EG Questions
Diunggah oleh
Hariprasath VisvanathanDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EG Questions
Diunggah oleh
Hariprasath VisvanathanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
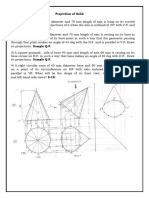
Projection of Planes A circular plate of diameter 50mm side lies in a plane inclined at 35 to the HP and perpendicular to VP.
Draw the projections of the plane. A hexagonal plate of side 30mm is resting on one of its edges on VP and inclined at 40to HP. Its surface is inclined 35 to VP. Draw its projections. A square lamina PQRS of side 40mm rests on the ground on its corner P in such a way that the diagonal PR is inclined at 45 o to the HP and the diagonal QS is inclined at 40o to the VP and parallel to the HP. Draw its projection. A hexagonal plate of side 20mm rests on the HP on one of its sides inclined at 45 to VP. The surface of the plate makes on angle of 30with HP. Draw the front and top views of the plate. A regular hexagonal lamina of 40mm side is resting on one of its corner on HP. Its surface is inclined at 45 to HP. The plan of the diagonal through the corner which on HP makes an angle of 45 with XY. Draw its projection. A square lamina PQRS of side 40mm rests on the ground on its corner P in such a way that the diagonal PR is inclined at 45o to the HP and apparently inclined at 30o to the VP. Draw its projection. A regular pentagon lamina of 30 mm side is resting on one of its edges on HP which is inclined at 30 to HP. Its surface is inclined at 45 to VP. Draw its projections. A rectangular lamina ABCD of sides 70 mm x 35 mm has its shorter side AD in HP and inclined at 45 to the HP and the shorter side is inclined at 30 to the VP. Draw its projection A hexagonal lamina of 20 mm side rests on one of its corners on HP. The diagonal passing through this corner is inclined at 45 to the HP. The lamina is then rotated through 90 such that the top view of this diagonal is perpendicular to the VP. The surface is still inclined at 45 to the HP. Draw its projections of the lamina. A thin rectangular plate of sides 50 mm x 25 mm has its shorter side in the HP and inclined at an angle of 30 to the HP. Project its front view when its top view is a perfect square of 25 mm. A circular lamina of 60 mm diameter rests on HP on a point on the circumference. The lamina is inclined to HP such that the top view of it is an ellipse of minor axis 35 mm. The top view of the point makes an angle of 45 with VP. Draw its projection. Draw the projections of a pentagonal sheet of 26 mm side, having its surface inclined at 30 to VP. Its one side is parallel to VP and inclined at 45 to HP. A hexagonal plate of 25 mm side is resting on HP such that one of its corners touches both HP and VP. It makes 30 with HP and 60 with VP. Draw its projections. A thin square plate EFGH of 40 mm side is having its corner G on HP. Diagonal GE is inclined at 40 to HP and diagonal FH inclined at 40 to HP and parallel to VP. Draw its projection. A hexagonal plate of side 35mm is resting on one of its edges on VP and inclined at 40to HP. Its surface is inclined 35 to VP. Draw its projections. A square lamina PQRS of side 30mm rests on the ground on its corner P in such a way that the diagonal PR is inclined at 45 o to the HP and the diagonal QS is inclined at 40o to the VP and parallel to the HP. Draw its projection. A rectangular lamina ABCD of sides 70 mm x 35 mm has its shorter side
AD in HP and inclined at 45 to the HP and the shorter side is inclined at 30 to the VP. Draw its projection A hexagonal lamina of 25 mm side rests on one of its corners on HP. The diagonal passing through this corner is inclined at 45 to the HP. The lamina is then rotated through 90 such that the top view of this diagonal is perpendicular to the VP. The surface is still inclined at 45 to the HP. Draw its projections of the lamina. Draw the projections of a pentagonal sheet of 32 mm side, having its surface inclined at 30 to VP. Its one side is parallel to VP and inclined at 45 to HP. A hexagonal plate of 30 mm side is resting on HP such that one of its corners touches both HP and VP. It makes 30 with HP and 60 with VP. Draw its projections. A thin rectangular plate of sides 50 mm x 25 mm has its shorter side in the HP and inclined at an angle of 30 to the HP. Project its front view when its top view is a perfect square of 30 mm. A circular lamina of 50 mm diameter rests on HP on a point on the circumference. The lamina is inclined to HP such that the top view of it is an ellipse of minor axis 30 mm. The top view of the point makes an angle of 45 with VP. Draw its projection. A pentagon lamina of side 30 mm rests on the ground on one of its corner with the side containing the corner being equally inclined to the ground. The side opposite to the corner on which it rests is inclined at 30 to the VP and is parallel to HP. The surface of the pentagon makes an angle 50 with the ground. Draw the top and front views of the lamina A rectangular plate 70 x 40 has one of its shorter edges in the VP inclined at 40 to the HP. Draw its top view if its front view is a square of side 40 mm.
