Parcial 1 Negocios Internacionales
Diunggah oleh
Samu RamírezJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Parcial 1 Negocios Internacionales
Diunggah oleh
Samu RamírezHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PARCIAL N1 NEGOCIOS INTERNACIONALES
21 Diciembre 2011 Profesor: Arcadio Cerda U. Ayudante: Samuel Arellano R. MATRICULA: _________________________________________________________________ Puntaje Total: ____ puntos. Observaciones: No abra el cuadernillo hasta leer todas las observaciones. Este control evala la lectura realizada por el alumno de los captulos 1 al 5 (Casos y materia) junto con los contenidos impartidos en todas las clases del curso hasta la clase del da 19/12/2011. Su ponderacin es del 10% de la nota final. El trabajo es individual. Existen 4 alternativas, de las cuales, slo una es la correcta. Debe estar seguro de su alternativa, una vez decidida, conteste, ya que si hace algn borrn, enmienda o algo similar, se considerar como respuesta mala. Por cada respuesta correcta recibir 0,25 puntos y por cada incorrecta se le descontar 0,1 puntos. El puntaje total es de 6 puntos, ms 1 punto base. Consultas en voz alta. Puede utilizar diccionario. Tiempo: 60 minutos.
XITO!
FORM: 1 1. One early response to the failure of the Heckscher-Ohlin theory to explain the observed pattern of international trade was the: A) B) C) D) theory of comparative advantage theory of cultural constraints product life-cycle theory theory of rising costs
2. Which of following pairs of religious beliefs are most likely to lead to economic development and growth? A) B) C) D) Christianity and Buddhism Confucianism and Islam Islam and Christianity Hinduism and Buddhism
3. Contrary to what the Heckscher-Ohlin theory would predict, the United States has been a primary importer rather than an exporter of capital goods. This apparent contradiction is known as the _________ paradox. A) B) C) D) Theler Ricardo Cormier Leontief
4. Country Look U.S.A. American popular imagination of the past 25 years associated free trade with: A) B) C) D) the displacement of low-skilled factory jobs countries from poor to rich the displacement of low-skilled factory jobs countries from poor to poor the displacement of low-skilled factory jobs countries from rich to rich the displacement of low-skilled factory jobs countries from rich to poor countries countries countries countries
5. Which of the following is not one of the major principles of Islam? A) B) C) D) being pretentious, rather than humble safeguarding the possessions of orphans respecting the rights of others honoring and respecting parents
6. The term __________ refers to a system that stresses the primacy of collective goals over individual goals. A) B) C) D) capitalism democracy collectivism individualism
7. Which of the following scholars (or teams of scholars) is not associated with the theory that follows his name? A) B) C) D) Michael Porter / National Competitive Advantage Eli Heckscher and Bertil Ohlin / Product Life-Cycle Adam Smith / Absolute Advantage David Ricardo / Comparative Advantage
8. The political system in which government is "by the people", exercised either directly of through elected representatives is referred to as: A) B) C) D) totalitarianism democracy individualism despotism
9. Which of the following is not one of the four major forms of totalitarianism that exist in the world today? A) B) C) D) collective totalitarianism tribal totalitarianism communist totalitarianism right-wing totalitarianism
10. The globalization of production refers to: A) the tendency among firms to move production facilities to foreign countries where wage rates are lower B) the tendency among firms to recruit production workers from foreign countries C) the tendency among firms to source goods and services from locations around the globe to take advantage of national differences in the cost and quality of factors of production D) the tendency among firms to use similar production methods
11. The two major categories of norms are: A) B) C) D) rites and rituals folkways and mores conduct and culture routines and values
12. The __________ theory stresses that in some cases countries specialize in the production and export of particular products not because of underlying differences in factor endowments, but because in certain industries the world market can support only a limited number of firms. A) B) C) D) new trade limited potential product life-cycle Heckscher-Olin
13. According to our textbook, the single most important technological innovation that has impacted international trade has been the: A) B) C) D) communications satellite development of optic fiber fax machine microprocessor
