Me Proposal MC Sajjad
Diunggah oleh
Shahid ShabbirDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Me Proposal MC Sajjad
Diunggah oleh
Shahid ShabbirHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PAPR reduction techniques for MC-CDMA Supervisor: Dr.
Abdul Waheed Umrani Associate Professor, TL Proposal
1. Background/Motivation
Co-supervisor: Dr. Fahim Aziz Umrani Assistant Professor, TL
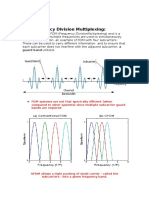
The requirements of high data rate transmission by modern wireless communication systems under practical time-varying channels leads to the fact that they cannot be designed without multi carrier transmission and that is most efficiently implemented in the form of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) [1]. The OFDM technology is well known for its capability to cope with frequency-selective fading channel due to multipath and its low complexity equalizer. Therefore, it becomes a popular candidate for various high data-rate wireless systems such as IEEE 802.11n WLAN, IEEE 802.16 WiMAX, 3GPP LTE, 3GPP2 UMB, etc. However, OFDM suffers from high peak-toaverage power ratio (PAPR). Furthermore, in multi-cell scenarios, the OFDM based access scheme, namely, orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) can suffer from severe co-channel interference from adjacent cells which makes one-cell universal frequency reuse non-trivial for OFDMA based cellular networks. On the other hand, code division multiple access (CDMA) is a technology being used in the 3G cellular networks such as 3GPP WCDMA and 3GPP2 CMDA2000. The most significant advantage of CDMA is that it can achieve the one-cell universal frequency reuse by deploying properly designed set of codes. Later, several technologies combining the benefits of OFDM with CDMA are reported in the literature, mainly in the form of multi-carrier CDMA (MC-CDMA) [1]-[3]. In MC-CDMA systems, the CDMA part provides multiple access ability as well as to spread each users data across the entire available frequency band. The spreading codes chips are then modulated on orthogonal subcarriers and spread across the time domain via the OFDM modulation which provides protection against the delay spread of the multipath channel. Therefore MC-CDMA technique can achieve high data rate transmission with protection against both frequency selective fading and time dispersion channel while at the same time offers a spectrum efficient multiple access strategy [3]. However MC-CDMA systems suffer from high PAPR which is one of the major drawbacks of all multicarrier transmission schemes. A wide dynamic range is required in the linear Power Amplifiers (PA) at the transmitter in order to transmit a signal with large PAPR. If the dynamic range of PA is insufficient, the signal could be distorted from the resulting nonlinearity which degrades the signal quality and leads to out of band (OoB) radiations and hence interfere with adjacent frequency bands [3]. A variety of schemes have been suggested in literature to combat PAPR issue in OFDM systems [1]-[7]. It is known that the Partial Transmit Sequence (PTS) and the Selected Mapping (SLM) are effective for OFDM [4]. In SLM multiple sequences are generated from the original data block and the sequence with the lowest PAPR is selected for transmission. In the PTS approach, disjoint subblocks of OFDM subcarriers are phase shifted separately after an inverse fast Fourier transform IFFT is computed. If the subblocks are optimally phase shifted, they exhibit minimum PAPR and consequently reduce the PAPR of the merged signal. The number of subblocks and their partitioning scheme determine the PAPR reduction. Typically, the receiver requires side information corresponding to the optimal phases in PTS and the transmitted sequences in SLM [5].
2.
Objectives
SLM and PTS are originally OFDM based schemes and can be transplanted to MC-CDMA system [6]. In [4] it is shown that SLM can reduce the PAPR of MC-CDMA more than the PTS at the same amount of side information. However the effect of SLM technique that employs convolutional codes to avoid the need for the transmission of side-information for MC-CDMA has not been studied. We aim to investigate the effects of SLM technique that employs convolutional codes for MC-CDMA.
3.
Research Methodology
We will study and investigate the performance of SLM technique that employs convolutional codes with simulations in terms of PAPR and BER using Matlab and Simulink.
4.
