Electromagnetic Wave
Diunggah oleh
Muhammad Zahin Irfan ZulkhairiDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Electromagnetic Wave
Diunggah oleh
Muhammad Zahin Irfan ZulkhairiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Electromagnetic Wave
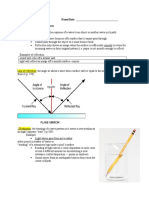
The meaning of electromagnetic wave
-A wave of energy having a frequency within the electromagnetic spectrum and propagated as a periodic disturbance of the electromagnetic field when an electric charge oscillates or accelerates. - Radiation consisting of waves of energy associated with electric and magnetic fields resulting from the acceleration of an electric charge
Information about electromagnetic wave
1. Electromagnetic waves are caused by the interaction between an electrical current and amagnetic field. Unlike other waves, the energy streams caused by the interplay of magnetic and electrical forces can travel through empty space. Just like an ocean wave, electromagnetic streams have peaks and troughs, caused by the forces pulling and pushing at one another. The wavelength is discovered by measuring the distance between two identical points of the wave from cycle to cycle. For instance, the distance between one crest and the next is the wavelength. 2. An electromagnetic wave is classified according to two main criteria: wavelength and energy. Higher-bearing energy waves, such as gamma rays, have short wavelengths. Waves with lower energy have a much longer wavelength. The scale that describes the different types of waves is called the electromagnetic spectrum. Radio waves are typically found at the bottom of the scale,while visible light sits in the middle and the high-powered, fast oscillating gamma rays top the scale. 3. Electromagnetic waves had been postulated for centuries but it was not until the 19th century that their existence became fully understood. James Clerk Maxwell, a physicist from Scotland, was able to create equations that explained the relationship between light and electromagneticwaves. Through his discoveries, science was finally able to grab hold of the concept and began to see the potential in manipulating the enormous streams of energy. Less than a century later, the electromagnetic wave had become a major part of human society through the invention of X-rays, microwaves, radio, and television transmission.
4. Whether or not an electromagnetic wave emits dangerous amounts of radiation depends on how much energy it bears. Radio waves carry very little energy and are generally considered to be perfectly safe, even when one is directly exposed to them. On the other end of the spectrum, gamma rays are the result of atomic explosions and can bear vast amounts of poisonous radiation. Exposure to high-energy waves can result in cell mutation, cancer, and possible death. However, experiments with high-level radiation are usually tightly controlled, and accidental exposure is unlikely. 5. Most information about outer space comes not from photos or probes but through studying theelectromagnetic wave. Radio astronomers are able to create pictures of faroff space by surveying the types of waves in the vicinity. Since it is impossible for humans on Earth to see deep space, electromagnetic waves are in fact one of the best ways of understanding what is out there. The need for better information has also lead to the construction of telescopes in space, as the Earth's atmosphere prevents some information from getting through to Earth-bound equipment.
