Question 2 - Kam Eu Siang (Chinese & English)
Diunggah oleh
2012PhCHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Question 2 - Kam Eu Siang (Chinese & English)
Diunggah oleh
2012PhCHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2012 PhC
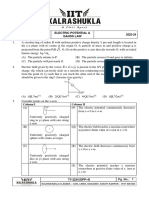
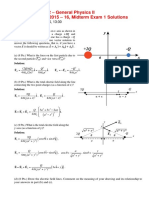
Physics CompetitionPhC2012 2 Question2
(a) X EA -q C
R r
RA RC 0
The net intensity of the electric field is the vector sum of electric field strength along RA and RC. The vertical components of EA and EB cancel each other, resulting 0 electric field strength.
E =EAcos + EBcos B +q
Meanwhile, the horizontal component is the net electric field strength Enet
EA=EBE=2EAcos
and therefore
1 2 2( 2 + )2 4
1 RA = 4
= 4 RC =
1 4
( 1
0
)2
along RA
2
cos =
substitute
E=4
0 2 2 + 4
1 2 2( 2 + )2 4
2 +(
)2
into the aforementioned equation, we get
(2 +
3 2 )2 4
= 4 (b) y
0 ( 1 0
)2
along RC
2
() = k Edipole
RX (along RX)
2 +(
)2
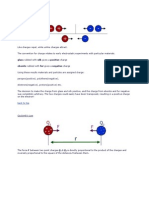
p 1 R 2 x Q a -Q
p
Let point P be any point on the surface of the sphere.
p V= ( - )
1 2 1 = kQ ( 2) 1 2
Then, the electric potential on point P, V
, 1 = 2 = ; 1 2 = 0
Since then
V=0
Hence, the electric potential V=0
Alternative Solution: Consider the Gauss's law on the surface of the conductor, since the enclosed charge inside the Gaussian surface is zero (-q + q = 0), the electric field on the conductor E = 0, therefore resulting a zero potential on the conductor. The conductor remains neutral since both positive charge and negative charge of same magnitude act on it simultaneously. (c)
Due to the fact that the energy U explicitly represents the electric potential energy generated between two particles (charges), hence, energy U
U =
2
(d) a<<R
[From A, if a<<R, Edipole]
qa R E [After the insertion of a positive point charge, q, a and R remain unchanged, therefore Edipole remains the same]
2012 6 13 copyright@13 June 2012 Kam Eu Siang
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Electric Charges FieldsDokumen19 halamanElectric Charges FieldsSridevi KamapantulaBelum ada peringkat
- 12th Physics Notes For State BoardDokumen62 halaman12th Physics Notes For State Boarddeepak hegdeBelum ada peringkat
- Last Minute Revision study material for Electric charges and fieldDokumen23 halamanLast Minute Revision study material for Electric charges and fieldchandra bose100% (1)
- Solution 7Dokumen2 halamanSolution 7Gowrisankar RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Full SyllabusDokumen25 halamanPhysics Full Syllabusshreyansh tanwarBelum ada peringkat
- λ and dividing the result λ we chose the z-axis parallel to kDokumen1 halamanλ and dividing the result λ we chose the z-axis parallel to kNeoHoodaBelum ada peringkat
- The Electric FieldDokumen12 halamanThe Electric FieldAman BhuttaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics Potential Energy and FluxDokumen4 halamanElectrostatics Potential Energy and FluxfireBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Study Material 12Dokumen220 halamanPhysics Study Material 12Ramesh PaikBelum ada peringkat
- Class 12 Electrostatics Electricity and Magnetism Made Simple NotesDokumen68 halamanClass 12 Electrostatics Electricity and Magnetism Made Simple Noteslplc791Belum ada peringkat
- 1021 Topper 21 101 4 4 136 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Up201607221852 1469193735 4819Dokumen13 halaman1021 Topper 21 101 4 4 136 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Up201607221852 1469193735 4819M abiBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 1b Report Marzan John Angelo M.Dokumen9 halamanPhysics 1b Report Marzan John Angelo M.Hahatdog QaBelum ada peringkat