References
[1] Miin-Jong Hao and Chiu-Hsiung Lai, Precoding for PAPR Reduction of OFDM Signals With Minimum Error Probability, IEEE Transaction on Broadcasting , Vol. 56, No. 1, pp. 120-128, March 2010. [2] Chia-Chin Chong, et al. On the Performance Comparision of VSF-OFCDMA and OFDMA, IEEE 19th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, 2008, pp. 1-6, September 2008. [3] Lin Yang, Mingli You and Jun Li, Optimized Spreading Code Reallocation Technique for PAPR Reduction in MC-CDMA systems IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, 2009, pp. 1-6, November 2009. [4] N. Ohkubo and T. Ohtsuki, A peak to average power ratio reduction of multicarrier CDMA using selected mapping IEEE 56th Vehicular Technology Conference, 2002, Vol. 4, pp. 2086 - 2090, December 2002. [5] Ghassemi, A and Gulliver, T PAPR reduction of OFDM Using PTS and Error-Correcting Code Subblocking IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 980-989, March 2010. [6] Hernandez, L.A.P and Otero, M.G User Reservation Approach for Peak-to-Average Power Ratio Reduction in MC-CDMA Systems IEEE 69th Vehicular Technology Conference, 2009, pp. 1-5, June 2009. [7] Khanza Khan and Shahzad Amin Sheikh, PAPR Reduction of OFDM Signals using Convolutional Codes, IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development, 2009, UPM Serdang Malaysia, pp. 26-28, November 2009.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Discrete Cosinetransform-Ii For Reduction in Peak To Average Power Ratio of Ofdm Signals Through - Law Companding TechniqueDokumen14 halamanDiscrete Cosinetransform-Ii For Reduction in Peak To Average Power Ratio of Ofdm Signals Through - Law Companding TechniqueJohn BergBelum ada peringkat
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksDari EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- A Review On OFDM: Concept, Scope & Its Applications: Manushree Bhardwaj, Arun Gangwar, Devendra SoniDokumen5 halamanA Review On OFDM: Concept, Scope & Its Applications: Manushree Bhardwaj, Arun Gangwar, Devendra SonipankajmudgilBelum ada peringkat
- Modeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEDari EverandModeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study of Ofdm and Cdma Technique: Lalit Singh Garia, Amit Shah, Deepesh RawatDokumen5 halamanComparative Study of Ofdm and Cdma Technique: Lalit Singh Garia, Amit Shah, Deepesh RawatInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- OQAM/FBMC for Future Wireless Communications: Principles, Technologies and ApplicationsDari EverandOQAM/FBMC for Future Wireless Communications: Principles, Technologies and ApplicationsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- A Novel Implementation of OFDM Using FPGA: M.A. Mohamed, A.S. Samarah, M.I. Fath AllahDokumen6 halamanA Novel Implementation of OFDM Using FPGA: M.A. Mohamed, A.S. Samarah, M.I. Fath Allahtsk4b7Belum ada peringkat
- 3G Evolution: HSPA and LTE for Mobile BroadbandDari Everand3G Evolution: HSPA and LTE for Mobile BroadbandPenilaian: 2.5 dari 5 bintang2.5/5 (4)
- Cnce 010103Dokumen6 halamanCnce 010103kiaraBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 15ec81 WC LteDokumen66 halamanModule 1 15ec81 WC LteVeeresh SoraturBelum ada peringkat
- Adaptive Active Constellation Extension Algorithm For Peak-To-Average Ratio Reduction in OfdmDokumen11 halamanAdaptive Active Constellation Extension Algorithm For Peak-To-Average Ratio Reduction in Ofdmsurendiran123Belum ada peringkat
- Papr Reduction Techniques and Their Bit Error Rate Measurement at Ofdm in Lte SystemDokumen16 halamanPapr Reduction Techniques and Their Bit Error Rate Measurement at Ofdm in Lte SystemijansjournalBelum ada peringkat
- TSP CMC 29563Dokumen12 halamanTSP CMC 29563Vᴀɪsʜɴᴀᴠ KᴀʀᴛʜɪᴋʜᴀBelum ada peringkat
- Single Carrier FDMA For Uplink Wireless TransmissionDokumen9 halamanSingle Carrier FDMA For Uplink Wireless Transmissionswapnil_mukkawarBelum ada peringkat
- Radon Transform PaperDokumen8 halamanRadon Transform Papersarin.gaganBelum ada peringkat
