CUNY City Tech PHY 1.2 Practice Final Exam
Diunggah oleh
beroodyHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CUNY City Tech PHY 1.2 Practice Final Exam
Diunggah oleh
beroodyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Problems: include all the details of your calculation and circle your nal answer.
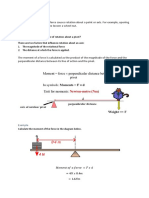
Problem 1 A crossbow with a mass of 30.0 kg is used to shoot a bolt whose mass is 0.050 Kg. The crossbow and the bolt are initially at rest. a) If a bolt leaves the crossbow with a speed of 100 m/s, what is the recoil speed of the crossbow? b) In which directions are the bolt and the crossbow moving? c) Compute the initial and nal kinetic energy of the bolt and the crossbow.
Problem 2 A block of wood is attached to the bottom of a lake by means of a rope and it is completely immersed in the water. The wood has a density of 0.25 103 kg/m3 (while water has a density of 1.0 103 kg/m3 ). a) If the the Volume of the block is V = 0.0136m3 , what is the tension in the string? b) If we cut the rope, the block will start accelerating towards the surface. Calculate the acceleration.
Problem 3 A block of wood whose volume is 0.01 m3 is attached to the bottom of a lake by means of a rope and it is completely immersed in the water. The wood had a density of 0.25 103 kg/m3 (while water has a density of 1.0 103 kg/m3 ). What is the tension in the rope?
Problem 4 The pressure in a cylinder lled with air is 1 atm when the volume is 0.03m3 . A temperature T = 27 C is kept constant. a) We compress the gas without changing the temperature until the pressure doubles. What is the nal volume? b) How many moles of air do we have in the cylinder?
Problem 5 A thermal engine performs 200 J of mechanical work and discards 300 J of heat in each cycle. How much energy should we provide to the engine (as heat) in each cycle? What is the eciency of the engine?
Problem 6 During each cycle, a thermal engine absorbs a quantity of heat of QH = 1000 J and discards QC = 750 J. What is the eciency of the engine? How much work will be produced in each cycle?
Problem 7 A swimming pool has a depth of 5.0 meter and it is lled with water ( = 1.0 103 kg/m3 ). The atmospheric pressure is patm = 1.013 105 Pa. Calculate: a) The pressure 1.0 meters below the surface of the water. b) The pressure at the bottom of the pool. c) The buoyant force acting on a block of volume 0.5 m3 located 3.0 meters below the surface of the water. d) What is the buoyant force acting on the same block if we place it at the bottom of the pool?
Problem 8 A sherman counts the number of water waves that pass under his boat. He counts 15 waves in one minute. He also measures that the displacement of his boat from the highest to the lowest position is 1.2 meters and that the distance between two consecutive wave crests is 3.0 meters. What are the frequency, the wavelenght, the period, the speed and the amplitude of the waves?
Newtons Law: F = ma Friction force (kinetic): f = k N Universal law of gravitation: F =G m1 m2 d2
G = 6.67 1011 Nm2 /Kg 2 Satellite motion: v= Circular motion (radius R and period T ) v= 2R T v2 R GME r
a= Mechanical Energy:
1 K = mv 2 2 U = mgh E =K +U Conservation of energy: Einit = Ef inal Work: W = F d cos Work-energy theorem: Einit + W = Ef inal Power: P = W/(t)
Denition of momentum: p = mv Conservation of momentum: pinitial = pf inal m1 v1,i + m2 v2,i = m1 v1,f + m2 v2,f Waves: v = f , f = 1/T Pascals law: p = pa + gh Buoyant force: B = f luid V g Density: = Heat: Q = mcT , Q = mL Temperature conversion (Kelvin-Celsius): TK = TC + 273.15 Pressure Conversion (atm-Pa): 1 atm = 1.013 105 P a Equation of Ideal Gas: pV = nRT R = 8.3145 J/(molK) First Law of Thermodynamics: U = Q W W = pV Eciency of a thermal engine: = QC W =1 QH QH m V
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chapter 1Dokumen44 halamanChapter 1John Jairo Ortiz Martinez91% (11)
- Energy Skate Park - UsedDokumen5 halamanEnergy Skate Park - UsedUntold StoriesBelum ada peringkat
- Seakeeping ExercisesDokumen26 halamanSeakeeping ExercisesRaniero FalzonBelum ada peringkat
- AssignDokumen10 halamanAssignkakaBelum ada peringkat
- PhysicsDokumen7 halamanPhysicsarchie bacud100% (1)
- Ihw 1Dokumen4 halamanIhw 1smagulovaBelum ada peringkat
- Problems 1Dokumen11 halamanProblems 1LogoBelum ada peringkat
- PHY130 Lab Report 2Dokumen7 halamanPHY130 Lab Report 2Declan Gale Anak DellyBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test For Midterm 3 Chapters 13, 15, 16, 17, 18 in Preparation For The Midterm ExamDokumen11 halamanPractice Test For Midterm 3 Chapters 13, 15, 16, 17, 18 in Preparation For The Midterm ExamRAIZZBelum ada peringkat
