Geography PW
Diunggah oleh
MMGamerzJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Geography PW
Diunggah oleh
MMGamerzHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Gemaakt door Loes uit TV3C Paragraaf 2 Water - Responsible for transporting nutrition and waste products in ecosystem
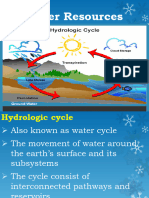
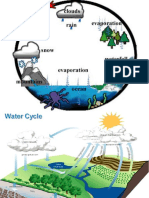
- Major role in formation of the earth Weathering and erosion -> wearing land away Sedimentation -> building up land Water balance - Shows how much water comes and goes out of an area - Water come into an area in two ways: 1. Precipitation; falls unevenly in the world. Not much useful precipitation in lots of countries, because of warmth -> evaporation 2. From other areas; lots of water comes to Netherlands, because we are the drain of Europe Water in the ground - Ground water; used by everything that lives on earth, top layer, not saturated - Subsurface water; water is stored here, bottom layer, saturated - Water is separated by the water table - Soil is like a sponge, water is stored during wet times and released during dry times - Due to buildings it is more difficult for water to sink - Aquifer; place under the ground where water is stored - Non-renewable supply; water that slowly comes in aquifer by filtration - Renewable supply; constantly replenished water (rain/rivers/ice) - Sustainable water management; only using renewable sources in a process or something else Paragraaf 3 Rivers - Horizontal erosion; wearing out wide bends - Vertical erosion; river goes more straight, cutting of bends - Slow-flowing water -> lots of sedimentation -> creates new channels -> cutting off sharp meanders (oxbow lake) -> after while is called a delta - Delta; Easily to built on Very fertile soil - Rivers/deltas are formed by; Rain water Melted ice water Water rising - Regime; fluctuation in discharge of water in a river in one year Norway; - in warm months lots of melting water Ireland; - in cold months lots of precipitation Germany; - equally amount of water - Peak charge; increased/very large discharge of a river - Wadi; river valley in desert -> mostly dry, sometimes filled with water
Lots of forests are cut down, and to let water drain faster deep channels have been dugged and rivers were straightened More surface has turned into stone -> water no longer filters down, drain away quickly -> river has to carry more often a peak charge
Paragraaf 4 Coast types 1. Ria coast; coastline with inlets, drawn out and branching off, formed by former river valleys flooded by rising sea level 2. Dune coast; is border between land and the sea, formed by a row or several rows of dunes 3. Cliff coast; steep coast, formed by breakers causing the rock to crumble 4. Fjord coast; coast with steep inlets, formed by glacial valleys flooded by rising sea levels Formation of coast/differences - Coast differences are caused by Sea levels rising and falling in the past Differences in material ->rock/sand - When sea level rises -> coastline moves inwards Sandy coast - very easily flushed away Rock coast - erodes slowly by the waves Threatened coast - Causes; 1. Spring tide - occurs when the sun, moon and earth are at the same line, a very high tide is created 2. Coast shape - areas where coast has such a shape that the water helps being pushed up 3. Estuaries - funnel-shaped river mouth, formed by the tide, here water can be pushed up high 4. Tropical cyclones - due to drop in the air pressure, water level is lifted 10cm + 10m high waves Paragraaf 5 Unequal distribution in water 1. Precipitation - very low where lands need it and very high in the countries with already a lot of water 2. Unfavourable precipitation regime - falls a lot in one half of the year, while the other half of the year the country dries out (shortage)(winter. summer changes)
Water stress - All problems that arise as result of a shortage in (clean) water - Major problem; Shortage of clean drinking water Shortage of irrigation water Disappearance of wetlands - Wetlands; wet ecosystem such as marshes, mangrove forests along tropical coast line -> work like sponge and filter polluted water before it goes into other water systems
Water stress will become worse, because; Population increases rapidly Prosperity is increasing Urbanisation is high Wetlands have been lost, because; Land reclamation -> agriculture Building shrimp breeding farms Pollution from supply rivers