- Potential Energy and Electrostatic PotentialDokumen92 halamanPotential Energy and Electrostatic PotentialBanani BhattacharyaBelum ada peringkat
- Class 12 Physics Energy of Charged ParticlesDokumen5 halamanClass 12 Physics Energy of Charged ParticlesCrazy about JunglesBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Potential and Gauss Law (06-05-2023)Dokumen6 halamanElectric Potential and Gauss Law (06-05-2023)Epic NationBelum ada peringkat
- +2 Four Mark Questions-2023Dokumen12 halaman+2 Four Mark Questions-2023spiderboy11307Belum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics (JEE MAIN Online) PDFDokumen15 halamanElectrostatics (JEE MAIN Online) PDFAnanya DwivediBelum ada peringkat
- EL CPP MegaDokumen8 halamanEL CPP MegaEklavya GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- XII Physics Chapterwise Topicwise Worksheets with SolutionsDokumen186 halamanXII Physics Chapterwise Topicwise Worksheets with SolutionsVikas KumarBelum ada peringkat
- +2 Three Mark QuestionsDokumen5 halaman+2 Three Mark Questionsspiderboy11307Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter-2 Electric PotentialDokumen29 halamanChapter-2 Electric PotentialKpBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Field StrengthDokumen12 halamanElectric Field StrengthSRISHTI SRIVASTAVABelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatic Energy EE 141 NotesDokumen13 halamanElectrostatic Energy EE 141 NotesdanielsandriaBelum ada peringkat
- PhysicsDokumen22 halamanPhysicsFurqan Ali CheemaBelum ada peringkat
- Plus Two Phy Imp Questions 2023-1Dokumen26 halamanPlus Two Phy Imp Questions 2023-1aizah thameemBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1: Electric FieldDokumen49 halamanTopic 1: Electric FieldpolplitocrisBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 12th Full Q&ADokumen115 halamanPhysics 12th Full Q&AKiranshreeBelum ada peringkat
- PHYSICS Test DemoDokumen20 halamanPHYSICS Test Demomohits822Belum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics: Topics To CoverDokumen16 halamanElectrostatics: Topics To CoverNissam SidheeqBelum ada peringkat
- ElectrostaticsDokumen11 halamanElectrostaticsZainab KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Class 12 Physics Formula Sheet (Coaching)Dokumen42 halamanClass 12 Physics Formula Sheet (Coaching)Atharva Maheshwari100% (1)
- +2 Four Mark QuestionsDokumen13 halaman+2 Four Mark QuestionsAshwin KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDokumen78 halamanElectrostatic Potential and CapacitanceGovind Mani BhattBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Potential (In Word) Chapter 1 02Dokumen14 halamanElectric Potential (In Word) Chapter 1 02Shubham TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Problems Chap 19 CutnellDokumen9 halamanSample Problems Chap 19 CutnellJoeBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance: UNIT-II: Chapter-02Dokumen19 halamanElectrostatic Potential and Capacitance: UNIT-II: Chapter-02Teju tejasBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Potential Practice ProblemsDokumen2 halamanElectric Potential Practice ProblemsAariya KumariBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Filed and PotentialDokumen16 halamanElectric Filed and Potentialsanjay sBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 2 Electric Field and Electric FluxDokumen17 halamanTopic 2 Electric Field and Electric FluxSmk Abdul Rahim DuaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 21Dokumen17 halamanChapter 21Pelin SoyluBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1 Introduction To The Theory of The FELDokumen14 halaman2.1 Introduction To The Theory of The FELHorenhop DolakovBelum ada peringkat