Projection of Solids A square prism of base side 30 mm and axis 60 mm rests on one of its longer edges with the rectangular faces equally inclined o the HP. The base nearer to the VP is at 25 mm from the VP and is parallel to the VP. Draw its projections. Draw the projections of a cone of base diameter 50 mm and axis length 70 mm when its lies on the ground on one of its generators with axis parallel to the VP. A regular hexagonal prism of base side 25 mm and height 70 mm rests on the HP on one of its base edges with the axis is inclined at 60 to the HP and parallel to the VP. Draw the projections of the prism. Draw the projections of a hexagonal pyramid of base side 25 mm and height 65 mm when one of its triangular faces is perpendicular to both the VP and HP. A pentagonal pyramid of base edge 25 mm and axis 60 mm length rests on one base side on HP such that the highest base corner is 20 mm above HP. Its axis parallel to the VP. Draw its top and front views. A cylinder of diameter 30 mm and axis length 50 mm is resting on HP on a point so that its axis is inclined at 45 to the HP and parallel to the VP. Draw its top and front views. A cylinder of base diameter 50mm and altitude 70mm is tilted until the axis makes an angle of 600 with the HP and parallel to VP. Draw the projections of the cylinder. Draw the projections of a hexagonal pyramid of base side 90mm height and of side 30mm when one triangular face of the pyramid is vertical. Hexagonal prism of base side 30mm and axis 60mm is resting on HP on one of its base side with its axis inclined at 400 to HP and parallel to VP. Draw its projections. Draw the projections of a square pyramid of 40mm side and axis 60mm long when its lies on the HP with its slant edge and axis parallel to VP. A pentagonal prism side of base 20mm and axis 50mm long rests with one of its shorter edges on HP, such that the base containing that edge makes an angle of 30 to HP, and its axis parallel to VP. Draw its projections. A hexagonal pyramid of side 25mm axis 50mm long lies with one of its triangular faces on HP and its axis is parallel to VP. Draw its projections. A hexagonal prism of base side 35mm and axis height 70mm is resting on the ground with two of the base edges perpendicular to VP, such that the axis is inclined to 60 to HP. Draw the projections. A pentagonal pyramid of base side 30mm, axis length 85mm has one of its slant edges in the VP and the axis parallel to and 40mm above HP. Draw its projections. Draw the projections of a cylinder 75 mm diameter and 100 mm long, lying on the ground with its axis inclined at 30o to the V.P. and parallel to the ground. A square pyramid of base side 30mm and altitude 40mm rests on the ground on one of its base edges such that its axis is 45 o to the ground. Draw its projection. A pentagonal prism, side of base 25 mm and axis 50 mm long, rests with one
of its edges on HP such that the base containing that edge makes an angle 30 to HP and its axis parallel to VP. Draw its projections. A hexagonal pyramid of base edge 40mm and altitude 80mm rests on one of its base edges on the HP with its axis inclined at an angle of 30 to the HP and parallel to the VP. Draw its top view and front view. A hexagonal prism, side of base 30 mm and axis 55 mm long, rests with one of its base corners on HP such that its base makes an angle 60 to HP and its axis parallel to VP. Draw its projections Draw the projections of a cone of base diameter 50mm and axis length 70mm when it lies on the ground on one of its generators with the axis parallel to the VP. A pentagonal prism of base 30mm and axis length 60mm is lying on the ground on one of its rectangular faces. Draw its front and top views when its axis is inclined at 30o to the VP.