- PAPR, Spectral Efficiency, BER and SNR Analysis of OFDM: A Novel Partial Transmit Sequence-Particle Swarm Optimization TechniqueDokumen15 halamanPAPR, Spectral Efficiency, BER and SNR Analysis of OFDM: A Novel Partial Transmit Sequence-Particle Swarm Optimization TechniqueijansjournalBelum ada peringkat
- Ofdm PDFDokumen5 halamanOfdm PDFnikitajanu100% (1)
- LTE in A Nutshell - Physical Layer PDFDokumen18 halamanLTE in A Nutshell - Physical Layer PDFMarco SignoriniBelum ada peringkat
- BER Analysis of MIMO-OFDM System Using BPSK Modulation SchemeDokumen7 halamanBER Analysis of MIMO-OFDM System Using BPSK Modulation SchemeAnthony WellsBelum ada peringkat
- Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple AccessDokumen10 halamanOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple AccessDarwinBelum ada peringkat
- Peak-to-Average Power Reduction in MIMO-OFDM Systems Using SLM TechniqueDokumen7 halamanPeak-to-Average Power Reduction in MIMO-OFDM Systems Using SLM TechniqueInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- Mathur 2021Dokumen18 halamanMathur 2021Noor AdilBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of LTE-1Dokumen343 halamanFundamentals of LTE-1Karunadu StatusBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless Cellular & LTE 4G Broadband: Key Enabling Technologies and Features of LTEDokumen22 halamanWireless Cellular & LTE 4G Broadband: Key Enabling Technologies and Features of LTENavaneethBelum ada peringkat
- Performance and Analysis of BER in Wavelets Based OFDM System With Different Channel EstimationDokumen16 halamanPerformance and Analysis of BER in Wavelets Based OFDM System With Different Channel Estimationزهراء عمادBelum ada peringkat
- Simulative Analysis of OFDMA System Under Pervasive EnvironmentDokumen5 halamanSimulative Analysis of OFDMA System Under Pervasive EnvironmentliiBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access NOMA As A PDFDokumen5 halamanNon-Orthogonal Multiple Access NOMA As A PDFHanif KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report On Broadband MIMO-OFDM Wireless CommunicationsDokumen10 halamanProject Report On Broadband MIMO-OFDM Wireless CommunicationsPreetam PolakiBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 WCCDokumen32 halamanModule 4 WCCKali LinuxBelum ada peringkat
- Lte Ofdm TechnologyDokumen2 halamanLte Ofdm Technologykapil singhBelum ada peringkat
- Hadamard Coded Modulation For Wavelet Based Radio Over Fiber NetworksDokumen5 halamanHadamard Coded Modulation For Wavelet Based Radio Over Fiber NetworksEditor IJRITCCBelum ada peringkat
- 1.4 Key Enabling Technologies and Features of LTE: 1.4.1 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)Dokumen39 halaman1.4 Key Enabling Technologies and Features of LTE: 1.4.1 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)rohan gowdaBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless and CELLULAR COMMUNICATION (18EC81) Module-4Dokumen37 halamanWireless and CELLULAR COMMUNICATION (18EC81) Module-4Vishwanath DesaigoudarBelum ada peringkat
- WCC Module-4 NotesDokumen22 halamanWCC Module-4 NotesUday Kumar DBelum ada peringkat
- LTE OFDM TechnologyDokumen2 halamanLTE OFDM TechnologyVishwaBelum ada peringkat
- Ijet V3i4p10Dokumen14 halamanIjet V3i4p10International Journal of Engineering and TechniquesBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To OFDMDokumen11 halamanIntroduction To OFDMVimal RajBelum ada peringkat
- Indjcse12 03 06 074Dokumen5 halamanIndjcse12 03 06 074dodo gogoBelum ada peringkat
- BER AND PAPR ANALYSIS OF 8X8 MIMO OFDM SYSTEM - USING SLM TECHNIQUE - Thesis - M.Tech PDFDokumen82 halamanBER AND PAPR ANALYSIS OF 8X8 MIMO OFDM SYSTEM - USING SLM TECHNIQUE - Thesis - M.Tech PDFabdul.azeezBelum ada peringkat
- Compare The Performance Analysis For FFT Based Mimo-Ofdm With DWT Based Mimo-OfdmDokumen5 halamanCompare The Performance Analysis For FFT Based Mimo-Ofdm With DWT Based Mimo-Ofdmjagadeesh jagadeBelum ada peringkat