- APPLIED PHYSICS LECTURE 1 ON ELECTRIC FIELDDokumen26 halamanAPPLIED PHYSICS LECTURE 1 ON ELECTRIC FIELDHussain CommunicationBelum ada peringkat
- Study Material 12 PhysicsDokumen117 halamanStudy Material 12 PhysicsVaishu UparkarBelum ada peringkat
- AP Lec#03Dokumen60 halamanAP Lec#03omerBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Charges and Fields ExplainedDokumen180 halamanElectric Charges and Fields ExplainedGahan Gowda SBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Charges and Fields ExplainedDokumen12 halamanElectric Charges and Fields ExplainedVinod MN50% (2)
- P102 M1 Summer 15-16 SolDokumen3 halamanP102 M1 Summer 15-16 SolRedion XhepaBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Charges and Fields Plus TwoDokumen29 halamanElectric Charges and Fields Plus TwovipinBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Forces and Fields Sample ProblemsDokumen4 halamanElectric Forces and Fields Sample ProblemsChristine Cayosa CahayagBelum ada peringkat
- Formulas of Physics XII: Fundamental Constants and LawsDokumen8 halamanFormulas of Physics XII: Fundamental Constants and LawsUday BhattacharjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics: (Physics)Dokumen6 halamanElectrostatics: (Physics)Piyush GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- 22 - Gauss's Law - R K ParidaDokumen9 halaman22 - Gauss's Law - R K ParidaMonicaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDokumen2 halamanChapter - 1 Electric Charges and FieldsSiddharth SubashBelum ada peringkat
- Namma Kalvi +2 Physics Study MaterialDokumen45 halamanNamma Kalvi +2 Physics Study MaterialVathi N. KhalleelulahBelum ada peringkat
- Important 2 and 3 Mark Questions and AnswersDokumen23 halamanImportant 2 and 3 Mark Questions and AnswersirannaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics Chapter 12: Coulomb's Law and Electric FieldDokumen39 halamanElectrostatics Chapter 12: Coulomb's Law and Electric FieldFatehBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-1 Electrostatics: Very Short and Short Answer QuestionsDokumen11 halamanUnit-1 Electrostatics: Very Short and Short Answer QuestionsGarry BroBelum ada peringkat
- 02.II PU Impt 2 and 3 Marks Qs and AnsDokumen23 halaman02.II PU Impt 2 and 3 Marks Qs and AnsLaxmiBelum ada peringkat
- Law of ElectrostaticsDokumen31 halamanLaw of ElectrostaticsYani AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsDari EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsBelum ada peringkat
- Problem 1 ResistorDokumen1 halamanProblem 1 Resistor2012PhCBelum ada peringkat
- Question 3 - Kam Eu SiangDokumen1 halamanQuestion 3 - Kam Eu Siang2012PhCBelum ada peringkat
- Question 3 - Teoh Han KhengDokumen1 halamanQuestion 3 - Teoh Han Kheng2012PhCBelum ada peringkat
- Question 2 - Teoh Han KhengDokumen1 halamanQuestion 2 - Teoh Han Kheng2012PhCBelum ada peringkat
- Question 1 (Han Kheng)Dokumen1 halamanQuestion 1 (Han Kheng)2012PhCBelum ada peringkat
- Kraus Helix IdeaDokumen10 halamanKraus Helix IdeaPavan NanduriBelum ada peringkat
- AD and DA ConversionDokumen15 halamanAD and DA ConversionmumamaduraiBelum ada peringkat
- JavaScript: The Programming Language of the WebDokumen15 halamanJavaScript: The Programming Language of the WebMary EcargBelum ada peringkat
- Precalculus Prerequisites A.K.A. Chapter 0' Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Sharealike 3.0 LicenseDokumen16 halamanPrecalculus Prerequisites A.K.A. Chapter 0' Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Sharealike 3.0 LicensejakeBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Structure TutorialDokumen38 halamanMicro Structure TutorialAditya KhannaBelum ada peringkat