A cone of base diameter40mm and height 60mm is freely suspended from one of its base points such that the axis is parallel to VP. Draw the projection.
A pentagonal prism of base 30mm and axis length 60mm is lying on the ground on one of its rectangular faces. Draw its front and top views when its axis is inclined at 45o to the VP.
A pentagonal pyramid of base side 30mm and axis length 75 mm is freely suspended by means of a string from one of its base corners with its axis parallel to VP. Draw its projections.
Section of Solids A cube of side 25mm rests on the HP on its faces with a vertical face inclined at 35 to the VP. A plane perpendicular to the HP and inclined at 50 to the VP cuts the cube, 3mm away from the axis. Draw the top view and sectional front view. A pentagonal pyramid of base side 20mm and altitude 55mm rests its base on the HP with one of the base edges perpendicular to the VP. It is cut by a plane inclined at 50 to the base. The cutting plane meets the axis at 15mm above the base. Draw the front view and sectional top view. A cylinder of diameter 40mm and height 50mm rests on its base on the HP. It is cut a plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 50 to the HP. The cutting plane meets the axis at a distance of 15mm from the top. Draw the front view and sectional top view. A right circular cone of base diameter 40mm and axis length 60mm rests on its base on the HP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the HP and inclined at 45 to the VP. The shortest distance between the cutting plane and the plan of the axis is 10mm. Draw the plan and sectional elevation. A hexagonal prism of base side 30mm and axis length 70mm rests on its one of its ends on the HP with two base sides parallel to the VP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 30 to the HP the cutting plane meets the axis at 30mm from the top. Draw its front and sectional top view. A square pyramid of base side 25mm and altitude 40mm rests on the HP on the base with the base edges equally inclined to the VP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 30 to the HP meeting the axis at 21mm above the HP. Draw the front and sectional top view of the pyramid. A hexagonal pyramid of base side 25mm and axis 55mm rests on its base on the HP with two base edges perpendicular to the VP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 30 to the HP meeting the axis at 20mm from the vertex. Draw the elevation and sectional plan. A cone of base diameter 50mm and altitude 60mm rests on its base on the HP. It cut by a plane perpendicular to the VP and parallel to one of the extreme generators, 10mm away from it. Draw its projection. A square pyramid of base side 25mm and altitude 40mm rests on the HP on the base with the base edges equally inclined to the VP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 30to the HP meeting the axis at 21mm above the HP. Draw the front and sectional top view of the pyramid. A cylinder of diameter 40 mm and axis 55 mm long stands vertically with its base on HP. It is cut by plane parallel to VP and passes at a distance of 10 mm from the axis. A hexagonal prism, side 25 mm and axis 60 mm long is resting on is base on HP, such that an edge of the base is parallel to VP. It is cut by a section plane inclined at 45 to VP and 10 mm away from the axis. Draw the projections of the solid. A cone of base diameter 60 mm and axis 70 mm long is resting on its base on HP. It is cut by a section plane, inclined at 60 to VP and 10 mm away from the axis. Draw the projections of the cut solid. A cone of diameter 40mm, axis height 65mm rests on HP with one of its base point. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to VP and axis inclined 50to