Water war - An armed conflict between nations over water - Integrated water management; a joint plan by countries a river runs through, which states how much water everybody is entitled to, how pollution is tackled and how environment along river can be improved - Example; if Turkey closes of the river by building dams, Iran and Iraq will be in trouble, because they really need the water for agriculture Paragraaf 6 Dealing with water stress - Increase water by; Holding on to water 1. Renewing wetlands (areas cant be used intensively) 2. Building dams (people have to move, not natural) Transport water from wet to dry areas (ecosystem will be affected) Deeper surface water/pumping up fossil water Desalinisation of seawater Saving water - In agriculture; 1. Hot areas -> drop irrigation instead of traditional irrigation, aridity index remains low 2. Drop irrigation prevent salinisation (increase of salt in water) 3. Is there salinisation? -> built crops that are resistant to salt 4. Use crops that use less water - In households/business; 1. Use less -> recycle more 2. Irrigation cant be reused, household/business water can be reused 3. Use water more efficiently Paragraaf 10 Types of polders - Sea polder; formed by building dykes around a part of the sea, located along the coast (Zeeland, Friesland) - Peat polder; came below sea level due to compaction, located in low-laying peat areas - Reclaimed polder; formed by pumping parts of seas/lakes dry (Haarlemmermeer, Ijsselmeer) Sinking - Peat compacts -> land sinks - Compact; sinking of the ground due to soft subsoil (peat/clay) sinking, especially as result of lowering water table - Retention areas; temporary water storage area in case of high water, in order to reduce the level of water in the river down stream
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Reporting Earth Sci M11Dokumen5 halamanReporting Earth Sci M11「 」Belum ada peringkat
- 2 2riversDokumen12 halaman2 2riversLK chanellBelum ada peringkat
- 1gm Ground WaterDokumen24 halaman1gm Ground WaterMohammad Zamir TaqwaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Notes Grade 8 ScienceDokumen5 halamanChapter 1 Notes Grade 8 ScienceRachel Anne MaglinteBelum ada peringkat
- Grade-Vi Science - Worksheet TERM-2 CH-14-WATERDokumen6 halamanGrade-Vi Science - Worksheet TERM-2 CH-14-WATERmohinderBelum ada peringkat
- Hydro SphereDokumen20 halamanHydro SphereS4ltysBelum ada peringkat
- Water ResourcesDokumen52 halamanWater ResourcesJestelle DianaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 15: Freshwater Resources: Natural Systems, Human Impacts, and ConservationDokumen6 halamanChapter 15: Freshwater Resources: Natural Systems, Human Impacts, and ConservationEva WuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 17 Water Use and ManagementDokumen5 halamanChapter 17 Water Use and Managementapi-263809475Belum ada peringkat
- Environmental Science Notes Topic 1: Water Properties of WaterDokumen5 halamanEnvironmental Science Notes Topic 1: Water Properties of WaterchifambaBelum ada peringkat
- Assingnment No 1Dokumen7 halamanAssingnment No 1AbhilashBelum ada peringkat
- Water Resources HandoutsDokumen4 halamanWater Resources HandoutsPhilip Jayson L. LestojasBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Science 7 4th QuarterDokumen30 halamanEnvironmental Science 7 4th QuarterBill FernandoBelum ada peringkat
- Abe 147Dokumen8 halamanAbe 147Miracle LakeBelum ada peringkat
- Aquaculture EngineeringDokumen113 halamanAquaculture EngineeringKarieDetoreTolonesBelum ada peringkat
- The Water Resource ManagementDokumen31 halamanThe Water Resource ManagementJehnylete DacalosBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Chapter 4Dokumen4 halamanSummary Chapter 4estefaniaelizabethdiaz0Belum ada peringkat
- 3.river FloodingDokumen2 halaman3.river FloodingNAZREEN SHANIYASBelum ada peringkat
- Ground Water and HydrologyDokumen11 halamanGround Water and Hydrologyammigalla swethaBelum ada peringkat
- Action of External Agents in Relief Final StudentsDokumen28 halamanAction of External Agents in Relief Final StudentsRitaMartínezPérezBelum ada peringkat
- Water Qual Background InfoDokumen19 halamanWater Qual Background InfoKevin NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Distribution of Water On EarthDokumen21 halamanDistribution of Water On EarthnayemBelum ada peringkat