14. The values of loyalty, reciprocal obligations, and honesty are central to the __________ system of ethics. A) B) C) D) Islamic Hindu Buddhist Confucian
15. The two main components of globalization are: A) B) C) D) the standardization of technology and the globalization of markets the globalization of markets and the globalization of production the globalization of advertising and the globalization of services the globalization of finance and the globalization of accounting
16. The two macro factors that seem to underlie the trend towards greater globalization are: A) a convergence in consumer tastes around the world, an increase in political tensions around the world B) the decline in political tensions around the world, formal and informal barriers to trade between countries C) the increase in barriers to the free flow of goods, services, and capital that has occurred since the end of World War II, the decline in economic pressures around the world D) the decline in barriers to the free flow of goods, services, and capital that has occurred since the end of World War II, and technological change
17. Given to countries Chile y Japan. Both countries use only one factor and have constant productivity. The wages in Chile are W=1 y and Japan W*=2. Given the following table which product are produced in Chile: Productividades Productos Cobre Vino Textiles Televisores Autos A) B) C) D) Only cooper Only Cooper and wine Only Cooper, wine and textils None of alternatives Chile 20 8 3 0,4 0,1 Japn 10 5 4 2 1
17. A firm's decision to invest resources in business activities outside its home country is referred to as: A) B) C) D) cross-national investment transnational commerce foreign direct investment international diversification
19. Given to countries Chile y Japan. Both countries use only one factor and have constant productivity. The wages in Chile are W=1 y and Japan W*=6. Given the following table which product are produced in Chile: Productividade s Chile Japn 20 10 8 5 3 4 0,4 2 0,1 1
Productos Cobre Vino Textiles Televisores Autos A) B) C) D) Only cooper Only cooper and wine Only cooper, wine and textils None of alternatives
20. The routine conventions of everyday life are referred to as __________. A) B) C) D) folkways rituals mores rites
21. McDonalds is able to prevent other companies from opening fast-food restaurants with the McDonalds name and the McDonalds golden arches because McDonalds has obtained __________ protection on its name and distinctive designs. A) B) C) D) patent intellectual property certificate copyright trademark
22. Swedish economists' __________ advanced a theory of trade that argued that comparative advantage arises from differences in national factor endowments. A) B) C) D) Durbin and Coles Rivette and Delhomme Hecksher and Ohlin Mouton and Penn
23. __________ initially proposed the product life-cycle theory in the mid-1960s. A) B) C) D) David Ricardo Michael Porter Bertil Ohlin Raymond Vernon
24. The most rigid system of stratification is a __________ system. A) B) C) D) degree class cross-cultural caste
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- DALETDokumen10 halamanDALETPlomeria Central100% (1)
- Orden-de-Servicio Evento EmpresarialDokumen2 halamanOrden-de-Servicio Evento EmpresarialElba Gomez Garcia100% (2)
- Precursores y Próceres de La Independencia para Tercer Grado de Primaria 2Dokumen6 halamanPrecursores y Próceres de La Independencia para Tercer Grado de Primaria 2Juan jose Carbajal ortiz100% (1)
- Definiciones Del Marketing para Las Nuevas RealidadesDokumen5 halamanDefiniciones Del Marketing para Las Nuevas RealidadesCristian Estela100% (1)
- Medidor de Cuadal WellfordDokumen6 halamanMedidor de Cuadal WellfordJavier Melendez RomanBelum ada peringkat
- Análisis Del Discurso Ideológico - Van DijkDokumen2 halamanAnálisis Del Discurso Ideológico - Van DijklucasperassiBelum ada peringkat
- Notas ActualizadasDokumen4 halamanNotas ActualizadasSamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Ayudantía 3Dokumen2 halamanAyudantía 3sarellano2441Belum ada peringkat
- Notas Actualizadas 3 de Junio 2012Dokumen2 halamanNotas Actualizadas 3 de Junio 2012Samu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Actualizadas 3 de Junio 2012Dokumen2 halamanNotas Actualizadas 3 de Junio 2012Samu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas ActualizadasDokumen1 halamanNotas ActualizadasSamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
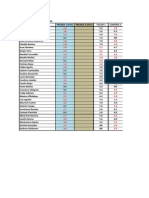
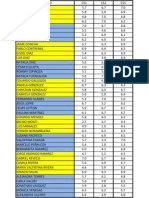