- 203 SP 04Dokumen3 halaman203 SP 04nicky1213aBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Physics Sample Papers Solved 05Dokumen24 halaman11 Physics Sample Papers Solved 05Shivam GargBelum ada peringkat
- Old Exams P101Dokumen146 halamanOld Exams P101Sandro SerdiñaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Hookes and SHM SolutionsDokumen10 halamanPractice Hookes and SHM SolutionsZhong Huang100% (1)
- Rangkuman Soal Dinamika KapalDokumen10 halamanRangkuman Soal Dinamika KapalAkbarPrasetyaBelum ada peringkat
- TP1HW Dimanalysis-PhasespaceDokumen3 halamanTP1HW Dimanalysis-PhasespaceSandro KobuliaBelum ada peringkat
- PCS125 Tutorial QuestionsDokumen52 halamanPCS125 Tutorial Questionsfurbac321Belum ada peringkat
- 3rdLESample PDFDokumen10 halaman3rdLESample PDFMarco ConopioBelum ada peringkat
- ScienceDokumen6 halamanScienceNicky NicorBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-09 (Solved)Dokumen23 halamanCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-09 (Solved)cbsesamplepaper0% (1)
- Simple Harmonic MotionDokumen39 halamanSimple Harmonic MotionJenievie EspinoBelum ada peringkat
- PHY 430 - 433 - Test - 4 August 2021Dokumen7 halamanPHY 430 - 433 - Test - 4 August 2021Aidil IkhwanBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Neraca Massa Dan EnergiDokumen13 halamanTugas Neraca Massa Dan EnergiAlya SholikhatulBelum ada peringkat
- Compilation Physics QuizDokumen40 halamanCompilation Physics QuizGwen MañegoBelum ada peringkat
- Work Sheet III For Pr-EngineeringDokumen6 halamanWork Sheet III For Pr-EngineeringXO MusicBelum ada peringkat
- Class 11 Physics Part 2Dokumen4 halamanClass 11 Physics Part 22786pq9wvrBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Midterm 03Dokumen7 halamanPractice Midterm 03Ha ViBelum ada peringkat
- PHYS 1110: Assignment 8Dokumen5 halamanPHYS 1110: Assignment 8Anson ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 140 Answers Smart Physics03Dokumen10 halamanPhysics 140 Answers Smart Physics03Shirsa Guha100% (1)
- (PHYS1112) (2017) (F) Final R8udkjdt 62165Dokumen18 halaman(PHYS1112) (2017) (F) Final R8udkjdt 62165black.widow.010300Belum ada peringkat
- AL-1 NotesDokumen244 halamanAL-1 NotesABDULLAH SHAHZADBelum ada peringkat
- PhycDokumen7 halamanPhycnicole jacusalemBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen24 halamanChapter 1Ahmad A OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Phy212 CH15 Worksheet-KeyDokumen3 halamanPhy212 CH15 Worksheet-KeyDeden MSBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan UTSDokumen13 halamanLatihan UTSAyu Patresia NababanBelum ada peringkat
- Model Question Solution Made By: Krishna Shah Group 'A': Answer ExplanationDokumen22 halamanModel Question Solution Made By: Krishna Shah Group 'A': Answer ExplanationKrishna ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsDokumen2 halamanMeasurement: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsRomou AlsaaqBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Exam FisdasDokumen13 halamanMid Exam FisdasipaclosefriendsBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 2075Dokumen5 halamanPhysics 2075sujeet.jha.311Belum ada peringkat
- F F F τ=0 F F τ=0: x y x y xDokumen3 halamanF F F τ=0 F F τ=0: x y x y xمؤمن الشديفاتBelum ada peringkat
- Units: Basic MathematicsDokumen38 halamanUnits: Basic MathematicsGraham MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Problems For Exam 1 Spring 2023Dokumen5 halamanPractice Problems For Exam 1 Spring 2023Sania MurtuzaBelum ada peringkat
- Problem - 7A PDFDokumen9 halamanProblem - 7A PDFMonicaBelum ada peringkat
- Prob Set 1Dokumen2 halamanProb Set 1bryanblooBelum ada peringkat
- Oscillations: Applied Physics BS 101 HomeworkDokumen2 halamanOscillations: Applied Physics BS 101 Homeworkzainab noorBelum ada peringkat
- PHYC2121 General Physics 1 WEEK 11-20 WEWODokumen28 halamanPHYC2121 General Physics 1 WEEK 11-20 WEWORina Finees OlegarioBelum ada peringkat
- Temperature ProblemsDokumen10 halamanTemperature ProblemsLakshyaBelum ada peringkat
- Examples 2 MeasurementDokumen43 halamanExamples 2 Measurementmoon starBelum ada peringkat
- 11th Physics Model Question Paper em PDFDokumen3 halaman11th Physics Model Question Paper em PDFAjitBelum ada peringkat
- 11th Physics Model Question Paper emDokumen3 halaman11th Physics Model Question Paper emAjit0% (1)
- Topper Sample Paper 2 Xi - Physics Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70Dokumen6 halamanTopper Sample Paper 2 Xi - Physics Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70microdotcdmBelum ada peringkat
- 120 Rad/sDokumen35 halaman120 Rad/sEzra Orita CeletariaBelum ada peringkat