- Water - A Precious ResourceDokumen15 halamanWater - A Precious ResourceHarshita RanjanBelum ada peringkat
- Earth'S Water: - Started As A Combination of Gasses Which Were Carried by Meteor That Collided WithDokumen5 halamanEarth'S Water: - Started As A Combination of Gasses Which Were Carried by Meteor That Collided WithEim NellaBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Movement of WaterDokumen10 halamanSurface Movement of WaterRadhika AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- BDST 2 Topic 1Dokumen10 halamanBDST 2 Topic 1Diganto HaqueBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 - Sources of Potable WaterDokumen4 halamanModule 2 - Sources of Potable WaterRochelleBelum ada peringkat
- 1 On Water ConservationDokumen26 halaman1 On Water Conservation2235 Jaydeep KonkarBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrosphere NotesDokumen10 halamanHydrosphere Notesmatthewsc2013Belum ada peringkat
- Group PresentationDokumen32 halamanGroup PresentationJulimar CabayaBelum ada peringkat
- (Pre-Final) Freshwater Resource ManagementDokumen31 halaman(Pre-Final) Freshwater Resource ManagementMarkBelum ada peringkat
- Acfrogahnlrg9gfzubln Vdk7wcu3htqrkv Nom6pklxd7arxpanp Kg7myzyeagdxvnyfzwej0ocu4lwsgv Zx9mkkvwrtjltgyv1nrj6m C2i1pkxytyvbupslkjwf5j0vsaxh6uidhodjtwdDokumen14 halamanAcfrogahnlrg9gfzubln Vdk7wcu3htqrkv Nom6pklxd7arxpanp Kg7myzyeagdxvnyfzwej0ocu4lwsgv Zx9mkkvwrtjltgyv1nrj6m C2i1pkxytyvbupslkjwf5j0vsaxh6uidhodjtwdLily May AguinaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Water Supply Use and ManagementDokumen39 halamanWater Supply Use and ManagementRoxette RoseteBelum ada peringkat
- RiversDokumen9 halamanRiversLuke .J. WuteteBelum ada peringkat
- M6L2.Water Cycle, HydrosphereDokumen27 halamanM6L2.Water Cycle, HydrosphereAngeilyn RodaBelum ada peringkat
- Distribution of Water On EarthDokumen25 halamanDistribution of Water On Earthjoy talosigBelum ada peringkat
- KV Sector 47 Chandigargh Class 11 SUBJECT: Fundamental of Physical GeographyDokumen8 halamanKV Sector 47 Chandigargh Class 11 SUBJECT: Fundamental of Physical GeographyRohiniBelum ada peringkat
- Water Year %Dokumen16 halamanWater Year %hussain korirBelum ada peringkat
- Earth ScienceDokumen3 halamanEarth Sciencesamantha.amameda02Belum ada peringkat
- 1.3 The HydrosphereDokumen5 halaman1.3 The HydrosphereAnaBelum ada peringkat
- Aquatic Ecosystem: I. LakesDokumen6 halamanAquatic Ecosystem: I. LakesJohn Paul Espiña CandoBelum ada peringkat
- InstructionsDokumen34 halamanInstructionsAyaanuddin MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Hydro SphereDokumen33 halamanHydro SphereAlvinBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 2 HydrosphereDokumen12 halamanLec 2 HydrosphereKhaled Hasan KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Water On Earth Is Distributed Across Various ReservoirsDokumen3 halamanWater On Earth Is Distributed Across Various ReservoirsDoung PichchanbosbaBelum ada peringkat
- Earth Science MLG 4Dokumen19 halamanEarth Science MLG 4Racquel BanaoBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 3 - Social Science 3º - WaterDokumen4 halamanUNIT 3 - Social Science 3º - WaterMaika RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- LAS For Summative Assessment Identify The Various Water Resources On Earth (Dokumen17 halamanLAS For Summative Assessment Identify The Various Water Resources On Earth (David Jonel RoceroBelum ada peringkat
- Source PlumbingDokumen52 halamanSource PlumbingdivugoelBelum ada peringkat
- Water Resource ManagementDokumen28 halamanWater Resource ManagementZhiyong HuangBelum ada peringkat
- The Structure of The HydrosphereDokumen19 halamanThe Structure of The Hydrospheremuneeba khanBelum ada peringkat
- CH 4 Water & Its ManagementDokumen10 halamanCH 4 Water & Its ManagementAyanBelum ada peringkat
- The Structure of The Hydrosphere: 8 Grade ScienceDokumen19 halamanThe Structure of The Hydrosphere: 8 Grade ScienceKeon JonesBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic Thermal Spring, Resulting From The Force of Super Heated Steam Within Constricted Subsurface ChannelDokumen20 halamanPeriodic Thermal Spring, Resulting From The Force of Super Heated Steam Within Constricted Subsurface ChannelAnonymous 781tGbsutBelum ada peringkat