HP and meets the axis at a point 20mm above the base. Draw the elevation and sectional plan. A hexagonal pyramid side of base 20mm and axis 50mm long rests with its base on HP and its edge of its base is perpendicular to VP. It is cut by a section plane perpendicular to VP inclined at 30 to HP and passing through a point on the axis 20mm below the apex. Draw the sectional top view of the pyramid. A square prism of base side 30mm and axis 60mm long, rests with its base on HP and one of its rectangular faces is inclined at 30 VP. A section plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 60to HP cuts axis of the prism at a point 20mm from its top end. Draw the sectional top view. A cylinder of diameter 60mm and height 80mm is lying on the HP with its axis parallel to both the HP and the VP. A vertical plane inclined at 25 to the VP cuts the cylinder and passes through the midpoint of the axis. Draw the sectional front view. A cube of side 35 mm is placed and cut by a plane in such a way that the sectioned shape is a hexagon. Draw the front and top views of the cube. A pentagonal pyramid of base 25 mm and altitude 50 mm rests on its base on HP with one of the base edges perpendicular to the VP. It is cut by a plane inclined at 45 to the base. The cutting plane meets the axis 20 mm above the base. Draw the front view, sectional top view. A hexagonal prism of base side 30mm and axis length of 60mm is resting on HP on one of its bases two of the vertical faces perpendicular to VP. It is cut by a plane inclined at 50 to HP and perpendicular to VP and passing through a point at a distance 12mm from the top base. Draw its front view and sectional top view. A cone of base diameter 50mm and axis length 75mm resting on HP on its base is cut by a plane inclined at 50 to HP and perpendicular to VP and it is bisecting the axis. Draw the front view and sectional top view. A cone of base diameter 50mm and axis length 60mm stands with its base on HP and it is cut by a section plane 45 to HP and perpendicular to VP and passing through a point on the base circle of the cone. Draw the sectional top view and front view. A square pyramid of base side 30 mm and altitude 40 mm rests on the HP on the base with the base edges equally inclined to the VP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 30to the HP meeting the axis at 21mm above the HP. Draw the front and sectional top view of the pyramid. A vertical cone of diameter 50 mm and axis height 70 mm is cut by a plane perpendicular to VP, inclined at 50 to HP and meets the axis 20 mm from the base. Draw the sectional plan and elevation. A pentagonal pyramid of base 25 mm and altitude 60 mm rests on its base on HP with one of the base edges perpendicular to the VP. It is cut by a plane inclined at 50 to the base. The cutting plane meets the axis 20 mm above the base. Draw the front view, sectional top view.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Questions of Projection of PlanesDokumen2 halamanQuestions of Projection of PlanesSubhajyoti DasBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 - Projection of SolidDokumen2 halamanUnit 3 - Projection of Solidranjith kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Projection Solids PrismDokumen2 halamanProjection Solids PrismKarthick DavoothBelum ada peringkat
- Projection of PlanesDokumen2 halamanProjection of PlanesanandandmeenaBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionsDokumen3 halamanQuestionsDhanushree DhanuBelum ada peringkat
- EG Question BankDokumen9 halamanEG Question BankdiduthegreatBelum ada peringkat
- 04 - Projection of SolidsDokumen33 halaman04 - Projection of SolidsCreative ThinkerBelum ada peringkat
- Ge8152 GC A & B QuestionsDokumen5 halamanGe8152 GC A & B QuestionsBalaChandarBelum ada peringkat
- Projection of Planes (CAED)Dokumen5 halamanProjection of Planes (CAED)Akarsh manBelum ada peringkat
- Aux Projection 240416Dokumen2 halamanAux Projection 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiBelum ada peringkat
- Question Plate For EgDokumen4 halamanQuestion Plate For EgNagaraj Muniyandi0% (1)
- Question Bank For Test 2 - (Unit 3 and Unit 4)Dokumen4 halamanQuestion Bank For Test 2 - (Unit 3 and Unit 4)A.R. Pradeep KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics Sample Paper, NIT CalicutDokumen3 halamanEngineering Graphics Sample Paper, NIT CalicutMATHEW GEORGEBelum ada peringkat
- Projection of SolidsDokumen1 halamanProjection of SolidsKHUSHBOO KHUSHBOOBelum ada peringkat
- EG Important QuestionDokumen1 halamanEG Important QuestionsenthurrBelum ada peringkat