- Notas ParcialesDokumen1 halamanNotas ParcialesSamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Control Negocios 22 de Noviembre PAUTADokumen3 halamanControl Negocios 22 de Noviembre PAUTASamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Dokumen2 halamanNotas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Samu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Control 1 Negocios Primavera 2011 PAUTADokumen3 halamanControl 1 Negocios Primavera 2011 PAUTASamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Guía para Opcional C.P.A Finanzas IDokumen2 halamanGuía para Opcional C.P.A Finanzas ISamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Dokumen2 halamanNotas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Samu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Dokumen2 halamanNotas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Samu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Dokumen2 halamanNotas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Samu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Dokumen2 halamanNotas Actualizadas 1/2/2012Samu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Grupos NegociosDokumen1 halamanGrupos NegociosSamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Negocios InternacionalesDokumen2 halamanNotas Negocios InternacionalesSamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Negocios InternacionalesDokumen2 halamanNotas Negocios InternacionalesSamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Negocios InternacionalesDokumen2 halamanNotas Negocios InternacionalesSamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Ayudantía 17 de EneroDokumen1 halamanAyudantía 17 de EneroSamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Finanzas I (C.p.a) - Ayudantía 3 "Bonos"Dokumen3 halamanFinanzas I (C.p.a) - Ayudantía 3 "Bonos"Samu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Notas Controles Semanales Negocios InternacionalesDokumen1 halamanNotas Controles Semanales Negocios InternacionalesSamu RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Macetero en Hierro - Google SearchDokumen1 halamanMacetero en Hierro - Google SearchAgustin AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Reseña Historica Del ComercioDokumen5 halamanReseña Historica Del Comercioluzi_g19Belum ada peringkat
- Analisis Del Cuento El Otro Yo de MarioDokumen9 halamanAnalisis Del Cuento El Otro Yo de Mariohenry castellBelum ada peringkat
- Infiorme de Recorrido Domingo 17-01-21Dokumen7 halamanInfiorme de Recorrido Domingo 17-01-21Jorge Mario Jesus Sum BurgosBelum ada peringkat
- Caso Del Grupo 08 - DemandaDokumen20 halamanCaso Del Grupo 08 - DemandaIsraelBelum ada peringkat
- Propuesta Generica Vida AhorroDokumen15 halamanPropuesta Generica Vida AhorroDeby AntilefBelum ada peringkat
- DIRECTORIO2Dokumen29 halamanDIRECTORIO2Gavino CarrancoBelum ada peringkat
- Mapa Conceptual Ley 1480 de 20211 - Carrie Estephan Escobar TarazonaDokumen1 halamanMapa Conceptual Ley 1480 de 20211 - Carrie Estephan Escobar Tarazonaauxiliar sgsstaBelum ada peringkat
- Antes de Que Sea TardeDokumen3 halamanAntes de Que Sea TardeScarlet DiazBelum ada peringkat
- RamanandaDokumen58 halamanRamanandaRadha K dasBelum ada peringkat
- Declaracion 872034585141Dokumen3 halamanDeclaracion 872034585141Dayto CobosBelum ada peringkat
- Literatura MedievalDokumen9 halamanLiteratura Medievalaguila19Belum ada peringkat
- Turno 4Dokumen7 halamanTurno 4Williams Durand ChavezBelum ada peringkat
- Teoría de La Conducta Vocacional y Desarrollo Del Concepto de Sí MismoDokumen7 halamanTeoría de La Conducta Vocacional y Desarrollo Del Concepto de Sí MismoMarbely Flores0% (1)
- Visión Actual Del Acto AdministrativoDokumen20 halamanVisión Actual Del Acto AdministrativoMarcelo AranedaBelum ada peringkat
- 4 2018 Declaración I Conferencia Iberoamericana de Ministros de Economía y Turismo. 6 PágsDokumen6 halaman4 2018 Declaración I Conferencia Iberoamericana de Ministros de Economía y Turismo. 6 PágsMartha Rosalía Sánchez LópezBelum ada peringkat
- Pildora de Liderazgo & Disciplina + ActividadDokumen2 halamanPildora de Liderazgo & Disciplina + ActividadDIANA CAROLINA CADAVID GARZON100% (1)
- La Dictadura Chilena: Alberto FagaldeDokumen232 halamanLa Dictadura Chilena: Alberto Fagaldefrancisco ArenasBelum ada peringkat
- Unidad 4 - Sesion 1 - Modulo DPCC - Quinto de SecundariaDokumen2 halamanUnidad 4 - Sesion 1 - Modulo DPCC - Quinto de SecundariaTania AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Homilía Ii Dom de Cuaresma CDokumen2 halamanHomilía Ii Dom de Cuaresma CRafa GonguzBelum ada peringkat
- AB980 - Estatuto de La UTEA (Vigente)Dokumen132 halamanAB980 - Estatuto de La UTEA (Vigente)Leo OOBelum ada peringkat
- Solidez de La EmpresaDokumen3 halamanSolidez de La EmpresavannearismendiBelum ada peringkat
- V.1.1 Setup Villa Expansiones PrinterfriendlyDokumen2 halamanV.1.1 Setup Villa Expansiones PrinterfriendlyArmand Guerre100% (1)
- Plano Corregimiento Panorama 2012 PDFDokumen1 halamanPlano Corregimiento Panorama 2012 PDFMai KissBelum ada peringkat