- Water CycleDokumen14 halamanWater Cycleapi-3731257100% (1)
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Ater CeansDokumen9 halaman© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Ater Ceansurs4everrrBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 4 NotesDokumen13 halamanTopic 4 NotesRaviBelum ada peringkat
- Water and Land ResDokumen24 halamanWater and Land ResRicBelum ada peringkat
- Earth's Fresh Water - Dynamic PlanetDokumen7 halamanEarth's Fresh Water - Dynamic Planetar_gon214Belum ada peringkat
- Kid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureDari EverandKid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureBelum ada peringkat
- Sea Level Changes or EustatismDokumen6 halamanSea Level Changes or Eustatismkalule elvisBelum ada peringkat
- Hawkes, Ernest William - The Labrador Eskimo (1916)Dokumen274 halamanHawkes, Ernest William - The Labrador Eskimo (1916)Mikael de SanLeon100% (1)
- Britain and The British Seas, Mackinder PDFDokumen428 halamanBritain and The British Seas, Mackinder PDFNapoléon DimanabasterBelum ada peringkat
- S. K. Manocha - Geography Workbook-I - For UPSC, PCS, NET and Other Examinations (2009, Pearson Education)Dokumen260 halamanS. K. Manocha - Geography Workbook-I - For UPSC, PCS, NET and Other Examinations (2009, Pearson Education)Yashu Darling100% (1)
- AUSTRALIA Vs NEWZELAND CHARTDokumen1 halamanAUSTRALIA Vs NEWZELAND CHARTOlivia AranzetaBelum ada peringkat
- EuropeDokumen5 halamanEuropeAmicus CuriaeBelum ada peringkat
- GEOGRAPHY - Lesson 4-6Dokumen8 halamanGEOGRAPHY - Lesson 4-6VINCE FRANCIS MESANA FAMORCANBelum ada peringkat
- Science 5 ADM Quarter 2 Module 6Dokumen23 halamanScience 5 ADM Quarter 2 Module 6Julien ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- SiphonophoresDokumen12 halamanSiphonophoresNicolasBelum ada peringkat
- East Iceland - Official Tourist Guide 2014-2015Dokumen196 halamanEast Iceland - Official Tourist Guide 2014-2015cavrisBelum ada peringkat
- Geology of Longyearbyen-Jochmann EngDokumen36 halamanGeology of Longyearbyen-Jochmann EngLeo Rescia100% (1)
- DU3035 Bahasa Inggris ASPD SMPDokumen8 halamanDU3035 Bahasa Inggris ASPD SMPAgri PuspitasariBelum ada peringkat
- Landforms Scavenger Hunt Geography ProjectDokumen2 halamanLandforms Scavenger Hunt Geography ProjectNatalia ShubinaBelum ada peringkat
- 200 Expressions - Speak English With VanessaDokumen28 halaman200 Expressions - Speak English With VanessaUtha ChiroBelum ada peringkat
- The Estuarine EcosystemDokumen223 halamanThe Estuarine EcosystemRodrigo AguayoBelum ada peringkat
- Written by Giselle Hajir, Isabel Pacheco and Stella WenczelDokumen23 halamanWritten by Giselle Hajir, Isabel Pacheco and Stella WenczelKarin GravinaBelum ada peringkat
- Norway Report (Humanities)Dokumen24 halamanNorway Report (Humanities)Aditya Vikram MahendruBelum ada peringkat
- BeachesAndCoasts Davis and FitzgeraldDokumen521 halamanBeachesAndCoasts Davis and FitzgeraldanibalBelum ada peringkat
- Landform Cards 19 ADokumen100 halamanLandform Cards 19 ANina StratukBelum ada peringkat
- Bodies of Water PicDokumen4 halamanBodies of Water PicLD MARY M. POLICARPIOBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Ujian Nasional Bahasa Inggris SMP Tahap 1A: The Following Text Is For Numbers 1 and 2Dokumen11 halamanLatihan Ujian Nasional Bahasa Inggris SMP Tahap 1A: The Following Text Is For Numbers 1 and 2Tangguh Pramasurya100% (1)
- Iceland Complete Classic Circle Tour: Full Itinerary & Trip DetailsDokumen9 halamanIceland Complete Classic Circle Tour: Full Itinerary & Trip DetailsManfredBelum ada peringkat
- Britainbritishse 00 MackuoftDokumen418 halamanBritainbritishse 00 MackuoftZelia GregoriouBelum ada peringkat
- Be A Better Campaign MasterDokumen134 halamanBe A Better Campaign MasterLoba100% (4)
- Geography Picture DictionaryDokumen4 halamanGeography Picture DictionaryEva Andersen VargaBelum ada peringkat
- GC LeongDokumen180 halamanGC Leongganesh sonkarBelum ada peringkat
- Anglo Norwegian Fisheries CaseDokumen17 halamanAnglo Norwegian Fisheries CaseKiko Rimban100% (1)
- Final Coral Reefs and EstuarineDokumen29 halamanFinal Coral Reefs and EstuarineNiña AmatoBelum ada peringkat
- Geography PamphletDokumen2 halamanGeography Pamphletapi-289612667Belum ada peringkat
- Norway NotesDokumen9 halamanNorway NotesterceroalasislaBelum ada peringkat