Application of electromagnetic wave
When we watch the television ,or when we cook our food in the micro wave ,we use the electromagnetic waves
Radio Waves - transmitting signals Micro Waves - for coooking Infa-Red - used to see body heat and such. Visible Light - so we can see Ultraviolet- Used in policing and reading secret messages etc X Rays - used to take pictures of bones Gamma Rays - for sunbeds.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Atomic Structure Cheat SheetDokumen39 halamanAtomic Structure Cheat Sheetmark Zukerberg50% (2)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Holography SlidsDokumen28 halamanHolography SlidsbhardwejanujBelum ada peringkat
- Propagation Over A Plane EarthDokumen5 halamanPropagation Over A Plane EarthMohana ManasaBelum ada peringkat
- Diffraction Grating: Done by Harish S From Team 1Dokumen10 halamanDiffraction Grating: Done by Harish S From Team 1dudeBelum ada peringkat
- PCN RfiDokumen44 halamanPCN RfiNdomadu100% (2)
- PROJOX ACADEMY/9953118716,9667944902: Physics CTSDokumen13 halamanPROJOX ACADEMY/9953118716,9667944902: Physics CTSAyush ChouhanBelum ada peringkat
- Fresnel's Equations For Reflection and Refraction: Incident, Transmitted, and Reflected BeamsDokumen19 halamanFresnel's Equations For Reflection and Refraction: Incident, Transmitted, and Reflected BeamsponiceBelum ada peringkat
- CA Lesson 1 Projectile MotionDokumen19 halamanCA Lesson 1 Projectile MotionfaBelum ada peringkat
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5Dokumen17 halamanYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5Salmizam IzamBelum ada peringkat
- Physic Lab Report 6: Sherry Carentona GalinDokumen6 halamanPhysic Lab Report 6: Sherry Carentona GalinNurl AinaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 Atomic Structure and PeriodicityDokumen77 halamanChapter 7 Atomic Structure and Periodicityabd jafBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Dynamics IIDokumen126 halamanFluid Dynamics IIBaba GBelum ada peringkat
- Background Radiation Adapted WorksheetDokumen1 halamanBackground Radiation Adapted WorksheetKHA HarrisonBelum ada peringkat
- Force and MotionDokumen7 halamanForce and MotionAIFAA NADHIRAH BINTI AMIR WARDIBelum ada peringkat
- Synthesis Basics 1Dokumen3 halamanSynthesis Basics 1simonballemusic100% (1)
- Discussions: 1. Calculate The Heat Loss and Efficiency For Both Co-Current and Counter Current Processes. Heat Loss, QDokumen7 halamanDiscussions: 1. Calculate The Heat Loss and Efficiency For Both Co-Current and Counter Current Processes. Heat Loss, Qrei ayanamiBelum ada peringkat
- Saturated Absorption Spectroscopy: 1 BackgroundDokumen7 halamanSaturated Absorption Spectroscopy: 1 Backgroundhoangloc NgoBelum ada peringkat
- B Motion in A Straight LineDokumen24 halamanB Motion in A Straight Linef20230069Belum ada peringkat
- Comsar-Circ.25 - Procedure For Responding To DSC Distress Alerts by ShipsDokumen3 halamanComsar-Circ.25 - Procedure For Responding To DSC Distress Alerts by ShipsNicolasMaregaBelum ada peringkat
- SUVAT Equations: Key Words & Definitions What Do I Need To KnowDokumen1 halamanSUVAT Equations: Key Words & Definitions What Do I Need To KnowAlex GoldsmithBelum ada peringkat
- Basic of Seismic RefractionDokumen43 halamanBasic of Seismic Refractionfitriah wulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Models of The Hydrogen Atom: ObjectivesDokumen11 halamanModels of The Hydrogen Atom: ObjectivesMon LuffyBelum ada peringkat
- 3 2 4 Teacher Notes Wave BehaviorDokumen6 halaman3 2 4 Teacher Notes Wave Behaviorapi-369706779Belum ada peringkat
- A Modified Formula For Defining Tissue Phantom RatDokumen7 halamanA Modified Formula For Defining Tissue Phantom RatHashir SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Sureshot Motion in PlaneDokumen4 halamanPhysics Sureshot Motion in PlaneAlphin FrancisBelum ada peringkat
- ProcIEEE 61 1443Dokumen42 halamanProcIEEE 61 1443Fitri AnaBelum ada peringkat
- Difference Between Surface Plasmon Resonance and SPPDokumen3 halamanDifference Between Surface Plasmon Resonance and SPPAparna ViswanathBelum ada peringkat
- PHY 483 - Lecture1Dokumen18 halamanPHY 483 - Lecture1Michael AdesanyaBelum ada peringkat
- 1.world CommunicatesDokumen30 halaman1.world CommunicatesSeanBelum ada peringkat
- 13-Lenses and Dispersion of LightDokumen8 halaman13-Lenses and Dispersion of LightGIEBelum ada peringkat