- 18ec81 WCC Module 5 NotesDokumen54 halaman18ec81 WCC Module 5 NotesmeghanaBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 1 LTE NotesDokumen60 halamanMODULE 1 LTE NotesKiran K Dhoni100% (1)
- Mobile Computing ReportDokumen21 halamanMobile Computing Reportakshata_pinks3Belum ada peringkat
- An Overview of The LTE Physical Layer Part IDokumen6 halamanAn Overview of The LTE Physical Layer Part IVenkat ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Papr Reduction and Bit Error Rate Evaluation in Ofdm System Using Hybrid TechniquesDokumen19 halamanPapr Reduction and Bit Error Rate Evaluation in Ofdm System Using Hybrid TechniquesijansjournalBelum ada peringkat
- Lte ScfdmaDokumen9 halamanLte ScfdmaQuoc NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- OFDMADokumen7 halamanOFDMAAmgadBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Chapter 1,2,3,4,5 (15%)Dokumen64 halaman6 Chapter 1,2,3,4,5 (15%)MANMOHAN SINGH CHANDOLIYABelum ada peringkat
- Comp An DingDokumen8 halamanComp An DingHeman JebakumarBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Input-Multiple Output Ofdm SystemsDokumen36 halamanMultiple Input-Multiple Output Ofdm SystemsLoukya KuttiBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1Dokumen26 halamanModule 1Varshini NBelum ada peringkat
- Articulo MIMO OFDMDokumen17 halamanArticulo MIMO OFDMppenalver8Belum ada peringkat
- 6 Chapter 1,2,3,4,5 (15%)Dokumen65 halaman6 Chapter 1,2,3,4,5 (15%)MANMOHAN SINGH CHANDOLIYABelum ada peringkat
- Estimation of UFMC Time-Varying Fading Channel Using Adaptive FilterDokumen6 halamanEstimation of UFMC Time-Varying Fading Channel Using Adaptive FilterpabloBelum ada peringkat
- FPGA Implementation of OFDM PDFDokumen6 halamanFPGA Implementation of OFDM PDFFausto Paco ValenzuelaBelum ada peringkat
- Interference Cancelation Scheme WithDokumen10 halamanInterference Cancelation Scheme WithhosamkhaledBelum ada peringkat
- BER Analysis of MIMO-OFDMDokumen10 halamanBER Analysis of MIMO-OFDMAbhijeet KumarBelum ada peringkat
- A Review Paper On OFDM PAPR Reduction Technique: Pooja Banwani, Dipak Ku Bhagat, Kaushal Yadav, Prof Shally GoyalDokumen6 halamanA Review Paper On OFDM PAPR Reduction Technique: Pooja Banwani, Dipak Ku Bhagat, Kaushal Yadav, Prof Shally GoyalRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- OFDM Basics Tutorial: ReferencesDokumen7 halamanOFDM Basics Tutorial: ReferencesDarwinBelum ada peringkat
- TL-WN823N V2 DatasheetDokumen3 halamanTL-WN823N V2 DatasheetCesart Hery AprianBelum ada peringkat
- TechSpace (Vol-4, Issue-02) PDFDokumen48 halamanTechSpace (Vol-4, Issue-02) PDFThit Htoo LwinBelum ada peringkat
- BSNL PlansDokumen32 halamanBSNL PlansTanush AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- ATT GSM CourseDokumen638 halamanATT GSM CourseJhon Vargas ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- LG K4 2017 X230DS - SVC - Manual - V1.0 - 170320 PDFDokumen122 halamanLG K4 2017 X230DS - SVC - Manual - V1.0 - 170320 PDFjsouza souzaBelum ada peringkat
- 3GPP TS 23.501Dokumen545 halaman3GPP TS 23.501silentBelum ada peringkat
- Open EPC TutorialDokumen123 halamanOpen EPC TutorialAlex Hunter100% (2)
- Lte Volte & CSFB E2E Service Quality Tuning Analysis & SolutionDokumen25 halamanLte Volte & CSFB E2E Service Quality Tuning Analysis & SolutionBelieverBelum ada peringkat
- MIMO ProjectDokumen8 halamanMIMO Projectabhi9998Belum ada peringkat
- 1.蔡宜學博士 5G Standardization 20160829Dokumen69 halaman1.蔡宜學博士 5G Standardization 20160829malli gaduBelum ada peringkat
- Smart1 DatasheetDokumen1 halamanSmart1 DatasheetJuan RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile Banking Security and Why ItDokumen2 halamanMobile Banking Security and Why ItAjayPanickerBelum ada peringkat
- Nokia Wcdma Frequency Refarming White PaperDokumen16 halamanNokia Wcdma Frequency Refarming White PaperuwaifotonyBelum ada peringkat
- Sms Sending Job DetailsDokumen2 halamanSms Sending Job DetailsLofojayBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Access Schemes FDMA TDMA CDMA For ClassDokumen26 halamanMultiple Access Schemes FDMA TDMA CDMA For Classmuhammad yaseenBelum ada peringkat