- ESAS Physics QuestionsDokumen22 halamanESAS Physics QuestionsErika Mae OrlinaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2225456Dokumen2 halamanAssignment 2225456Anonymous fmV9u5F8E7Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Questions ImportantsDokumen130 halamanPhysics Questions Importantsblackbumber69Belum ada peringkat
- Phys PP1 MSDokumen7 halamanPhys PP1 MSMusaBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen4 halamanUntitledOlajuwonBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise Chapter 1 and 2 Kelompok 9Dokumen5 halamanExercise Chapter 1 and 2 Kelompok 9Puskesmas BatusepuluhBelum ada peringkat
- PHYSICS (Theory) : SAMPLE PAPER-03 (Unsolved)Dokumen4 halamanPHYSICS (Theory) : SAMPLE PAPER-03 (Unsolved)ANKUR ACHARJEEBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5: Further Application of Newton'S Laws: Friction, Drag, and ElasticityDokumen5 halamanChapter 5: Further Application of Newton'S Laws: Friction, Drag, and ElasticityCedric KouakouBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Problems ThermodynamicsDokumen5 halamanPractice Problems ThermodynamicsJana ChambersBelum ada peringkat
- SJPO General Round 2009 With AnswersDokumen21 halamanSJPO General Round 2009 With AnswersHaha XiBelum ada peringkat
- HW-1 2Dokumen4 halamanHW-1 2Ozan YakarBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Newton Laws of Motion Revision Notes QuizrrDokumen38 halaman02 Newton Laws of Motion Revision Notes QuizrrVani VydyulaBelum ada peringkat
- Density and Specific GravityDokumen8 halamanDensity and Specific GravityHaste OsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts in Calculus IIDokumen240 halamanConcepts in Calculus IIcantor2000Belum ada peringkat
- Statics of Rigid Bodies PDFDokumen8 halamanStatics of Rigid Bodies PDFBESAY REUELBelum ada peringkat
- The Coriolis Effect - Uche UmekweDokumen14 halamanThe Coriolis Effect - Uche UmekwemrtrixsBelum ada peringkat
- Coriolli's Component of Acceleration ApparatusDokumen7 halamanCoriolli's Component of Acceleration Apparatustinkusk24Belum ada peringkat
- Moment of A Force (With Worked Examples)Dokumen5 halamanMoment of A Force (With Worked Examples)A BarrettBelum ada peringkat
- Motion Numerical Problems PDFDokumen64 halamanMotion Numerical Problems PDFAshok PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Unit 1 MechanicsDokumen49 halamanPhysics Unit 1 Mechanicsamir hamza100% (1)
- Calculation Report For Fence Foundation Model HP3000: REV Description Engineering Approval Boss DateDokumen9 halamanCalculation Report For Fence Foundation Model HP3000: REV Description Engineering Approval Boss DateGerardo JoseBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 6.1-Circular motion: Formulae =2π/T F=mv /r=m rDokumen8 halamanTopic 6.1-Circular motion: Formulae =2π/T F=mv /r=m rJerry DBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - Pulleys and Systems PracticeDokumen3 halaman5 - Pulleys and Systems PracticeCalebBelum ada peringkat
- Specific Criteria For Calibration Laboratories in Mechanical Discipline: MASS (Weights)Dokumen24 halamanSpecific Criteria For Calibration Laboratories in Mechanical Discipline: MASS (Weights)kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Work and Energy Theorem 1Dokumen2 halamanWork and Energy Theorem 1Jack RobinsBelum ada peringkat
- Induced Emf.: Faraday's Law. Lenz's LawDokumen18 halamanInduced Emf.: Faraday's Law. Lenz's LawDedar RashidBelum ada peringkat
- Adamson University Manila: Experiment 3Dokumen9 halamanAdamson University Manila: Experiment 3Ron PascualBelum ada peringkat
- Rotational Motion Multiple Choice-2012!05!15-1Dokumen8 halamanRotational Motion Multiple Choice-2012!05!15-1deepBelum ada peringkat
- G7 BmiDokumen9 halamanG7 Bmierika rapsingBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsDokumen1 halamanElectric Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsBelum ada peringkat
- Airlift Geyser PumpDokumen4 halamanAirlift Geyser PumpAchmad RidhonyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 17 20Dokumen20 halamanChapter 17 20yanela100% (1)
- HW 2Dokumen3 halamanHW 2JeeveshBelum ada peringkat
- BFC+1043 (1) MathDokumen13 halamanBFC+1043 (1) MathFakeyha RashidBelum ada peringkat
- 200 Puzzling Physics ProblemsDokumen23 halaman200 Puzzling Physics ProblemsNguyen Duc HiepBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge Pre-U CertificateDokumen40 halamanCambridge Pre-U CertificateemiliaBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 DLP First QuarterDokumen96 halamanScience 8 DLP First QuarterSarah Nefty100% (2)
- Worksheet - 11th Physics-Kanha Makhan Millennium School PDFDokumen2 halamanWorksheet - 11th Physics-Kanha Makhan Millennium School PDFuniverseerBelum ada peringkat