- Unit IV Questions (Iae III)Dokumen5 halamanUnit IV Questions (Iae III)Anonymous 4p20nXgWDZBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5Dokumen7 halamanAnna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5florenceprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics AssignmentDokumen5 halamanEngineering Graphics AssignmentVegeta899 vegetaBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-VDokumen2 halamanDepartment of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-Vramu vasaBelum ada peringkat
- Projection of SolidsDokumen4 halamanProjection of SolidsSharon ElijahBelum ada peringkat
- Development of Surfaces 240416Dokumen7 halamanDevelopment of Surfaces 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiBelum ada peringkat
- Projection of SolidsDokumen2 halamanProjection of SolidsanandandmeenaBelum ada peringkat
- Projection of SolidsDokumen5 halamanProjection of Solidsap0885501Belum ada peringkat
- QuestionBank Projection of SolidsDokumen4 halamanQuestionBank Projection of SolidsAmritanshu AmritBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 5 CONCISE Q A Sections of Solids and Development of SolidsDokumen9 halamanUNIT 5 CONCISE Q A Sections of Solids and Development of SolidsVathyasamBelum ada peringkat
- EnggqpDokumen4 halamanEnggqpRambabuDaraBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics Question BankDokumen8 halamanEngineering Graphics Question BankSriram JBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics II Answer Any Five Questions 5 X 20 100Dokumen1 halamanEngineering Graphics II Answer Any Five Questions 5 X 20 100muthuramprodBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics Unit-IV Question BankDokumen5 halamanEngineering Graphics Unit-IV Question BankRaam IsramBelum ada peringkat
- Qus PaperDokumen6 halamanQus PaperBalamurugan KarnanBelum ada peringkat
- Eg Unit 4Dokumen6 halamanEg Unit 4rajasekaran23230% (1)
- Assignment Sheet No. 5 & 6 PDFDokumen2 halamanAssignment Sheet No. 5 & 6 PDFArnav Anuj KasarBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics QB PDFDokumen8 halamanEngineering Graphics QB PDFKarthi SanBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question BankDokumen8 halamanAnna University Engineering Graphics Question BankflorenceprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-2-Projection of SolidsDokumen3 halamanUnit-2-Projection of Solidsvinith kumarBelum ada peringkat
- EgDokumen8 halamanEgmbeaelnaaBelum ada peringkat
- Eg QPDokumen5 halamanEg QPSurulivelrajantBelum ada peringkat
- 22ME160-Engg Graphics Worksheet 6 - 2023-24Dokumen1 halaman22ME160-Engg Graphics Worksheet 6 - 2023-24ShankarBelum ada peringkat
- GE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFDokumen8 halamanGE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFSivakumar LBelum ada peringkat
- GE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFDokumen8 halamanGE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFSivakumar LBelum ada peringkat
- Projections of Solids With Axis Inclined To Both HP and VPDokumen17 halamanProjections of Solids With Axis Inclined To Both HP and VPVivek Singh100% (1)
- Drawing AssignmentDokumen6 halamanDrawing AssignmentJitendra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- EG Practice QuestionsDokumen2 halamanEG Practice QuestionsAjithkumar K.TBelum ada peringkat
- Section of Solids 240416Dokumen11 halamanSection of Solids 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiBelum ada peringkat
- EGDokumen4 halamanEGbalajimeieBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank Engineering Graphics (GE6152) : Unit-I Plane Curves & Free Hand SketchingDokumen14 halamanQuestion Bank Engineering Graphics (GE6152) : Unit-I Plane Curves & Free Hand Sketchingnandhu20Belum ada peringkat
- Caed NotesDokumen46 halamanCaed Notesrohanshetty5512Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 8Dokumen1 halamanAssignment 8mohimab230105eeBelum ada peringkat
- Solids HWDokumen2 halamanSolids HWnavneet patilBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics - Question BankDokumen15 halamanEngineering Graphics - Question BankimamuddeenBelum ada peringkat