- Recurrence and Master TheoremDokumen35 halamanRecurrence and Master Theoremwseries50% (2)
- Radiation Heat Transfer Lab SessionDokumen5 halamanRadiation Heat Transfer Lab SessionusamaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Factors That Affect Intention To Use E-Wallet Through The Technology Acceptance Model Approach (Case Study - GO-PAY)Dokumen8 halamanAnalysis of Factors That Affect Intention To Use E-Wallet Through The Technology Acceptance Model Approach (Case Study - GO-PAY)Nhi NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises in Nonlinear Control SystemsDokumen115 halamanExercises in Nonlinear Control SystemsAshk Nori ZadehBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Paper-At-2324-Class-Vii-P1-At+pcbmDokumen23 halamanSample Paper-At-2324-Class-Vii-P1-At+pcbmnirmal krisnaBelum ada peringkat
- Allen: Pre Nurture & Career Foundation DivisionDokumen7 halamanAllen: Pre Nurture & Career Foundation DivisionSaketBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Learning: An Introduction to Predicting the Future from Past ExperienceDokumen65 halamanMachine Learning: An Introduction to Predicting the Future from Past ExperienceAnilBelum ada peringkat
- Letusc (By Yashvant Kanetkar) Chapter 1 SolutionDokumen20 halamanLetusc (By Yashvant Kanetkar) Chapter 1 Solutiontooba mukhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Model Paper DiscussionDokumen15 halamanModel Paper Discussionseyon sithamparanathanBelum ada peringkat
- 2D Transformations in Computer GraphicsDokumen32 halaman2D Transformations in Computer GraphicsIAGPLSBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE - PHYSICS - Mensuration DPPDokumen6 halamanCBSE - PHYSICS - Mensuration DPPAncha RambabuBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement and Instrumentation (ELE 306) (Make Up) RCSDokumen2 halamanMeasurement and Instrumentation (ELE 306) (Make Up) RCSVibhav PawarBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise Paper On Photoelectric EffectDokumen4 halamanExercise Paper On Photoelectric EffectJohn Lorenzo100% (1)
- Homework Solutions - X - MOP (Blue-Black) 2012Dokumen5 halamanHomework Solutions - X - MOP (Blue-Black) 2012Ayush AryanBelum ada peringkat
- Dudman (1984) Conditional Interpretations of If-SentencesDokumen62 halamanDudman (1984) Conditional Interpretations of If-SentencesbrunellusBelum ada peringkat
- Planer Kinetics of Rigid BodyDokumen56 halamanPlaner Kinetics of Rigid BodydffdfdfdfBelum ada peringkat
- 80 Cấu Trúc Tiếng Anh Hay GặpDokumen6 halaman80 Cấu Trúc Tiếng Anh Hay GặpTrang Bui100% (2)
- MSY11 FullbookDokumen508 halamanMSY11 Fullbookapostle.kayvaanBelum ada peringkat
- Functions for Physics ClassDokumen294 halamanFunctions for Physics ClassdjinachhgdgyudfgBelum ada peringkat
- Discrete Mathematics Solved MCQsDokumen8 halamanDiscrete Mathematics Solved MCQsamna_shifaBelum ada peringkat
- Database Management System - DBMS (COMPUTER SCIENCE) Video Lecture For GATE Preparation (CS IT MCA)Dokumen3 halamanDatabase Management System - DBMS (COMPUTER SCIENCE) Video Lecture For GATE Preparation (CS IT MCA)Vishal SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- ElMehdi EMINESUM6PMorocco ResearchArticleDokumen17 halamanElMehdi EMINESUM6PMorocco ResearchArticleLộc Cao XuânBelum ada peringkat
- Priority Encoder: 4-To-2 Bit Binary EncoderDokumen6 halamanPriority Encoder: 4-To-2 Bit Binary EncoderAditya Prakash100% (1)
- LA Tall Buildings Structural Design Council 2020 ProcedureDokumen94 halamanLA Tall Buildings Structural Design Council 2020 ProcedureMir Shabir Ali TalpurBelum ada peringkat
- Problem 1 SolutionDokumen24 halamanProblem 1 Solutionnitte5768Belum ada peringkat