvesDokumen6 halamanProduction Possibility CurvesFari AliBelum ada peringkat
- MR Moyo - Economics Revision Basic Economic Problem, Resource Allocating, PPC, Money Citrusperibus, Assignment 1 AsDokumen14 halamanMR Moyo - Economics Revision Basic Economic Problem, Resource Allocating, PPC, Money Citrusperibus, Assignment 1 AsFaryalBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Unit 3 SupplyDokumen4 halamanWorksheet Unit 3 SupplyPriya Yadav100% (1)
- Submitted By: Biki Das Class - XI Stream - Commerce Roll No. - 5Dokumen42 halamanSubmitted By: Biki Das Class - XI Stream - Commerce Roll No. - 5Biki DasBelum ada peringkat
- Economics Ppt. 1Dokumen15 halamanEconomics Ppt. 1manasBelum ada peringkat
- IBDP Economics P3 - Revision WorksheetDokumen4 halamanIBDP Economics P3 - Revision WorksheetSahana Rao100% (1)
- MacroEconomics Written Assignment 2Dokumen6 halamanMacroEconomics Written Assignment 2Thais HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 Review QuestionsDokumen2 halamanTopic 1 Review Questionsharshini kotaBelum ada peringkat
- Test - Economics - PED and PES, Firms and Population MarkschemeDokumen6 halamanTest - Economics - PED and PES, Firms and Population MarkschemeDhrisha GadaBelum ada peringkat
- IB Econ Chap 16 Macro EQDokumen11 halamanIB Econ Chap 16 Macro EQsweetlunaticBelum ada peringkat
- We Love EconomicsDokumen26 halamanWe Love EconomicsR Ahmad Anggi Hakim100% (1)
- Demand and Supply Practice PacketDokumen8 halamanDemand and Supply Practice PacketVal Basil100% (1)
- Unit 5 Paper 1 Section 1 Short AnswerDokumen7 halamanUnit 5 Paper 1 Section 1 Short AnswerKashf GilaniBelum ada peringkat
- Economic Issues IGCSE (Business Studies)Dokumen4 halamanEconomic Issues IGCSE (Business Studies)an4Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 The Allocation of Resources: How The Market Works Market FailureDokumen12 halamanUnit 2 The Allocation of Resources: How The Market Works Market FailureJada CameronBelum ada peringkat
- Inflation Causes in PakistanDokumen71 halamanInflation Causes in PakistanShahid Mehmood100% (1)
- 6.1 International Trade and Specialization: Igcse /O Level EconomicsDokumen10 halaman6.1 International Trade and Specialization: Igcse /O Level EconomicsAvely AntoniusBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ'S: EconomicsDokumen73 halamanMCQ'S: EconomicsHabib MughalBelum ada peringkat
- Psychology P3 and P4 (MS)Dokumen675 halamanPsychology P3 and P4 (MS)Khadija BakhtawarBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam ReviewDokumen19 halamanFinal Exam ReviewJeromy Rech100% (1)
- Demand and SupplyDokumen25 halamanDemand and SupplyAyyappaGolluBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Economics - Demand and SupplyDokumen54 halamanMicro Economics - Demand and SupplyDr Rushen SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Economics 1Dokumen1 halamanEconomics 1Sandy LBelum ada peringkat
- AJANTA PHARMA LIMITED Annual ReportDokumen24 halamanAJANTA PHARMA LIMITED Annual Reportajay goudBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-3: Restructuring & Responsibility Matrix in BSNLDokumen13 halamanChapter-3: Restructuring & Responsibility Matrix in BSNLsfdwhjBelum ada peringkat
- All Types of Cost Incurred For That Product. Detailed Description of Each Type of Cost. Cost Sheet For Per Unit As Well As For 100 UnitsDokumen2 halamanAll Types of Cost Incurred For That Product. Detailed Description of Each Type of Cost. Cost Sheet For Per Unit As Well As For 100 UnitsakashniranjaneBelum ada peringkat
- Required: Indicate Each Account's Classification and Normal Balance by Placing (/) Marks. TheDokumen1 halamanRequired: Indicate Each Account's Classification and Normal Balance by Placing (/) Marks. TheBebie Joy UrbanoBelum ada peringkat
- Loma 357 C5Dokumen25 halamanLoma 357 C5May ThirteenthBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring and Forecasting Earnings of A CompanyDokumen38 halamanMeasuring and Forecasting Earnings of A CompanySoumendra RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Case 3 - 1: Maynard Company (B) : DR Ashish Varma / IMTDokumen4 halamanCase 3 - 1: Maynard Company (B) : DR Ashish Varma / IMTkunalBelum ada peringkat
- NCPAR Sample Review QuestionsDokumen7 halamanNCPAR Sample Review QuestionsJonathan Tumamao FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Income From Other SourceDokumen20 halamanIncome From Other SourceRewant MehraBelum ada peringkat
- Inventory EstimationDokumen4 halamanInventory EstimationShy Ng0% (1)
- Hand Note For Bank VivaDokumen15 halamanHand Note For Bank Vivaইরফানুল আলম সিদ্দীকিBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report ON "To Study of Npa Management"Dokumen64 halamanProject Report ON "To Study of Npa Management"Dhiraj KokareBelum ada peringkat
- Audit of ReceivableDokumen14 halamanAudit of ReceivableMr.AccntngBelum ada peringkat
- Annual Recertification FormsDokumen11 halamanAnnual Recertification FormsDBHAAdminBelum ada peringkat
- Feasibility Study Plan: LabadabangoDokumen38 halamanFeasibility Study Plan: LabadabangoCocoy Llamas HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Fania Qinthara Azka - Case Chapter 2Dokumen3 halamanFania Qinthara Azka - Case Chapter 2Fania AzkaBelum ada peringkat
- CMS Base II - Plan Segment DetailsDokumen27 halamanCMS Base II - Plan Segment DetailsKrishna KingBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas MK Dasar Akuntansi Pertemuan Ke-15Dokumen2 halamanTugas MK Dasar Akuntansi Pertemuan Ke-15Mochamad Ardan FauziBelum ada peringkat
- Managerial Economics Q4Dokumen2 halamanManagerial Economics Q4Willy DangueBelum ada peringkat
- FAR 2 Final Departmental Examination 2022Dokumen35 halamanFAR 2 Final Departmental Examination 2022ILOVE MATURED FANSBelum ada peringkat
- 2016 SALN Form - JudithdocDokumen2 halaman2016 SALN Form - JudithdocNDAP DavaoBelum ada peringkat