- Projection of SolidDokumen7 halamanProjection of SolidMe Samarth BadsalBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Sheet CAEGDokumen1 halamanProblem Sheet CAEGPrabal JainBelum ada peringkat
- Unit IV Section of SolidsDokumen14 halamanUnit IV Section of SolidsPrashant UbarhandeBelum ada peringkat
- GE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankDokumen11 halamanGE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankNatarajan AgoramBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank EGDokumen7 halamanQuestion Bank EGMohd AbrarBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaDokumen6 halamanEngineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaDamo Daran GBelum ada peringkat
- Section of Solid and Development of SurfacesDokumen2 halamanSection of Solid and Development of SurfacesPrashantBelum ada peringkat
- Caed Manual-Apr2823Dokumen45 halamanCaed Manual-Apr2823Aditya KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- ProblemDokumen3 halamanProblemRajesh JunghareBelum ada peringkat
- Math 4 q4 Week 3 DLLDokumen7 halamanMath 4 q4 Week 3 DLLMitchz TrinosBelum ada peringkat
- Gr2 Wk26 3D Its Not Just For Movies PDFDokumen2 halamanGr2 Wk26 3D Its Not Just For Movies PDFRosnani Binti Abdul HamidBelum ada peringkat
- Student Lesson 10.1Dokumen8 halamanStudent Lesson 10.1lizbet08Belum ada peringkat
- Form 2 AssigmentDokumen22 halamanForm 2 AssigmentAimy RaisBelum ada peringkat
- Volume of Prisms HomeworkDokumen7 halamanVolume of Prisms Homeworkafmoczaee100% (1)
- WiproDokumen41 halamanWiprosuganya004Belum ada peringkat
- SASMO 2021 Invitation PackageDokumen11 halamanSASMO 2021 Invitation PackageLeonBelum ada peringkat
- Three Dimensional ShapeDokumen16 halamanThree Dimensional ShapeJulie EligoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Letter 201 Ass AnsDokumen4 halamanTutorial Letter 201 Ass Anssumaya20% (5)
- Objective: To Describe Properties of Solid Such As Perpendicular andDokumen34 halamanObjective: To Describe Properties of Solid Such As Perpendicular andmolina_xBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheets 5Dokumen4 halamanWorksheets 5LEILA SILVESTREBelum ada peringkat
- CrystallographyDokumen68 halamanCrystallographyMajid AliBelum ada peringkat
- Rubik Cube Solution For Beginners, by Jasmine LeeDokumen9 halamanRubik Cube Solution For Beginners, by Jasmine Lee4gen_5Belum ada peringkat
- 3º ESO Cuadernillo BilingueDokumen159 halaman3º ESO Cuadernillo BilinguelunesmalditoBelum ada peringkat
- Bury Me in The Rift v2.0 PDFDokumen7 halamanBury Me in The Rift v2.0 PDFBrett ChamberlinBelum ada peringkat
- Quant ChecklistDokumen60 halamanQuant ChecklistKiran KumariBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Test - Mathematics 6Dokumen6 halamanDiagnostic Test - Mathematics 6Melanie Joan Abao PaconBelum ada peringkat
- DLL in Math V Q4 Week 3Dokumen14 halamanDLL in Math V Q4 Week 3Uola HDBelum ada peringkat
- TesseractDokumen35 halamanTesseractSteven WeiBelum ada peringkat
- Maths ProjectDokumen35 halamanMaths ProjectPriya Kakkar100% (1)
- Year 1 Maths: Booster PackDokumen27 halamanYear 1 Maths: Booster PackSeanLaiBelum ada peringkat
- q3 Math 5Dokumen6 halamanq3 Math 5nicaangelenecomiaBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet For Volume GR 6Dokumen1 halamanWorksheet For Volume GR 6Darren Jane LacernaBelum ada peringkat
- Written Works in Mathematics 6Dokumen9 halamanWritten Works in Mathematics 6Jessmiel LabisBelum ada peringkat
- Solid GeometryDokumen3 halamanSolid GeometryJirah GicangaoBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Visualising Solid ShapesDokumen11 halamanNCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Visualising Solid ShapesR.Pearlsis SophiBelum ada peringkat
- Book PCDokumen254 halamanBook PCNargish AkterBelum ada peringkat
- GAT MathsDokumen51 halamanGAT Mathsasad nadeem100% (1)
- Canadian Math Kangaroo Contest: Grade 7-8 2016Dokumen7 halamanCanadian Math Kangaroo Contest: Grade 7-8 2016LinoBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Reviewer - Grade 6Dokumen13 halaman3rd Reviewer - Grade 6Joseph Bryan VictoriaBelum ada peringkat