- S1.3 (IMDA Singapore) Update On 5G Development in Singapore PDFDokumen9 halamanS1.3 (IMDA Singapore) Update On 5G Development in Singapore PDFdtvt40Belum ada peringkat
- Special Edition 2002 SIM CloningDokumen13 halamanSpecial Edition 2002 SIM Cloningjai25jaiBelum ada peringkat
- D9102 User Manual: 1. USB Interface 2. SIM Card 3. Modem Cap 4. Guide Light 5. Cover of SIM CardDokumen5 halamanD9102 User Manual: 1. USB Interface 2. SIM Card 3. Modem Cap 4. Guide Light 5. Cover of SIM CardInussi Mitas JúniorBelum ada peringkat
- Swot AnalysisDokumen9 halamanSwot Analysisapi-251927329Belum ada peringkat
- LTE Actix Drive ReportDokumen120 halamanLTE Actix Drive ReportPranjulDwivediBelum ada peringkat
- MoveInSync Native Android Mobile AppDokumen12 halamanMoveInSync Native Android Mobile AppRismaBelum ada peringkat
- Lte Interface OverviewDokumen1 halamanLte Interface OverviewTerry BacchinBelum ada peringkat
- Grupo Uno: IntegrantesDokumen2 halamanGrupo Uno: IntegrantesAlisson ZambranoBelum ada peringkat
- AdMob Mobile Metrics Dec 09Dokumen26 halamanAdMob Mobile Metrics Dec 09TechCrunchBelum ada peringkat
- CSFB FinalDokumen13 halamanCSFB FinalBlack-Talent Ken Narotso100% (2)
- Ipho Ne 4 Te Eardown N: Step 1 - Iphon Ne 4 Teard DownDokumen22 halamanIpho Ne 4 Te Eardown N: Step 1 - Iphon Ne 4 Teard Downinfo_enicsBelum ada peringkat
- IcrDokumen1 halamanIcrNaveen VengaldasBelum ada peringkat
- 4G GPS Tracker Price ListDokumen3 halaman4G GPS Tracker Price Listrongli leeBelum ada peringkat
- Blackberry Market StrategyDokumen33 halamanBlackberry Market StrategygunpriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Model Spec Thai Prices: AppleDokumen3 halamanModel Spec Thai Prices: AppleKyaw Thu TunBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsDari EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxDari EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (67)
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Dari EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Belum ada peringkat
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamDari EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamBelum ada peringkat
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDari EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringDari EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (40)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsDari EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsBelum ada peringkat
- Networking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366Dari EverandNetworking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366Belum ada peringkat
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNDari EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Azure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectDari EverandAzure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectBelum ada peringkat
- Cybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityDari EverandCybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- ITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideDari EverandITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideBelum ada peringkat
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationDari EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionDari EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsDari EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsBelum ada peringkat
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksDari EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- 5G/5G-Advanced: The New Generation Wireless Access TechnologyDari Everand5G/5G-Advanced: The New Generation Wireless Access TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignDari EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignBelum ada peringkat
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamDari EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)